1ST SEM MIDTERM: Ancient Greek Architecture
1/211
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
Greece
A country in southeastern Europe known for its rich history, culture, and contributions to art, philosophy, and democracy.
Religion
plays a significant role in the development of Greek architecture
architecture started in the service of religion
Geography of Greece
south-eastern Europe
Surrounded by three major seas:
Ionian Sea (WEST)
Aegean Sea (WEST)
Mediterranean (SOUTH)
Mountainous, fertile land
Dorian Tribe
located in the ruins of Sicily and southern Sicily
Ionian group
located at the lands of Asia Minor
Crete
largest island located at the southern part of the Mediterranean Sea
Climate of Greece
intermediate between Cold and Hot
City-States
Independent regions in ancient Greece, each with its own government and laws, such as Athens and Sparta.
Geology in Greece
Marble (chief mineral in Greece)
Other minerals found in the mountains:
gold
iron
lead
bronze
silver
Marble
chief mineral in Greece
most monumental and most beautiful of all building materials
Religion in Greece
Aegean Religion
worships nature, priestess rather than a priest
Greek Religion
worship of nature and a group of superhuman Gods and Goddesses
Aegean Religion
primitive stages
worships nature
priestess rather than a priest conducts religious rites
sacred bull
horns of consecrations
sacrificial altars
Rhea (fertility/mother-goddess)
Rhea
fertility or mother-goddess
priestess
Aegean religion
Greek religion
based on the worship of nature
and of a group of superhuman gods and goddesses
natural phenomena in which a god is personifying
12 Olympians (major gods in Greece)
Zeus
Hera
Athena
Apollo
Aphrodite
Demeter
Poseidon
Ares
Dionysus
Artemis
Hephaestus
Hades
Zeus
King of all Gods
Hera
wife of Zeus
representation of an excellent wife and motherly qualities
Athena
Goddess of Wisdom
Patron Goddess of Athena
emerged fully-grown at Zeus’s head
Apollo
God of light, music, sun, healing, and male beauty
Aphrodite
Goddess of love and beauty
bor out of sea foam
Demeter
mother of nature and earth
watches over planting and harvest time
Poseidon
God of the seas
brother to Zeus
Ares
God of war and battles
Dionysus
God of spring
wine
gay
Artemis
Goddess of the forest and the moon
a huntress
sister of Apollo
Hephaestus
Blacksmiths for the Gods
Hades
ruler of the Underworld
Social Structure in Ancient Greece
Upper class (elite)
Middle class (professional workers)
Lower class (freed slaves)
Slaves (prisoners of war, infants of criminals, course slaves)
Upper Class
the elite
men who:
did not have any jobs that dealt with economics (trading)
had slaves
had property and material value
had time for politics, philosophy, leisure, etc.
Middle Class
professional workers:
merchants
contractors
craftsmen
managers
many were non-citizens (not slaves, but of foreign birth)
Lower Class
freed slaves
Slaves
prisoners of war
infants of criminals
course slaves
few people were of Greek race
Ancient Greece was peopled by:
Ionians
Dorians
Aeolians
Corinthians
Ancient Greece Timeline
Early Periods (3000 BC - 700 BC)
Aegean/Minoan - rough and massive
Mycenean
Dark Ages (1100 BC - 500 BC)
Archaic Period
Aegean/Minoan architectural character
rough and massive
Aegean/Minoan characteristic features
rough and massive structures
low pitch / flat roof on multi-storey structure
stairway for vertical circulation
capital (square abacus) circular bulbous echinus
cyclopean walls: large stones without mortar, on clay bedding
megaron (houses)
palaces were principal building types
Cyclopean walls
large stones without mortar on clay bedding
3 Major Cultures in the Aegean Civilization
Cycladic (Venus figurines in white marble)
Minoan (animal imagery, images of harvest, unwarlike architecture)
Mycenaean (gold masks, war-faring imagery, sturdy architecture)
Cycladic
“Venus” figurines
carved in white marble
Minoan
animal imagery
images of harvest
light, breezy, unwarlike architecture
antithesis of the Mycenaean art
Mycenaean
gold masks
war-faring imagery
sturdy architecture
citadels
tunnels into the bedrock
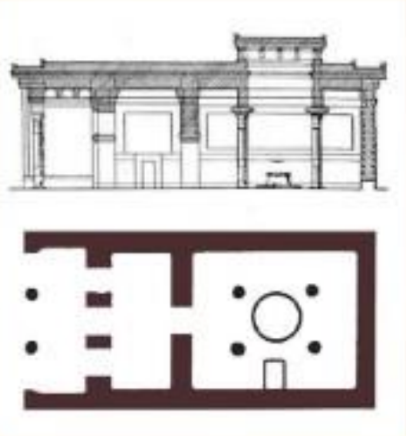
Megaron
Mycenaean
The Great Hall in the Palace of Pylos
square rooms with 4 columns
place for religious rituals
represents the origin of the Greek temples in the next period
hearth in the center
clerestory ceiling
single-storey dwelling with
Enclosed porch
Living apartment or megaron proper
“Thalamus” sleeping room
Thalamus
sleeping room
Megaron Plan: Citadel of Troy
large rectangular hall
has a room that’s nearly square
deep porch formed by extending the side walls

