Storage Unit Flashcards
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Types of Storage
Magnetic (hard drive)
Optical
Soild State
How many TB are there in 831, 500, 250 MB
851.500250 TB
How many KB are there in 851.50025 GB
831, 500, 250 KB
Soild State Drive
Optimally split evenly across all NAND cells to reduce the wear on a particular cell
Types of layers
Single layer cell (best)
Triple layer cell (second best)
Multi layer cell (worst)
Hard Disk Drive Advantages
Cheaper
longer disk retention
more capacity
Hard Disk Drive disadvantages
Slower
bulky
Potential data loss from vibrations
Soild State Drive advantages
Faster
smaller
not affected by vibrations
Solid state disadvantage
Expensive
smaller capacity
shorter data retention
What does SMART stand for
Self monitoring analysis report technology
What does HAMR stand for
Heat Assisted magnetic recording
What is HAMR
The heated tip expands data space, the data contacts when the heat is taken away
Order of storage capacity
Bit
byte
kilo
mega
giga
tera
peda
Signs of HDD failure
freezing/ files not saving
Loud pitch sounds
Whirling (can't find file)
Clicking (head moving back and forth)
What does POST stand for
Power on self test
What does CMR stand for?
Conventional magnetic recording
What does SMR stand for?
Shingled magnetic recording
Benefits of CMR
Data is more far apart
Better and safer
Benefits of SMR
Cheaper
More storage capacity
Disadvantages of SMR
Slower
More prone to data corruption
What does RAID stand for
Redundant Array of Independent disks
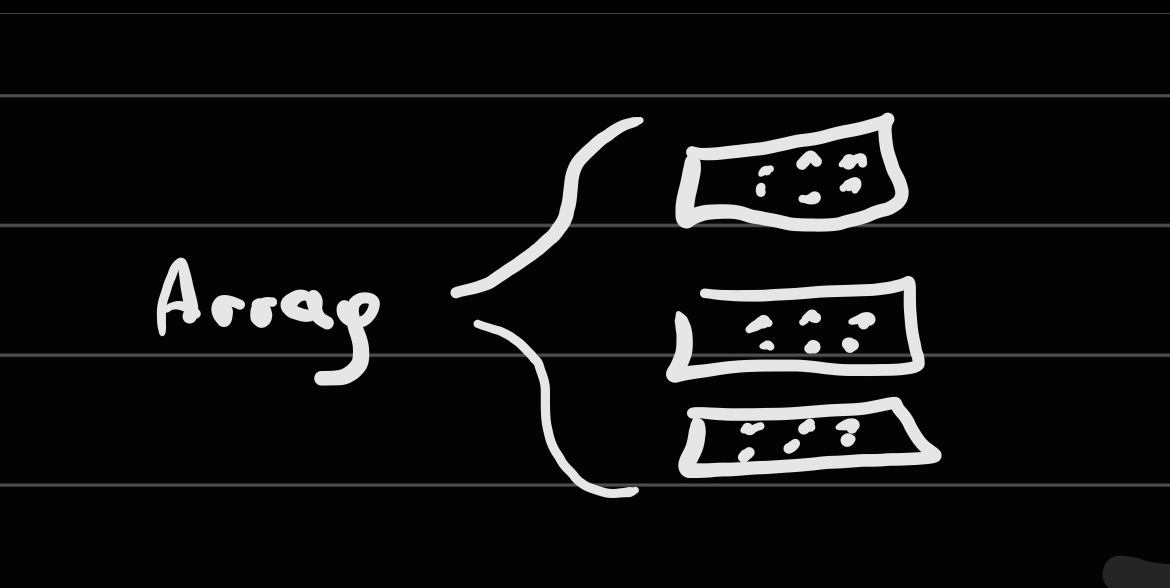
RAID 0
Data is split evenly (50 50) across the MINIMUM OF 2 DISKS
No redundancy
Combined capacity
Faster transfer speed
Array is corrupt of one fails
RAID 1
Data is copied identically MINIMUM OF 2 DISKS
Mirror redundancy
Half capacity
Slower transfer speed
If one fails, the other acts as back up
RAID 5
Data is compressed in parity drives MINIMUM OF 3 DISKS
Parity redundancy
70% total capacity
Normal speed
Can take 1-2 drive failures
Easier to replace
RAID 10
RAID 1+0
Data is split evenly across two disks then mirrored to other two disks
MINIMUM OF 4 DISKS
Half capacity
Normal transfer speed
If more than one goes bad, the entire array could be corrupted
What is disk defragment
It reorganizes files into more optimal locations
What is disk clean up
It removes fragments from temporary files or uninstalled programs
What is f disk
It formats disk obsolete disk operating system (DOS) command to partition disk
What is the capacity of a zip disk
100 MB
What did /r do (includes /f)
“Recovers” scans for bad sectors and recovers data
Slower than /f
What is the capacity of a Compact disk
700 MB
What is the capacity of a DVD
4.7 GB
What is the capacity of a BluRay
25 GB