BIOLOGY DNA & GENETICS
1/47
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
DNA structure
Sugar Phosphate Backbone, Double helix, anti-parallel, phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, nitrogenous base ACTG (Complementary base pair rule)
DNA wrapped around histones
DNA Replication
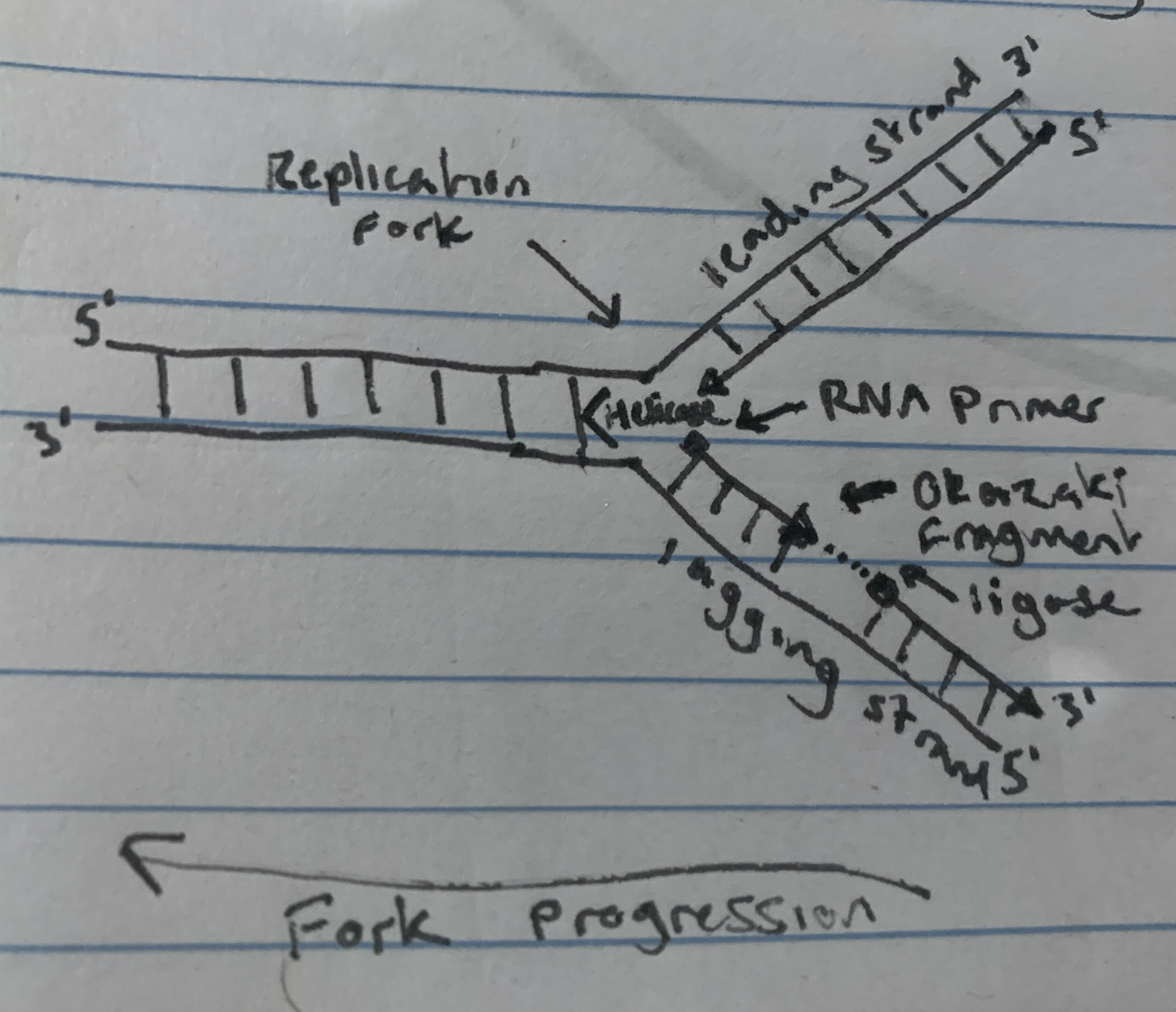
Replication occurs at multiple sites along chromosomes to increase speed
Helicase breaks hydrogen bonds linking complementary base pairs.
Double helix unwinds and separates into two template strands, the point of separation is the replication fork
Primase attaches a primer to the template strands at a complementary sequence, creaking a 3’ position
Free DNA nucleotides pair up (A-T C-G) and form hydrogen bonds with template strands
DNA Polymerase joins nucleotides together in a 5’ to 3’ direction forming S-P backbone
Leading strand (5’ to 3’) forms towards replication fork and can synthesis continuously
Lagging strand is synthesised discontinuously away from replication fork, in 5’ to 3’ direction forming Okazaki fragments
Okazaki fragments are joined together by Ligase
Each new identical DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesised strand. (Semi-conservative Replication)
DNA Replication Diagram
Crossing Over
Occurs during Prophase-1
Matching regions on homologous chromosomes break and reconnect to the other chromosome. Results in genetic recombination.
