Anatomy 1 Chapter 6
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Skin
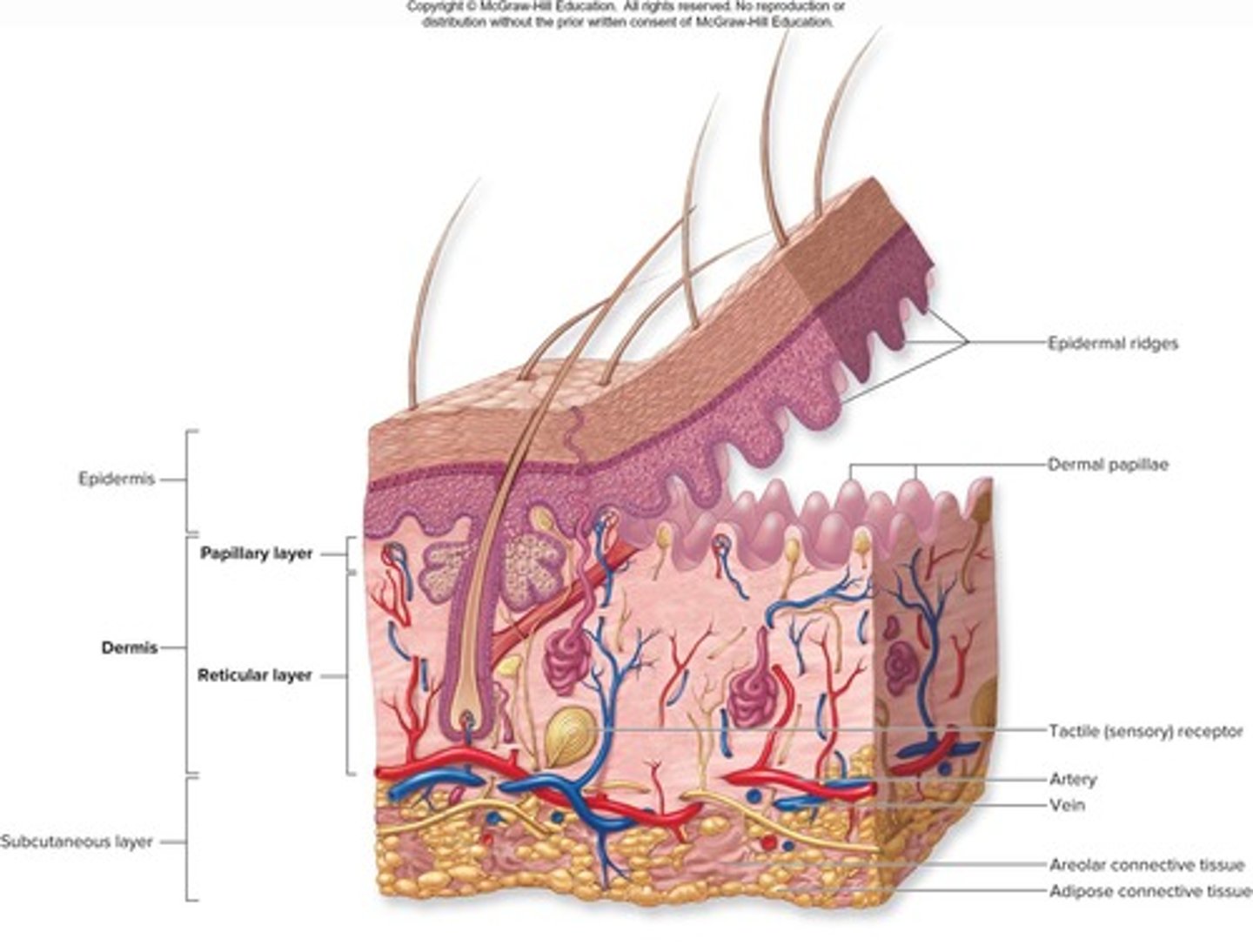
Integument consisting of two distinct regions: Epidermis and Dermis.
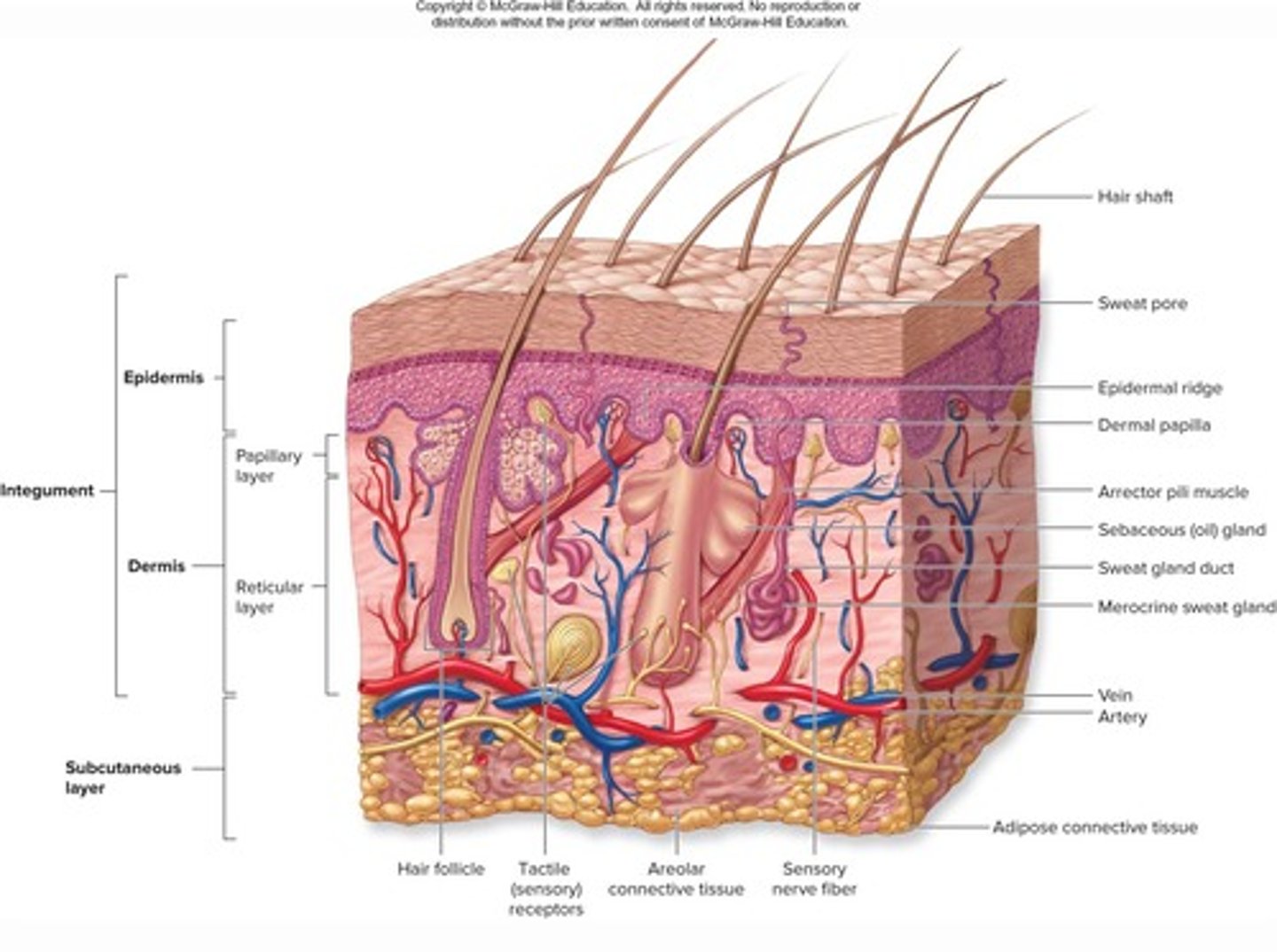
Epidermis
Superficial region of skin made up of epithelial tissue.
Dermis
