contemporary psychodynamic and humanistic therapies
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what are psychodynamic therapies
definition: a group of therapeutic approaches that explore unconscious processes and past experiences to understand and address current psychological difficulties, often focusing on the influence of early relationships and unresolved conflicts
originate from psychoanalysis
now shorter and less focused on analysis
focus on unconscious processes that impact client’s present behaviour
e.g.,
short-term psychodynamic theory
mentalization-based therapy
transference-focused psychotherapy
uses transference processes on the therapist to allow the client to improve relationships with other people in their life
what are humanistic/experiential therapies
originate from client-centered therapy
based on premise that individuals are “self-actualizing”
they want to be the best versions of themselves
e.g.,
gestalt therapy
existential therapy
emotion-focused therapy
interpersonal psychotherapy
pretty good for depression and BN
second-line treatment if CBT isn’t working
what are the seven things that distinguish these therapies
focus on affect and the expression of patient emotions
exploration of the patient’s attempts to avoid topics or engage in activities that hinder therapy progress
identification of patterns in patient’s actions, thoughts,
feelings, experiences, relationships
an emphasis on past experiences
focus on patients’ interpersonal experiences
emphasis on the therapeutic relationship
exploration of patients’ wishes, dreams, or fantasies (clues to unconscious functioning)
what is “a focus on affect and the expression of patient emotions”
intellectual insight isn’t sufficient
also need emotional insight
tune in when you’re having an emotional response
not just walk through the motion, actually feeling it
encourage expression of emotions rather than management or control
avoid/empty feelings that have been bottled up in a safe setting such as therapist's office
draw attention to feelings the patient sees as uncomfortable
what is “an exploration of the patient’s attempts to avoid topics or engage in activities that hinder therapy progress”
explore these disturbances to uncover unconscious meaning
talking about the therapy process
whether or not they’re trying to say something they don’t have the words for
e.g.,
redirect conversation
not complete homework
miss session
not pay bill
what is “identification of patterns in patient’s actions, thoughts, feelings, experiences, relationships”
identify patterns beyond those in thoughts
how patterns in interpersonal functioning repeat over time, settings, and people
can mirror early childhood relationship
patterns are identified through interpretations
the therapist suggesting some type of pattern that they’ve noticed
sharing with client and seeing if it resonates with them
and what they’re reaction is to them
what is “an emphasis on past experiences”
identify origin of patient difficulties and understand how they have manifested in lifetime (both past and present)
emphasize both pre-adult and adult past
recent trend for PI treatment to be more present-focused
can be difficult to do since it’s such a ST treatment
what is “a focus on patients’ interpersonal experiences”
problematic relationships interfere with ability to fulfill needs and wishes
what needs are being filled through maintaining a problematic
compare and contrast patient functioning with that of others
impact patient has on other people
especially useful for personality disorders to highlight how they’re hurting others
what is “an emphasis on the therapeutic relationship”
therapeutic relationship is a vehicle or medium of change
if they can work on the therapeutic relationship with the therapist then they can do the same with the relationships in their life
transference = patient’s projections onto therapist
therapist elicits feedback about client’s reactions to therapy
how do they feel sharing their emotions
what is the goal of ST psychodynamic therapy
symptom relief and limited (but significant) character change
secondary goal is the character change (personality and interpersonal)
work on one circumscribed area of focus (very important for ST treatments)
what is the structure of ST psychodynamic therapy
once per week for less than one year (e.g., 16 sessions)
therapist must maintain therapeutic eye on chosen focus
