biochemical tests
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
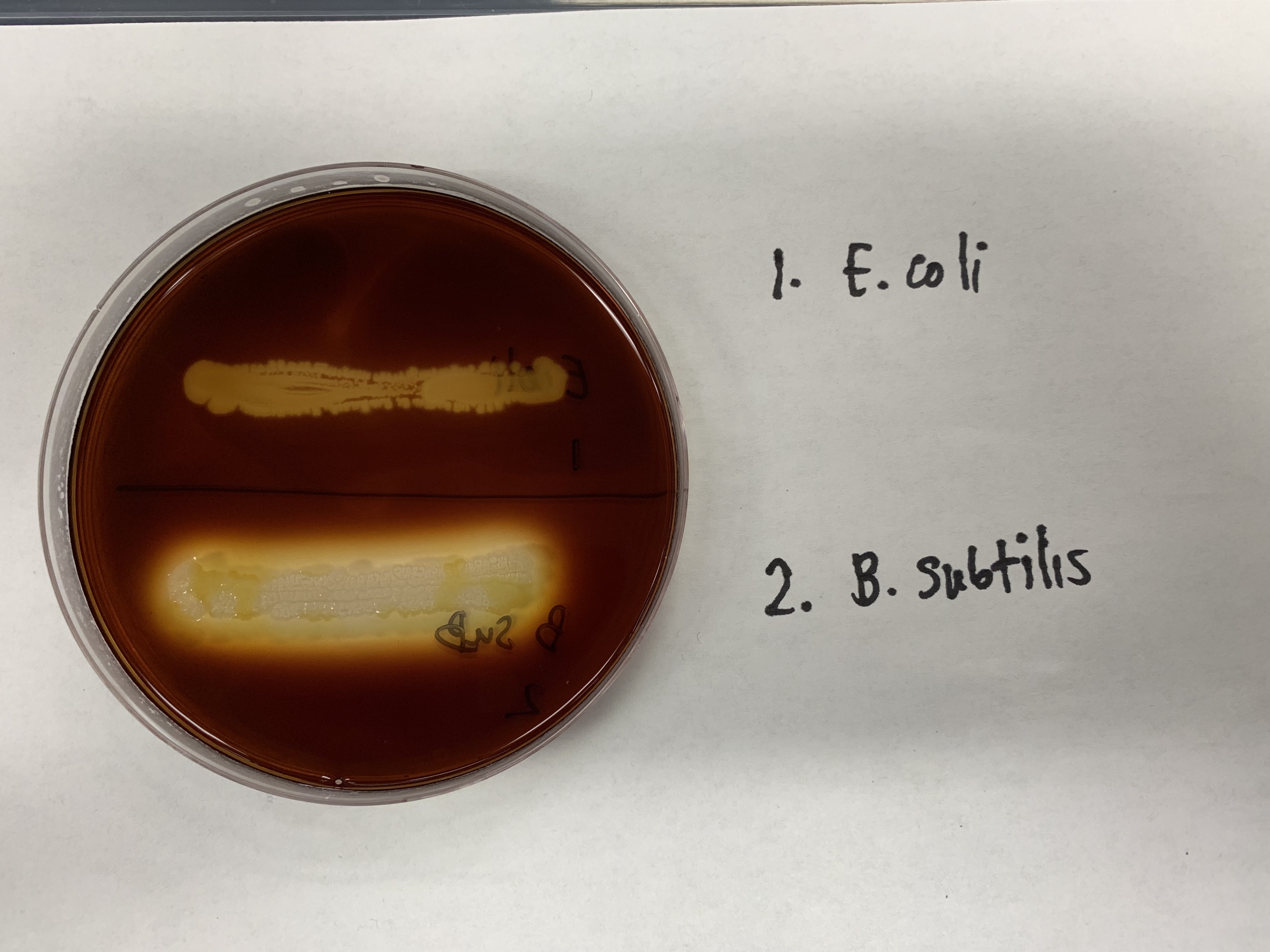
#11: Hydrolysis Of Starch
Medium: Starch Agar
Substrate: Scratch
Enzyme: Amylase (exoenzyme)
Reagent: Iodine
End Product: Maltose
Disaccharide composed of glucose 2
Positive: Amber no starch
Negative: Black starch is present

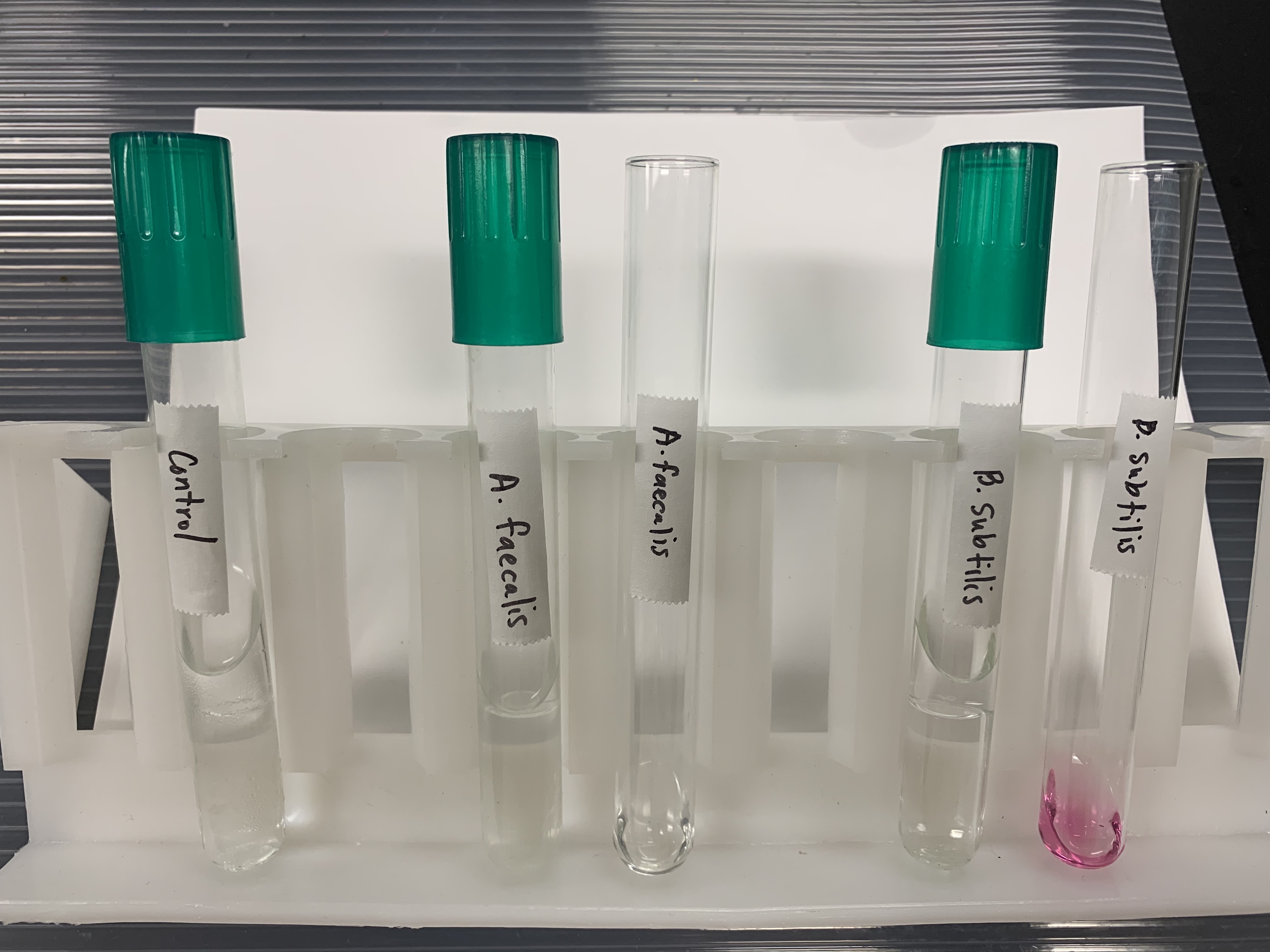
#12 Hydrolysis of Gelatin
Medium: Gelatin
Substrate: Gelatin
Enzyme: Gelatinase (Exoenzyme)
Reagent; n.a
End product: Amino acids
Positive: Liquid; produces gelatinase
Broke down into amino acids
Negative: Solid; does not produce gelatinase.

#13 Fermentation of Carbohydrates
Medium: Phenol broth + protein
Sugars will make acidic products
Protein will make basic products
Substrates: Glucose, Sucrose, Lactose, Mannitol
Pathway: Glycolysis
Reagent: Phenol Red
End Product: Pyruvic acid, ATP, +/- CO2
Positive: Acid. Acid/Gas; only using sugars
Negative: Magenta color like the control; only using proteins
#14 Reactions in Litmus Milk
All mediums and reagents are Litmus milk
CO2 is only formed in Fermentation reactions

#14.A Fermentation Litmus Milk
Substrate: Lactose
Pathway: Fermentation
If CO2. glycolysis occurred
End products: Organic acids, ATP, +/- CO2
Positive: Pink milk, +/- hard curd. 1

#14.B Reduction of Litmus Milk
Substrate: Litmus
Pathway: ETP
End Products: leucolitmus (White/clear) at bottom plus ATp
Positive: white acidic milk, apple basic juice

#14.C Alkalinization of Litmus Milk
Substrate: Casein
Enzyme: Proteases
End products: Small peptides and ammonia
Positive: Blueberry milk
#14.D Peptonization
Substrate: Casein and lactalbumin
Enzyme: Proteases
End Products: Free amino acids and ammonia
Complete hydrolysis
Breaks down both proteins in milk
Positive: Grape/apple juice (Reduction occurs) +/- soft curd
#14.E Curd Formation
Substrate: Acidic or basic conditions
Pathway: Fermentation or peptonization
Fermentation: Hard curd
Peptonization: Soft curd
End product: Curd
Positive: Hard or soft curd
Negative: No curd

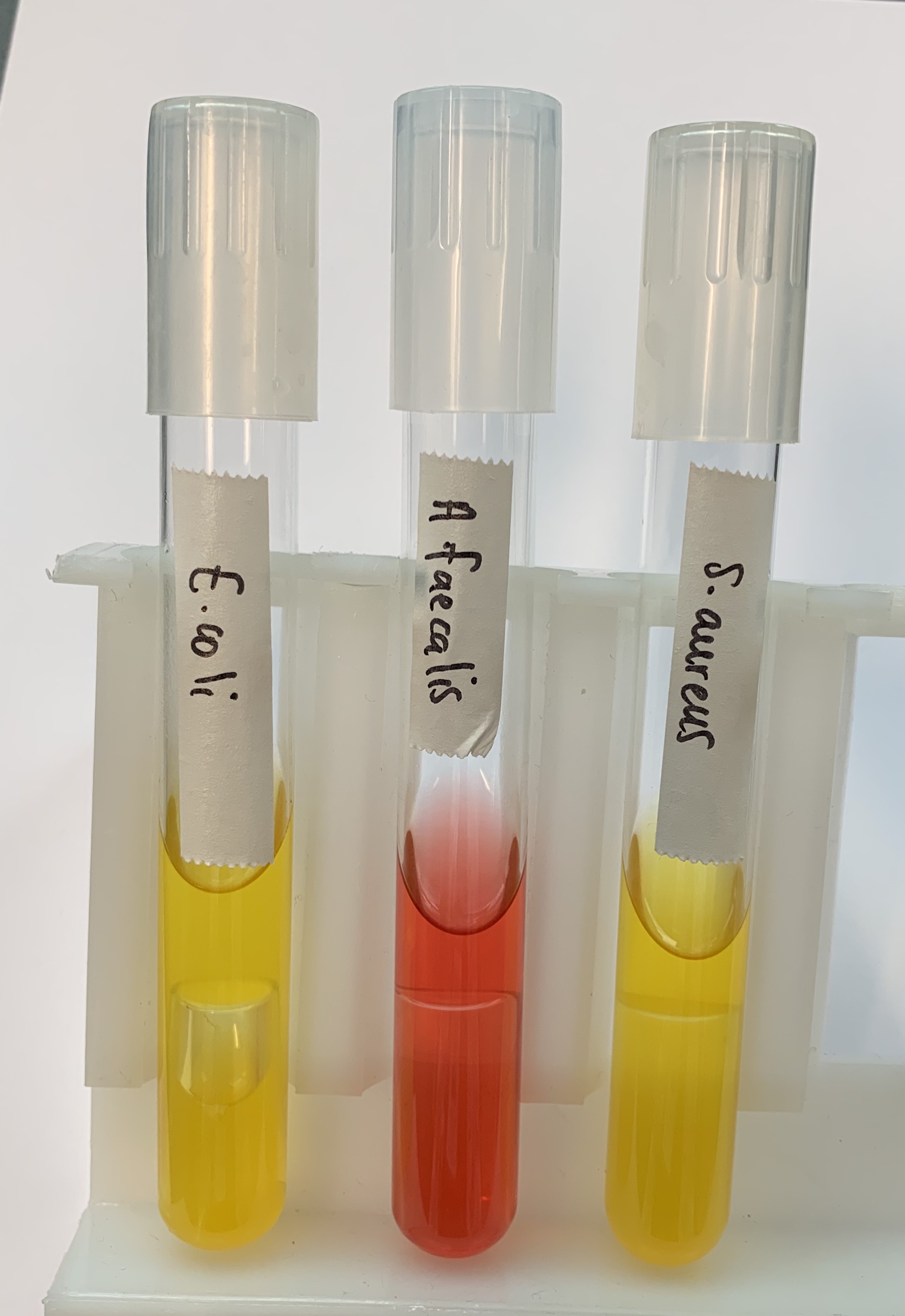
#15 Reduction of Nitrates
Medium: Nitrate Broth
Substrate: KNO3
Pathway: ETP
Reagent: DAN, sulfuric acid
End product: ATP and KNO2
Positive: Magenta; can reduce to nitrite.
Negative: Any other color, like control or peach
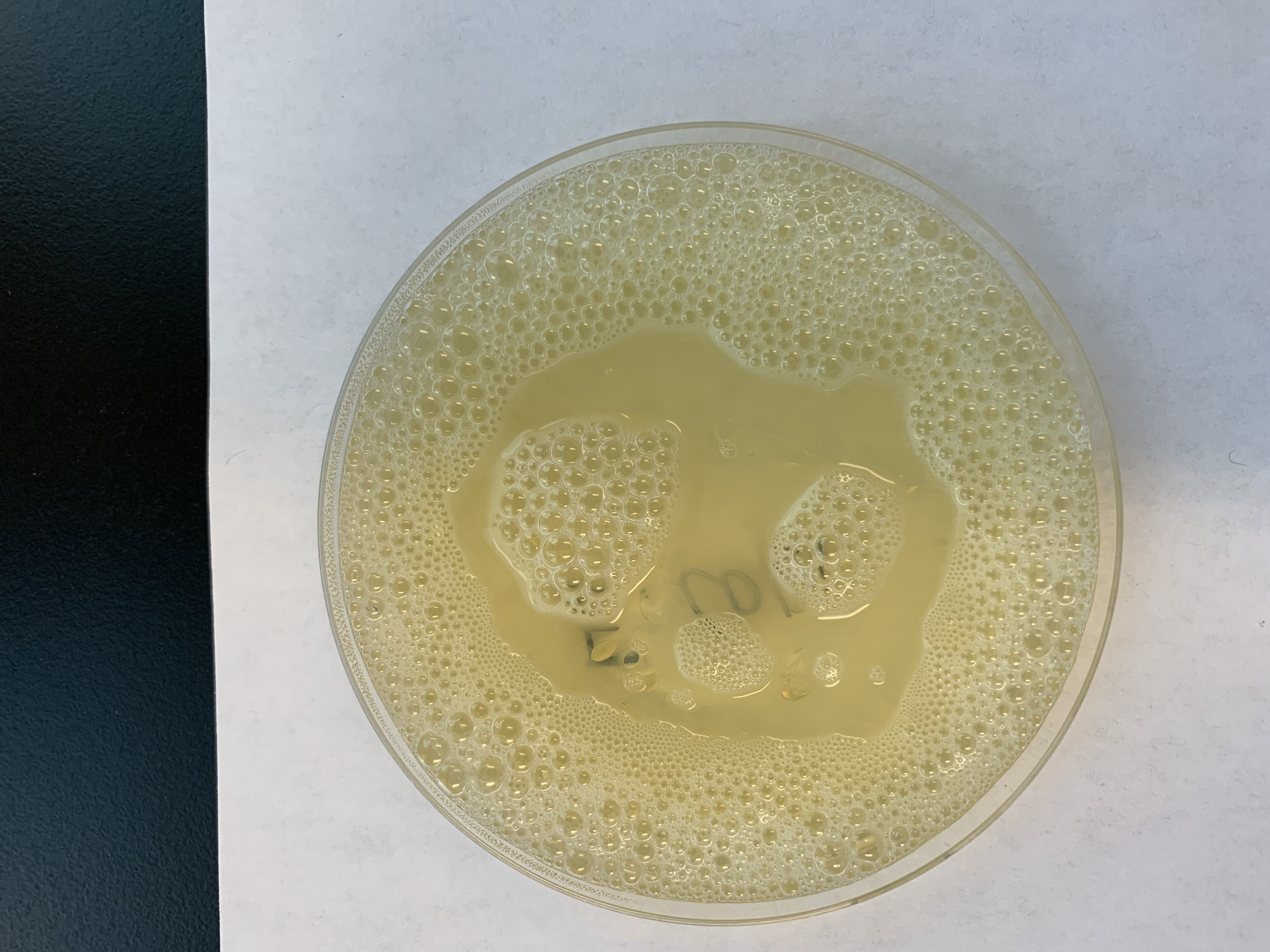
#16 Reduction of Catalase
Medium: TSA plate/Microscope Slide
Substrate: Hydrogen Peroxide
Enzyme: Catalase
Reagent: Hydrogen Peroxide
End product: Oxygen bubbles and water
Positive: O2 bubbles on colonies
Negative: No bubbles
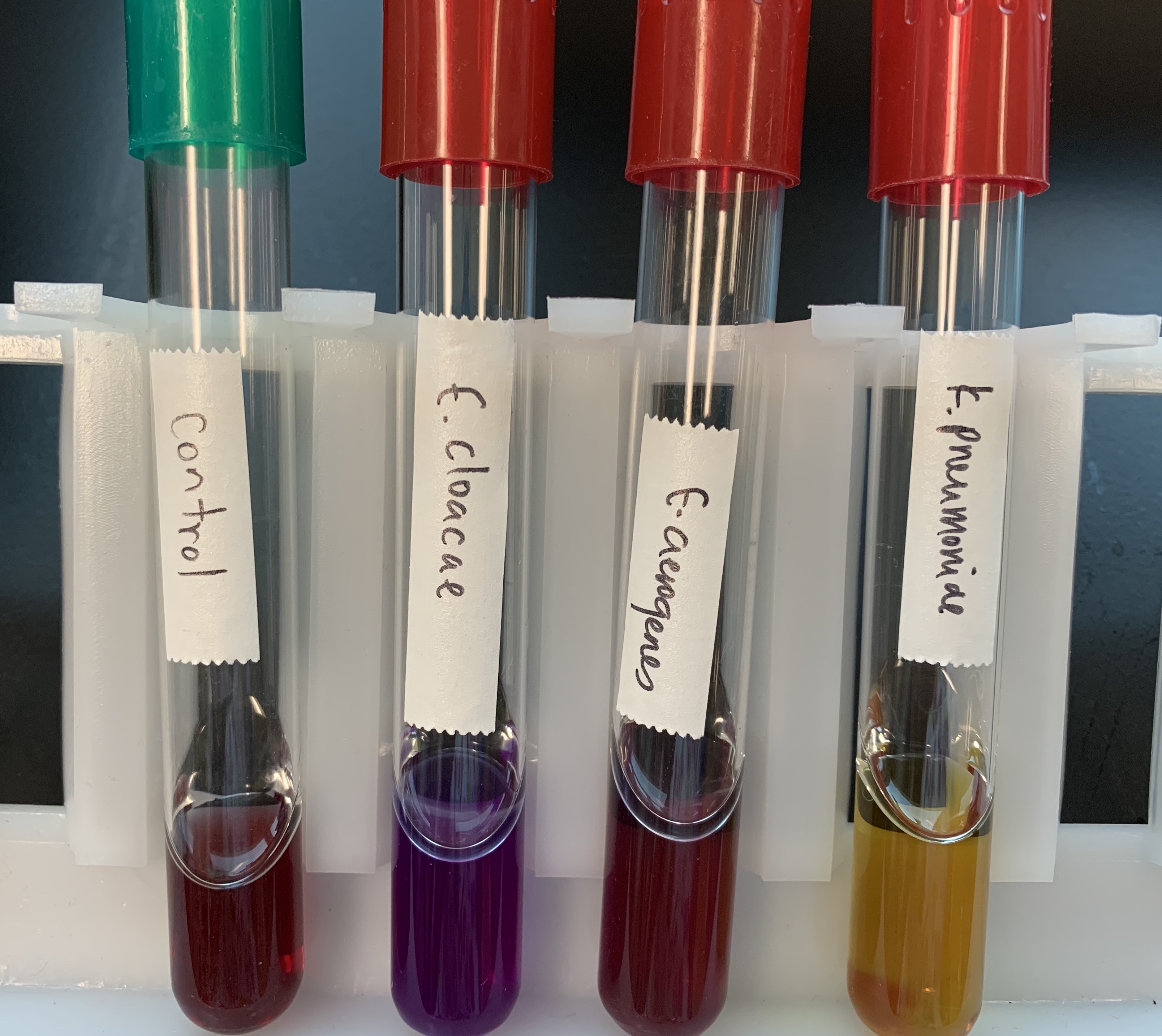