Underlies the epidermis and is mostly fibrous connective tissue.
Hypodermis
Subcutaneous layer deep to skin, not part of skin but shares some functions, mostly adipose tissue that absorbs shock and insulates.
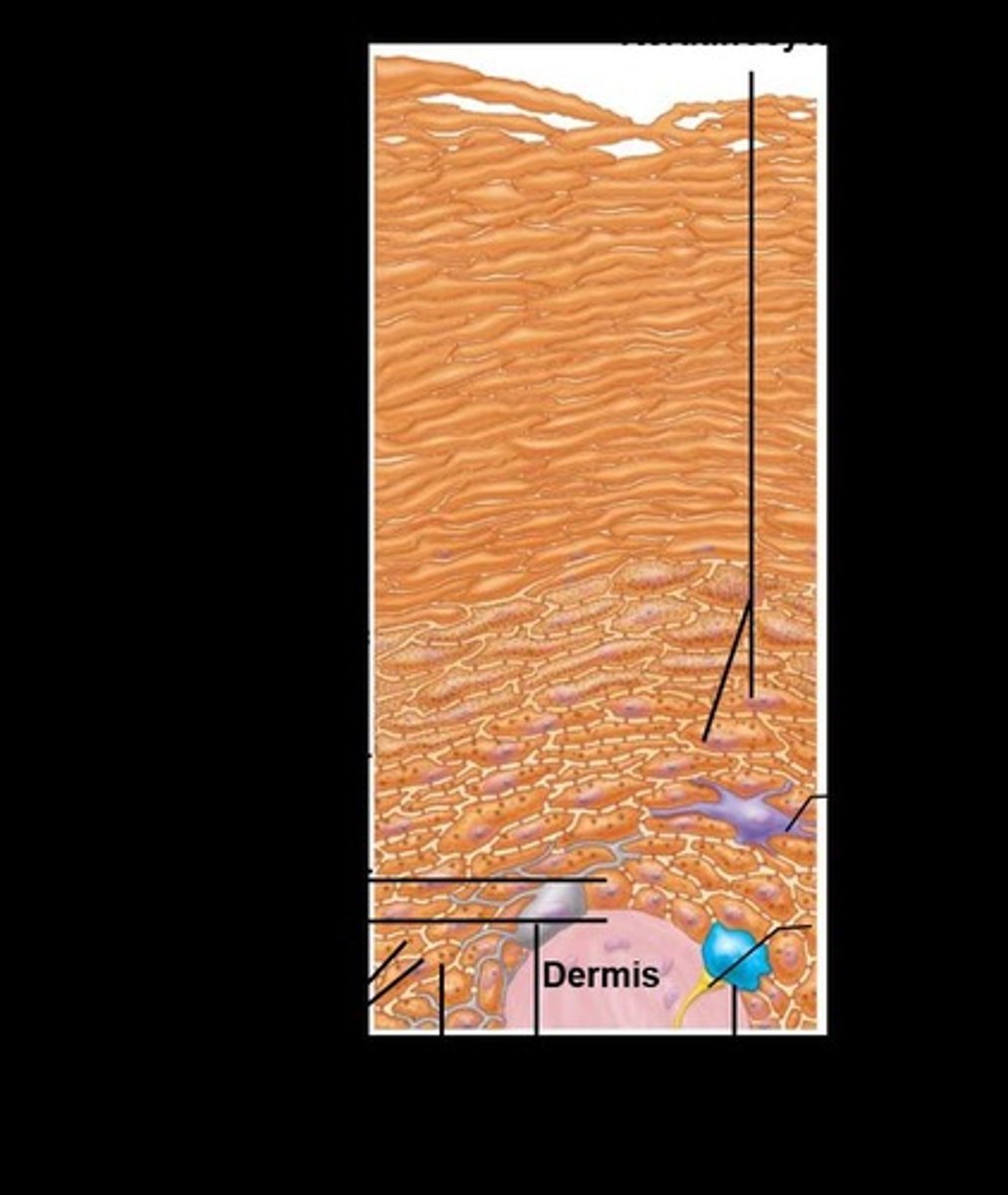
Stratum basale
The deepest layer of the epidermis.