therapist’s job is to help keep the sessions on track on the circumscribed area of focus since it’s ST
what is the candidature for ST psychodynamic therapy
patients should be psychologically minded, insightful, motivated
to be able to make significant change in such a short period of time = need to have this motivation
capacity to engage readily and disengage easily
what are the techniques used by ST psychodynamic therapy
supportive
defining the therapeutic “frame”
boundaries around therapy
therapist isn’t your friend; there for a job
demonstrating genuine interest and respect
noting gains
helps people feel that they’re making progress and helps them move forward more quickly
maintaining here-and-now perspective
expressive
offering empathic comments
confrontation
questioning people if they aren’t attuned to how they affect other people
interpretation
not drawing conclusions but suggesting patterns
monitoring countertransference
how you might be reacting to the client
can slow down potential for progress
efficacy of ST psychodynamic therapy
american journal of psychiatry 2017 (steinert)
meta-analysis of 23 RCTs comparing psychodynamic therapy to an established treatment
both treatments use manuals
tested for equivalence of two treatments
what is the primary and secondary outcomes of the efficacy study in ST psychodynamic therapy
primary: target symptoms (e.g., depression)
secondary: general symptoms and psychosocial functioning
what were the findings of the efficacy study in ST psychodynamic therapy
no meaningful or statistical difference between psychodynamic and comparator treatments at post-treatment and follow-up
difference favouring psychodynamic treatment for functioning at follow-up (slight statistical meaning but not really meaningful)
slightly better for general bettering of the individual
emotion-focused therapy (EFT)
developed by leslie greenberg
aka process-experiential therapy
16-20 sessions
key determinant of self-organization: emotions
emotions useful from an evolutionary standpoint
tell us about when we need to act/retreat
who we need to keep contact with
how we make sense of our emotional experiences = influenced by culture
what are the types of emotions according to emotion-focused therapy (EFT)
primary: direct initial reaction (e.g., sadness from loss) — instinctive
secondary: secondary to primary emotions (e.g., guilt over sadness)
adaptive: primary emotions that communicate information — evolutionary (e.g., fight-or-flight)
maladaptive: “old familiar feelings” that do not change with situation
what are the three principles targeted in treatment in emotion-focused therapy (EFT)
emotion awareness
emotion regulation
emotion transformation
emotion awareness — three principles targeted in treatment in emotion-focused therapy (EFT)
become aware of primary adaptive emotions
to be able to use this information
not thinking about feeling but actually feeling the emotion
can allow a lot of work to be done in therapy to process them
accept rather than avoid emotional experiences
express emotions, including what you feel in words
what does that emotion make you want to do
what does it feel like in the body
emotion regulation — three principles targeted in treatment in emotion-focused therapy (EFT)
work to determine which emotions need to be regulated
adaptive vs maladaptive and appropriate in specific situations
teach emotion regulation skills, including tolerance and self-soothing
emotion transformation — three principles targeted in treatment in emotion-focused therapy (EFT)
process of changing emotion with emotion
undo maladaptive emotional response with more adaptive emotion
in CBT: it’s thinking about the emotion differently
techniques used in emotion transformation:
shifting attention
positive imagery
remembering another emotion (thinking about another time when you were feeling a different emotion)
other techniques in EFT
two-chair dialogue for self-critical conflicts
person is trying to gain confidence but is highly critical of themselves, which makes it difficult to do so
the person would play out both sides of the conversation
trying to externalize and look at yourself from an outside perspective
reacting to the negative mean things that you’re saying to yourself
empty-chair work for unfinished business
e.g., if you still have conflict with someone who is dead, estranged, etc.
