The Psychodynamic approach
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Basic assumptions
- Conscious mind is the tip of the iceberg, most is made up of Unconscious, biological Drives and Instincts that influence our behaviour and personality
- Early childhood experiences play key role in determining individuals mental/emotional state and outcomes in later life
Tri-partite Structure of personality
Id - Present at birth, follows the Primitive Pleasure Principle
Ego
- Develops around 2
- Operates on Reality Principle
- Mediator for the Id + Ego using Defence Mechanisms
Superego
- Follows the Morality principle
- Represent Right and Wrong
- Forms around age 5
Id
- Present at birth
- Operates on Pleasure principle
- Consists of Unconscious drives + Instincts
- Important to ensure survival
Ego
- Mediates between demands of the Id + Superego
- Develops at around age 2
- Operates on reality principle
- Uses Defence Mechanisms to mediate
Superego
- Our Internalised Sense of Right and Wrong
- Forms at end of Phallic stage arounf 5
- Operates on Morality principle
- Moral standards are learnt from childs same sex parent
Defence mechanisms
Strategies used by the Ego to reduce the anxiety from the conflict of the Id and Superego
Repression
- Pushing unpleasant memories to the Unconscious mind
Denial
- Refusing to accept the reality of an unpleasant situation
Displacement
- Directing strong emotion to a neutral person or object, reducing anxiety.
Repression
Denial
Displacement
Pushing unpleasant memories to the Unconscious mind
Refusing to accept the reality of an unpleasant situation
Directing strong emotion to a neutral person or object, reducing anxiety
Psychosexual stages
Oral 0-1 years - Focus of pleasure is from the mouth. Oral fixation can lead to smoking, biting nails, sarcasm
- Anal stage 1-3 years - Focus of pleaure is from the anus gaining pleasure from expelling faeces. Anally retentive means to be obssesive and a perfectionist, Anally expulsive means to be thoughtless and messy
-Phallic stage 3-6 years - Focus of pleasure is from the genital area. Unresolved conflict leads to phallic personality; narcissistic and reckless
- Latency stage 6-11 years - libido (sexual energy) is displaced throughout the body
What are the three Levels of Consciousness
Conscious
- Part of mind we are aware of
Preconscious
- Just below the surface where "Freudian slips" (Parapraxes) lie
Unconscious
- Hidden depth of the iceberg that hold information the individual may be unaware of
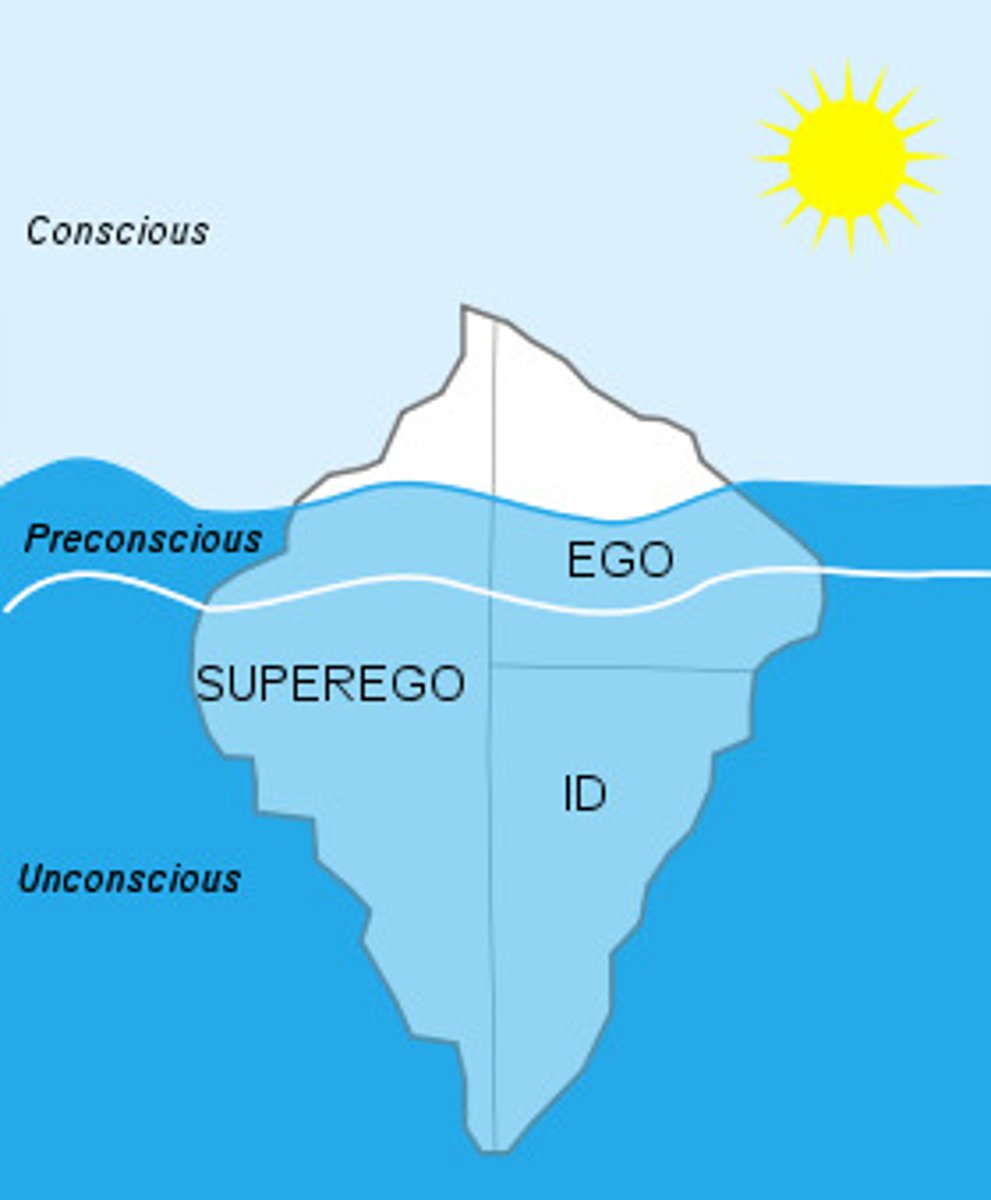
The Conscious Mind
Tip of the iceberg
Part of the mind we are aware of
The Preconscious mind
Just below the surface of the Conscious mind
Holds Dreams and Freudian slips
Believed dreams revealed secret fears + desires
Freudian slips - reveal Secret, Repressed feelings
The Unconscious mind
- Hidden Depths of the iceberg
- Holds info + feelings the individual may be unaware of
- Psychoanalysis is necessary to access these thoughts
What are the Psychosexual stages
5 stages of child development
Child must deal with conflict at each stage to progress to next stage
Unresolved conflict leads to Fixation
Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latent, Genital
Fixation
Result of unresolved conflict from a stage
Where behaviours associated with that stage are brought into adult life
Oral stage
Age 0-1
- Mouth is the focus of pleasure, Breastfeeding
- Conflict can arise from too much or too little breastfeeding
- Unresolved Conflict leads to Oral fixation eg smoking, biting nails, overeating
Anal stage
Age 1 - 3
- Anus is focus of pleasure
- Conflict arises from toilet training
