Networks Cloud computing and Link Layer
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is cloud computing
A Model for enabling ubiquitous and convenient on demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resource such as servers storage networks applications and services.
A cloud is a collection of network accessible IT resources,
The cloud models enable consumers to hire a providers IT resource as a service
Cloud computing characteristics
Broad Network Access
Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere over the internet using various devices and platforms, enabling flexibility and convenience for users.
Resource Pooling
Providers share computing resources among multiple users dynamically, improving efficiency and allowing flexible allocation based on demand.
Rapid Elasticity
Cloud resources can be quickly scaled up or down as needed, helping organizations handle changes in workload without overprovisioning.
Measured Service
Cloud systems automatically track and optimize resource use, enabling pay-as-you-go billing and supporting better capacity planning and transparency.
On-demand Self-service
Consumers can provision computing resources like server time or storage instantly through a self-service portal, without needing to contact the provider—making the process fast, flexible, and efficient.
Benefits of cloud Computing Part 1 of 3
Part 1 of 3
Business Agility
Cloud computing enables rapid resource provisioning, supporting faster innovation and reducing the time it takes to bring new products or services to market.Reduces IT Costs
It lowers energy and space usage, minimizes upfront investments in hardware, and optimizes resource use, leading to overall cost savings.High Availability
Cloud services ensure resources are available as needed and include fault-tolerant features to minimize downtime and service disruption.
Benefits of cloud Computing Part 2 of 3
Part 2 of 3
Business Continuity
Cloud solutions help minimize the impact of outages by providing features like automated backups and disaster recovery, ensuring operations can continue with minimal disruption.Flexible Scaling
Resources can be automatically and unilaterally scaled up or down based on demand, allowing businesses to handle changing workloads efficiently.Flexibility of Access
Cloud services can be accessed from any location and device, removing reliance on specific hardware and supporting remote work and mobility.
Benefits of cloud Computing Part 3 of 3
Part 3 of 3
Application Development and Testing
Cloud platforms allow large-scale development and testing across multiple environments, speeding up deployment and improving software quality.Simplified Infrastructure Management
Users only manage essential resources, while the cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure, reducing operational burden.Increased Collaboration
Cloud services support real-time sharing and joint access to data and tools, enhancing teamwork and productivity.Masked Complexity
Technical complexities are hidden from end users, making cloud services easier to use without needing deep IT knowledge.
What are the 3 cloud service Models Specified by NIST and what is a cloud service Model:
A cloud service model specifies the services and the capabilities provided to consumers:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
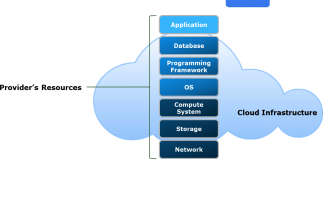
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
IaaS provides consumers with virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. Users can install and manage their own operating systems and applications while the cloud provider handles the physical infrastructure.
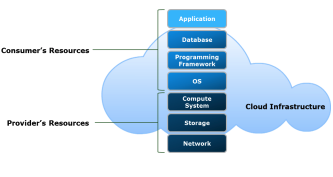
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS allows consumers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure. It provides a platform with pre-configured development tools, libraries, and services, giving users control over their applications and environment settings while the provider manages the rest.
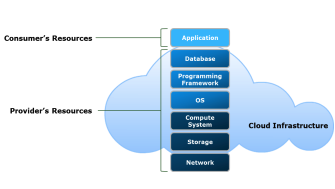
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully functional applications over the internet, accessible via web browsers or APIs. Consumers use the software without managing the infrastructure or platform beneath it, with only minimal control over user-specific settings.
What is a cloud service Brokerage (CSB)
Cloud Services Brokerage (CSB) is a business model where a third party acts as an intermediary between cloud service providers and consumers, adding value through services like aggregation, customization, integration, or management to better meet the consumer's needs.
What are the categories of cloud services Brokerage:
Service intermediation: Broker enhances and adds value to a given service
Service aggregation: The broker combines and integrates multiple services into one or more fixed new services. (Does not typically change)
Service arbitrage: Similar to service aggregation except that services being aggregated may vary depending on time or between customers
TLDR;
Intermediation: Enhances and adds value.
Aggregation: Combines multiple services into fixed offerings.
Arbitrage: Combines multiple services but the components vary flexibly.
What is a cloud deployment model and what are the deployment models specified by NIST:
A cloud deployment model specifies how a cloud infrastructure is built, managed, and accessed
The four models are:
– Public
– Private
– Community
– Hybrid
Public Cloud
Public cloud infrastructure is provisioned for open use by the general public and is owned, managed, and operated by a business, academic, government entity, or a combination, hosted on the provider’s premises.
Private Cloud
Private cloud infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization with multiple consumers, and may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or both, located on or off premises.
On premise private cloud: On-premises cloud infrastructure is deployed within an organization’s own data centers, offering full control over infrastructure and data while enabling standardization of IT resources and services.
Externally hosted private cloud: Community cloud infrastructure is outsourced to an external provider, hosted on their premises, with consumers securely connecting and isolated by access policies.