Stratum spinosum
The layer above the stratum basale in the epidermis.
Stratum granulosum
The layer above the stratum spinosum in the epidermis.
Stratum lucidum
A layer found only in thick skin, above the stratum granulosum.
Stratum corneum
The outermost layer of the epidermis.
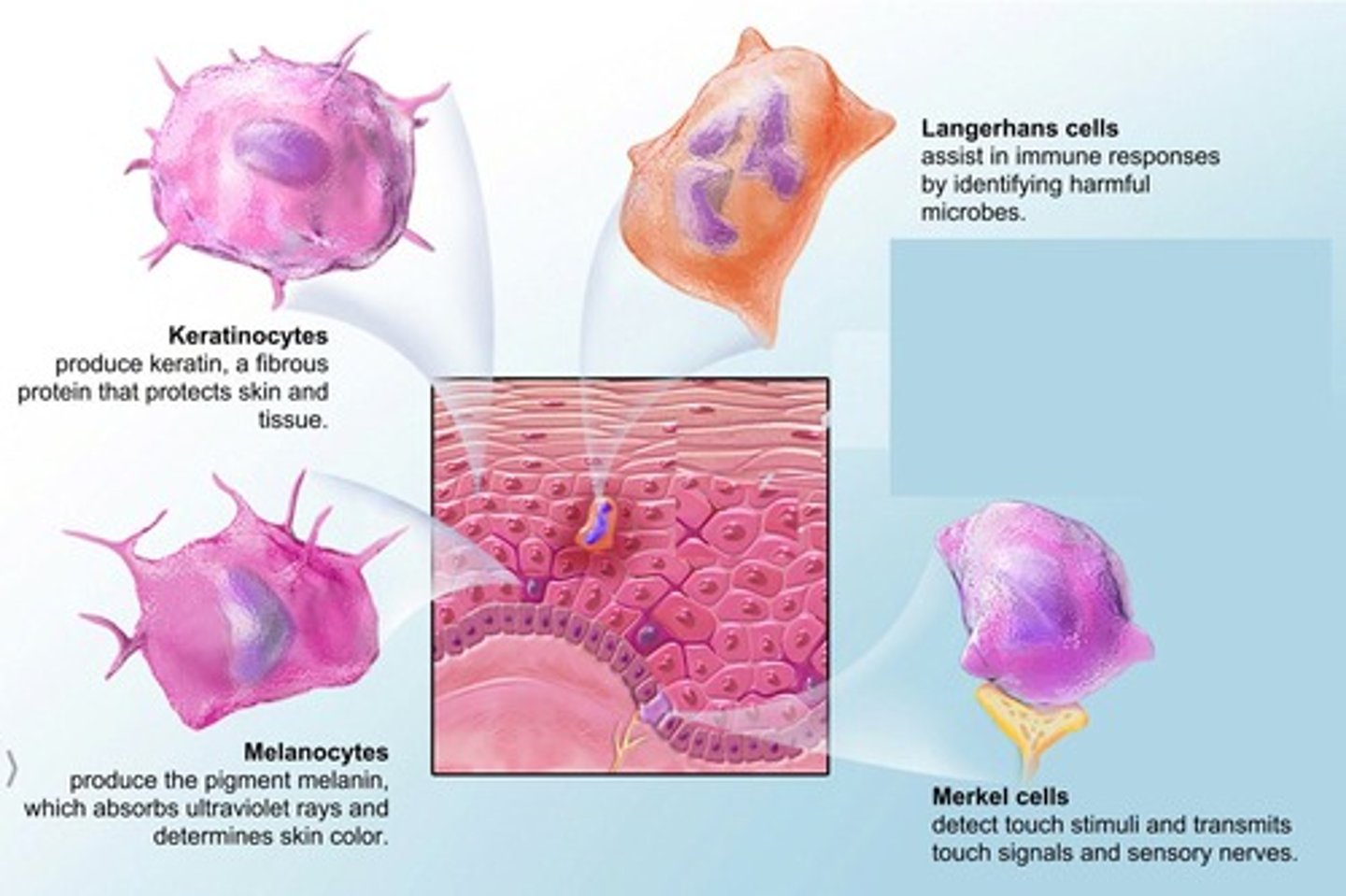
Keratinocytes
The primary cell type found in the epidermis.
