Chemistry - Core Practicals: 1-8
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
CORE PRACTICAL 1
measure out fixed volume of hydrochloric acid in conical flask
add known mass of sodium carbonate to conical flask
connect gas syringe delivery tube
allow reaction to go to completion
record volume of carbon dioxide produced
repeat experiment with different masses of sodium carbonate
assumptions made about experiment:
amount of gas lost between adding sodium carbonate + connecting delivery tube is minor
delivery tube set up is airtight = no gas lost
reaction does go to completion
CORE PRACTICAL 1 ANALYSIS + RESULTS
results are plotted onto a graph
mass of sodium carbonate on x-axis + volume of carbon dioxide produced on y-axis
anomalous results ignored + one line of best fit added
CORE PRACTICAL 1 APPLICATION
experiment used to determine identity of unknown metal in a metal carbonate, MCO3
- process can be applied to thermal decomposition of metal carbonates + reaction with acid
hazards, risks + precautions core practical 1
hazards associated with acids depend on type + concentration of acid
dilute acids require no hazard symbol/an irritant = require symbol = harmful to health
eye protection worn when handling
moderately concentrated acids are often corrosive
wear eye protection, gloves should be worn
concentrated acids are oxidising = cause/intensify a fire
eye protection + gloves are necessary when handling concentrated acids + the use of a fume cupboard
CORE PRACTICAL 2
using a measuring cylinder place 25cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 copper(II) sulphate solution into polystyrene cup
weigh about 6g of zinc powder = an excess
draw a table to record initial temperature + time every half minute up to 9.5 minutes
put thermometer in cup, stir + record temperature every half minute for 2.5 minutes
at 3 minutes, add zinc powder to cup (DON’T RECORD TEMPERATURE AT 3 MINUTES)
continue stirring + record temperature for an extra 6 minutes
for calculations, some assumptions are made about the experiment:
specific heat capacity + density of solution is same as pure water
specific heat capacity of container is ignored
reaction is complete + minor heat loss
why is a temperature correction graph used
reactions that aren’t instantaneous = before maximum temperature reached
- during delay = substances themselves lose heat to surroundings = true maximum temperature never reached
- use graphical analysis to determine maximum enthalpy change
how to make a temperature correction graph
take temperature reading before adding reactants for a few minutes
add second reactant + continue recording temperature + time
plot graph + extrapolate cooling part of graph until intersect time at second reactant added
CORE PRACTICAL 3
measure known volume of solutions via volumetric pipette + place it into conical flask
The other solution is placed in the burette
To start with, the burette will usually be filled to 0.00 cm3
drops of indicator added to solution in conical flask
tap on burette is opened + add solution at a portion to conical flask until indicator change colour
getting near to end point, flow of burette should be slow down
should be able to close tap on burette after 1 drop has caused colour change
multiple runs carried out until concordant results are obtained
concordant results within 0.1 cm3 of each other
CORE PRACTICAL 4
weigh out precise amount of solid
add small volume of water + pre-dissolve solid
transfer to volumetric flask
rinse beaker with distilled water + add rinsings to flask
mark up to scratch mark with distilled water + add stopper + mix contents
CORE PRACTICAL 5
acidified silver nitrate used to measure rate of hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes
set up 3 test tubes in 50C water bath with mixture of ethanol + acidified silver nitrate
add a drops of chloroalkane, bromoalkane + iodoalkane to test tube + start stop watch
time how long it takes for precipitates to form
white precipitate = chloroalkane
