Glacial erosion and deposition
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Glacial Abrasion
Rocks/particles transported at base, scratches
Glacial Plucking
an erosional process by which rocks are pulled out of the ground by a glacier
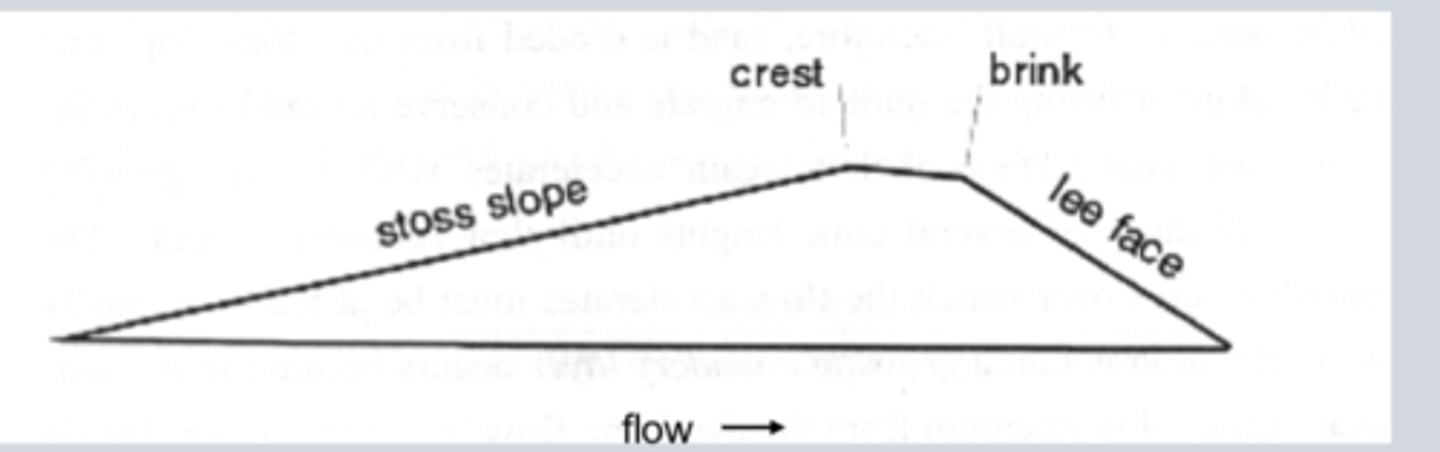
stoss and lee
Erosional Landforms
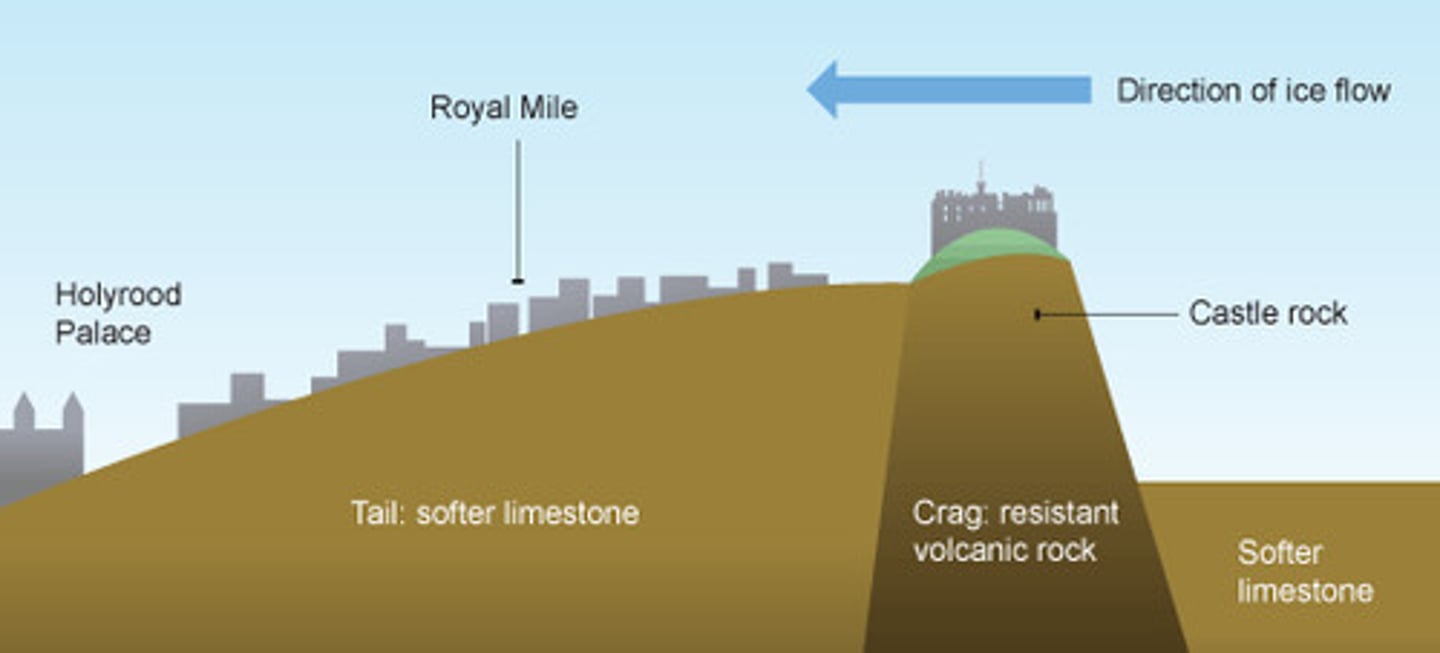
crag and tail
A glacially eroded hill with a tail of till formed down-glacier of it
Erosion by Glacial Meltwater
Fluvial abrasion and cavitation
what determines the amount of subglacier abrasion
rate and temperature
types of drift
stratified and non stratified
Stratified Drift
- Transported by moving water
- Fluvioglacial or glaciofluvial( under or infront of glacier)
• Well-sorted, clasts are more rounded
more glaciers are
dirty
drift
glacially deposited sediment
Nonstratified Drift
Till is single most variable type of sediment
- Angularity/roundness(if in middle of glacier)
- Particle size
- Transportation by glacier• Valley glaciers receive more from above
Lodgement till
sediment that accumulates at the base of a glacier and typically has a wide range of grain sizes (including clay) and is well compacted
- stuff lodged into the ground
Deformation till
Soft sediment deformation by glacial shear stress
- glacier as plow
flow till
- falls/pushed off front of glacier
sand bar
A long underwater ridge formed by sand deposited offshore, outwash plain
kettled sandbar
sandbar+kettle holes
moraine
A ridge formed by the till deposited at the edge of a glacier.
kames and esker
dominated by outwash
End of moraine/terminal
marks the farthest advance of the glacier
drumlin
-A long mound of till that is smoothed in the direction of the glacier's flow
drumlin formation reason why deposition
-subglacial depositional features
- subglacial molding into streamlined shape
-or infilling if cavities cut into basal ice by meltwater
drumlin formation reason why erosion
ice erodes, transports, streamlines existing deposits , if truly erosional see less till and more abrasion
kames
- tend to be hills
- made out of outwash/stratifies drift
- isolated hills with stratified drift
delta kames
lake seperated by huge blocks of ice
- meltwater to delta
kettle
glacial formed lakes when chunk of ice broke off and heavy enough to leave depression in topography,
esker
- depositis of subgalcial river
- heat energy through flowing water easier for flowing water to move up
most recent glacial advance
wisconcian