#17 Production of Decarboxylase
Medium: Decarboxylase Broth
Substrate: Arginine, Lysine, Ornithine
Enzyme: Decarboxylase
Reagent: Bromocresol Purple
End Product: Amine and Increase in CO2
Positive: Violet Color (basic)
Negative: Control or yellow (acidic)
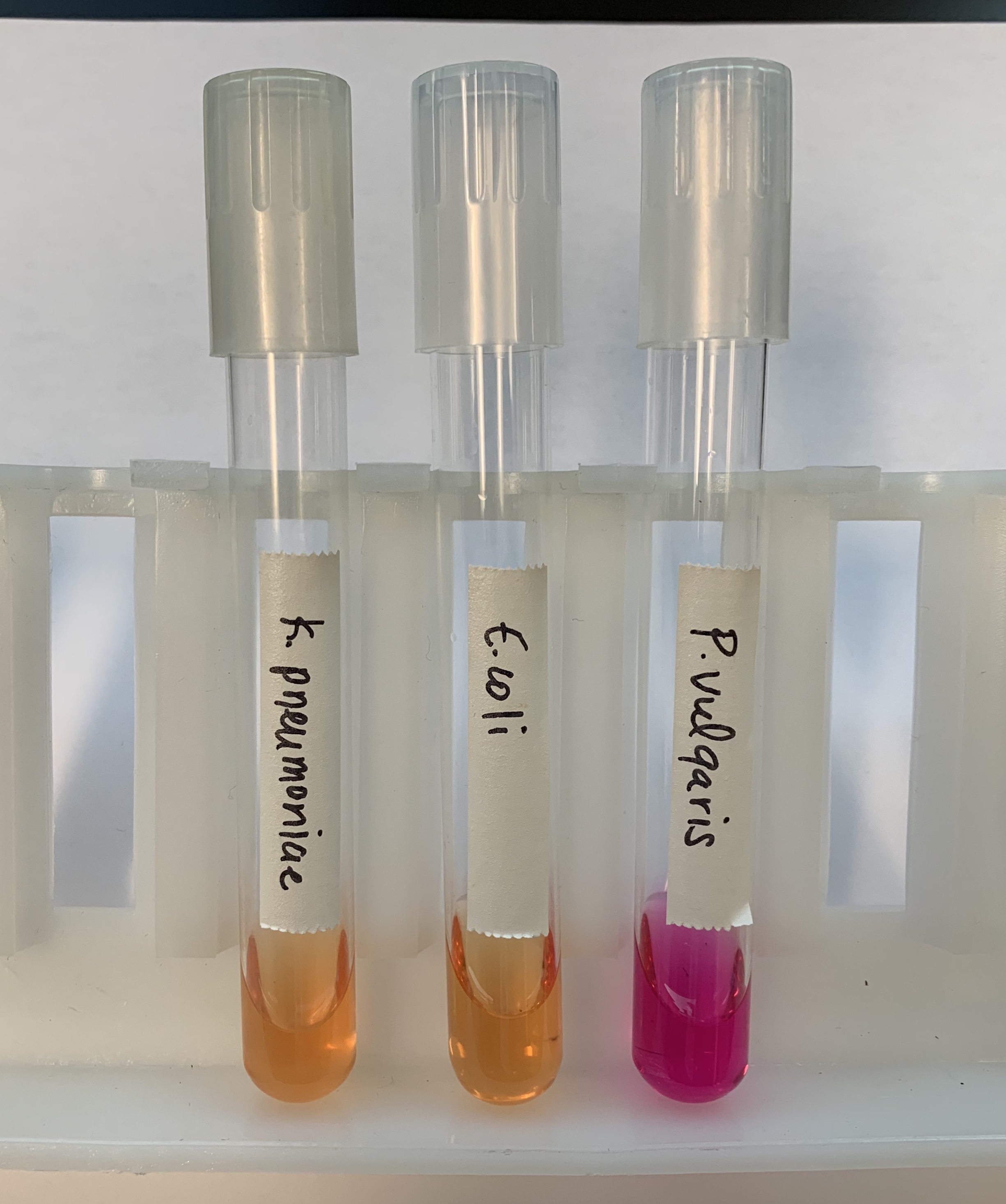
#18 Hydrolysis of Urea
Medium: Urea Broth
Substrate: Urea
Enyzme: Urease
Reagent: Phenol Red
End Product: CO2, NH3 (ammonia)
Positive: Hot pink
Negative: Yellow to gold (acidic)

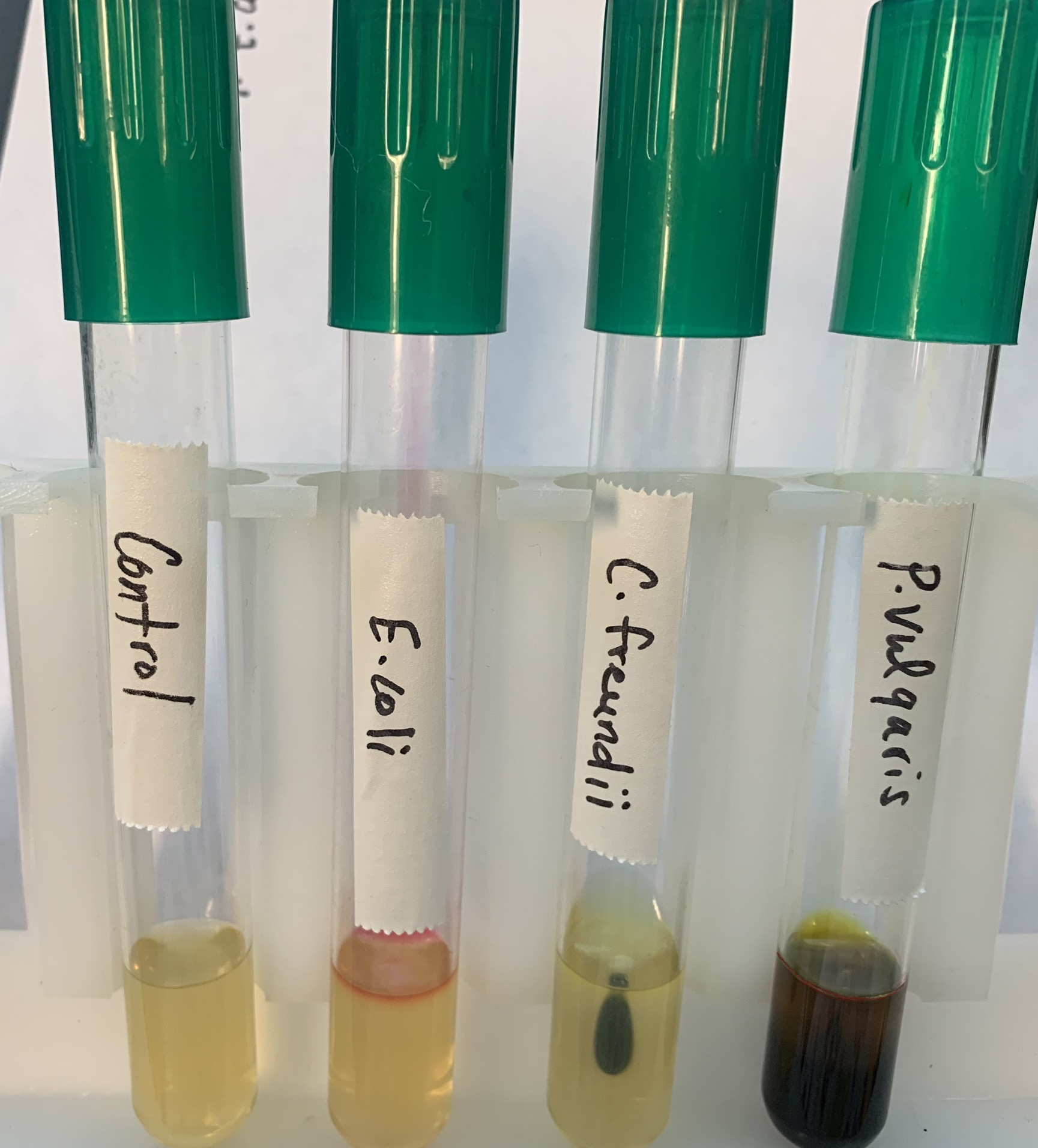
#19 S.I.M.S Test
S - Production of Hydrogen Sulfide
Substrate: Cysteine, H2S + FeSO4
Pathway: ETC
End Products: H2S + ATP; FeS + H2SO4 (iron sulfide + Sulfuric acid)
Positive: Black precipitate Iron Sulfide
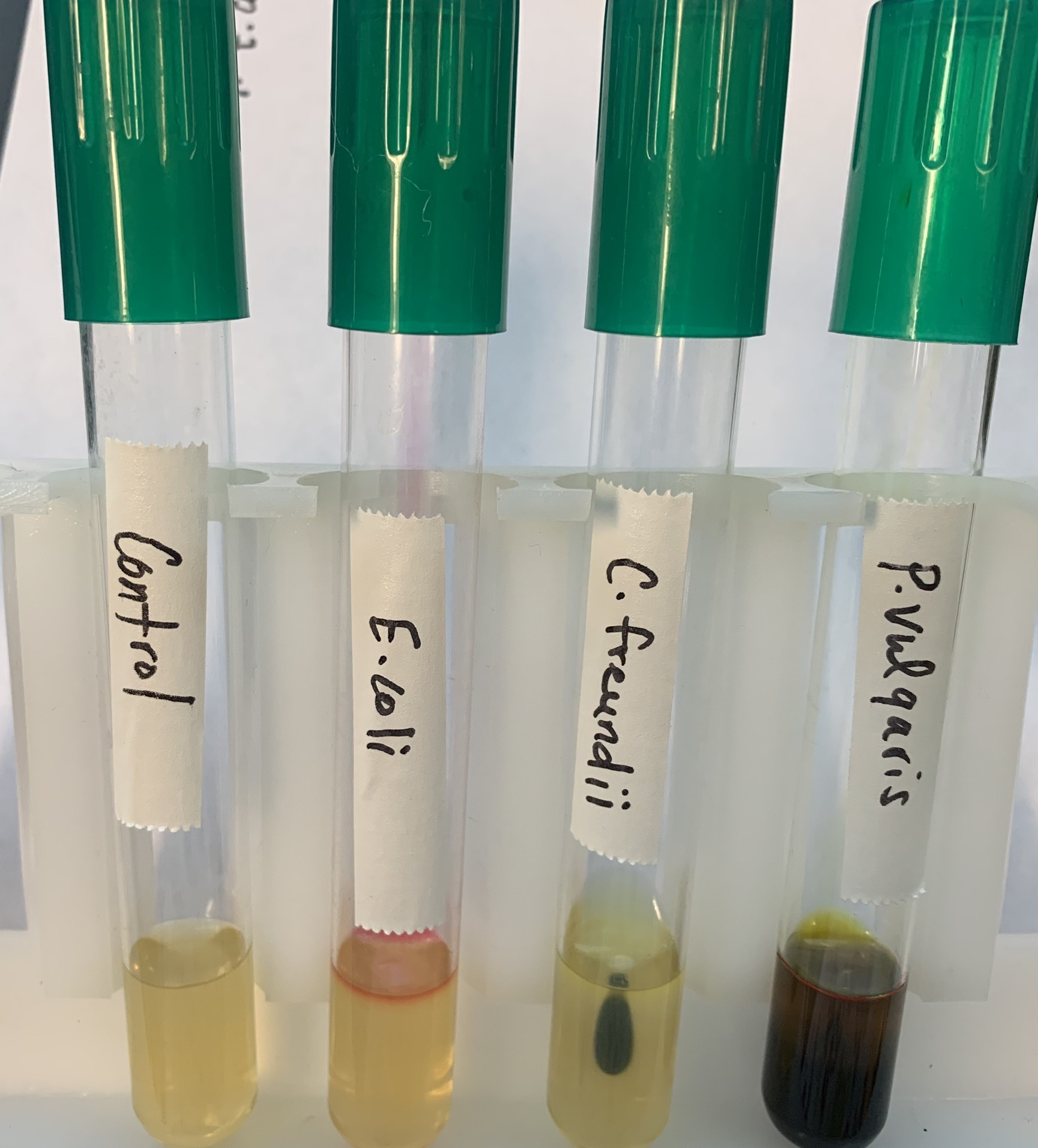