Community Cloud
Community cloud infrastructure is exclusively used by a specific group of organizations with shared concerns, and can be owned, managed, and operated by the community, a third party, or both, on or off premises.
On premise community cloud:
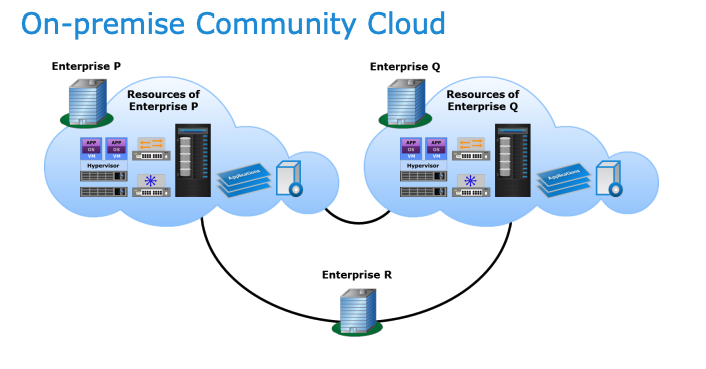
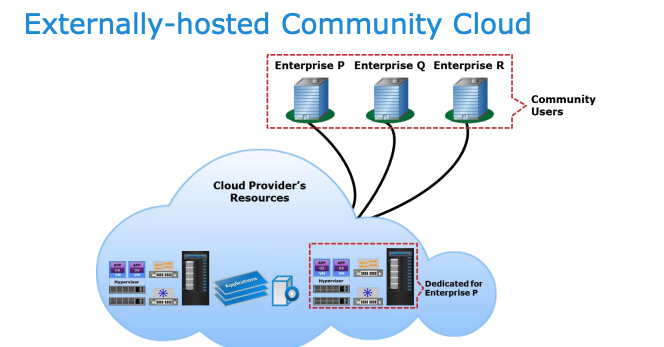
off premise (External) community cloud:
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud infrastructure combines two or more distinct clouds (private, public, or community) that remain separate but are connected by technology enabling data and application portability.
Hybrid cloud use cases
Cloud bursting: Temporarily using public cloud resources to manage peak workloads.
Web application hosting: Running less critical apps like e-commerce on the public cloud.
Migrating packaged applications: Moving standard apps (e.g., email) to the public cloud.
Application development and testing: Building and testing apps in the public cloud before release.
Start of Link Layer
What is the responsibility of the Link Layer (Terminologies):
Hosts and routers are nodes, communication channels that connect adjacent nodes along communication path are links (they can be wired and wireless links as well as LAN) Layer -2 packet is a frame which encapsulates a datagram.
data-link layer has responsibility of transferring datagram from one node to adjacent node over a link
Link Layer Functionalities:
Framing: Encapsulates network-layer datagrams into frames for transmission over the link.
Medium Access Control (MAC): Determines how nodes share the link and coordinate access to avoid collisions.
Reliable delivery: Ensures data is correctly delivered to the next node (used in reliable links).
Flow control: Prevents overwhelming a slower receiver by regulating data transmission.
Error detection and correction: Identifies and possibly corrects errors in the transmitted data using checksums or codes.
IPv4 Address. vs MAC Address
IPv4 Address vs. MAC Address:
MAC Address: Assigned by the manufacturer and managed by IEEE; like a Social Security Number—unique and portable across networks.
IP Address: Assigned based on network location; like a postal address—changes with network/subnet, not portable.
MAC is flat (non-hierarchical) and portable; IP is hierarchical and tied to the device’s current network.
IPv4 Address. vs MAC Address (CONT…)
IPv4 Address vs. MAC Address:
IPv4 Address (32-bit):
A network-layer address used to route datagrams to the correct destination subnet.
Hierarchical and changes with network location.
MAC Address (48-bit):
A link-layer address used to deliver frames between physically connected devices on the same network.
Permanently set in the NIC’s ROM (though sometimes changeable via software).
Unique, flat address; also called hardware, physical, or LAN address, and shown in hexadecimal.
LAN Addresses and ARP
Each computer (node) connected to a LAN (wired or wireless) has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address, assigned to its network interface card (adapter).
The MAC address is a hardware address used for local communication on a LAN.
There's a special address, FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF, which is the broadcast MAC address — this sends a message to all devices on the LAN.
Key Concept – ARP (Address Resolution Protocol):
When one device wants to send data to another on the same LAN, it might know the target's IP address, but it needs the MAC address to actually send the data.
It uses ARP to ask the network, “Who has this IP?” and the device with that IP replies with its MAC address.
MACs in Frame
When device A wants to send an IP datagram (packet) to device B on the same LAN:
A looks up B’s MAC address (possibly using ARP).
A creates a data frame (link-layer frame) containing:
B's MAC as the Destination MAC
A's MAC as the Source MAC
The actual IP packet (with source and destination IPs) inside
This frame is then sent across the LAN to B.
Data Encapsulation Layers (Bottom Part):
Shows how data is structured:
Segment: Application data with source/destination ports
Packet: Includes IP addresses
Frame: Includes MAC addresses
At the very bottom, the data is turned into bits for transmission.
Review from slides ARP, NIC, Sending across the same LAN, sending across Seprate LANS, DNS Envolvment