4 Methods of walling surface finishes
Cyclopean (masonry made-up of huge stone blocks laid mortar)
Polygonal (masonry with stones having polygonal faces)
Rectangular (block of stone cut into rectangular shapes)
Inclined blocks (stones with inclined blocks)
Cyclopean
masonry made-up of huge stone blocks laid mortar

Polygonal
masonry which is contructed with stones having polygonal faces

Rectangular
block of stone cut into rectangular shapes

Inclined blocks
stones with inclined blocks

Typical Minoan Character
stairways
light wells
colonnades
cypress wood
drainage & sanitation system
the planning is chaotic but a result of organic growth

Palace of Minos at Knossos
minoan character example

Mycenean or Helladic
end of Bronze age civilization
advent of the Iron age in Greece
Pelasgic, Cyclopean or Primitive Period
Mycean or Helladic architectural characteristics
Rough walling of large stone blocks
Corbel system, true arch
Palace of Mycenae
Part of the citadel palace of Agamemnon

Lion Gate of Mycenae
Relief carving of two lions facing a central column

Corbels
horizontal courses of stones were laid, projecting one beyond the other until the apex was reached
triangular opening (above the doorways of the Tholos Tombs)
apparent arch (gallery at Tiryns)
dome shaped roof (Treasury of Atreus)
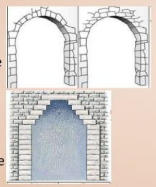
Treasury of Atreus (Tomb of Agamemnon)
Mycenaean
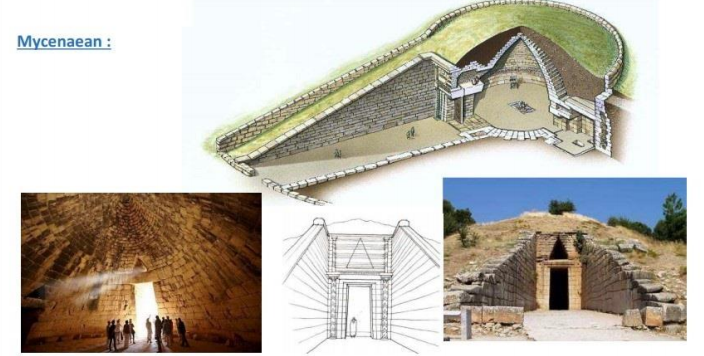
Tholos or beehive tombs (monumental symbols of wealth and power)
place for gathering, trade, and rituals
Kings were buried outside the cities in beehive tombs
Corbelled dome (covered with earth to form conical hill)
2 half columns and stone lintel above the entrance
Kinds of masonry for walls in Minoan & Mycenaean architecture
Cyclopean (rough stones piled on each other, smaller blocks put between larger ones)
Rectangular (rectangular blocks arranged in regular courses, joints between stones are not always vertical; seen in Mycenaean architecture — entrance passage in beehive-tombs)
Polygonal (many sided blocks accurately placed to fit together)
Corbels (horizontal courses of stones laid until an apex is reached; triangular opening and dome shaped roof in Treasury of Atreus)
Cyclopean (masonry in Minoan & Mycenaean architecture)
rough stones piled on each other
smaller blocks put between larger ones)

Rectangular (masonry in Minoan & Mycenaean architecture)
rectangular blocks arranged in regular courses,
joints between stones are not always vertical;
seen in Mycenaean architecture
entrance passage in beehive-tombs

Polygonal (masonry in Minoan & Mycenaean architecture)
many sided blocks accurately placed to fit together

Corbels (masonry in Minoan & Mycenaean architecture)
horizontal courses of stones laid until an apex is reached;
triangular opening in Treasury of Atreus
dome shaped roof in Treasury of Atreus