#19 SIMS Test
I - production of Indole
Substrate: Tryptophan
Reagent: Kovacs
End product: Indole, pyruvic acid, ammonia
Positive: Red ring

SIMS TEST
Motility
Positive: Movement from the line
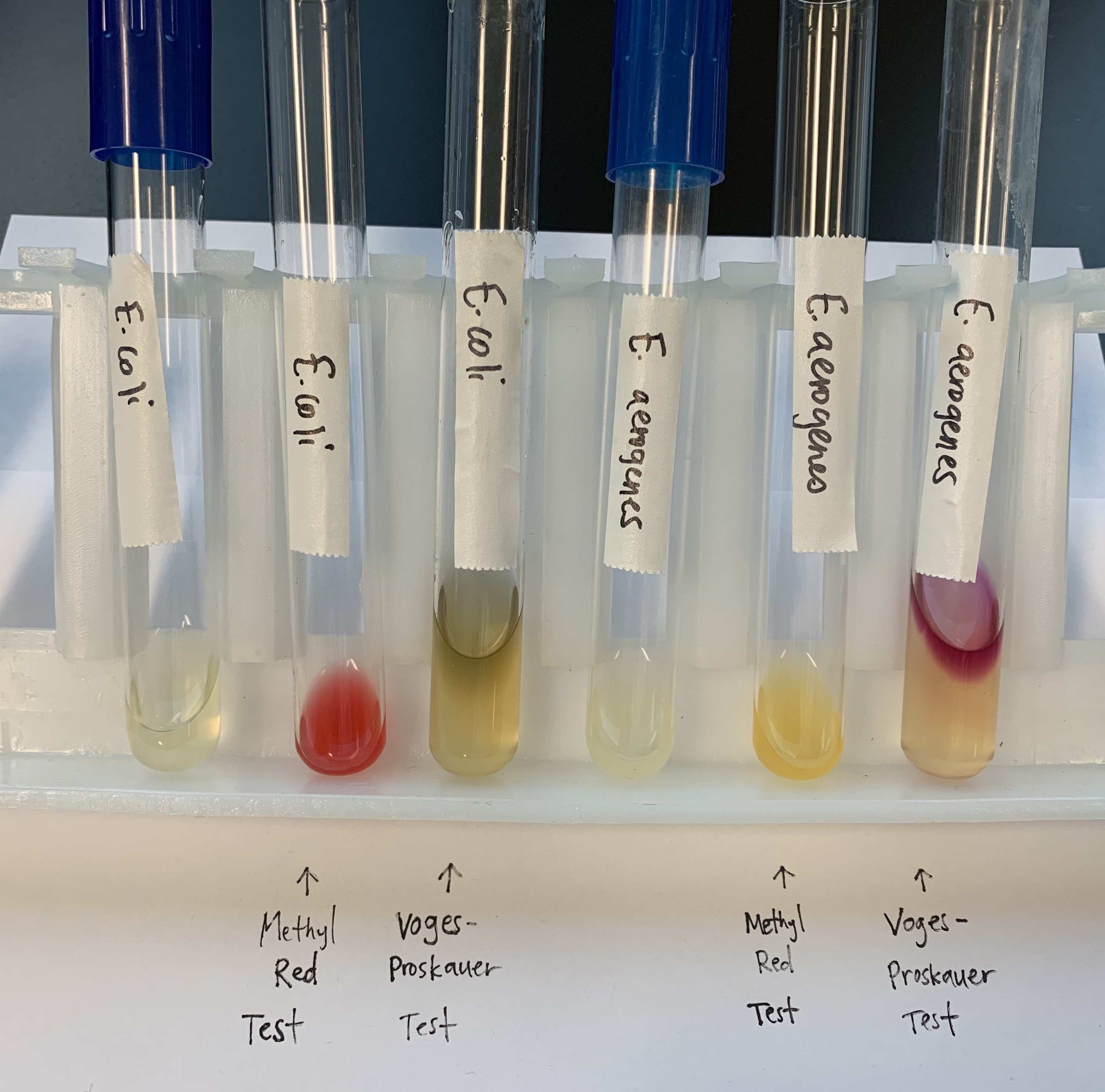

#20 MR.VP Test
Methyl-Red (MR)
MR - Methyl Red
Medium: MR broth
Substrate: Glucose
Pathway: Glycolysis
Reagent: Methyl Red
End Product: ATP, Pyruvic Acid
Positive: Red; presence of strong acid (organic acids)
Negative: Control, yellow basic; absence of strong acid
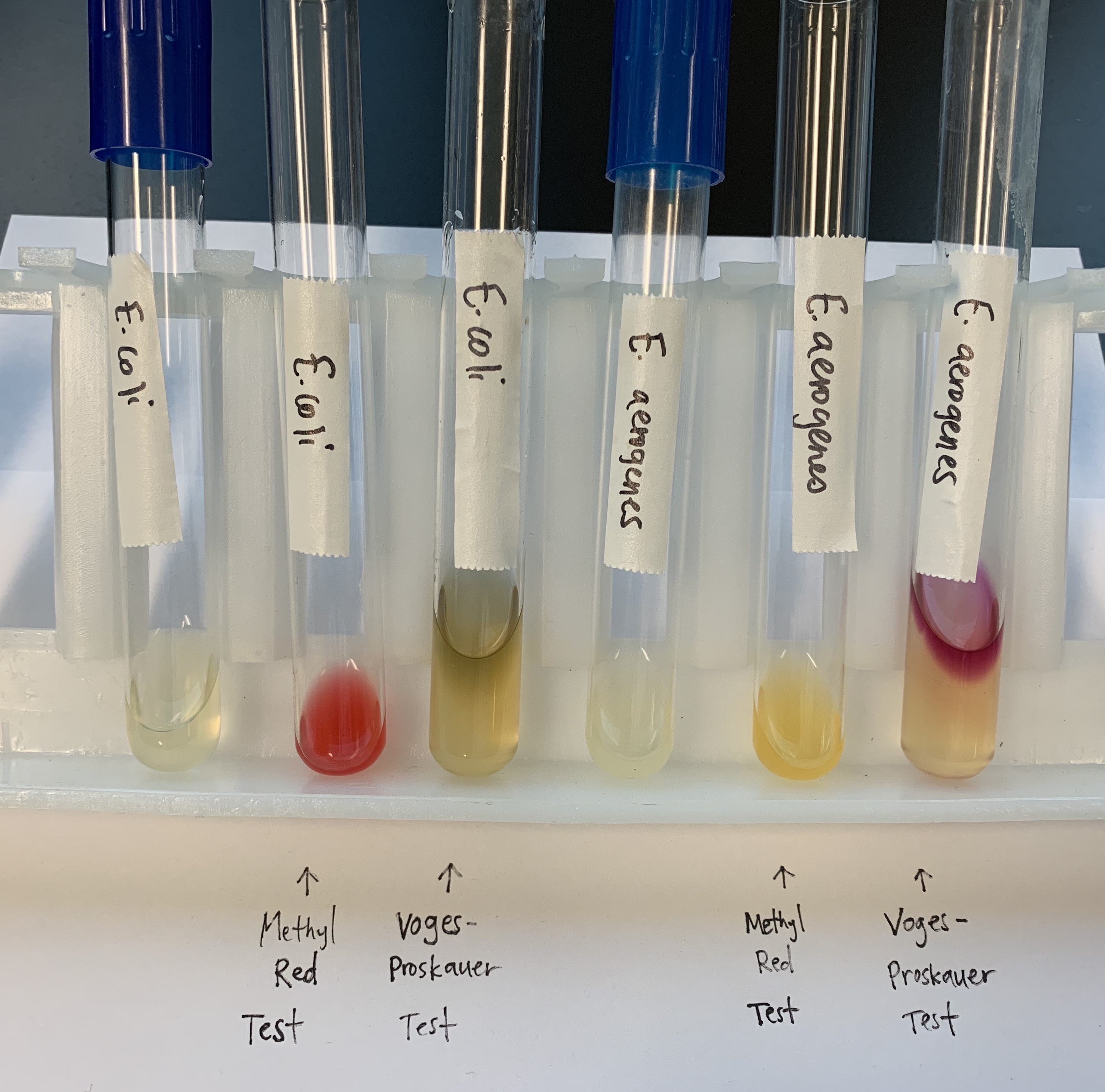

#20 MR.VP Test
Vogues Proskauer Test
VP: Vogues Proskauer
Medium: VP broth
Substrate: Glucose
Pathway: Alternative enzyme pathway
Reagent: D. Napthol, KOH Creatine
End Product: ATP, AMC, Organic acids and alcohols
Positive: Red ring on top
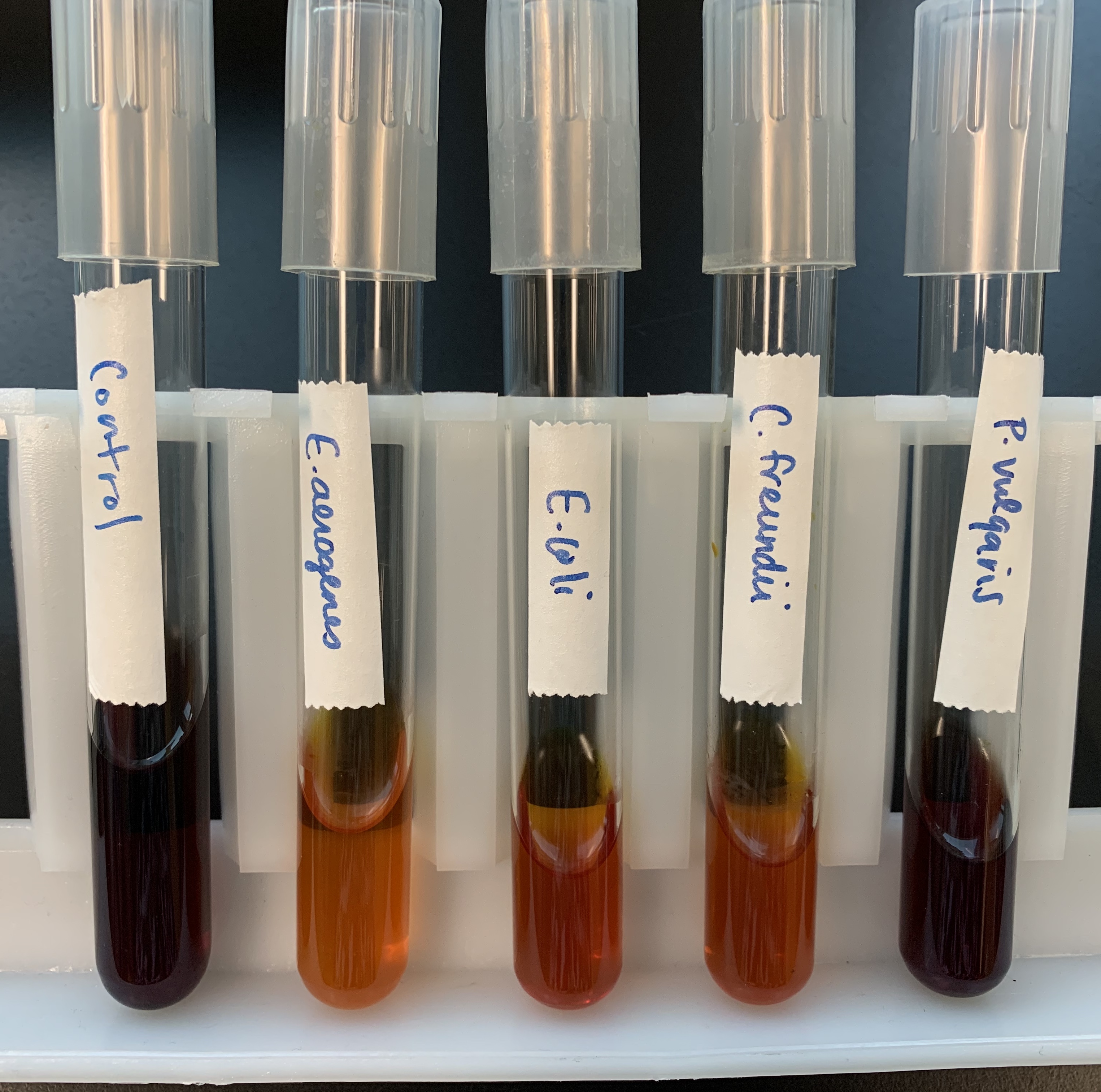

#21 Utilization of Unusual Nitrogen (Ammonium Phosphate)
Medium: Ammonium Phosphate Broth
Substrate: Ammonium Phosphate
Reagent: Bromcresol Purple
End Product: Ammonia and Phosphoric Acid
Positive: Yellow (acidic)
Negative: Burgundy/purple (basic)
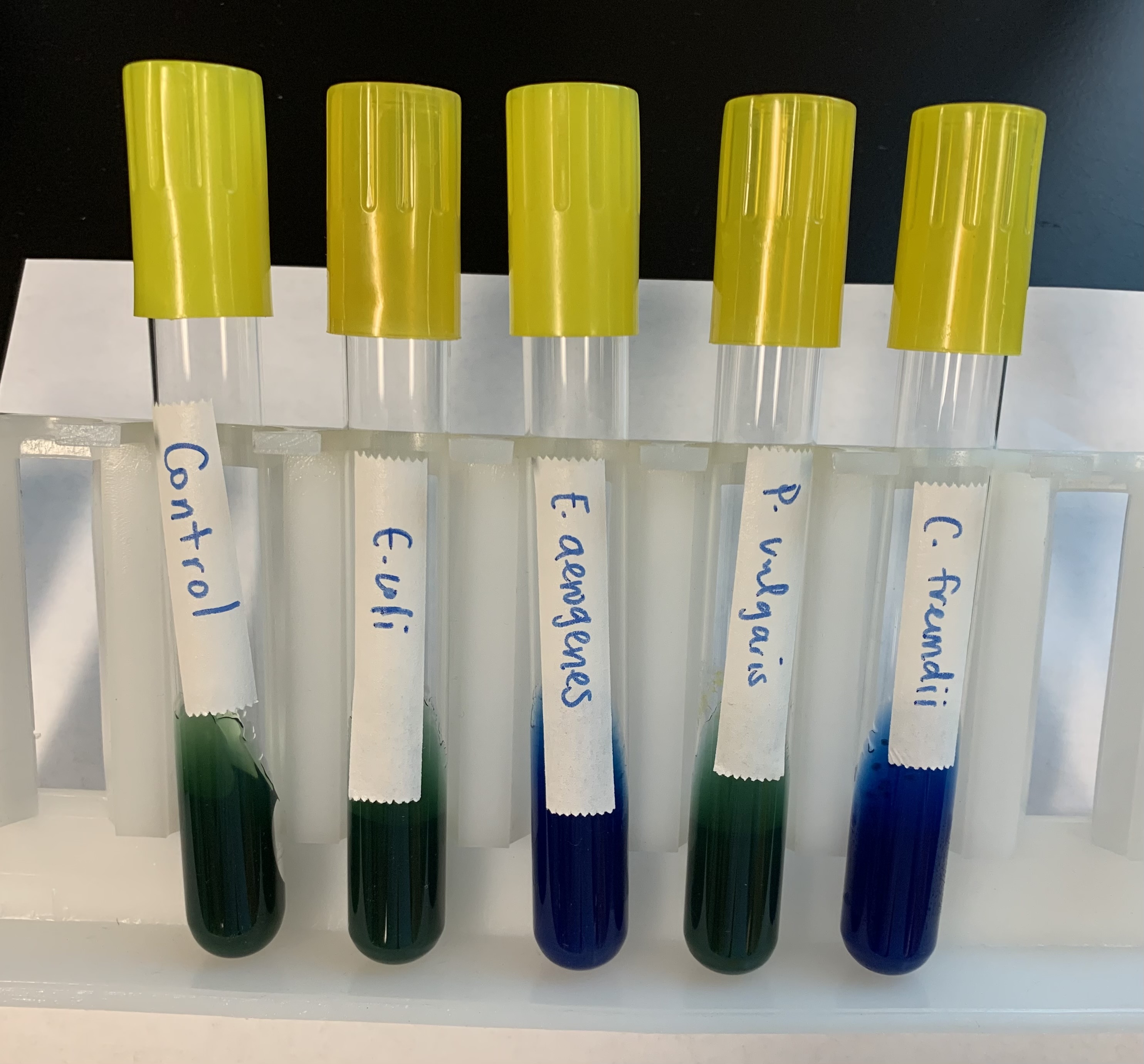

