BIS 101 lecture 2: Transcription
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
define Gene
sequence of DNA at a specific location in the genome that encodes information
to direct the synthesis of a biological end product (biomolecule)
such as a protein or RNA.
a gene is the P…. and F….. U….. of H….
a gene is the Physical and Functional unit of Hereditary
define genome
the complete set of DNA, (including all of its genes), in a cell/ organism/ species
what is a genotype
the different variations of genes that an individual possesses for a particular trait.
what is the phenotype
observable and measureable traits and behaviours
what is gene expression?
the cellular production of biological molecules
driven by the information encoded in the DNA sequence
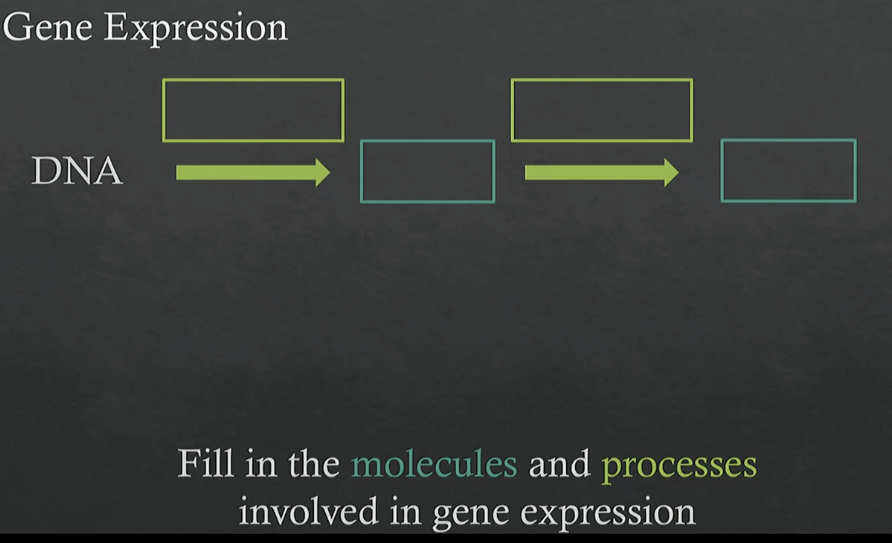

how does genotype → phenotype
via gene expression
what is transcription?
process of reading a single strand of DNA template and building an RNA molecule based off the DNA template
3 steps of transcription?
initiation: specific proteins recognise a gene to start transcription
elongation: synthesising the RNA transcript
Termination: RNA synthesis stopped and RNA is released
what is a promoter?
where is it found?
Why is it important?
a promoter is a DNA sequence found upstream o0f the transcription start site of a gene
it is required to begin the transcription of a gene
the promoter sequence is recognised by a protein which binds to it. the protein initiates transcription
what portion of the DNA is in the mRNA
only the transcribed region
where is the transcription start site?
the +1 site on the DNA strand is where transcription begins
it is the first base in the mRNA
what are the promoters in prokaryotes
what binds to the promoters
the -35 box and the -10 box
sigma factors bind to the promoters
how is transcription initiated in prokaryotes?
the sigma factor binds to the -35 and -10 box simultaneously.
the RNA polymerase core enzyme attaches to the sigma factor
This forms RNA polymerase hollow enzyme
RNA polymerase hollow enzyme begins transcribing → forms RNA
why doesnt the RNA polymerase core enzyme just bind to the promoter sequence?
it has poor promoter binding
how does the prokaryote’s machienary know which genes to transcribe
there are multiple sigma factors which match the promoter sequence
each sigma factor has a slightly different version of the 35 10 consensus
only when the sigma factor which matches the 35 10 promotor, the gene is transcribed
the cell regulates the sigma factors that are present
what is the main sigma factor in prokaryotes?
sigma 70
it is used for most prokaryote genes including housekeeping genes: genes that are continuously on
local impact vs global impact
local impact: affects expression of only the mutated gene
global impact: affects many genes at the same time
which directions does RNA polymerase work in
it synthesises in the 5’ to 3’ direction (5’ phosphate group is attached to the 3’ -OH group on the previous nucleotide.)
it reads in the 3’ to 5’ direction.
which direction do the RNA, template and coding strands go in?
are they complementary and parallel nature relative to the RNA strand
RNA strand: 5’ to 3’
coding strand: 5’ to 3’ → identical to RNA strand (except T instead of U) → non-complementary and parallel to RNA strand
template strand: 3’ to 5’ _> antiparallel and complementary to RNA strand
what are the major themes for termination?
what are the 2 major theories for termination?
there is a terminator sequence in the DNA
it signals for the RNA polymerase to detach and stop synthesis
it is transcribed into the RNA which catalyses termination
theories:
a) a protein binds to the terminator sequence on RNA → RNA polymerase detaches
b) the terminator sequence on RNA folds on itself → RNA polymerase detaches