MHA 707 Exam D Study Guide
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What groups of Americans were largely uninsured when the ACA was being considered?
-Unemployed,
-Employed with no ESI (employer-sponsored ins)
-Young employees
-Those who didn't take ESI
-Those who chose not to be insured
Why didn't the ACA go to a single-payer or an NHI format? What was the Public potion?
Each had its own stakeholder with invested interest in continuing their role in the HC system. Allow many to purchase medicaid with means tested premium employers shift twd medicaid b/c it was cheaper than having private ins
What were the hoped advantages of achieving expanded coverage under the ACA?
Reduce increased care, expand rationing of care, costly exacerbation of health conditions, uncompensated care for providers (academic providers)
What features of the ACA were designed to increase coverage? What are pre-existing conditions and guaranteed issue? How were they Impacted by ACA?
•Mandated that private health insurance plans meet minimum standards
•Cannot discriminate against people with preexisting conditions (guaranteed issue)
•Cannot impose lifetime and annual limits on coverage
Must extend dependent coverage to age 26
What are pre-existing conditions and guaranteed issue?
Made changing employer/insurance practical and more fair
Helped many who could not get insurance because of early life events
Removed disincentives to practice “less-healthy” lifestyles
stop smoking, lose weight, etc.
Allowed people to “game the system” – buy insurance only when a health problem arises and be uninsured (not pay premiums) otherwise.
What are Health insurance exchanges?
State-based health insurance exchange for individuals and small businesses to compare plans, apply for financial assistance, purchase coverage
What is SHOP?
Small Business Health Options Program Helped firms with 50 or less employees to have insurance to cover them.
What was the individual mandate and its design? What happened to it?
Mandated that most citizens and legal residents have health insurance.
distributes health care costs over people in poor health and good health (community rating)
How did ACA aim to reduce health care cost?
-Medicare fraud, excessive payment for prescription drugs, shift cost to the state (stronger federal partnership in Medicaid), series of HC reforms would save $349 billion by 2021 and $480 billion by 2023, $1 Trillion in the following decade
What was the Center for Medicaid and Medicare Innovation?
•Established to develop cost savings through health services research that evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of health care treatments (Like NICE in United Kingdom)
•Testing various payment and service delivery models to achieve better care for patients, better health for communities, and lower costs
What are the source of funds for the ACA?
Prevention and public health fund
Cuts in government spending (Dr. and hospital) and new revenues (tax penalties)
What is Medicaid expansion?
Expansion supports local economics, level of financial protection, drops uninsurance rate cost of expansion is minimal, decreases cost-shifting issues, delay to dr. dr doesn't have to accept Medicaid
Expansion would stp benefits of private ins
What were the major achievements of the ACA?
•Specific ACA policies benefited many people
•Mandated coverage for preexisting conditions
•Mandated minimum benefit plans [stop "street insurance"]
•Subsidies for low- and moderate-income individuals
•Guaranteed issue policy helped people in transition—people who leave a job, are laid off, start a business or retire early
Death Spiral
a snowball effect refers to a condition of the insurance markets, where premiums are rapidly increasing because low-risk individuals are continuously priced out of the market
ACA effects on Uncompensated Care? Pros and Cons
Burdens fell sharply, 2.3% of operating cost
Savings access all hospitals in Medicaid Medicaid expansion ($6 B)
Overall effect on HC cost by ACA?
Revenue decreased after ACA (private care, government care, pay more) providers didn't want the ACA (40% private, 60% govt, 0% uncompensated care)
What was Repeal and Replace
Efforts by republican-Trump Admin
Republicans had voted to repeal and replace ACA 2016- there was no republican support
What are predictive analytics and big data and their effects on the system?
•looking at a patient's past patterns in behavior and use of services, coupled with current health needs to predict the future use of resources
-Big data used to make forecasts about a broad range of health issues (population level)
What is personalized medicine?
Avoiding side effects or ineffective treatment, picking better medicine for an individual
Ex: certain BP meds work better in African-Americans than other racial groups
What is the triple aim?
•Improve the patient experience
•Improve the health of populations
•Reduce the per capita costs of health care
What are NGOs and their future role in HC?
Non-government organizations
Population health changes, increased involvement
How does the aging population affect HC?
More than 20% of the population is over 65 by 2030
Medical care system will become focused on the care of those over 75 due to more chronic conditions, needs long term care service, life expectancy service, end of life services
Will the efforts to form integrated networks improve patient outcomes?
no real evidence yet
Price vs efficiency as the primary driver in HC markets?