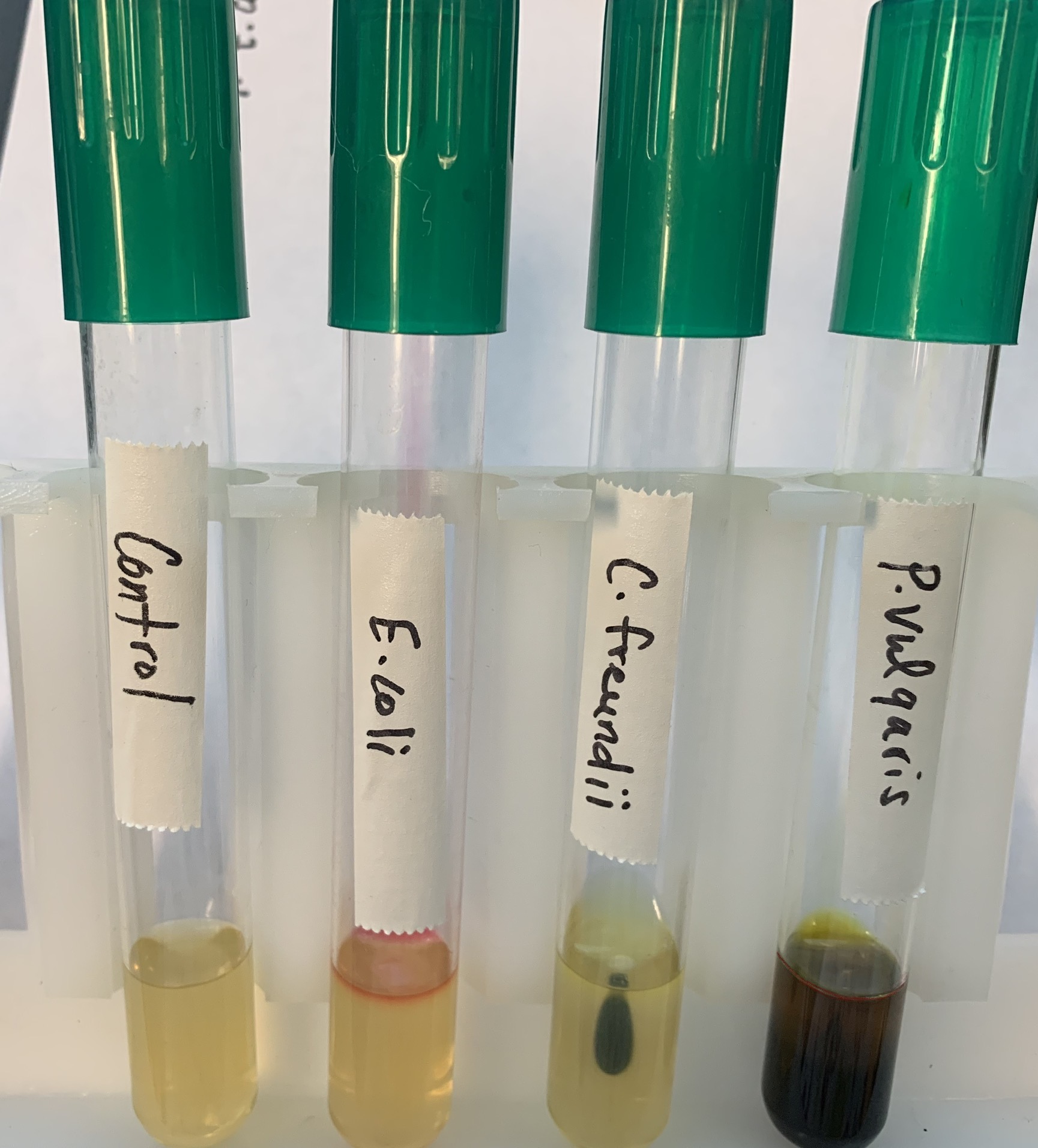
#22 Utilization of Unusual Carbon
Medium:
Citrate Agar
Substrate:
Citrate, ammonium
Enzyme: Citratase
pH indicator: Bromthymol blue
End Product
Pyruvate, ammonia
Positive
Blue (basic)
Negative
Green (acidic)
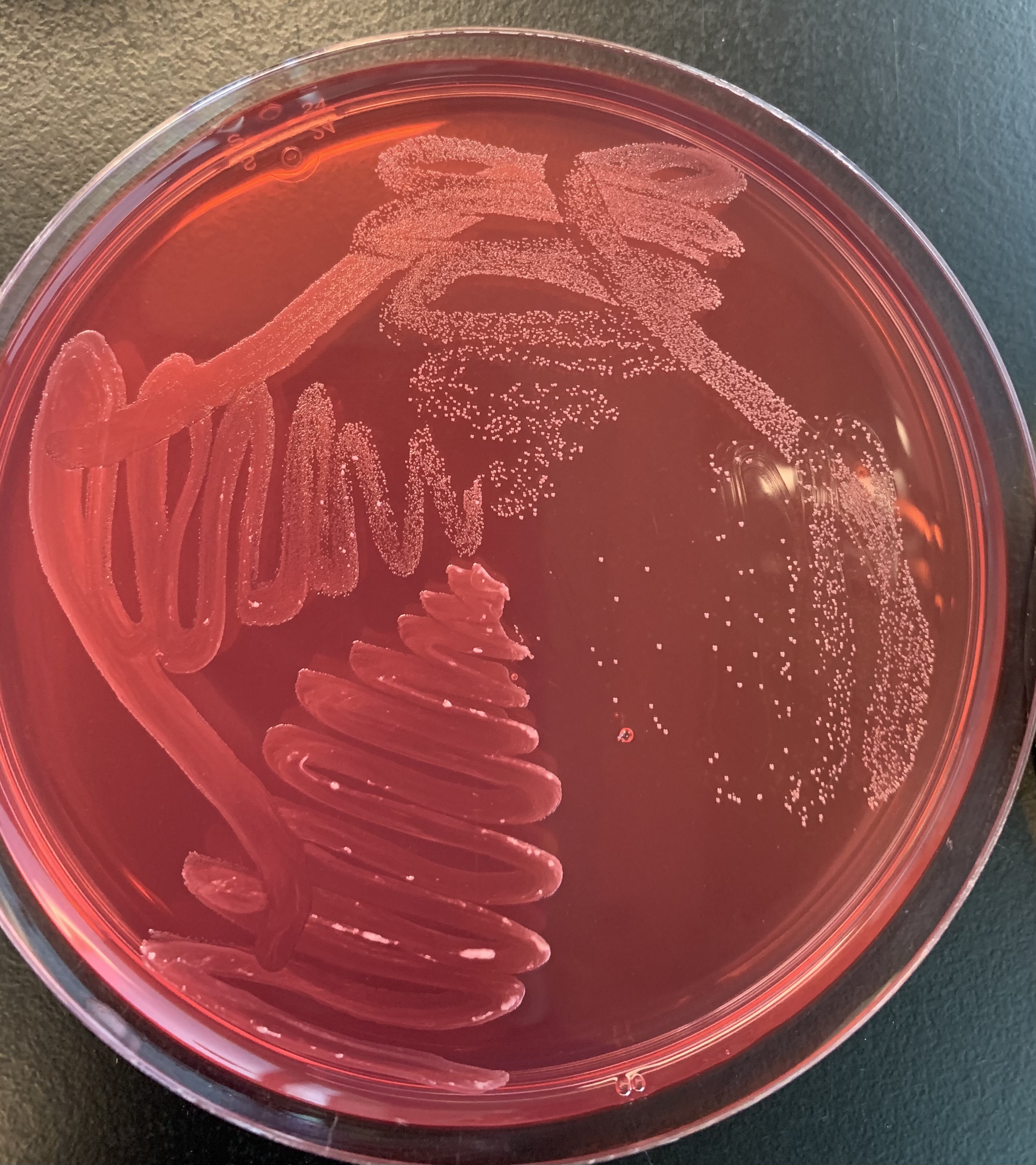
#24 MSA-Mannitol Salt Agar
Medium: MSA
Substrate: Mannitol
Pathway: Glycolysis
Reagent/pH indicator: Phenol Red
End Product: Organic acids, ATP
Positive: Yellow; agar turns yellow, acidic product.
Negative: Red
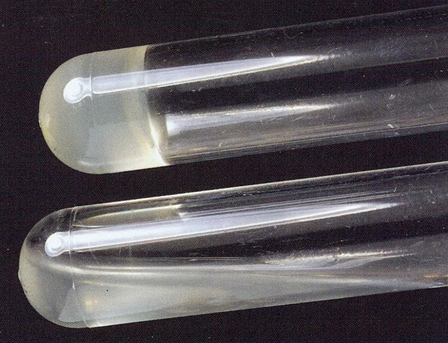
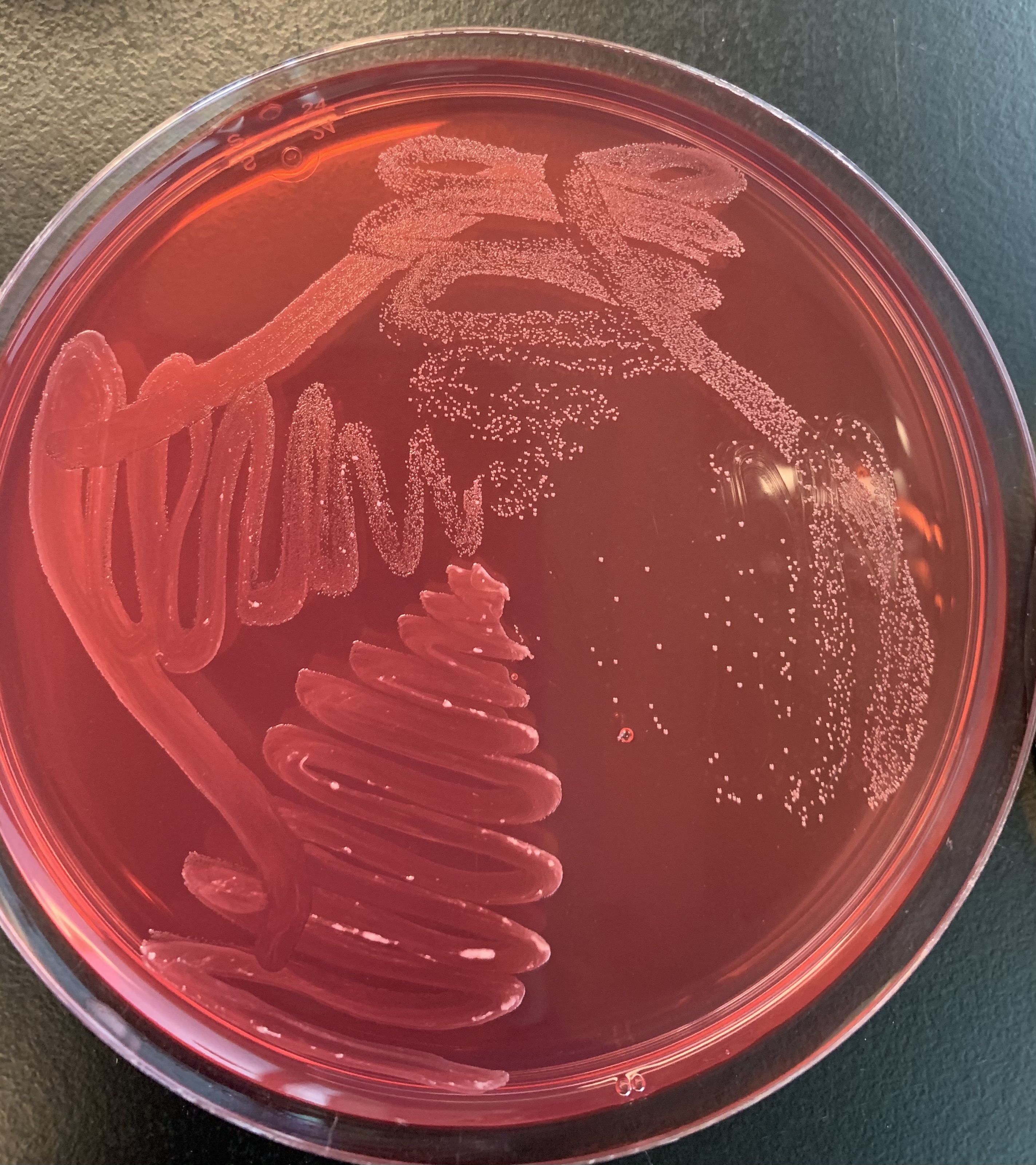
#25 Coagulase Production
Medium: Rabbit Plasma and Sodium Citrate
Substrate: Sodium Citrate
Enzyme: Coagulase
End products: Clotted plasma
Positive: Liquid plasma = IT HAS COAGULASE.
Increase in virulence
Negative: Solid media.
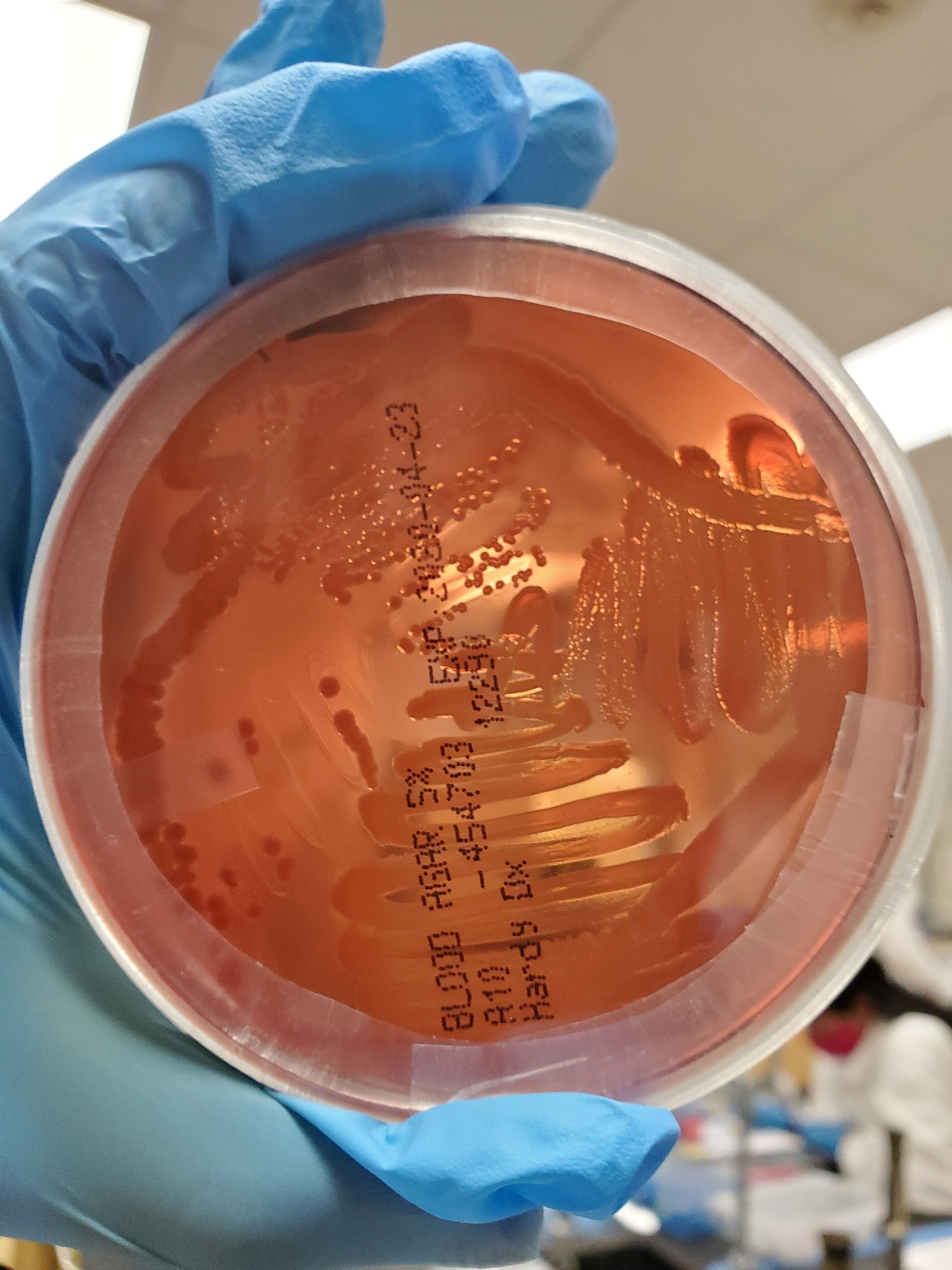
#26 Hemolysin Production
ALPHA
Alpha: Incomplete
Medium: Blood agar
Substrate: RBC, partial hemoglobin, NO iron
Pathway: Incomplete
Positive: Greenish colonies
The green colonies means that it doesn’t digest iron.
Incomplete hemolysis.
Examples
Strep Pneumoniae
Strep Aureus.
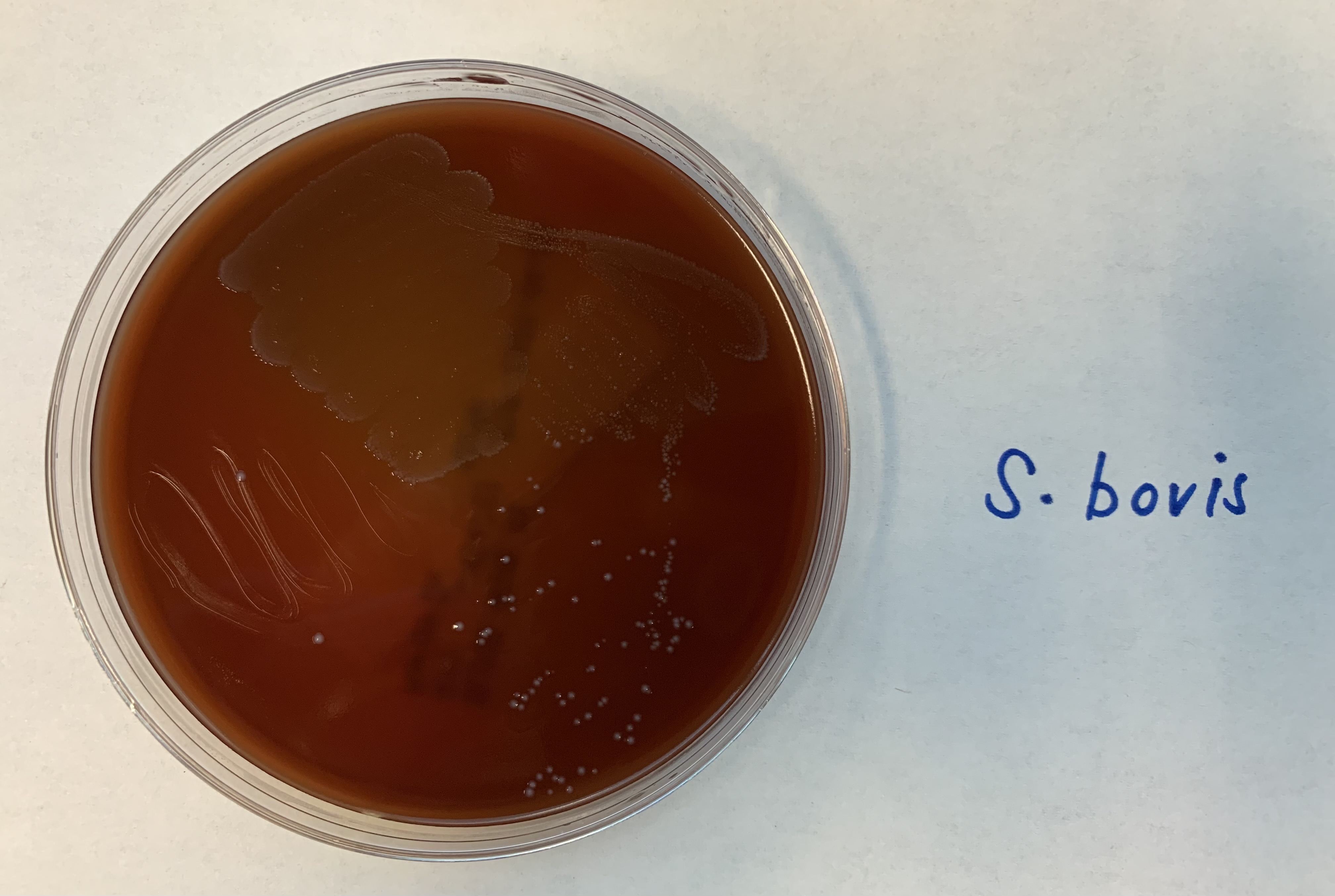
#26 Hemolysin Production
BETA
Beta: Complete
Medium: Blood agar
Substrate: RBC, Hemoglobin, plasma protein, iron
Pathway: Complete
Positive: Clear zones
Examples:
Strep equi
S. Bovis.
#26 Hemolysin Production
GAMMA
Medium: Blood agar
Substrate: plasma proteins
Positive: Red agar
Pathway: incomplete
It only goes after the plasma proteins
Staph. Epidermidis
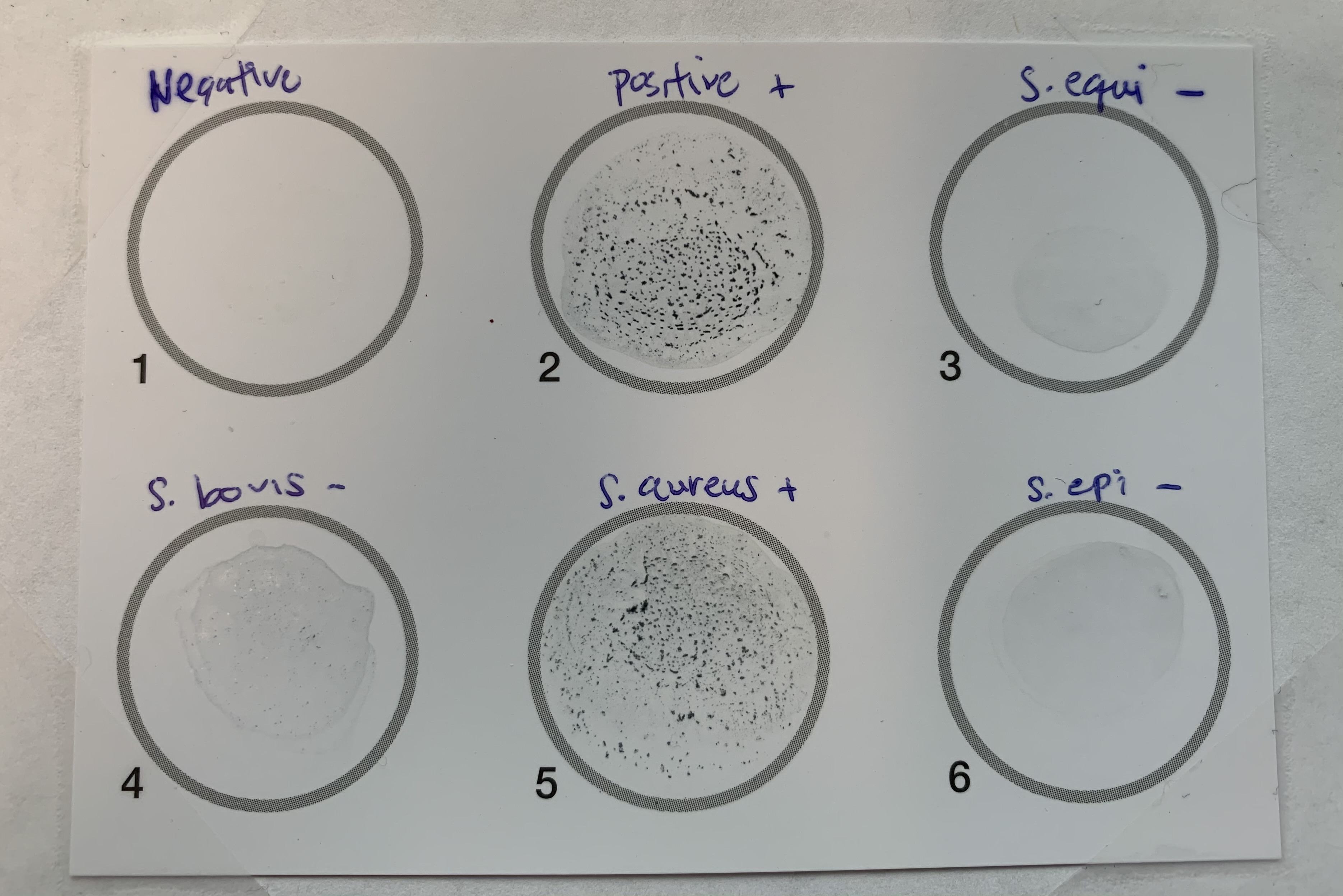
#27 Latex Agglutination
Medium: Latex beads coated with antibodies against coagulase
Positive: clumps
Negative: no clumps
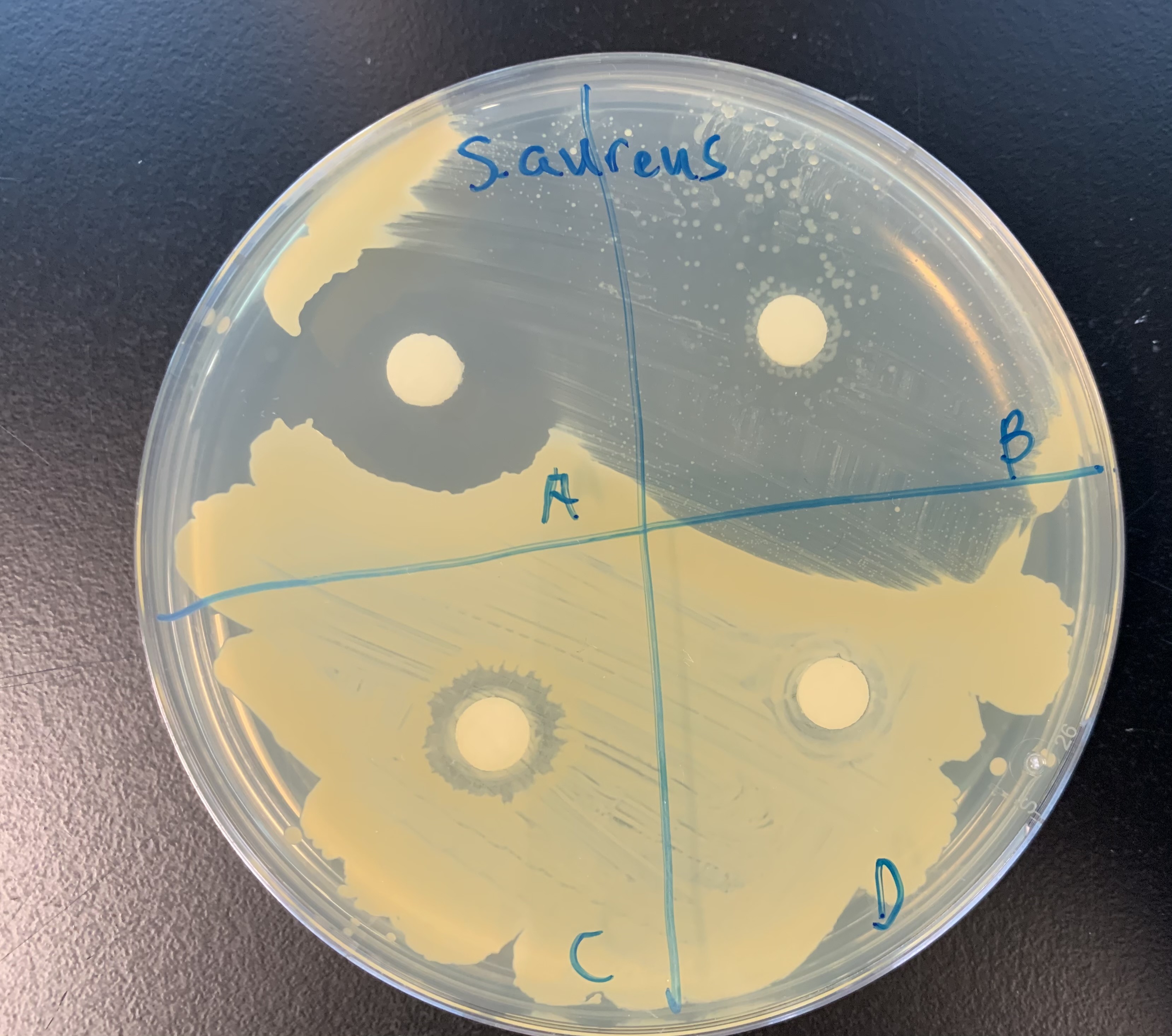
#33 Zone of Inhibition
Clear zone around the discs
Increase diameter: effective at inhibiting growth
Decrease diameter: not effective at inhibiting growth
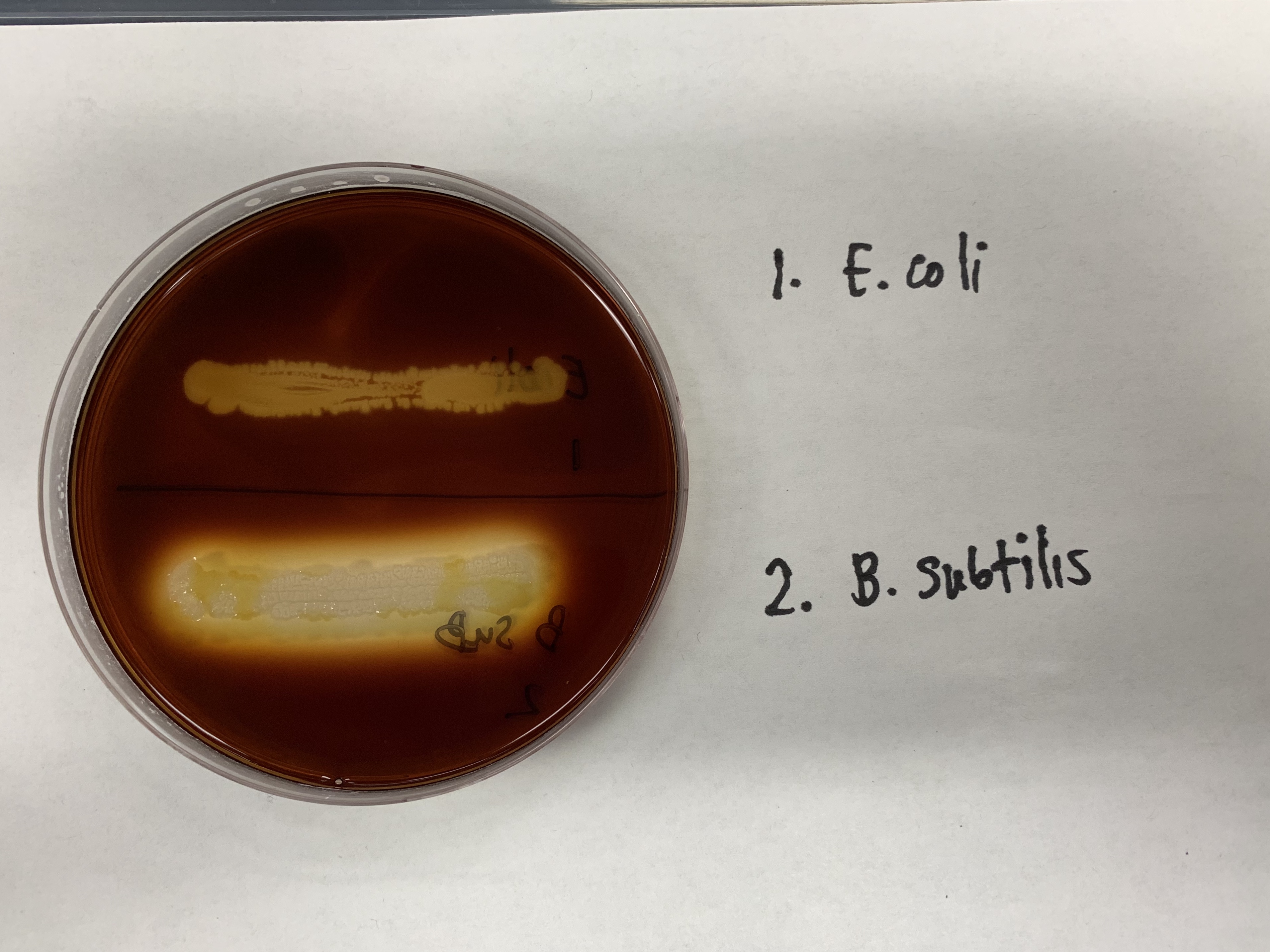
Which is positive and negative for Hydrolysis of Starch and why?
B. Sub is positive while E. Coli is negative.
B Sub produces amylase which produces an amber color making it positive.
E. Coli is DOES NOT produce amylase which means that it is negative( black color)
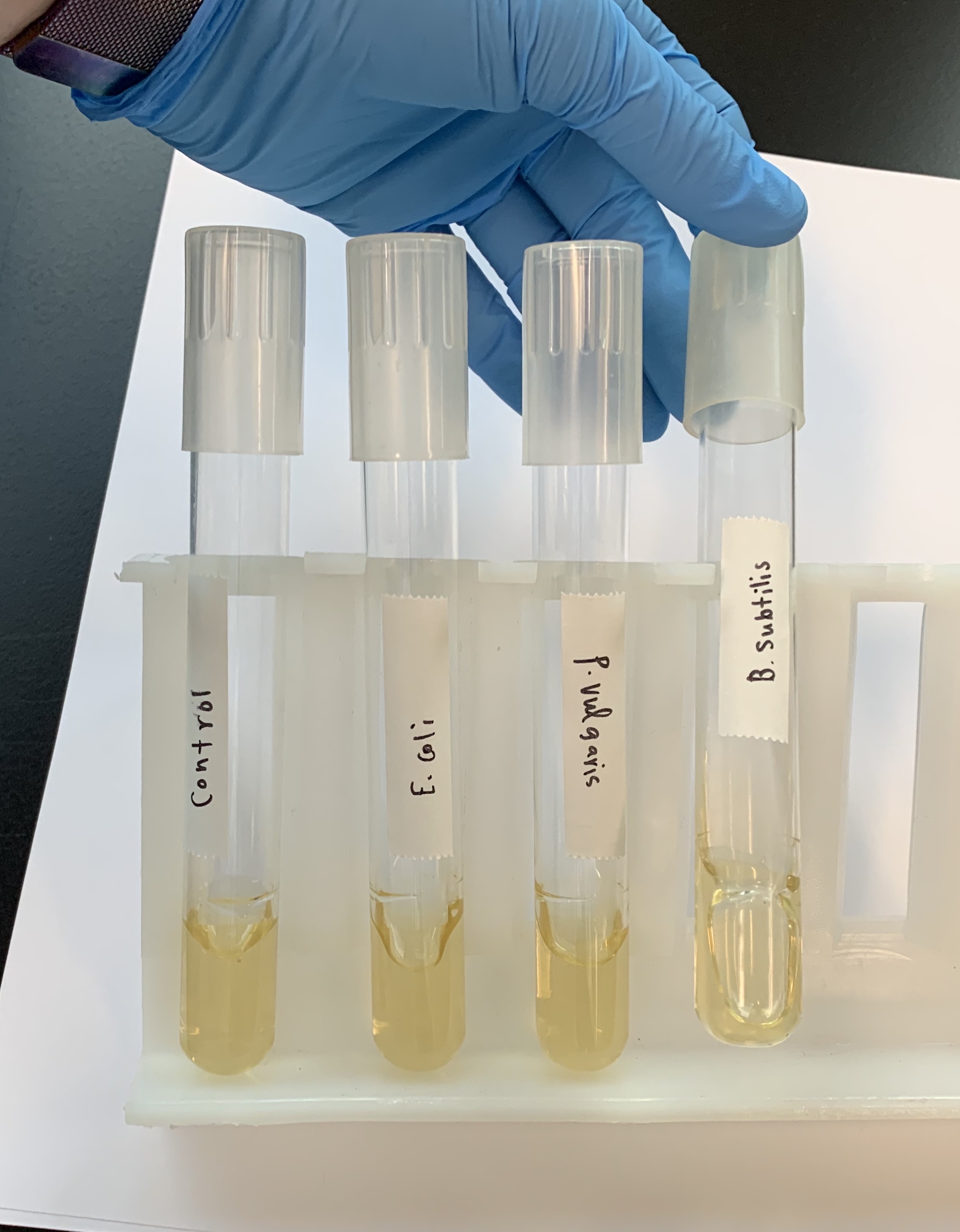