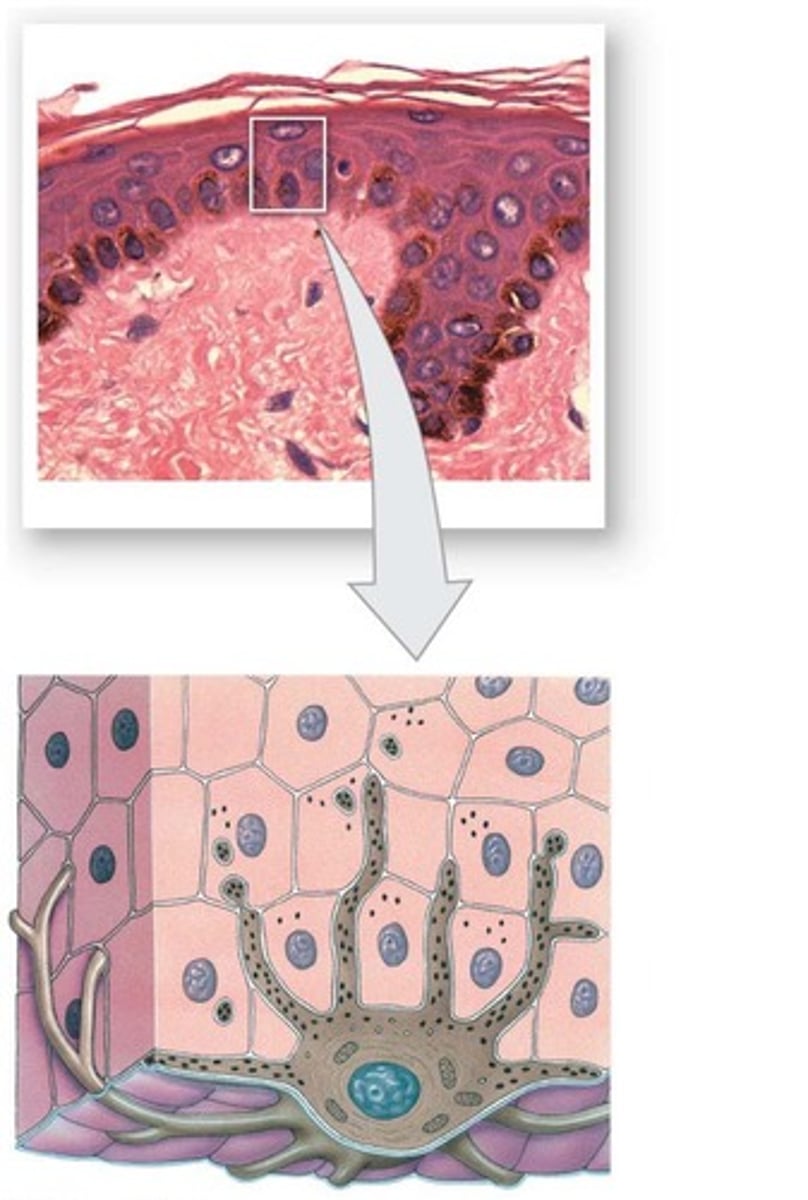
Melanocytes
Cells in the epidermis that produce melanin.
Dendritic (langerhans) cells
Immune cells found in the epidermis.
Tactile (merkel) cells
Cells in the epidermis that are involved in touch sensation.
Thick skin
Contains all five layers of epidermal strata; found in palms of hands and soles of feet; has sweat glands but no hair follicles or sebaceous glands.
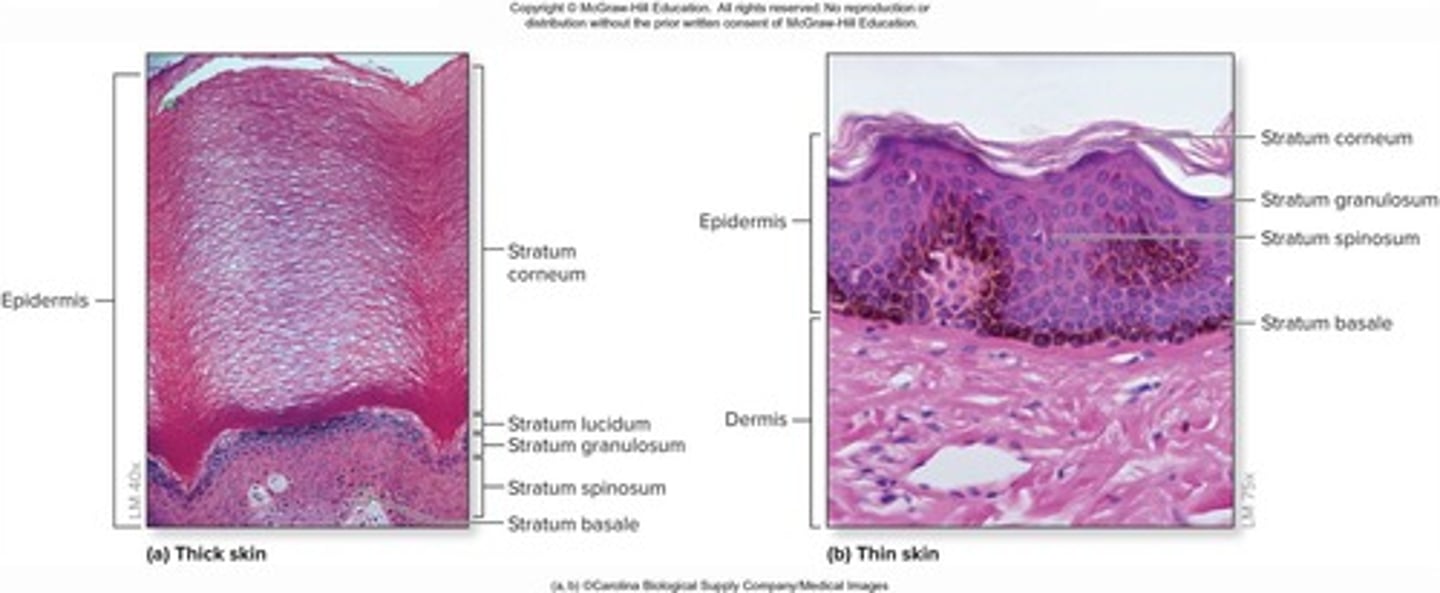
Thin skin
Covers most of the body; lacks a stratum lucidum; contains sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands.