- Harsh toilet training leads to Anal retentive behaviour eg neatness, perfectionist
- Lenient toilet training leads to Anal expulsive behaviour eg messiness, insensitivity
Phallic stage
Age 3-6
- Genital area is focus of pleasure
- Conflict arises from Oedipus or Electra complex
- Resolved by identifying with father or mother
- Unresolved conflict leads to Phallic personality eg Narcissistic, reckless
Latency stage
6-Puberty
- Previous Conflicts become repressed
- Focus on Cognitive development + Forming Relationship
- No conflicts
Genital stage
Puberty onwards
- Genitals are Focus of Pleasure
- Sexual desires become conscious
- Unresolved conflict leads to Genital Fixation eg Difficulty in forming heterosexual relationships
Dream analysis
- In dreams the Id is able to fulfil desires + fantasies
- If we actually dreamt the Id desires, all dreams would be violent + sexual, offending our Superego
- Ego deals with this by converting the true meaning of our dreams into harmless symbols + quickly forgetting most of our dreams
- If we work out the underlying conflicts, we can address them in conscious mind and overcome them
Oedipus complex
- A boy's Unconscious Desire for Mother
- Sees father as a rival and envys him
- Experiences Castration Anxiety as a punishment for this desire
- Resolved by identifying with father, forming the Superego
Castration anxiety
The unconscious fear that a boys father will remove his testicles as a punishment
Causes hatred + envy towards father in the Oediupus complex
Electra complex
- Girls Unconscious Desire for Father during Phallic stage
- Sees Mother as a rival and feels Hatred towards her
- Experiences Penis Envy
- Resolved by identifying with mother, forming the Superego
Little Hans study
Freud Collected information on Hans behaviours and dreams from letters + reports from his Dad
Dad reported;
Fear of horses (especially white horses with blinkers),
Dreams about giraffes,
Curiosity about genitals and having a baby,
Freud interpreted these as Oedipus complex, castration anxiety, and the psychosexual stages of development.
Psychic Determinist criticism of Freuds theory
- Theory is Psychic Deterministic
- Suggests Behaviour is determined by unconscious drive
- In society we hold criminals accountable under the assumption of Free Will
- Freuds theory allows individuals to blame harmful behaviour on unconscious trauma or childhood repression
- This conflicts with the UKs moral and legal views
- Therefore if we accept this theory, it raises ethical questions on whether people should be punished or treated
Unfalisifiability criticism of Psychodynamic theory
- Ideas cannot be empirically tested
- eg id, ego and superego are difficult to operationalise, test and measure
- Because of this the theory is Unfalsifiable + lacks objective research support
- Reduces validity compared to more scientifically credible theories like the Biological approach
Transformative strength of Psychodynamic theory
- Changed how effects of early childhood is viewed
- Freud highlighted the long term impacts of early relationships
- Has inspired future psychologists eg Bowlbys attachment theory, also emphasises impact of early bonding experiences on emotional development
- Also influenced child psycho therapy, now widely used
- Therefore increases external validity
Psychoanalysis key parts
Transference
- Patient projects feelings about significant others (e.g. parents) onto the therapist.
Free Association
- Patient says whatever comes to mind, helping reveal unconscious thoughts.
Dream Analysis
- Interpreting dreams to uncover unconscious desires and conflicts.