Price
What is disruptive innovation? Examples
>Opportunities to gain "market share" from emergency departments and private physician practices
(EX: Rapid spread of urgent care centers)
-Creating access to providers by e-mail or by telehealth tools (This is a big one! But, need to expand with caution)
-Encouraging the use of apps that help people manage their chronic conditions (could be helpful)
Trends in financing HC of employers and insurance markets?
Systems still not workings to ensure access to care for all American system are encouraging efficient, value-oriented HC delivery in communities, employees weren't providing insurance coverage, price of ins becomes unaffordable, for many working Americans
Ever-increasing healthcare spending is__________ other use of tax revenues like education, defense, public works, etc.
crowding out
Challenges of people leading healthier lives?
improving access to affordable healthy food and poor choice about what to eat.
Lack of evidence-based policies or intervention funds for inventing evidence of efficiency
Finding funds
What is the fundamental cost problem?
•Delivery of elective or discretionary services to those who want, but don’t necessarily need them
•High prices likely caused by using a market approach to setting prices, tech diffusion, and access in “non-markets”
•Unhealthy lifestyles
Trends in quality outcomes research and the patient experience?
EHR,
-big data for evidence-based approach to delivering care
-Providers too often see insurers as their customers (follow the $), rather than patients
Changes for providers?
income or slow income growth for physicians –(higher $ for mid-levels initially, then ↓)
Changes for policy makers
-Preoccupation with Medicare and Medicaid costs
-Concerns over aging of population (demographic shift)
-Continued debate over government's role in health care
-Varied approaches to expanding Medicaid in states
-States will be interested in new organizational and reimbursement approaches that lower the per beneficiary costs of Medicaid
Changes for Insurance companies
-Face competition from insurance plans by health systems (direct contracting)
-Access for providing services related to the insurance operations at health systems
-Single-payer, medicine for all
What are some changes for consumers
-The increased activity of consumer advocacy groups (Ex: American CA Society, AARP)
-Greater influence of consumer voices in shaping policy
-Tough decisions individually about costs versus benefit of HDHP, out-of-pocket expenses, MSA/HSAs, etc.
-Risk assessment regarding large deductibles and copays
What does Dr. Bost think will happen to the US HealthCare System?
•Present system will continue for 5 - 7 years, through much debate and some tweaking
•Medicaid will continue for impoverished, but NEW Medicaid (Public Option) will appear and be available to higher and higher income levels through premiums based on ability to pay (means-tested, gov't subsidized health insurance - NHI)
•Eventually, NEW Medicaid will "Crowd out" traditional health insurance for all but the "well off" who will continue to buy health insurance at high prices but, still enjoy "Full Service". Costs in the NEW Medicaid system (NHI) will be ratcheted down by "rationing" although it won't go by that name... (Global budgets, fixing prices , and constructive barriers to access - like Canada - are most likely)
•Innovation and tech diffusion will slow dramatically either through market forces (↓ $) or ↑ regulation
•End-product = 2-tier medical system (unless courts don't allow it)
What quality improvement came form Florence Nightingale?
mortality in field hospitals during Crimean War
What quality improvement came form Codman?
post-surgical mortality, must keep patient records, organized medical staffs
What quality improvement came form Shcwart?
statistical process controls (telephones); Studied differences in production "batches"
What quality improvement came form Donabedian?
differentiated the quality measures related to process, structure and outcomes
What quality improvement came form Batalden and Nelson?
scorecards and dashboards
What 2 events often prompt process improvement projects?
>Accountability for use of clinical, financial and physical resources
>Continuously develop and improve the services provided
Improve clinical outcomes
What was the 1999 IOM Report To Err is Human? Main points?
>Medical errors accounted for 45,000 - 98,000 deaths annually
>More deaths than Breast CA or MVAs
>1.7 Million patients acquired nosocomial infections
>Cost = $20-30B annually
What was Crossing the Quality Chasm? What did it call DHHS to do?
- Patient safety
- Cost
- Care fragmentation
- Waste/inefficiency/over- and under-use of services
- Patient waiting times
What are the Six aims of the National Agenda for Improvement (IOM)?