Stratum Basale (Basal Layer)
Deepest epidermal layer, also called stratum germinativum; firmly attached to dermis; single row of stem cells that are actively mitotic.
Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer)
Only present in thick skin; thin, translucent band superficial to the stratum granulosum; contains a few rows of flat, dead keratinocytes.
Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer)
20-30 rows of dead, flat, anucleate, keratinized membranous sacs; constitutes three-quarters of epidermal thickness; protects deeper cells from the environment and water loss.
Stratum Granulosum (Granular Layer)
Thin layer with four to six cell layers; cells flatten, nuclei and organelles disintegrate, and keratinization begins.
Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer)
Several layers thick; cells contain a web-like system of intermediate prekeratin filaments attached to desmosomes; abundant melanosomes and dendritic cells.
Cell Differentiation in Epidermis
Cells change from stratum basale to stratum corneum through a specialized form of apoptosis; nucleus and organelles break down, plasma membrane thickens.
Apoptosis
Controlled cellular suicide that allows cells to slough off as dandruff and dander; approximately 50,000 cells are shed every minute.
Keratohyaline granules
Cells accumulate these granules in the stratum granulosum that help form keratin in upper layers.
Lamellar granules
Cells accumulate these in the stratum granulosum; their water-resistant glycolipid slows water loss.
Epidermal strata
The layers of the epidermis, including stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum.
Desmosomes
Structures that tightly connect keratinocytes in the epidermis.
Melanosomes
Cell organelles that package melanin produced by melanocytes.
Stem cells
Cells in the stratum basale that are actively mitotic and produce daughter cells.
Apical surface
The uppermost surface of a cell, which in keratinocytes is protected from UV damage by melanin.
Fibroblasts
Cells in the dermis that produce collagen and elastin fibers.
Macrophages
Immune cells in the dermis that help protect the body from pathogens.
Melanin
Pigment produced by melanocytes that protects the apical surface of keratinocyte nucleus from UV damage.
Epidermal thickness
Three-quarters of the epidermis is made up of the stratum corneum.
Stem cells in stratum basale
One cell remains in stratum basale as a stem cell while the other journeys to the surface.
Time to surface
It takes 25 - 45 days for a cell to journey from the basal layer to the surface.
Cell shedding rate
Shed approximately 50,000 cells every minute.
Papillary layer
One of the two layers of the dermis.
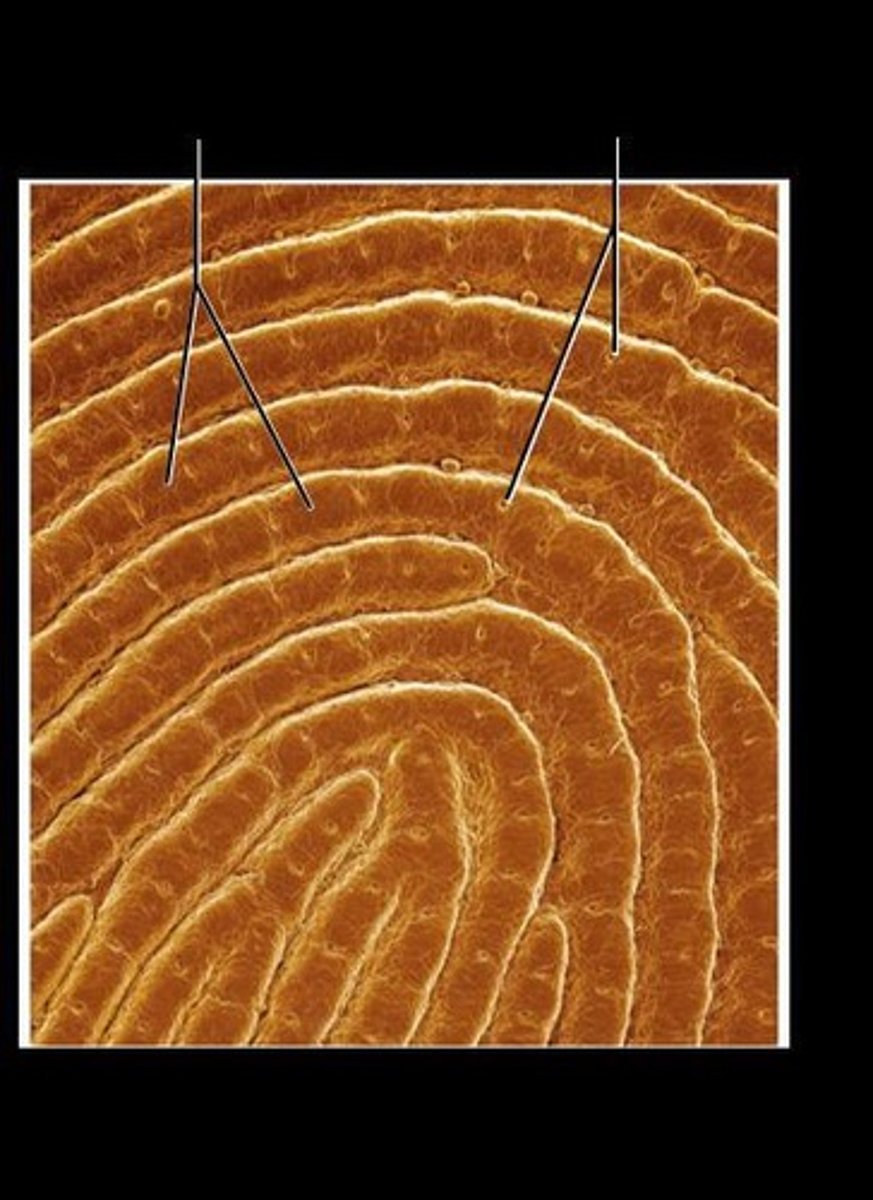
Dermal Papillae
Superficial peg-like projections that enhance gripping ability and contribute to sense of touch.