Random Assortment
Occurs during metaphase-1
Paternal and maternal chromosomes are randomly arranged on each side of the equator, and are therefore randomly pulled to each pole.
Sexual Reproduction
Mother and Father both contribute half the offspring’s DNA, and therefore the offspring will have a random mix genes.
Haploid cell + haploid egg combine to produce diploid cell
Non-Disjunction
Any error during meiosis resulting in an abnormal number of chromosomes in the daughter cells.
ie spindle fibres taking both pairs of homologous chromosomes, instead of one.
Comparing Cell Division

Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein
Allele
An alternative form of a gene; codes for same trait, but different versions of the trait
Mutation
A permanent change in the DNA sequence, chromosome structure or number of chromosomes.
Induced Mutation
Caused by exposure to a mutagen
Spontaneous Mutations
Occur by chance during DNA replication or cell division.
Different causes of mutation
Mutagens - Chemical; Nitric Acid causes substitution. Physical; UV Radiation
Biological Agent - HPV
Errors in DNA Replication or Cell Division
Germline mutations
occur during meiosis, can be passed onto offspring if gametes are fertilised, does not affect health of original individual, but can result in infertile offspring
Somatic mutations
occur during mitosis, adult is affected, offspring is unaffected, can lead to cancer
Dominant
Only one copy of the allele is needed to be expressed in the phenotype
Recessive
Phenotype masked by the presence of a dominant gene - only expressed if two recessive alleles are present
Incomplete Dominance
Occurs when two different alleles are present, but neither allele is completely dominant
-Both alleles partially contribute to the phenotype and a third, intermediary phenotype is observed
Codominance
Occurs when two alleles are completely dominant
-Both alleles equally expressed in the phenotype
Polygenic Inheritance
For one characteristic, two or more genes and therefore two or more sets of alleles contribute to the phenotype
Coding DNA
DNA that is transcribed and translated
Noncoding DNA
DNA that does not get translated and therefore does not code for proteins.
Autosomal Recessive
Unaffected parents have affected offspring (skips a generation)
Autosomal Dominant
Affected offspring must have affected parent
Sex-linked Recessive
Affected males must express phenotype
Affected daughter must have an affected father
Affected mother must have affected sons
Sex-linked Dominant
Condition should appear in every generation
Affected males will not pass affected allele on to their sons - sons inherit father’s Y chromosome
Affected males will pass it onto their daughters because daughters always inherit father’s X chromosome
Sex-Linked Inheritance
Daughters get an X from mother and father
Sons get X from mother
Mitosis - Process
Interphase
Growth-1: Cell grows and carries out it’s normal tasks