>Safe – primum non nocere (“First, do no harm”)
>Effective – Evidence-based, Best practices
>Patient-centered - patient values should guide all clinical decisions (joint decision models)
>Timely – reduce wait times and harmful delays, but not prematurely either
>Efficient – avoid wasting resources (stuff, but also time and energy)
>Equitable – provide care that does not vary due to gender, race, ethnicity or SES
What are 2 features necessary for successful QI initiatives?
>Leadership
-Committed - resources and time
-Willing to test hypotheses and attempt change
>Corporate Culture - Set of shared values, beliefs, practices, and systems that characterize and influence behavior within an organization
What are Characteristics of Organizations that Support QI
-Quality improvement is discussed in all meetings
- Environment of "psychological safety" where mistakes are seen as opportunities to learn and improve ("Blame the process, not the people")
- Staff at all levels "speak up" when there are safety concerns
- Quality measures are integrated with performance review system
- Continuous improvement mindset where status quo is frequently challenged
-Organizational learning through knowledge management and sharing of ideas horizontally and vertically across the organization
What are useful purposes for Quality measures?
>Evaluating and Benchmarking performance
>Comparing interventions
>Comparing patient groups
>Monitoring changes over time
>Identifying substandard or exceptional performance
Ex: Best practices, P4P
What is a Shewhart Circle (PDSA)?
Plan, Do, Study, Act. The heart of quality improvement
Plan
State objectives
Make predictions
Develop plan to carry out cycle
Do
•Carry out the test
•Document problems and unexpected observations
Study
•Summarize what was learned
Act
Determine what changes are to be made
Who was W. Edwards Deming?
>Revolutionized manufacturing in post WWII Japan
"The Father of Modern Management"
He developed a 14-point plan to help executive lead their organizations based on principles of performance improvement.
What were the 14 points?
-Create constancy and purpose to improve products and services
-Cease dependence on inspection to ensure quality
-Management should drive out fear/help people work better (85% system/15% people)
