Geography final exam study guide (units 1-4 vocab)
4.8(5)Studied by 27 people
Card Sorting
1/171
Last updated 2:33 PM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1
New cards
Geography
the study of the earth and the ways people live and work on it
2
New cards
Physical Geography
Physical Attributes (land forms, water, rocks, animals, etc.)
3
New cards
Human Geography
People, population, settlements, economic activities, transportation, religion
4
New cards
Absolute Location
Mathematical, Adress, coordinate.
5
New cards
Relative Location
where something is in relation to at least 3 other locations.
6
New cards
Human Characteristics of Place
Examination of the human elements of an area: language customs, population, government type, culture, etc.
7
New cards
Physical Characteristics of Place
Describes the land forms, vegetation, types of wild life, climate of the location, etc.
8
New cards
Human Environment Interaction (H.E.I.): Adapt
Changes that the human population has made to or for themselves to better fir in the environment in which they live.
9
New cards
Human Environment Interaction (H.E.I.): Modify
Changes the human population has made to the environment in which they live to better suit human habitation.
10
New cards
Human Environment Interaction (H.E.I.): Depend
Elements in the environment that humans depend upon or need to survive.
11
New cards
Movement: People
the “permanent” movement of people from one location to another.
12
New cards
Movement: Goods
imports and exports, moving locally or globally.
13
New cards
Movement: Ideas
movement of styles, processes, and methods.
14
New cards
Formal Regions
An area within which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics. EX: Language, economic activities, environmental properties, government structures.
15
New cards
Functional Regions (Nodal Region)
an area organized around a node or focal point. is defined by the area serving a specific function. EX: cell phone coverage area.
16
New cards
Perceptional Regions (Vernacular Region)
is a place that people believe exists as a part of their cultural identity. EX: "The north”
17
New cards
Toponyms
Names of locations that have reference to the site features of that location
18
New cards
Imports
Items that are traded into a location.
19
New cards
Exports
items that are traded out of a location.
20
New cards
Hearth
The origin of the studied characteristic.
21
New cards
Node
Major areas that see the diffusion patterns first.
22
New cards
Cultural Ecology
the relationship between culture and the environment, dealing with human adaptations to various environments.
23
New cards
Geographic Information System (GIS)
computer systems that store geographical data.
24
New cards
Geographical Positioning System (GPS)
a system that determines the precise position of something on earth through the use of satellites.
25
New cards
Remote Sensing
gaining of data by scanning the earths surface from satellites orbiting the earth (pictures)
26
New cards
Case Study
an intensive analysis of an individual unit ( person, group or event) stressing developmental factors in relation to context.
27
New cards
Model
An abstract representation of reality created to simplify complex systems
28
New cards
Cartography
the science of mapmaking.
29
New cards
Hemispheres
a half of the earth, usually as divided into northern and southern __halves__ by the __equator__
30
New cards
Latitude
measures the position north or south of the equator
31
New cards
Longitude
measures the position east or west of the Prime Meridian.
32
New cards
Great Circle
Surround the circumference of the entire earth.
33
New cards
Goods Projection
interrupts the oceans and tucks Australia and New Zealand father west than in reality.
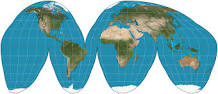
34
New cards
Mercator Projection
Stretches the poles from one length to the size of the equator
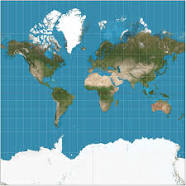
35
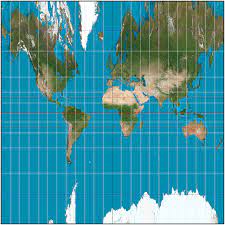
New cards
Equal Area (cylindrical) Projection
represents areas correctly, but distorts shape
36
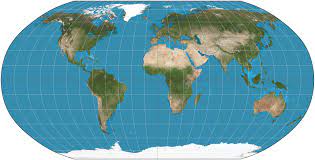
New cards
Robinson Projection
Frequently used and distorts size and shape but not too much.
37
New cards
Isoline map
connects points of equal value
38
New cards
Chloropleth map
puts features into classes and then maps classes for each region.
39
New cards
Cartogram map
adjusts the size of the country: corresponds to the magnitude of the mapped feature.
40
New cards
Proportional Symbol map
size of the symbol corresponds to the magnitude of the mapped feature.
41
New cards
Dot Distribution map
each dot represents some frequency
42
New cards
Environmental Possiblism
The people, not the environment are the architects of their own cultures or behavior. (adjusting to the environment using technology)
43
New cards
Environmental Determinism
The physical environment is the dominant force in shaping cultures or human behavior.
44
New cards
Distribution
The arrangement of features within space
45
New cards
Density
the frequency with which something is distributed in space.
46
New cards
Arithmetic Density
the total number of objects in a given space such as: people/square mile. High population of a state or area doesnt necessarily mean high density.
47
New cards
Physiological density
the number of people per unit of arable land (farmland/cropland.)