Synthesis: DNA Replication - DNA Molecules in nucleus form exact copies
Growth-2: Cell prepares for division
Cell Division
Prophase: chromosomes condensed and visible, centrioles at opposite poles, phase ends with breakdown of nuclear membrane
Metaphase: Chromosomes align along equator, spindle fibres connect centrioles to chromosomes
Anaphase: Spindle fibres contract breaking the centromere, chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles
Telophase: Spindle fibres disintegrate, nuclear membrane reforms
Cytokinesis
Animal Cell: Ring of filaments form around equator and tighten to split the cell
Plant Cell: New cell wall is created, splitting the two cells
Meiosis - Definition and Process
The process by which sex cells (gametes) are made in the gonads. It involves the division of a diploid germline cell into four genetically unique haploid daughter cells
Prophase-1: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form pairs (bivalents), crossing over occurs, centrioles move to opposite poles
Metaphase-1: Bivalents line up along equator of cell, spindle fibres from opposing centrioles connect to centromeres
Anaphase-1: Spindle fibres contract and homologous chromosomes move to opposing poles
Telophase-1: Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms, cell divides (cytokinesis) to form two haploid daughter cells
Prophase-2: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrioles move to opposite poles
Metaphase-2: Sister chromatids line up along equator, spindle fibres connect to centromeres
Anaphase-2: Spindle fibres contract, the sister chromatids are pulled apart, and the centromere breaks
Telophase-2: Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms, cells divide (cytokinesis) into four unique haploid daughter cells
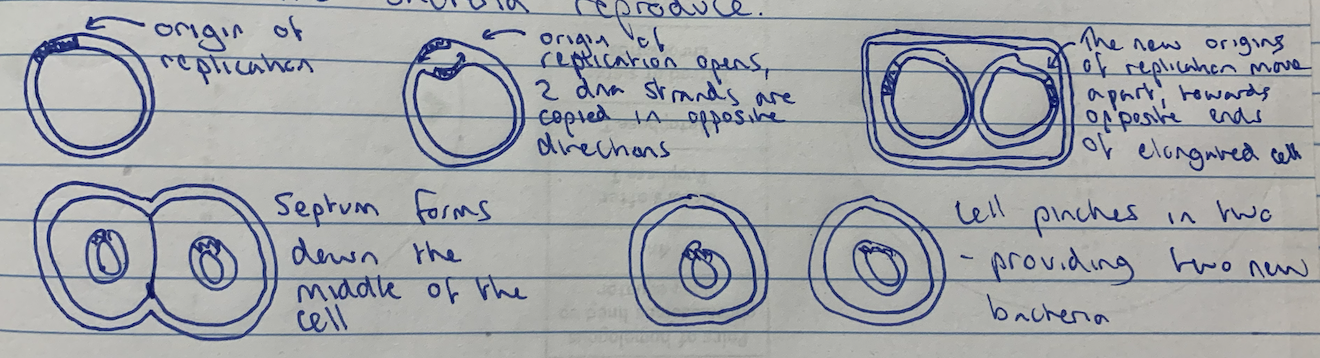
Binary Fission - Definition and Process
A process of asexual reproduction whereby a prokaryotic cell divides into two identical daughter cells
Prior to binary fission, single chromosome is tightly coiled
Genetic material in chromosome and plasmid replicates and separates
Original and replicated chromosomes attach to cell membrane; are pulled to separate poles as cell elongates
New cell wall (septum) starts to grow; cleavage furrow develops in cell membrane
New septum fully develops
Two cells are separate, forming two identical daughter cells, chromosomes become tightly coiled again
Gene Mutations
Substitution
Addition
Deletion
Substitution
A nucleotide swap, which can result in:
Synonymous - Mutation codes for same amino acid so effect is neutral
Missense - Codes for a different amino acid
Nonsense - Prematurely codes for a stop codon, halting translation. Results in a short useless polypeptide - harmful
Addition
Addition of one nucleotide - creates a frameshift resulting in a completely new sequence of amino acids, additionally, either synonymous, missense or nonsense mutations
