Cell Cycle (Interphase)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
cell cycle control system
-Monitors for mistakes like alloploidy, polyploidy, etc.
-Checkpoints put on brakes of cell cycle if theres issues
-prolonged G1: Cell can extend G1 phase if it doesn't know whether it wants to apoptosis or continue in cycle. Phase is slowed down but still happening → S phase will occur faster in cells with prolonged G1 phase
G1 phase
-growth phase
-Organelles grow throughout the cell's life so that when division happens, the cell doesn't get smaller and smaller
G1 Checkpoint
-3 options: terminal differentiation (leave cycle), go to G0, or proceed to S phase.
-heart cells create scar tissue, NOT new cells
-Liver cells can create new cells
-Bones can create new cells
APC/C role
inactivates Cdks by adding ubiquitin
Antagonism between Cdks and phosphatases
Phosphatases dephosphorylates Cdk target proteins (ex: M-cdk protein gets inactivated) → causes cell to move to M phase (mitosis)
cell cycle initiation & Rb protein
-Rb protein = Retinoblastoma protein
-Removal of Rb protein → transcription starts for genes that cause the cell to enter S phase
-Rb protein mutation → transcription of genes cant occur → cell can't enter S phase properly → cell cycle not regulated well → cancer
S Phase initiation
Phosphorylation → only 1 round of replication occurs
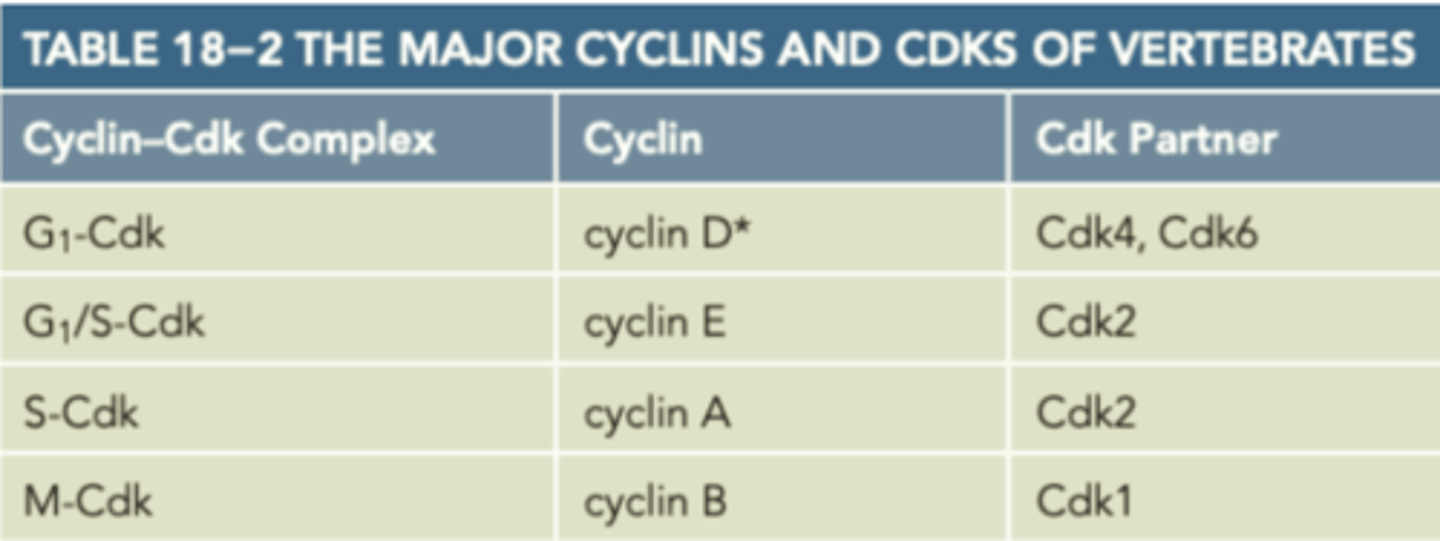
cyclins and CDKs of the cell cycle
G1 Phase
The first gap phase; the cell grows, produces RNA and proteins, and prepares for DNA replication.
S Phase
The synthesis phase where DNA is replicated, doubling the genetic material.
G2 Phase
The second gap phase; the cell grows further, synthesizes proteins, and checks for DNA replication accuracy.
M Phase
The mitotic phase, where chromosomes are segregated and the cell divides; includes mitosis and cytokinesis.
G0 Phase
A quiescent state where the cell exits the cycle and may remain inactive or differentiate permanently.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Regulatory control points (late G1, G2/M, and mid-M phase) that ensure the cell only proceeds when conditions are right.
G1 Checkpoint ("Start")
A key decision point where the cell commits to DNA replication; influenced by nutrients, DNA integrity, and mitogens.
G2/M Checkpoint
Ensures DNA is fully replicated and undamaged before entering mitosis.
Spindle Checkpoint (Mid-M)
Ensures all chromosomes are correctly attached to the spindle before proceeding with anaphase.
Phosphorylation/Dephosphorylation
Major regulatory mechanisms in the cell cycle; modify activity of key proteins like Cdks.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (Cdks)
Protein kinases that drive the cell cycle forward when activated by binding to specific cyclins.
Cyclins
Regulatory proteins that bind to and activate Cdks; their levels fluctuate cyclically through the cell cycle.
Cyclin Accumulation
Cyclins increase gradually via transcriptional regulation, and activate Cdks when abundant enough.
Cyclin Degradation
Occurs rapidly through ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation, ensuring one-way cycle progression.
Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)
A ubiquitin ligase that targets mitotic cyclins for degradation to allow exit from mitosis.
Cyclin-Cdk Complex Regulation
Controlled not only by cyclin binding but also by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation events.
Cdk Inhibitor Proteins (CKIs)
Proteins that bind to and inhibit Cyclin-Cdk complexes, acting as brakes on cell cycle progression.
Antagonism Between Cdks and Phosphatases
Balancing act that determines whether the cell moves past checkpoints, especially at G1/S.
Mitogens
Extracellular signals that stimulate cell cycle entry by promoting cyclin expression and Cdk activation.
Cell Cycle Entry Decision
Largely made at the G1 checkpoint; requires mitogens and proper internal conditions.
Retinoblastoma Protein (Rb)
A tumor suppressor that inhibits progression from G1 to S by binding E2F; phosphorylation by Cdk releases E2F to promote S phase.
DNA Damage Checkpoint (G1 Arrest)
Pauses the cycle to allow DNA repair; if damage is too severe, can trigger apoptosis.
S Phase Initiation
Involves loading of replication machinery and activation of origins of replication; tightly regulated to prevent re-replication.
Order of Phosphorylation by Cdks
Cdks phosphorylate many targets in a specific sequence depending on binding affinity, creating an orderly cascade.
Positive Feedback in M-Cdk Activation
Once active, M-Cdk promotes further activation of its own complex, creating a sharp transition into mitosis.