Reticular Layer
Deeper, major portion of dermis, comprising ~80% of dermal thickness.
Dense Fibrous Connective Tissue
Type of tissue in the reticular layer providing strength and resiliency.
Cleavage Lines
Lines in the skin where most collagen fibers are parallel to the skin surface, important for surgical incisions.
Appendages of the Skin
Derivatives of the epidermis including hairs, nails, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands.
Hair
Dead keratinized cells of hard keratin, more durable than soft keratin of skin.
Hair Follicles
Structures extending from epidermal surface to dermis, containing a two-layered wall.
Vellus Hair
Pale, fine body hair of children and adult females.
Terminal Hair
Coarse, long hair of eyebrows and scalp, appearing at puberty.
Hair Growth Rate
Average growth of hair is 2.25 mm per week.
Nails
Scale-like modifications of epidermis that serve as a protective cover for fingers and toes.
Nail Matrix
Area responsible for hair growth.
Sweat Glands
Also called sudoriferous glands, present on all skin surfaces except nipples and parts of external genitalia.
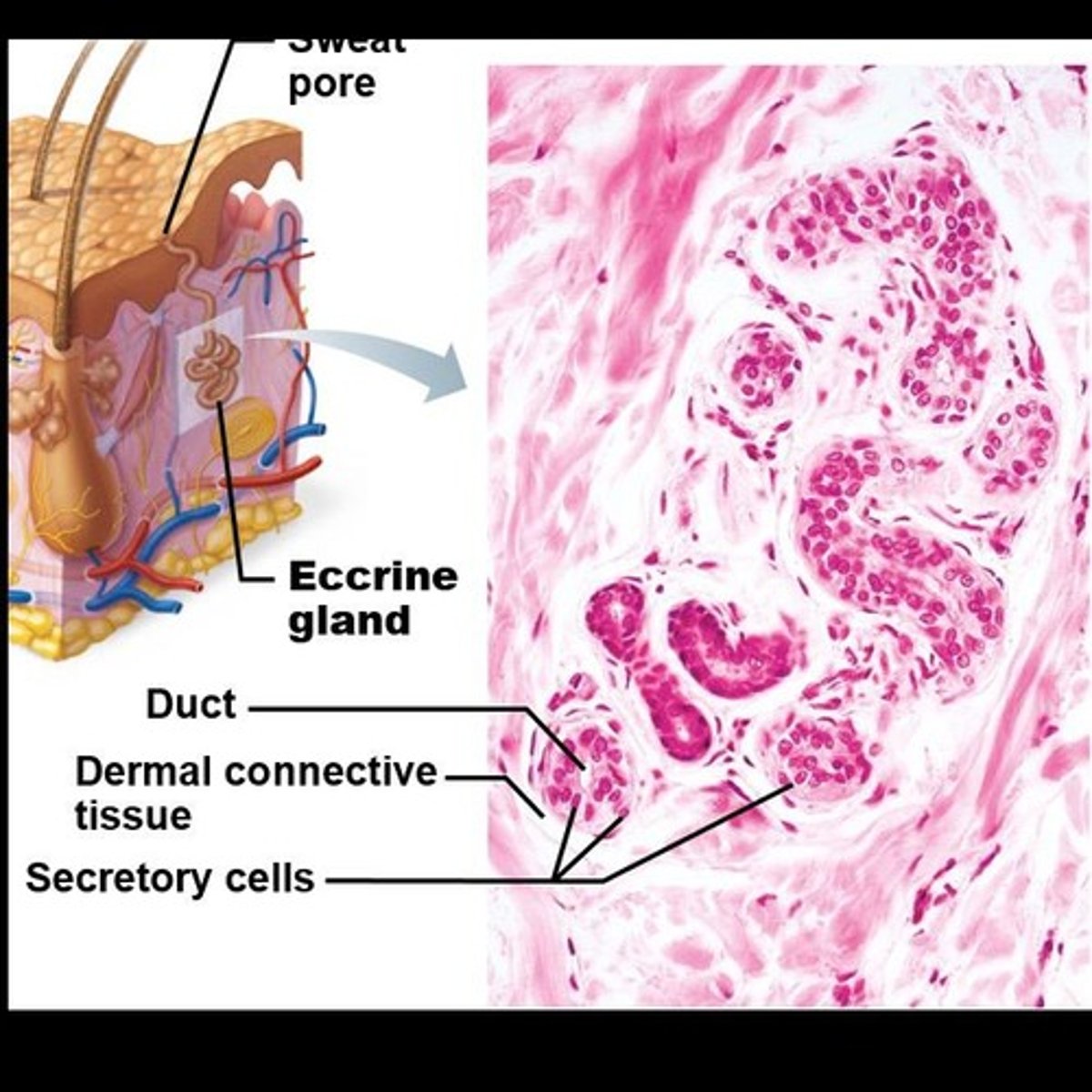
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Most numerous sweat glands, abundant on palms, soles, and forehead, involved in thermoregulation.
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Sweat glands confined to axillary and anogenital areas, beginning function at puberty.
Sebaceous Glands
Glands that secrete sebum, widely distributed but not in thick skin of palms and soles.