-Break down barriers between departments (Everyone works toward the goal)
-Institute a vigorous program of education and self-improvement
What quality framework did Donabedian develop?
Structure - equipment, training, people and payments
Process - actions involved in caring for patients (clinical pathways, workflow, safety checklists, timeouts, etc.
Outcomes - outputs of care delivery;
- clinical
- patient experience/satisfaction/engagement
Who translated Deming's 14 points for healthcare?
Drs. Donald Berwick and Paul Batalden
In 1991, Berwick created________________
IHI to drive improvement in healthcare - Supported national projects using collaborative approached focused on safety, critical, chronic, and end-of-life care
- Introduced the Triple Aim while CMS Director in Obama administration
What was the triple aim?
improving the experience of care,
improving the health of populations,
reducing per capita costs of health care.
What is Six Sigma?
- any process can be defined, analyzed, improved and controlled to a level of error less than 6 standard deviations of normal (error rate of 0.003% or 3.4 defects /1 million opportunities, i.e., 99.9996% error-free
What is the six sigma method?
(DMAIC)
>Define the problem
>Measure the steps in the process
>Analyze the data
>Improve the process – usually involves a small-scale “pilot” study
>Control – implement the process and continually improve it
What is the goal and intent of the "lean" model of six sigma developed by Toyota?
Goal - remove any non value-added activity or step (Value stream map)
- line up value-creating steps to gain process/material efficiency and improve the customer experience
Intent - involve the entire team in the process of improvement
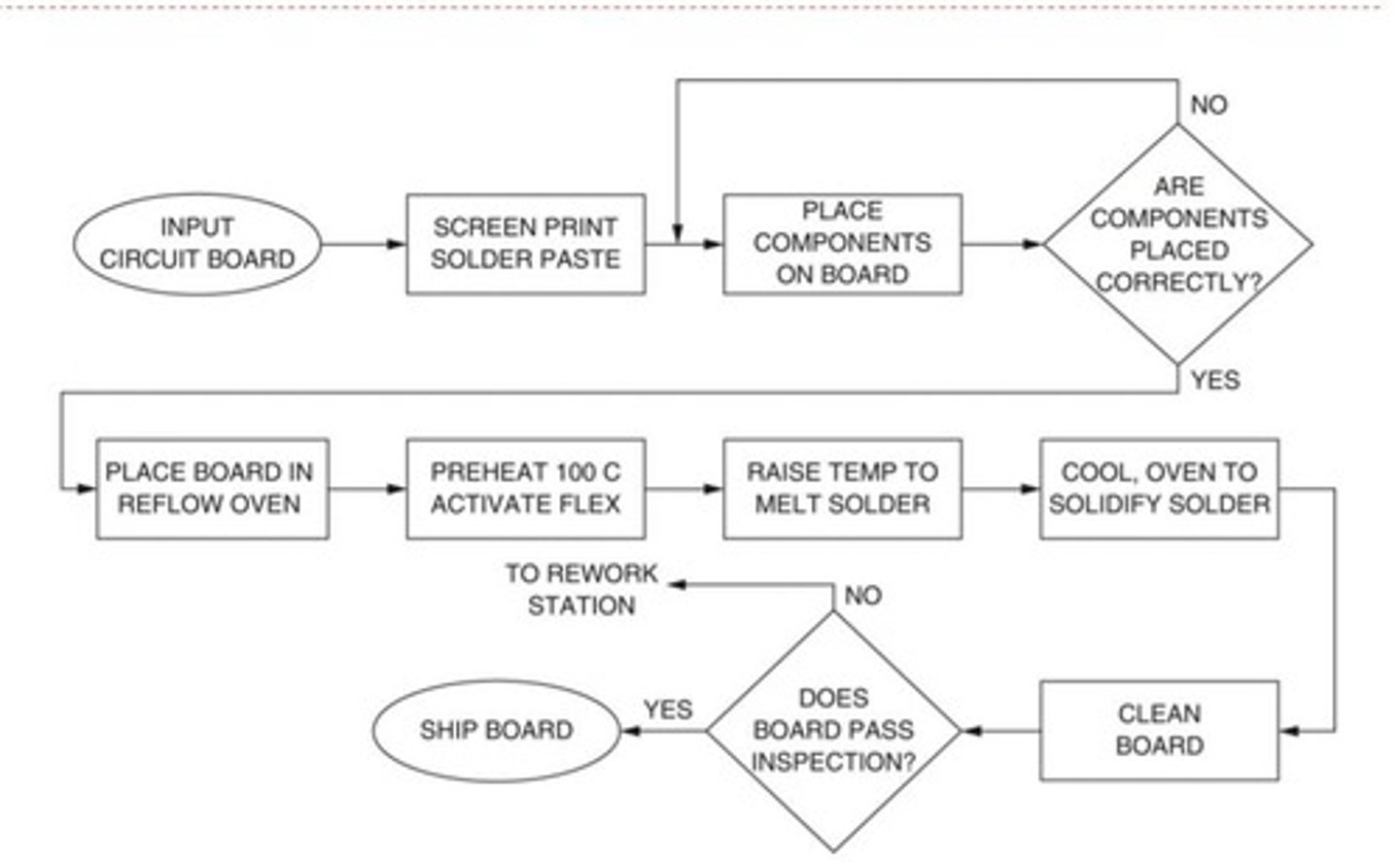
What are flow charts?
>Identify as the actual flow or sequence of events in a process
>Clearly identifies the boundaries of the process with a distinct beginning and end
>May show unexpected complexity, problem areas, redundancy and unnecessary loops where simplification and standardization may be possible
>Highlights areas where additional data can be collected and researched
>Helps train new personnel
What does a flow chart look like?