What does a POSITIVE test of Hydrolysis of Gelatin look like?
Liquid media.
This means that it produces GELATINASE, which breaks down amino acids.
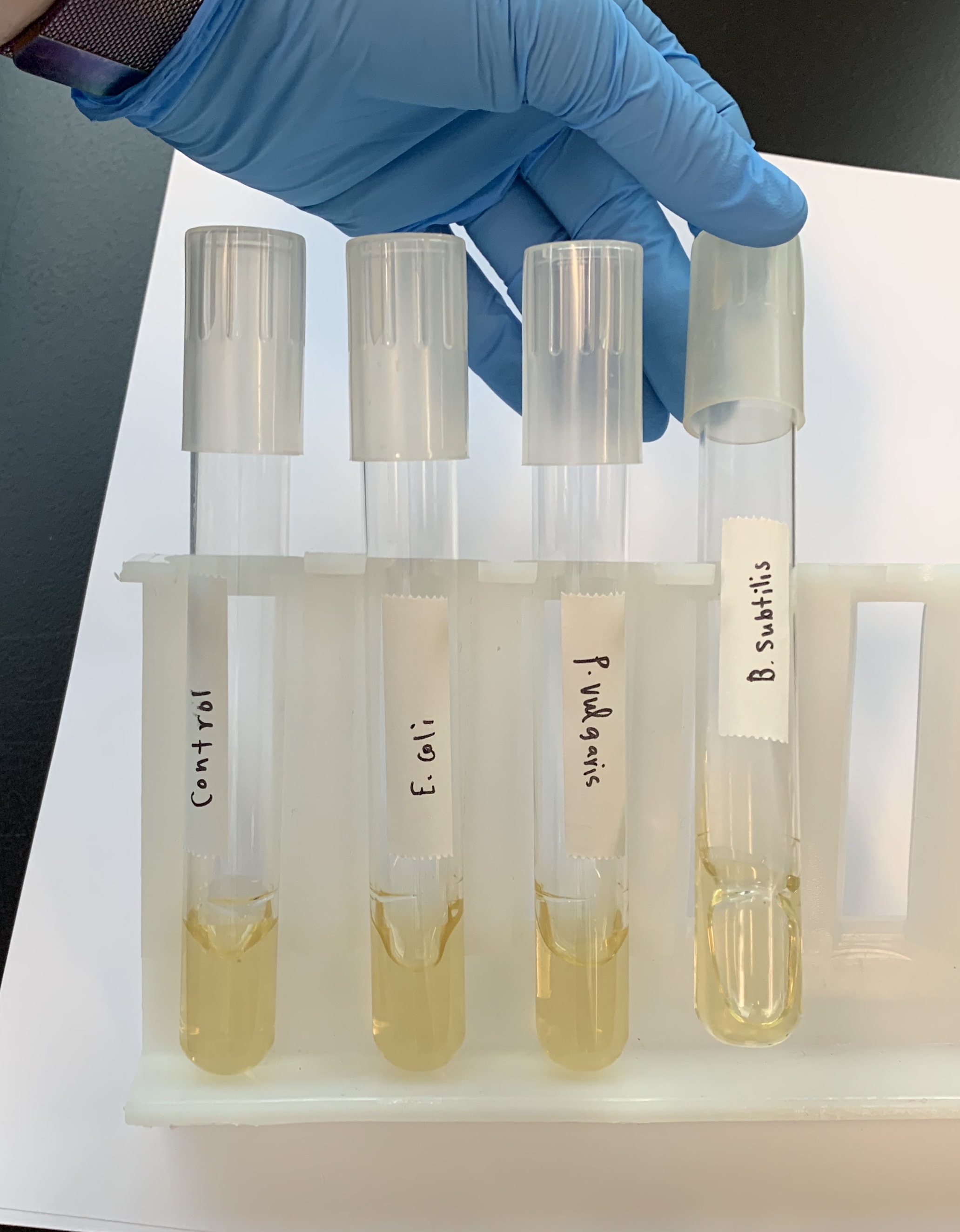