allows you to get rid of those feelings even though they aren’t in your life anymore
research evidence for EFT in major depression
outcomes similar in EFT and CBT
greater decrease in interpersonal problems in EFT compared to CBT
symptom remission greater in EFT compared to client-centered therapy
interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT)
developed by klerman and weissman
concerned with interpersonal context
relation factors that predispose (vulnerability factors), precipitate (factors that come just before the onset of the distress), and perpetuate (maintenance factors) distress
structure: 12-16 sessions
suitability:
secure attachment (not for abusive relationships)
specific interpersonal focus of distress
good support system
interpersonal triad (she didn’t talk about this though)
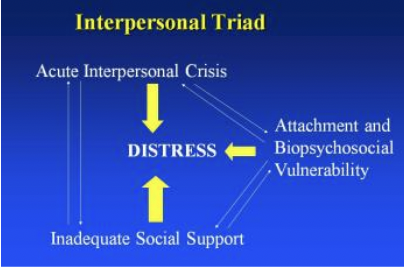
IPT problem areas
role transitions (e.g., moving, new job, divorce)
role disputes (e.g., infidelity, unmet expectations)
grief
interpersonal sensitivity (difficulty forming and maintaining relationships
general patterns that have occurred throughout interpersonal relationships
last resort time of focus because you get less out of it since it’s more vague and less focused on a specific relationship
IPT structure
interpersonal inventory administered to choose problem area
work collaboratively to develop solutions to problem
patient implements solution(s) between sessions
IPT techniques
interpersonal incidents
detailed retelling of the incident
communication analysis
going through things you could’ve done differently
analyzing each step of the detailed recounting of the incident
therapist is talking through the situation and bringing them to problem-solving
noticing the pattern and bringing it back to past interpersonal conflict
problem-solving and role-playing
figure out how it went or how it’ll go
practice the situation before it occurs (with the therapist)
encouragement of affect — content vs. process
process of just having these discussions, which can be difficult for some people
IPT research evidence
depression (meta-analysis of 62 RCTS of IPT)
d=.62 (medium) in favour of IPT compared to control treatments
d=0.06 for IPT compared to other psychotherapies
bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder
CBT more rapidly improves BN symptoms compared to IPT
but treated with IPT = continue to improve post-treatment
clients are learning skills to improve their interpersonal relationships, their communication skills and continue to practice after the treatment is done, which continues to help them
group IPT comparable to group CBT for binge eating
Which of the following is NOT an example of a contemporary humanistic therapy?
a) | Existential therapy |
b) | Emotion-focused therapy |
c) | Transference-focused therapy |
d) | Gestalt therapy |
a) | Existential therapy |
b) | Emotion-focused therapy |
c) | Transference-focused therapy |
d) | Gestalt therapy |
Which of the following is TRUE about the Steinert et al., 2017 meta-analysis on psychodynamic therapy?
a) | All treatments in the studies included in the meta-analysis used treatment manuals |
b) | The meta-analysis used traditional significance testing to determine whether psychodynamic therapy outperforms comparator treatments |
c) | Only studies using longer (i.e., 6 months-1 year) versions of CBT were included in the meta-analysis |
d) | Comparator treatments significantly outperformed psychodynamic therapy at post-treatment and follow-up |
a) | All treatments in the studies included in the meta-analysis used treatment manuals |
b) | The meta-analysis used traditional significance testing to determine whether psychodynamic therapy outperforms comparator treatments |
c) | Only studies using longer (i.e., 6 months-1 year) versions of CBT were included in the meta-analysis |
d) | Comparator treatments significantly outperformed psychodynamic therapy at post-treatment and follow-up |
Which of the following is LEAST likely to be a primary emotion, as defined by emotion-focused therapy?
a) | Shame |
b) | Sadness |
c) | Fear |
d) | Anger |
a) | Shame |
b) | Sadness |
c) | Fear |
d) | Anger |
Which of the following is NOT one of the three principles targeted in emotion-focused therapy?
a) | Emotion transformation |
b) | Emotion regulation |
c) | Emotion adaptation |
d) | Emotion awareness |
a) | Emotion transformation |
b) | Emotion regulation |
c) | Emotion adaptation |
d) | Emotion awareness |
In the video example of interpersonal psychotherapy, which interpersonal problem area was MOST likely the target of therapy?
a) | Role transition |
b) | Grief |
c) | Interpersonal sensitivity |
d) | Role dispute |
a) | Role transition |
b) | Grief |
c) | Interpersonal sensitivity |
d) | Role dispute |