A frameshift mutation near the start of an amino acid sequence will have much more effect than one at the end
Deletion
Deletion of one nucleotide - creates a frameshift resulting in a completely new sequence of amino acids, additionally, either synonymous, missense or nonsense mutations
A frameshift mutation near the start of an amino acid sequence will have much more effect than one at the end
Chromosomal/Block Mutations
Deletion
Inversion
Translocation
Duplication
Deletion
Middle piece of the chromosome falls out and the two ends rejoin
Results in a loss of genetic material
Inversion
Middle piece of the chromosome falls out, rotates 180° and rejoins
No loss of genetic material
Translocation
A piece of a chromosome breaks off and joins onto another non-homologous chromosome - when the chromosomes are passed to gametes some will receive extra genes, while some will be gene deficient
Duplication
A piece is lost from one chromosome and added to its homologue. One will be deficient while the other receives double the genes.
Euploid, Aneuploid, Monosomy, Trisomy
Euploid: A cell containing chromosomes correctly organised into complete sets
Aneuploid: A cell missing one or more chromosomes.
Monosomy: One copy of a chromosome that should be present in two copies
Trisomy: Third copy of a chromosome that should be present in two copies
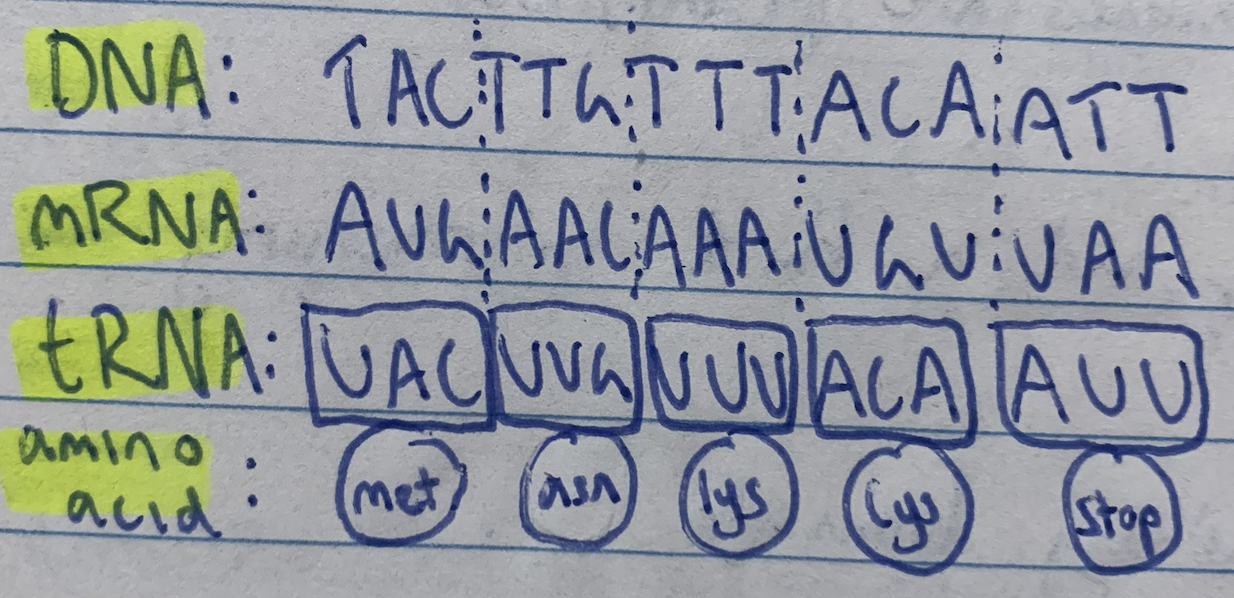
Transcription
DNA code is copied into mRNA
DNA unwinds and unzips due to helicase, which breaks the hydrogen bonds
This exposes the nitrogenous bases of the template strand (3' to 5’)
RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter region
mRNA is synthesised from the start codon
RNA Polymerase makes mRNA by adding nucleotides under the complementary base pair rule, in a 5’ to 3’ direction
Instead of thymine, uracil pairs with adenine
mRNA synthesis finishes when the RNA Polymerase reaches the terminator region after the stop codon at the end of the gene
The mRNA released is single stranded and contains introns and exons
mRNA undergoes splicing, where introns are removed
The DNA zips up and the mRNA leaves the nucleus via a nuclear pore
Translation
mRNA at the ribosome is used to build a polypeptide
mRNA attaches to the ribosome at the start codon (AUG)
tRNA molecules each carry a specific amino acid
Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that corresponds with a specific mRNA codon
As the ribosome reads the mRNA codons, tRNA molecules bring the appropriate amino acid in the correct sequence
tRNA detaches and collects another amino acid from the cytoplasm
Adjacent amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds
When the stop codon is reached, the mRNA is released from the ribosome
The polypeptide chain detaches and folds into a protein
DNA to mRNA to tRNA to Amino Acid
Punnett Square Marking Key
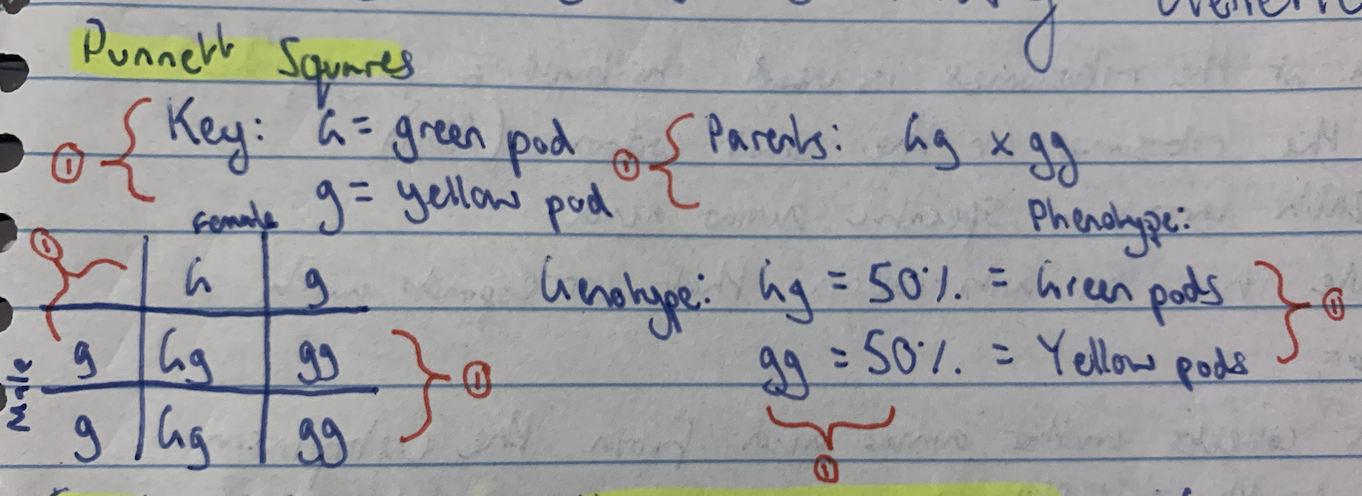
Polygenic Inheritance vs Monogenic Inheritance

Comparing DNA and RNA

Comparing nDNA and mtDNA