What does a NEGATIVE Hydrolysis of Gelatin Test look like?
Solid media.
This means that it DOES NOT PRODUCE Gelatinase.
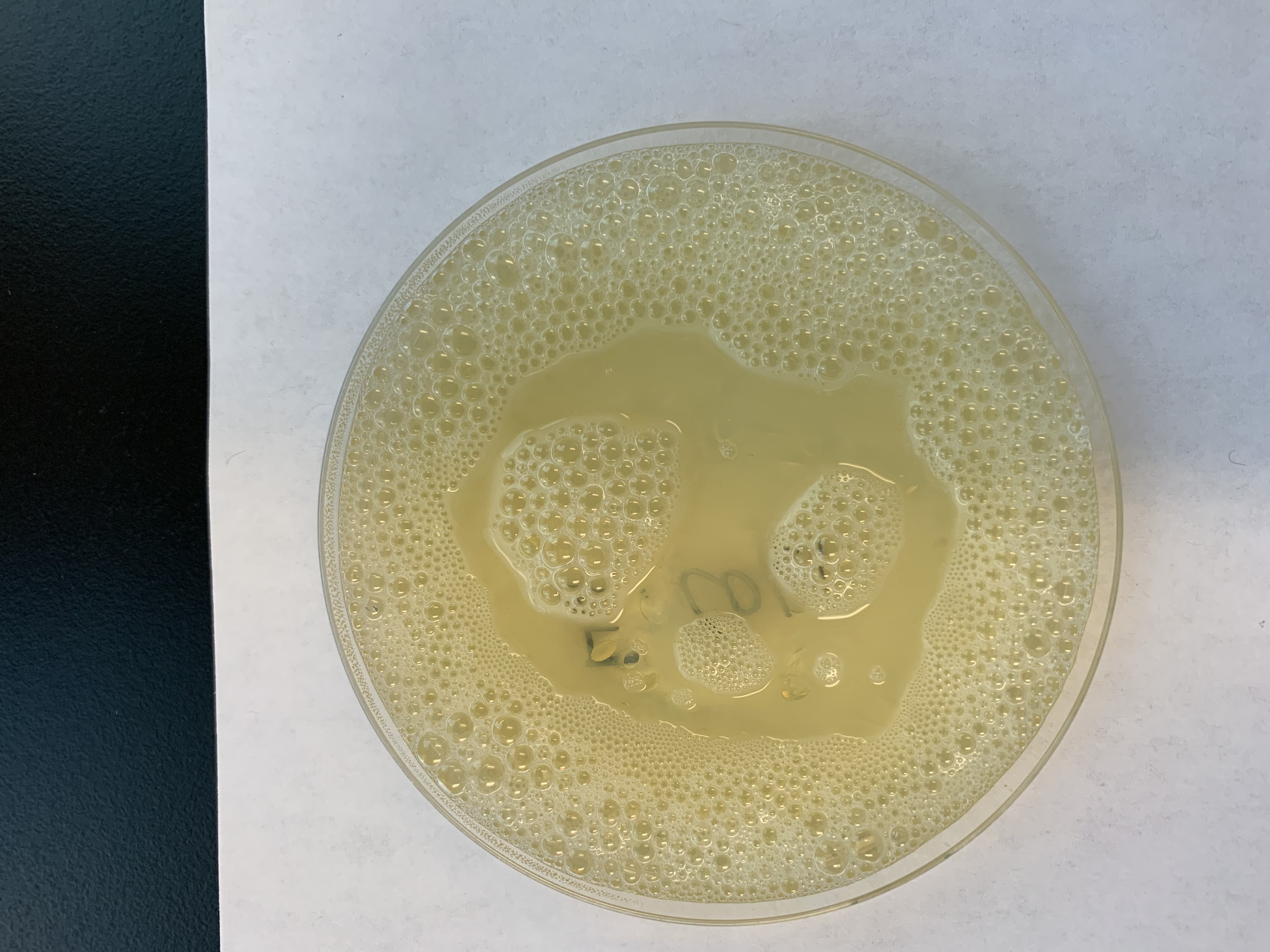
Is this POSITIVE or NEGATIVE for #16 Reduction of Catalase?
This is Positive.
Since it produced bubbles, it is positive for Catalase.
What does it mean if a Catalase Test is negative?
There would be no bubbles and Catalase negative.
What type of bacteria can produce Catalase?
Aerobic and Facultative Anaerobic.
What type of bacteria cannot produce Catalase?
Obligate Anaerobes.
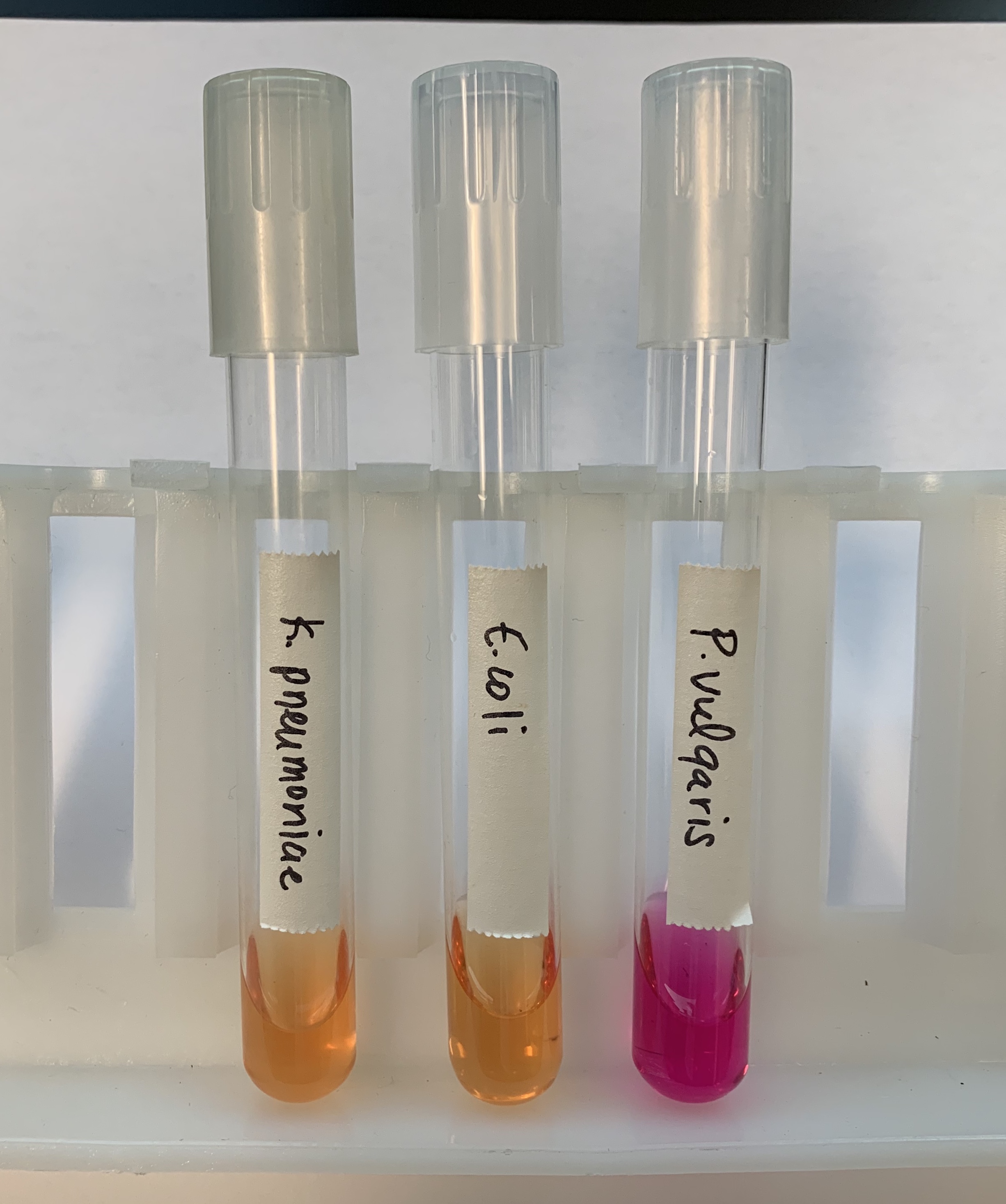
What does a positive and negative test mean for Hydrolysis of Urea?
Positive: HOT PINK
BASIC
Produces UREASE
Negative: YELLOW - GOLD `
ACIDIC
Does NOT produce UREASE
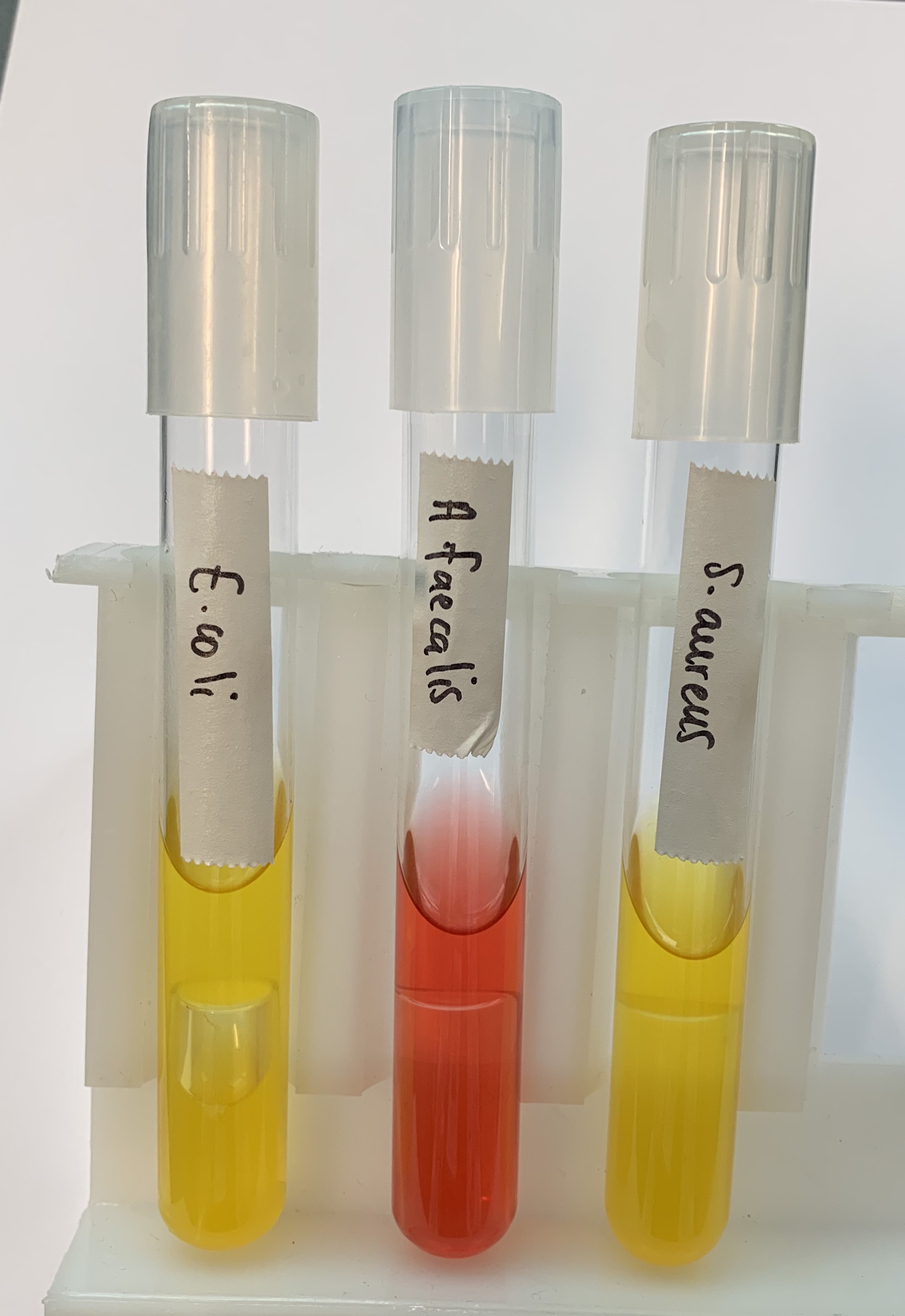