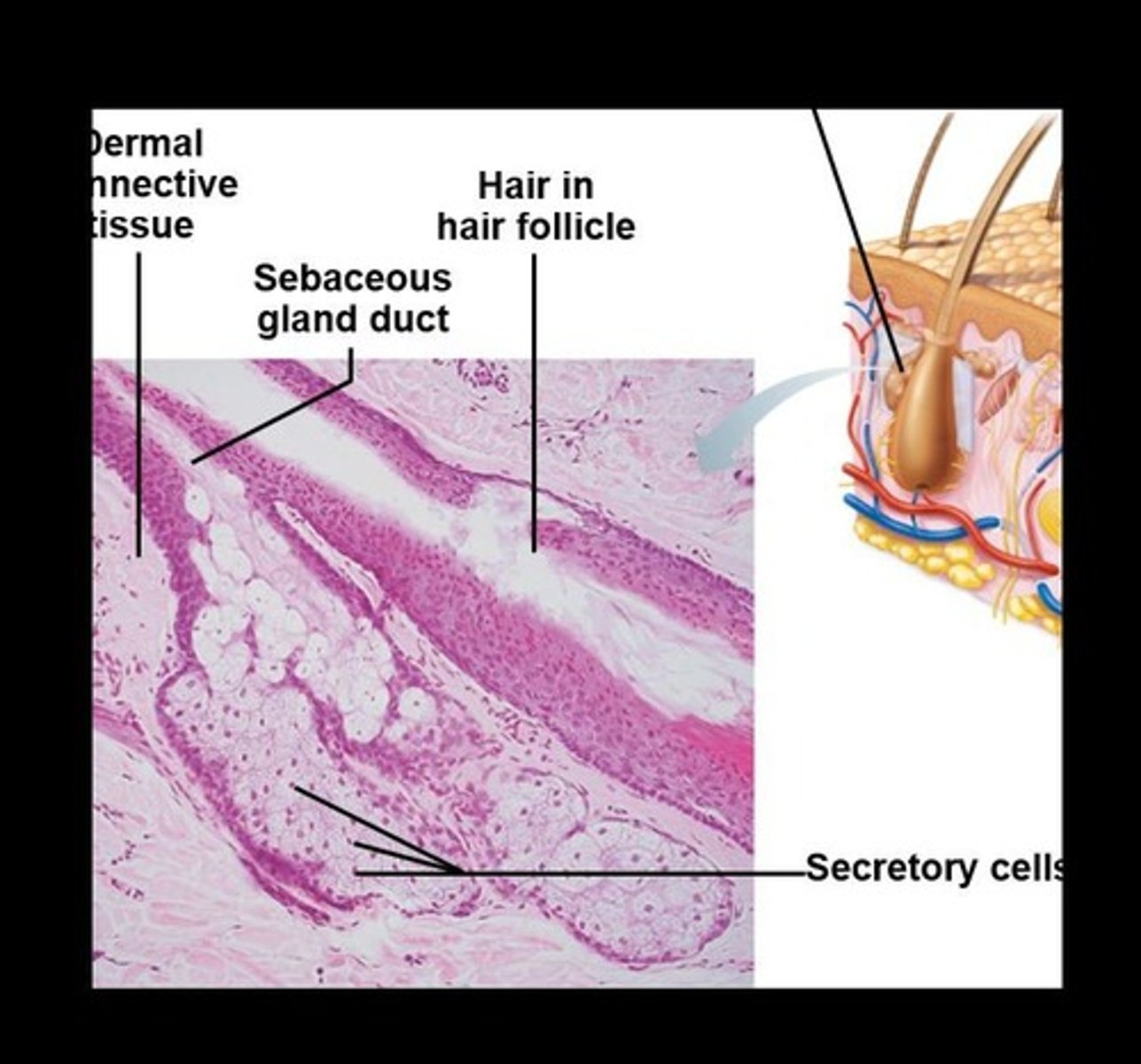
Sebum
Oily holocrine secretion that softens hair and skin.
Hair Bulb
Expanded deep end of hair follicle containing sensory nerve endings.
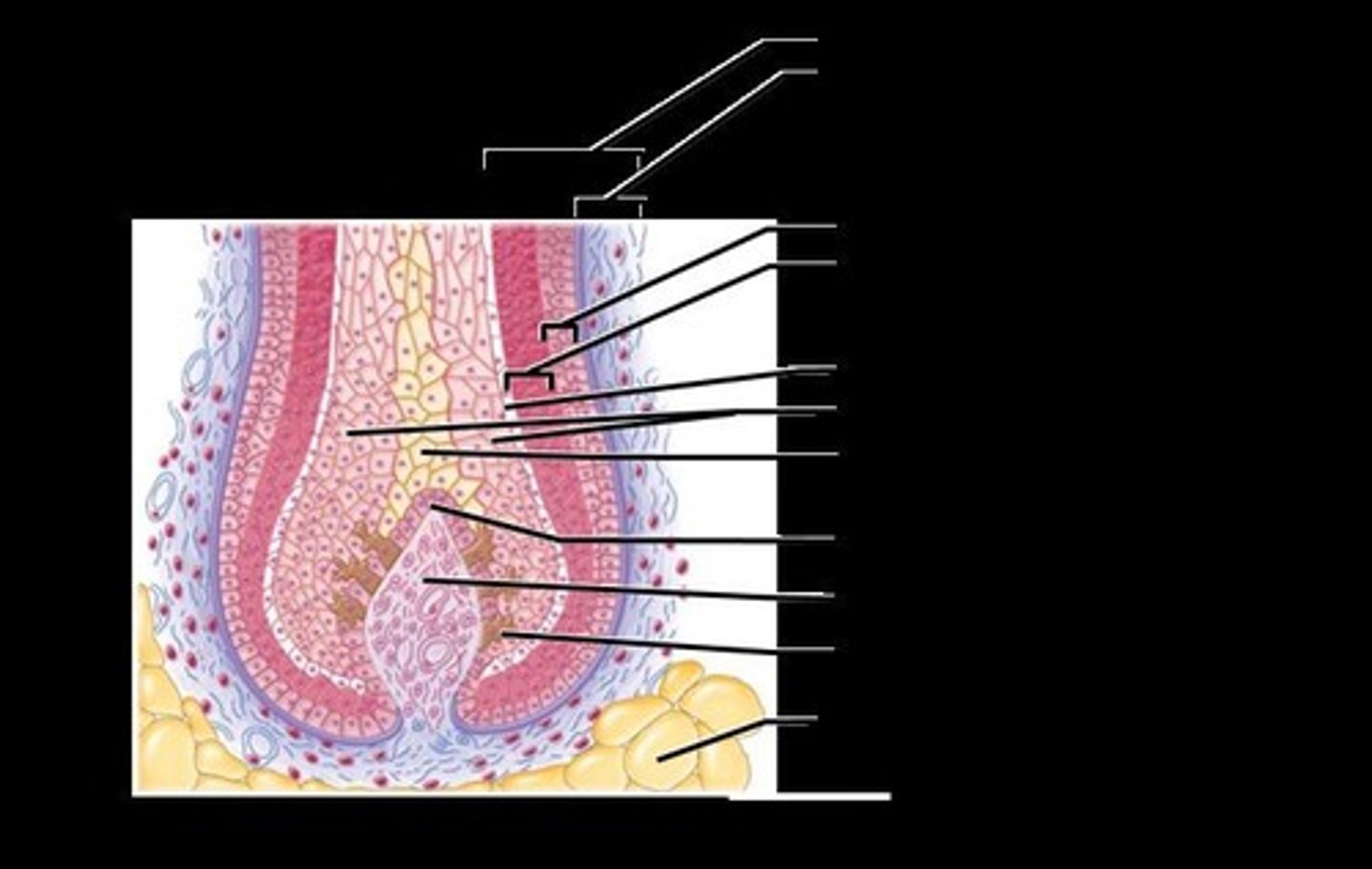
Arrector Pili
Smooth muscle attached to hair follicle responsible for 'goose bumps'.
Hair Papilla
Dermal tissue providing blood supply to hair follicles.
Ceruminous Glands
Modified apocrine glands lining the external ear canal that secrete cerumen (earwax).
Mammary Glands
Modified apocrine glands that secrete milk.
Skin Color
Determined by three pigments contributing to the pigmentation of the skin.
Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
Glands that secrete sebum, an oily holocrine secretion that softens hair and skin.
Hair Matrix
Actively dividing area within the hair bulb responsible for hair growth.
Hair Pigments
Melanins (yellow, rust, brown, black) and trichosiderin in red hair; gray/white hair results from decreased melanin and increased air bubbles.
Myoepithelial Cells
Cells that contract upon nervous system stimulation to force sweat into ducts.
Friction Ridges
Collectively formed ridges from dermal papillae that enhance gripping ability.
Average Hair Growth Rate
Average growth rate of hair is 2.25 mm per week.
Daily Hair Loss
Average person loses 90 scalp hairs daily.
Freckles
Local accumulations of melanin.
Sun exposure
Stimulates melanin production.
Sunspots
Fungal infection (tinea versicolor) not related to melanin.
Skin cancers
Any cancer of epithelial tissue is a carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma
Most common skin cancer, originates in stratum basale.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Found in more superficial layers of the skin.
Malignant melanoma
Most dangerous skin cancer, usually begins from a mole and can metastasize through the lymphatic system.
Carotene
Yellow to orange pigment, most obvious in palms and soles, accumulates in stratum corneum and hypodermis.
Vitamin A
Can be converted from carotene for vision and epidermal health.
Hemoglobin
Gives a pinkish hue to fair skin and bright red color upon binding oxygen.