Dark Ages to Archaic Period
1100 BC — 500 BC
Dark Ages
the Mycenaean civilization started to collapse
it was abadoned and destroyed
due to climatic and environmental catastrophes
+ due to the invasion of Dorians
Why did the Mycenaean civilization collapse?
due to climatic and environmental catastrophes
due to the invasion of Dorians
Archaic Period
revival of Greece
city states were developed
rise of aristocratic families
marks the beginning of Greek monumental stone sculpture and architecture
Polis / city state
cities which are ruled as independent nations
emerged as the natural and desirable political entity
Early examples of city states
Mainland
Athens
Corinth
Argos
Sparta
Eastern Aegean
Samos
Chios
Smyrna
Ephesus
Miletus
Classical Period & Hellenistic Period
650 BC - 30 BC
Classical, Hellenic period
golden age of Greece
culmination of Greek arts and architecture
before the time of Alexander the Great
columnar and trabeated; carpentry in marble
timber, stone, and terracotta
structures were ornamented with sculptures, colors, and mural paintings
the temple became the chief building type
humanism
Materials used during the Classical, Hellenic period
timber
stone
terracotta
Type of architecture the Classical, Hellenic period
columnar and trabeated
carpentry in marble
the temple
classical, hellenic period
became the chief building type
admired from the outside, not intended for internal worship
sculptures for deities to whom they were dedicated
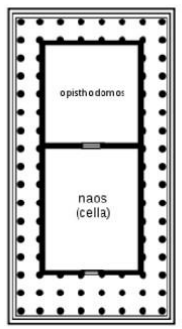
Plan of a Temple (Classical, Hellenic period)
stood upon a crepidoma of three or more steps
NAOS - contained statues of gods and goddesses
PRONAOS - front portico
OPISTHODOMOS / EPINAOS - rear portico
sometimes there are treasury chambers
the smallest buildings were surrounded by colonnades
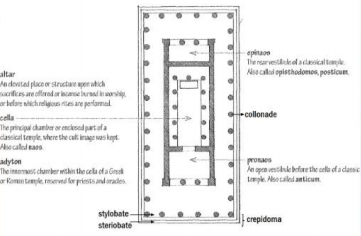
NAOS (Temple, Hellenic period)
contained the statues of gods and goddesses
PRONAOS (Temple, Hellenic period)
front portico
OPITHODOMOS / EPINAOS
rear portico
Elevation of a Temple (Classical, Hellenic period)
double colannades to carry the roof (made of timber, covered with terra cotta)
light was let in through cut-holes on the large tiles of the roof
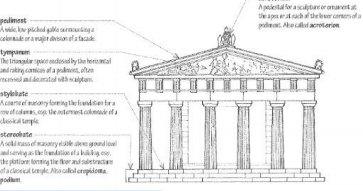
triangular-shaped pediment and tympanum on the ends of temples (terminates roof span)
doors were placed within the pronaos on the east front
windows were rare in temple buildings
Eaves in the Temples (Classical, Hellenic period)
antefixa
antefix
antifixae

3 sections from the ground up in a temple (Classical, Hellenic period)
platform
colonnade (columns)
superstructure (what rests on the columns)
Temple as described according to:
Number of columns on the entrance front
Arrangment of the exterior columns in relation to the naos
Number of columns on the entrance front
Henostyle - 1 column
Distyle - 2 columns
Tristyle - 3 columns
Tetrastyle - 4 colums
Pentastyle - 5 columns
Hexastyle - 6 columns
Heptastyle - 7 columns
Octastyle - 8 columns
Enneastyle - 9 columns
Decastyle - 10 columns
Dodecastyle - 11 columns
Number of columns in front + 1 by the side
a hexastyle temple = 6 columns in front, 13 on the side

stylos
“style”
Greek word for column
Arrangement of exterior columns in relation to the naos (temple)
prostyle: columns across the front porch only
amphiprostyle: columns across the front and back
peristyle: columns around the cella
dipteral: double rows of columns around the cell
pseudo dipteral: only an outermost row of columns
anta: posts/pillars on either side of a doorway or entrance
prostyle
columns across the front porch only

amphiprostyle
columns across the front and back porch

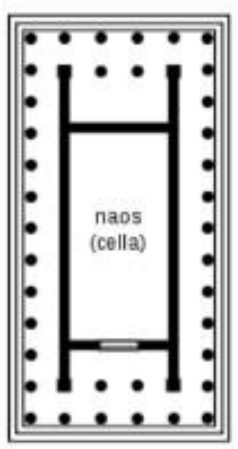
peristyle
columns around the cell
Variations of Peristyle
peripteral
dipteral
peripteral
single row of columns around the cell
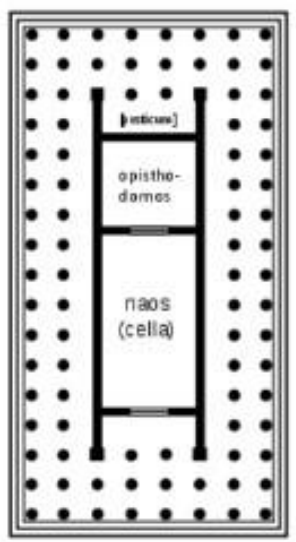
dipteral
double rows of columns around the cell
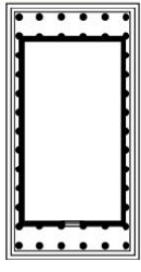
pseudodipteral
temples with a room behind the naos (cella)
pseudoperipteral
temples, the naos room is closed by walls from four sides
Anta
posts or pillars on either side of a doorway or entrance of a Greek temple

Humanism
classical, hellenic period
a belief in the worth, significance, and dignity of an individual
Structure decorations in the classical, hellenic period
sculptures
colors
mural paintings
Highest achievements in the Classical, Hellenic period
Temple of Zeus at Olympia
Parthenon in Athens
Hellenistic period
after Alexander the Great’s death
modified by foreign elements
diversion from religious building types
civic structures
inspiration for Roman architecture
symmetrical and orderly design and layout
moldings for decorations
Structure decorations in the Hellenistic period
moldings
Important Features of Greek Architecture
mouldings
intercolumnation