cream precipitate = bromoalkane
yellow precipitate = iodoalkane
yellow precipitate form fastest
C-I bond = lowest bond enthalpy = easiest to break + I- ions to form fastest
white precipitate form slowest
C-Cl bond = highest bond enthalpy = hardest to break + Cl- ions to form slowest
CORE PRACTICAL 6
measure 8cm3 of 2-methylpropan-2-ol in measuring cylinder
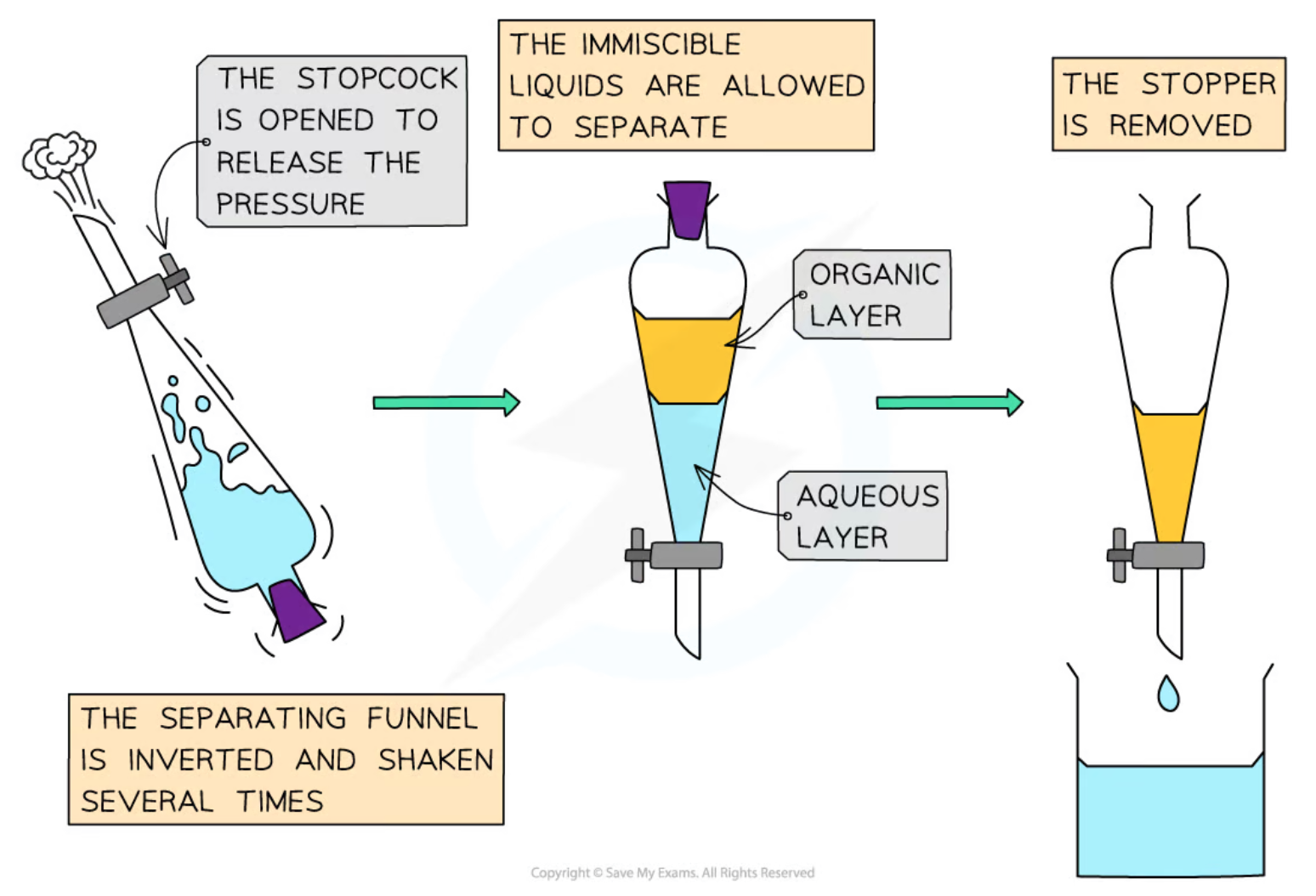
pour 2-methylpropan-2-ol in separating funnel
via fume hood, add 20cm3 concentrated hydrochloric acid to separating funnel in small portions of 2-3cm3 = ensure to release pressure by opening stopper
leave separating funnel to stand in fume hood for 20 minutes + gently shake separating funnel at 2 minute intervals
allow layers to separate + dispose lower aqueous layer by opening tap
add sodium hydrogen carbonate solution in small portions to funnel + gently shake funnel = release pressure at regular interval = removes acidic impurities
layers have separated, open tap again dispose of aqueues layer
pour organic layer in clean dry conical flask + add 2 spatulas of magnesium sulfate = remove water
once clear, decant liquid into distillation apparatus
distill liquid + collect distillate in range of 47-53C
oxidation of alcohols core practical 7
primary alcohols oxidised = aldehydes = further oxidation = carboxylic acids
- propan-1-ol oxidised = ethanal’s produced + oxidised further propanoic acid formed
CORE PRACTICAL 7
add 20 cm3 of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution to 50 cm3 pear-shaped flask + cool flask in iced water bath
set up reflux apparatus keeping pear shaped flask cool
place anti-bumping granules to pear shaped flask
measure out 1 cm3 of propan-1-ol
via pipette add propan-1-ol drop wise in reflux condenser
propan-1-ol added, remove ice bath + warm up to room temperature
position flask over electric heater in a water bath + heat for 20 minutes
purify product using distillation apparatus
propan-1-ol is flammable = naked flames shouldn’t be used when heating
hazards, risks + precautions in core practical 7
alcohols are flammable and often harmful to health, e.g, propan‐1‐ol, butan‐1‐ol, pentan‐1‐ol
- alcohols kept away from naked flames
- avoid contact with skin + breathing in vapour
- fume cupboard used for harmful alcohols
- potassium dichromate is strong oxidising agent + handled with care
- spillages should be mopped up
CORE PRACTICAL 8 (AMMONIUM IONS)
about 10 drops of solution with ammonium ions added to clean test tube
about 10 drops of sodium hydroxide added via pipette
test tube swirled carefully to ensure mixed well
test tube of solution placed in beaker of water + beaker of water placed above bunsen burner = become water bath
solution’s heated, fumes produced
tongs used to hold damp piece of red litmus paper near mouth of test tube = test fumes
red litmus paper changes colour = turns blue in presence of ammonia gas
CORE PRACTICAL 8 (CARBONATE IONS)
small amount of dilute hydrochloric acid added to test tube via pipette
equal amount of sodium carbonate solution added to test tube via clean pipette
as soon as the sodium carbonate solution is added, bung with delivery tube should be attached to test tube
delivery tube transfer gas formed to a different test tube which contains small amount of limewater
carbonate ions react with hydrogen ions from acid to produce carbon dioxide gas
carbon dioxide gas turn limewater milky
CORE PRACTICAL 8 (SULFATE IONS)
acidify sample with dilute hydrochloric acid add a few drops of aqueous barium chloride
sulfate’s present = white precipitate of barium sulfate is formed
Ba2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) → BaSO4 (s)
CORE PRACTICAL 8 (FLAME TESTS)
dip the loop of nichrome metal wire such in concentrated acid + hold it in blue flame of a bunsen burner until no colour change
cleans wire loop + avoids contamination
dip loop into solid sample + place it in edge of the blue Bunsen flame
avoid letting wire getting hot that it glows red otherwise can be confused with flame colour