Oxygenated blood
Is bright red.
Body temperature increase
Dilates superficial blood vessels in dermis, resulting in flushed, red skin color.
Temporary constriction of blood vessels
Results in pale skin.
Cyanosis
A bluish coloration that occurs when blood oxygen supplies are diminished.
Vitamin D3
Formed by epidermal cells, converted from a cholesterol-related steroid when exposed to sunlight.
Calcitriol
Converted from vitamin D3 by the liver and kidneys, essential for absorption of calcium and phosphorus.
Inadequate vitamin D3
Can lead to weak and flexible bones.
Functions of the Integumentary System
Includes protection, body temperature regulation, cutaneous sensation, metabolic functions, blood reservoir, and excretion.
Chemical barriers
One of the three types of barriers in skin protection.
Physical barriers
Another type of barrier in skin protection.
Keratin and glycolipids
Block most water and water-soluble substances.
Limited penetration of skin
Lipid-soluble substances, plant oleoresins (e.g., Poison ivy), organic solvents, salts of heavy metals, some drugs, drug agents.
Biological Barriers
Dendritic cells of epidermis present foreign antigens to white blood cells.
Macrophages of dermis
Present foreign antigens to white blood cells.
DNA
Its electrons absorb UV radiation; radiation converted to heat.
Body temperature regulation
If body temperature normal ~500 ml/day of routine insensible perspiration (if environmental temperature below 31-32° C).
Dilation of dermal vessels
Increased sweat gland activity (sensible perspiration) cools the body when body temperature rises.
Cold external environment
Dermal blood vessels constrict; skin temperature drops to slow passive heat loss.
Cutaneous sensations
Cutaneous sensory receptors (part of nervous system) detect temperature, touch, and pain.
Metabolic functions
Synthesis of vitamin D precursor and collagenase; chemical conversion of carcinogens and activation of some hormones.
Blood reservoir
Up to 5% of body's blood volume.
Excretion
Nitrogenous wastes and salt in sweat.
Burns
Tissue damage caused by heat, electricity, radiation, certain chemicals.