What does a POSITIVE and NEGATIVE test mean for Fermentation of Carbohydrates?
Positive
ACID. ACID/GAS
Produces a yellow color because it only uses sugars.
Negative
BASIC
MAGENTA color like control.
Only uses proteins.
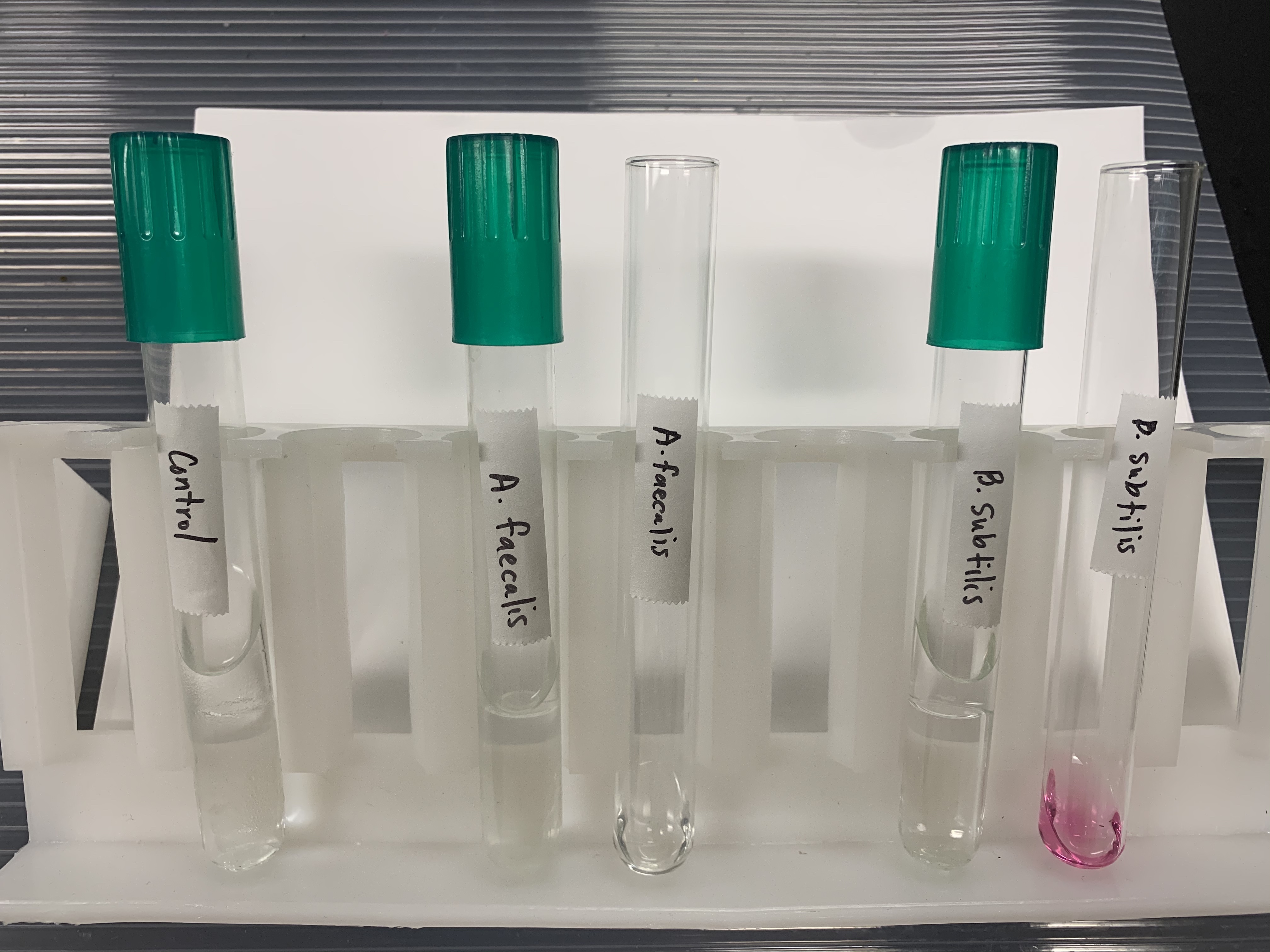

What does a POSITVE and NEGATIVE test mean for Reduction of Nitrates?
Positive
Magenta color
This means that Nitrate can reduce to Nitrite.
Negative
Control/Peach color
This means that it does not reduce Nitrate to Nitrite.
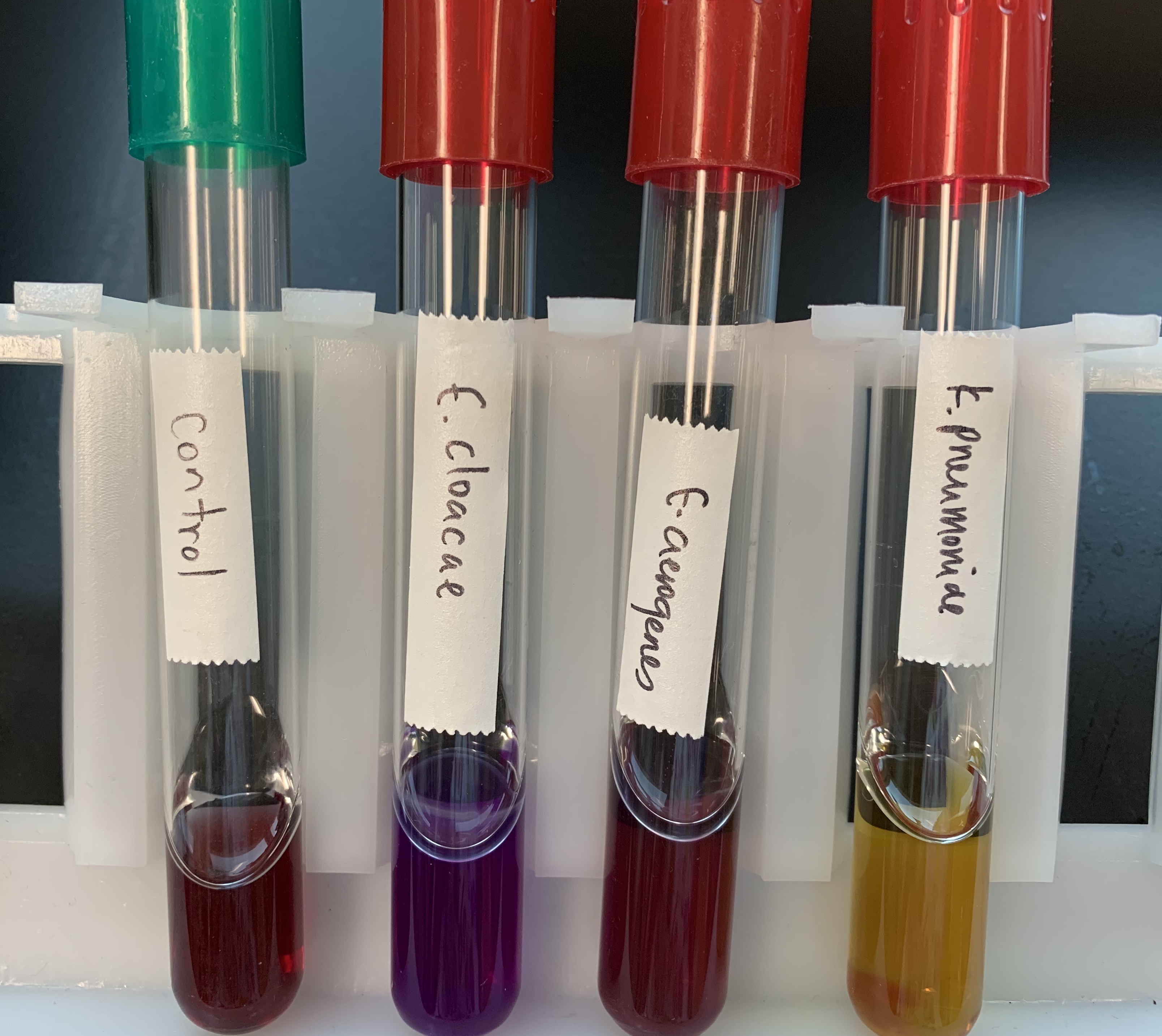

What does a Positive and Negative Test mean for Production of Decarboxylase?
Positive
Violet Color
Produces Decarboxylase making it BASIC.
Negative
Control or Yellow
Does not produces Decarboxylase, making it ACIDIC.
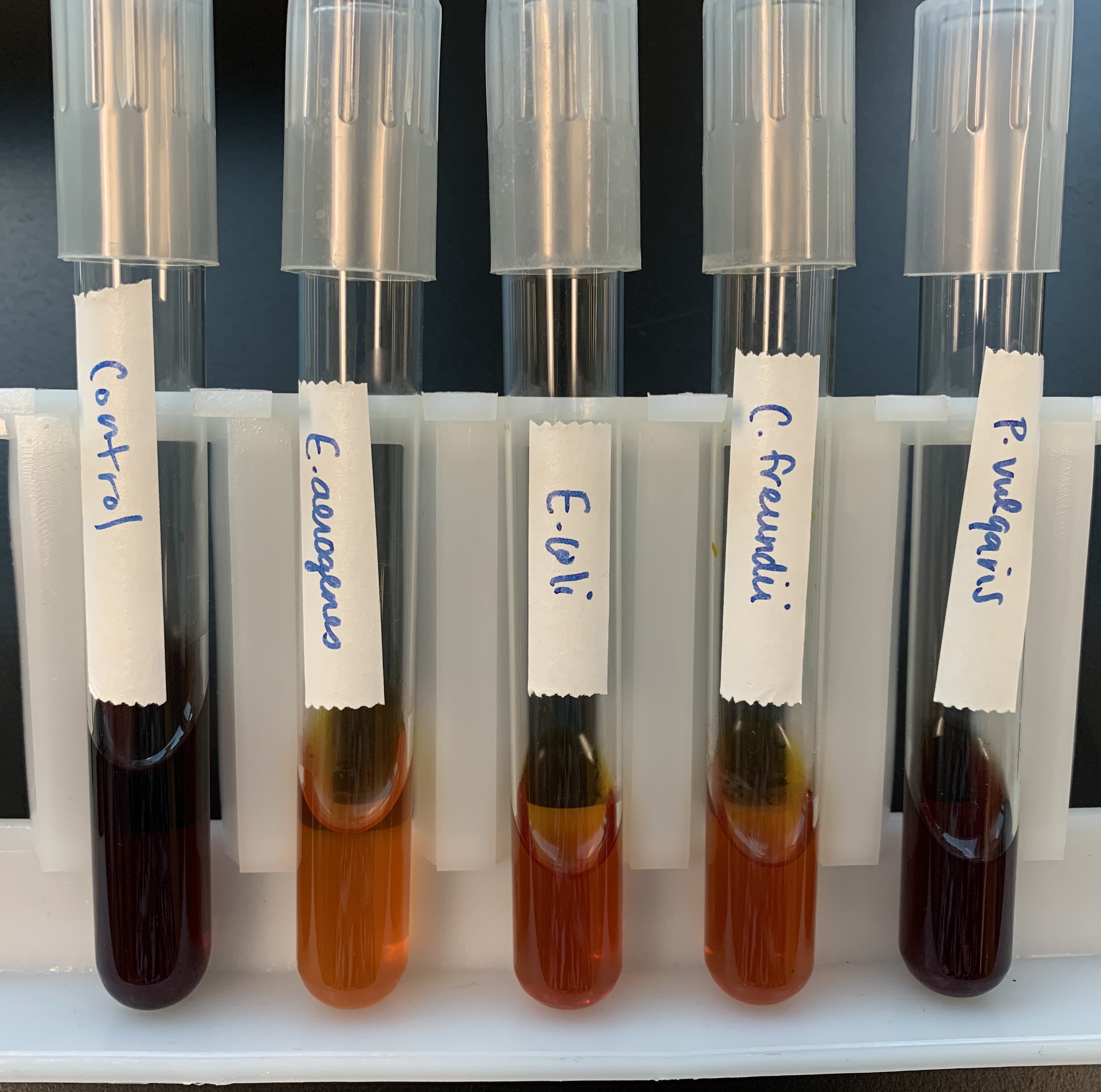