48
New cards
Diffusion Patterns
How characteristics are spread across a space or from one place to another over time.
49
New cards
Absorbing barriers
completely halt diffusion
50
New cards
Permeable Barriers
Allowing part of the innovation wave to diffuse, but acting to weaken and slow the continued spread.
51
New cards
Distance decay
the further away one group is from another the less likely the 2 groups are to interact.
52
New cards
Time-Space compression
the likelihood of diffusion depends upon the connectedness among places.
53
New cards
Hierarchical diffusion
Ideas leapfrog from one node to another, temporarily bypassing some. Spreads from authority. EX: military
54
New cards
contagious diffusion
Spreads in a wavelike pattern, like a disease.
55
New cards
Stimulus diffusion
A specific trait is rejected, but the idea is accepted.
56
New cards
Relocation Diffusion
Occurs when individuals migrate to a new location varying new ideas or practices with them.
57
New cards
Demography or Demographic
The scientific study of population characteristics is known as demography.
58
New cards
Census
an official count of the population by a government every ten years to gather data.
59
New cards
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
number of live births per thousand population.
60
New cards
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
Number of deaths per thousand people.
61
New cards
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI) or Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
Measures the % by which a population grows or declines in a given year. The term natural means that the rates exclude migration
62
New cards
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman of childbearing years would have in her lifetime.
63
New cards
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
Is the annual number of deaths of infants under age one, compared with total live birth (CBR).
64
New cards
Life Expectancy
Is the average \# of years a newborn infant can expect to live if current mortality rates (CDR and IMR) were to continue for the rest of their lives.
65
New cards
Dependency Ratio
the \# of people who are too young or too old to work compared to the \# of people in their productive years.
66
New cards
Population Pyramid
Graphic device (graphic model) that shows sex and age distribution of a population.
67
New cards
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
Geographic model that displays 3 key population demographics (CBR, CDR, NIR/RNI). The demographic transition consists of 4 stages, which move from high CBR and CDR, to declines first in CDR then CBR and finally to a stage of low CBR and CDR.
68
New cards
Ecumene
Is the portion of the earth with permanent human settlement, has expanded to cover most of the world’s land area.
69
New cards
Arithmetic Density
Is the number of people per total land area.
70
New cards
Physiological Density
Is the number of people per arable land area. (farm Stuff)
71
New cards
Carrying Capacity
Is the land's ability to support a population
72
New cards
Sustainable Development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
73
New cards
Overpopulation
When a population has exceeded the carrying capacity of an area.
74
New cards
Under Population
when birth rates fall lower than the mortality rates.
75
New cards
Migration
A type of diffusion (relocation) where an individual or group makes a permanent move to a new location.is a form of mobility which is a more general term covering all types of movements from one place to another.
76
New cards
Push Factors
factors that cause people to leave their homeland and migrate to another region.War, persecution, political, environmental
77
New cards
Pull Factors
Pull: factors that pull or attract people to another locationGood economic opportunities, high salaries, favorable climate
78
New cards
Immigration
is a migration to a location.
79
New cards
Internal Migrant
the movement of people within a country
80
New cards
External (International) Migrant
Refugees who have moved from their original state (country) of origin.
81
New cards
Emigration
is a migration from a location.
82
New cards
Net-in Migration
If the \# of immigrants exceeds the \# of emigrants, the net migration is positive
83
New cards
Net-out Migration
If the \# of immigrants is lower than the \# of emigrants, the net migration is negative
84
New cards
Brain Drain
The migration of individuals who are highly skilled/educated from less developed regions to more developed regions.
85
New cards
Refugee
Are people who have been forced to migrate from their homes and cannot return due to safety or fear of persecution.
86
New cards
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
Refugees who are still located in their state of origin.
87
New cards
Voluntary Migration
The migrant makes the decision to move.*Most migration is voluntary.
88
New cards
Chain Migration
immigrants from a particular area follow others from that area to a particular destination
89
New cards
Circular Migration/Guest Workers
A type of temporary migration.Known as “Guest Workers”Associated with agricultural work.
90
New cards
Involuntary (Forced) Migration
Forced international migration has historically occurred for 2 main reasons: slavery and political instability.
91
New cards
Undocumented Immigrants
\
* **anyone residing in any given country without legal documentation**.
* **anyone residing in any given country without legal documentation**.
92
New cards
State/
independent unit that occupies a territory and has full control
93
New cards
Sovereignty
has full control of if internal and external conflicts ( total control of country.
94
New cards
Country
Piece of land
95
New cards
Nation
group of people with common culture living in a territory and having sense of unity.
96
New cards
Nation state
Nation and state occupying the same area
97
New cards
Stateless Nation
Group without territory
98
New cards
Multi National State
Politically controlled area with sovereignty but has no single dominant ethnic group .
99
New cards
Multi state nation
A nation governed by more than one state.
100
New cards
Colonialism
a territory that is legally tied to a sovereign sate rather than being independent.