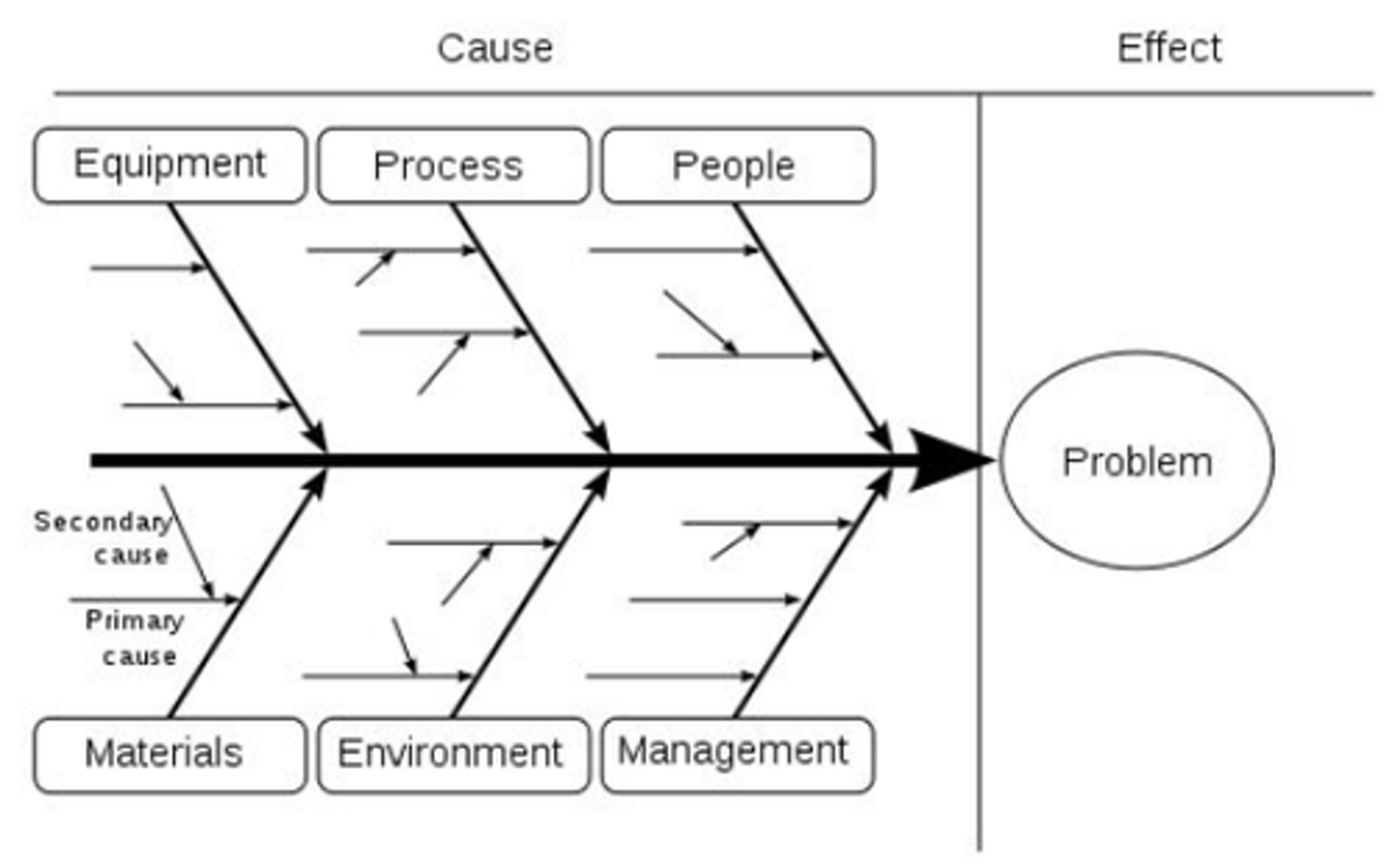
What is a cause and effect diagram? (Ishikawa)
- Visual tool used to collect and organize potential underlying causes to a specific problem
- Helpful tool when teams are brainstorming all possible causes of a problem to go beyond the first stage of investigation
What does a Ishikawa Diagram look like?
What is the brainstorming phase of creating quality improvement?
>Allow everyone to participate
>No idea is bad
>Write all ideas down where they are visible to the group
>Review the list for clarity and discard duplicates
>Participants build on the ideas of others
>Encourages group identity
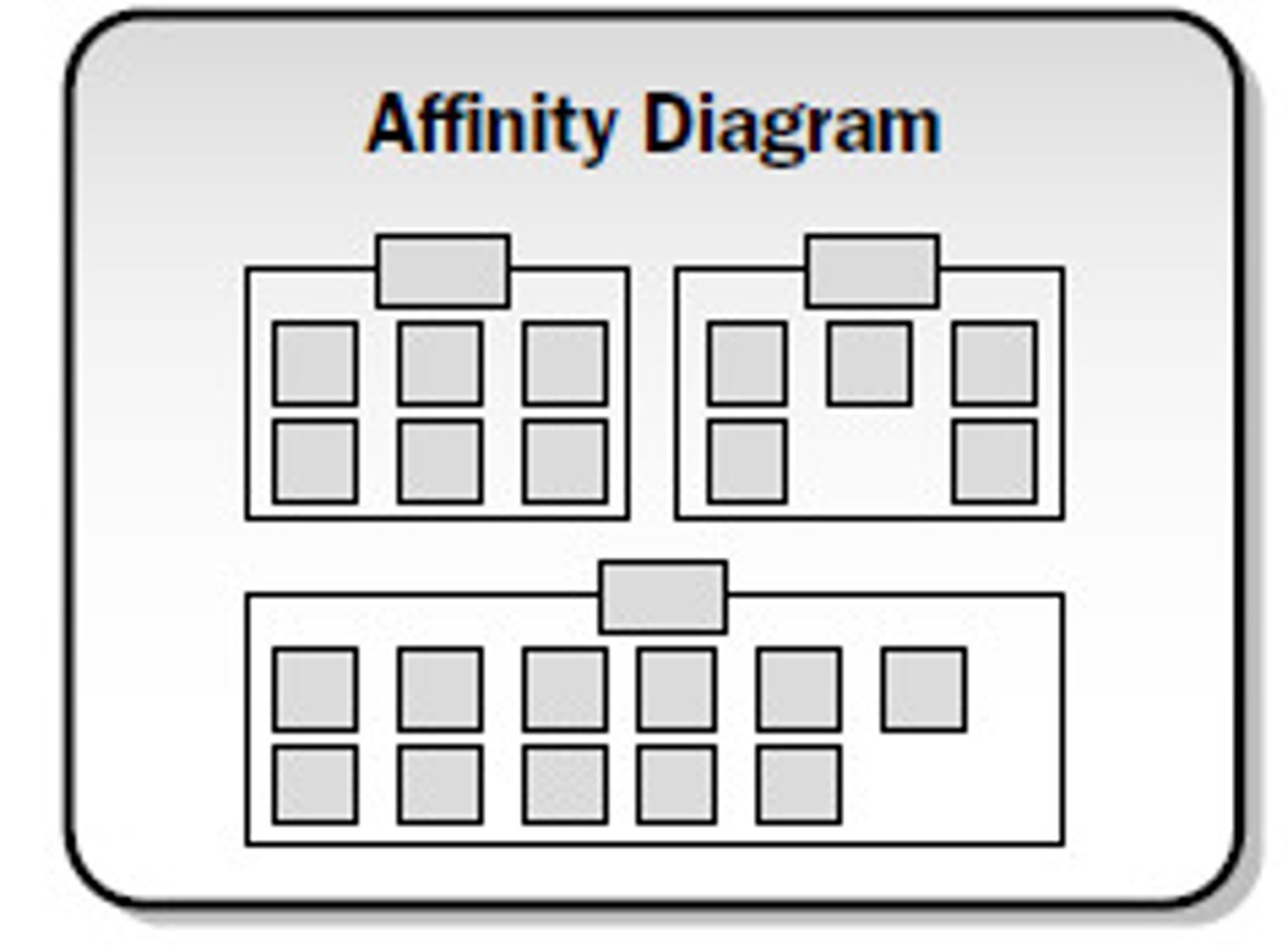
What are Affinity diagrams?
>Allows a team to organize and summarize ideas after a brainstorming session to better understand the essence of a problem
What does an affinity diagram look like?
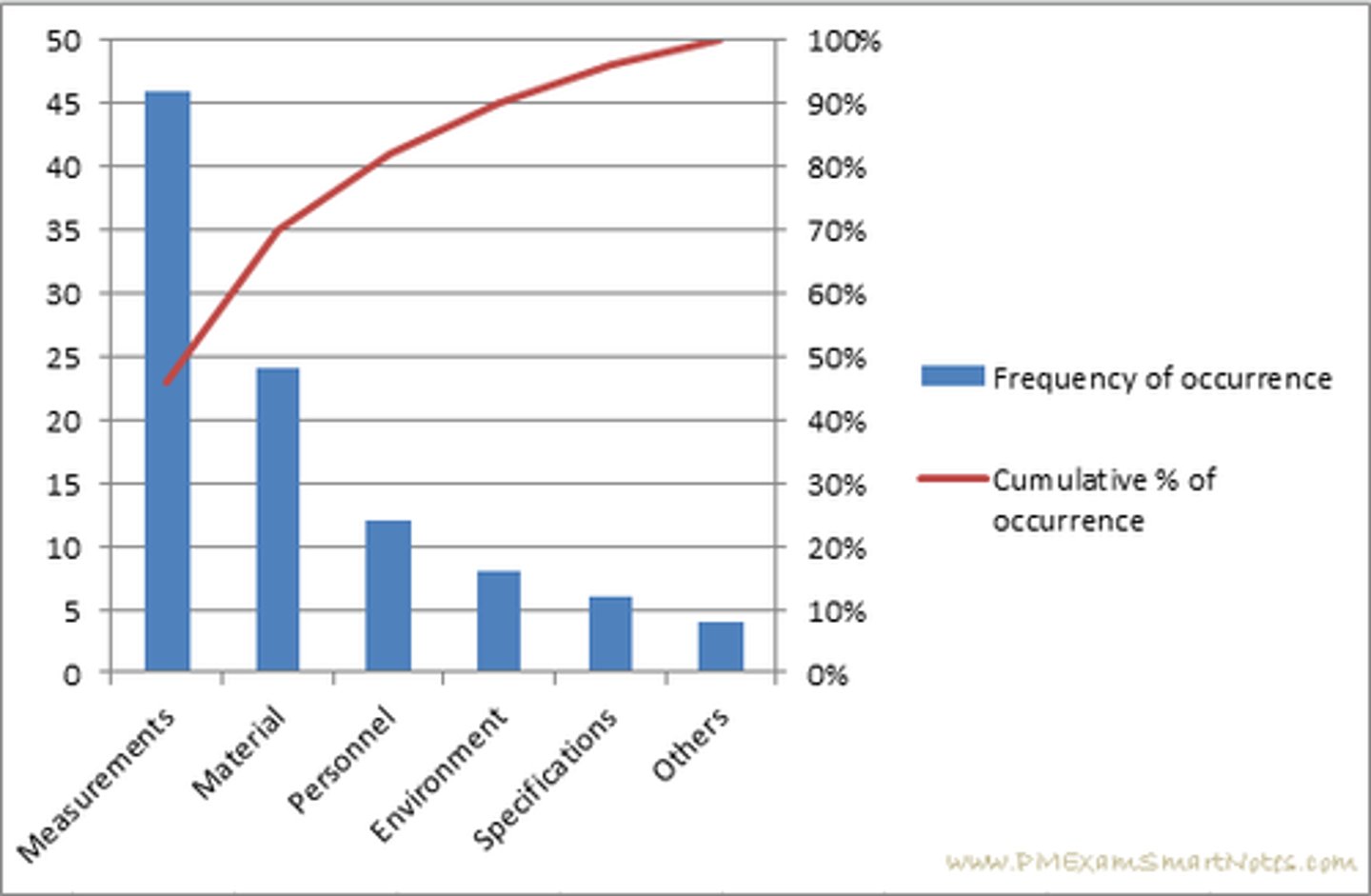
What is a Pareto diagram?
>Graphically shows the relative contribution of each cause to the problem (L > R)
>Allows group to develop a hierarchy of causes and attack largest cause first – prioritize!
What is the Pareto Principle?
"20% of the cause (events) is 80% of the problem"
What does a Pareto diagram look like?
What is a baseline measurement?
needed to "calibrate" more sophisticated assessments, okay for benchmarking, but limited
What are trending measurements?
Used to identify trends by measuring changes in structure, processes, or outcomes over time
What is benchmarking?
>Comparing performance to an ideal standard - external
>Comparing performance over time - internal
What is the achievable benchmark of care? (ABC)
>Measurable and attainable
>Based on best performance
>Provide an appropriate number of cases for analysis
Beware of __________ when benchmarking
Comparability
>Apples aren't oranges
What is a scatter plot?
demonstrates the degree of correlation between 2 variables
What are run charts?
Graphical display of data plotted over time (L to R) with data set's median as the center line
- Provides simple method to determine if process is demonstrating non-random patterns (i.e., "signals")
- Displays data to make process performance visible
- Can help determine if changes result in performance improvement
According to run chart rules what is a run?
is 2 or more consecutive points above or below the median.
- the number of runs equals number of times line crosses the median + 1
According to run chart rules what is a shift?
is 6 or more consecutive points above or below the median.
According to run chart rules what is a trend?
is 5 or more consecutive points moving in one direction
(may cross the median).
According to run chart rules what is a astronomical data point?
is extremely far from the median (an outlier)
What are control charts used for?
more sensitive than Run Charts (usually more advanced)
>Usually used for process measures
>are like Run Charts with control limits added above and below the center line (median)
UCl
Upper Control Limit
LCL
Lower Control Limit
UCL and LCL lines are usually_________ above and below the mean
3-Std.Dev.
What is common cause variation?
>Variations we expect to occur naturally
>They commonly occur
>Data that falls within control limits is considered common cause
What is special cause variation?
>Variations that we would not expect to happen
>They are not a usual occurrence
>They are true outliers and require further investigation