What does a positive and negative test mean for Ammonium Phosphate?
Positive
Yellow (acidic)
NH3 is metabolized, remaining phosphate is yellow
Negative
Purple (basic)
NH3 is not metabolized, remaining basic.
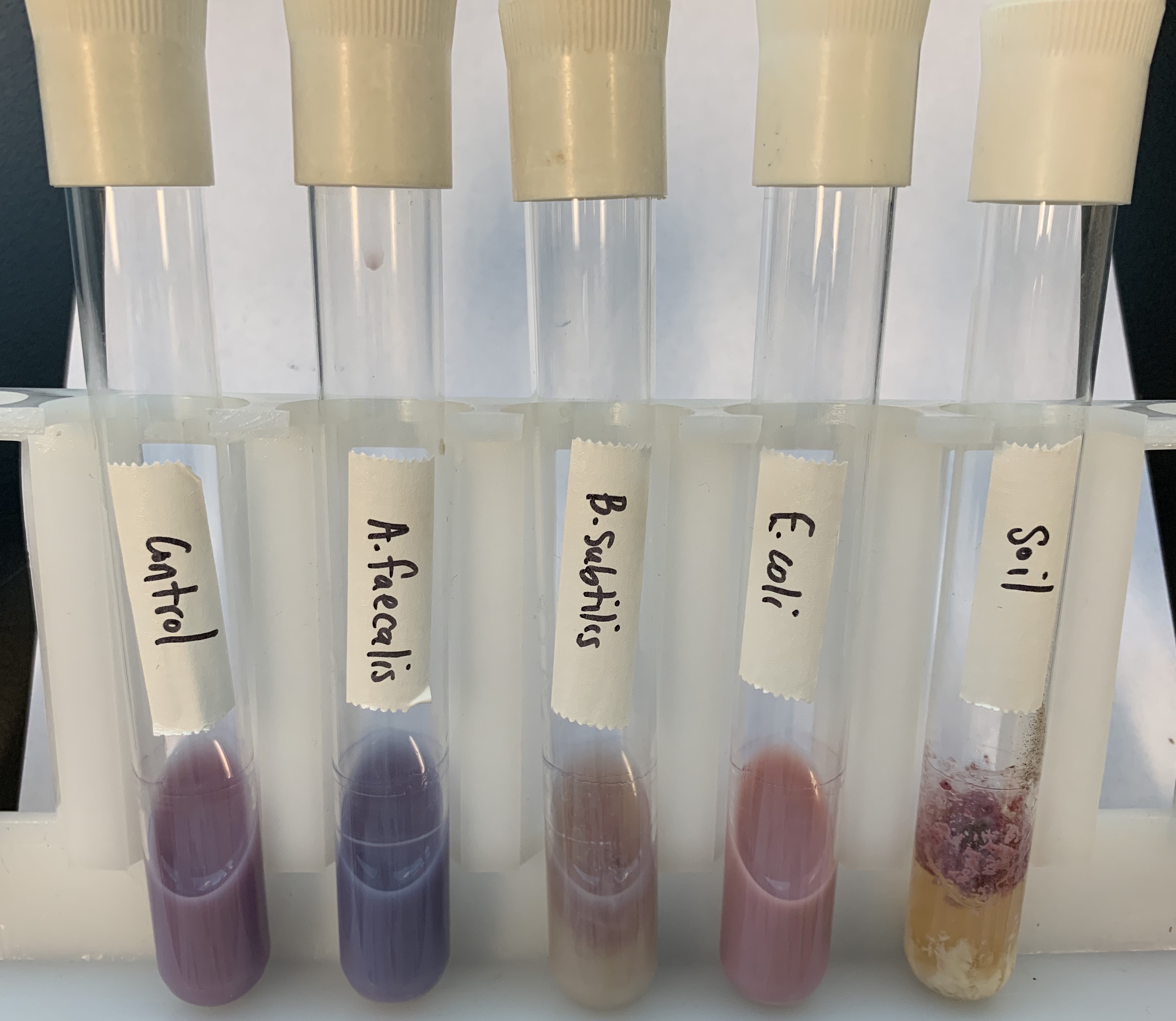

What are the following results for the Litmus Milk Tests?
Fermentation
Positive: PINK MILK, +/- hard curd
Reduction
Positive: White acidic milk, apple basic juice
Alkanization
Positive: Blueberry milk
Peptonization
Positive: Grape/apple juice, +- soft curd
Curd Formation
Positive: Hard or soft curd
Negative: No curd

What are the following results for SIM tests?
S - Hydrogen Sulfide
Positive: Black Precipitate
Hydrogen Sulfide reacts with Iron Sulfate resulting in Iron Sulfide,.
I - Production of Indole
Positive: Red Ring
Kovac Reagent is used to determine positivity for indole.
M - Motility
Positive: Movement from the line.
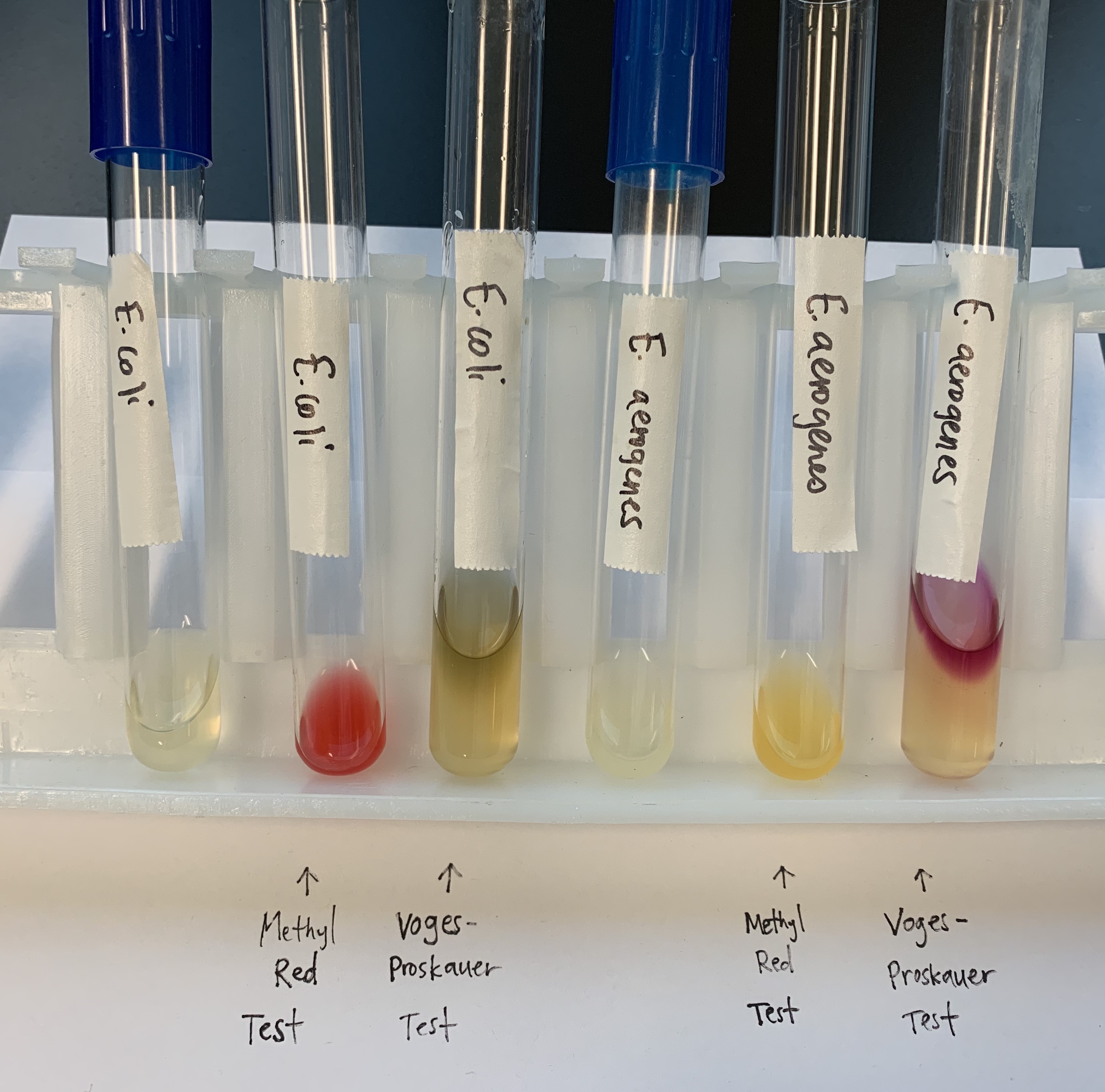

What does a positive and negative test mean for the MRVP tests?
MR
Positive: RED
Presence of strong acid meaning it can ferment carbohydrates
Negative: Control/Yellow
There is no acids.
VP
Positive: RED RING ON TOP
This indicates the presence of AMC.
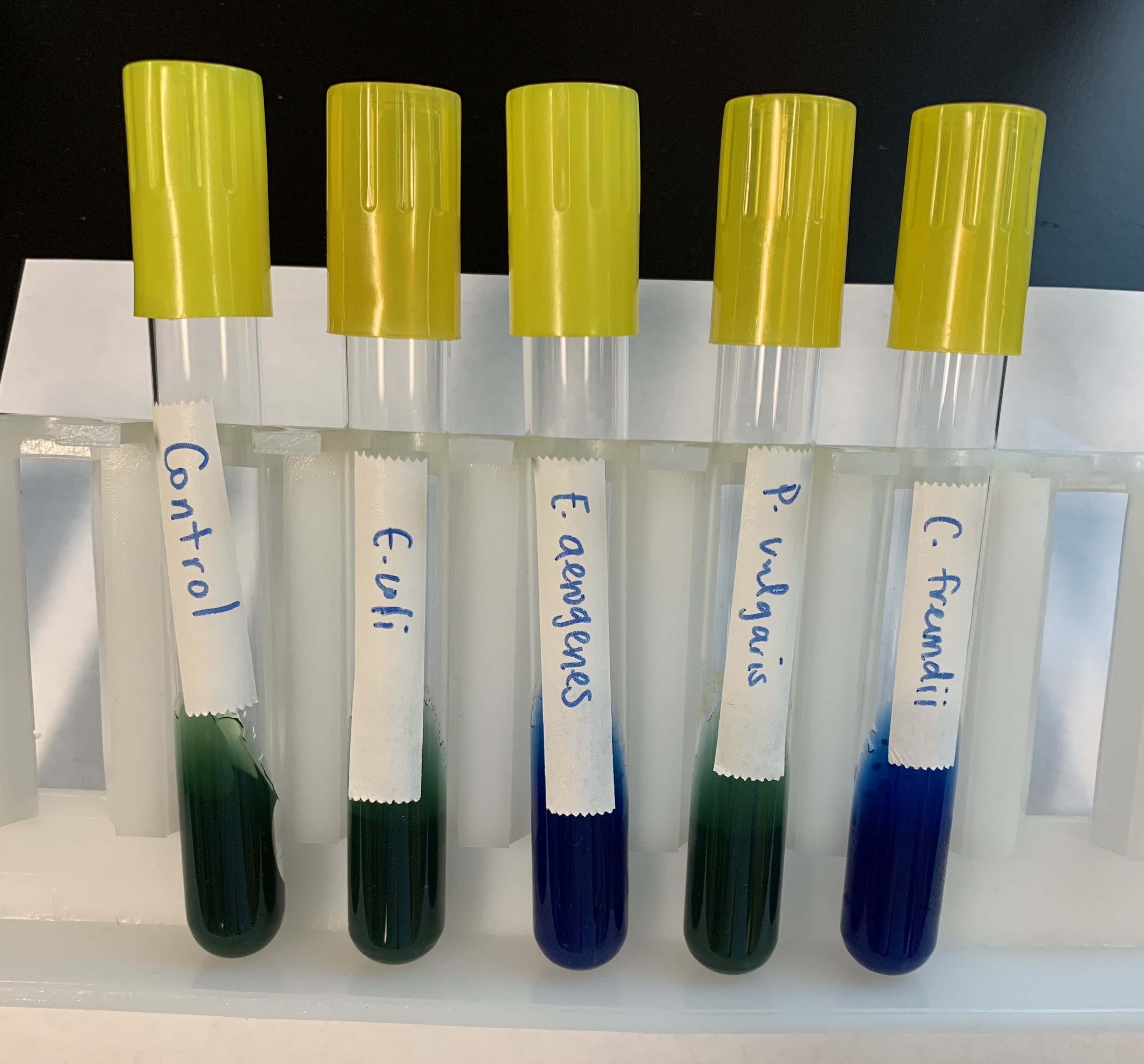

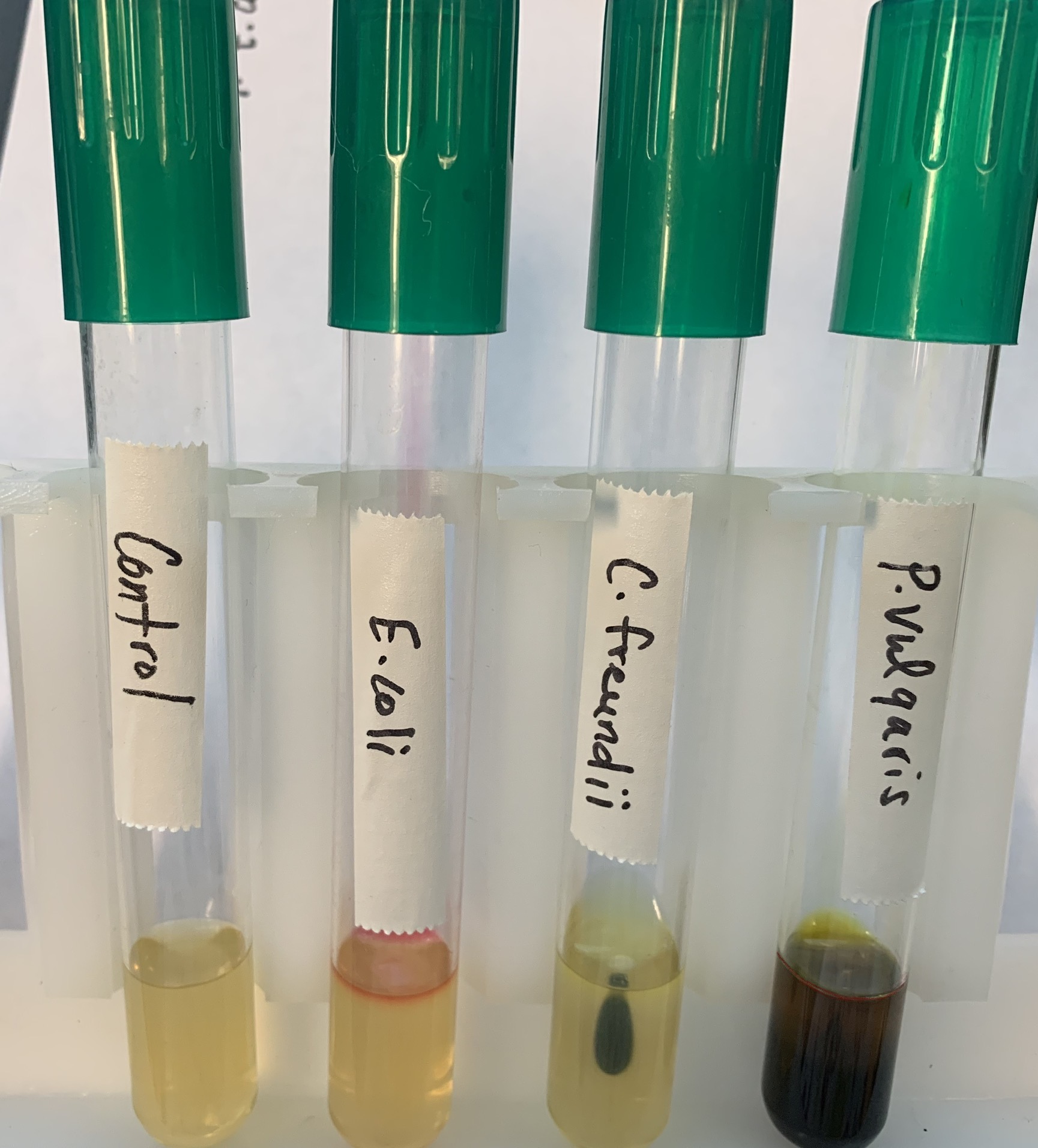
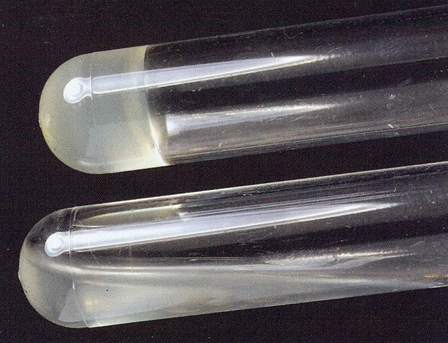
What does a positive and negative test mean for Sodium Citrate test?
Positive:
Blue (BASIC)
It can metabolize citrate.
Negative:
Green (ACIDIC)
No metabolization of citrate
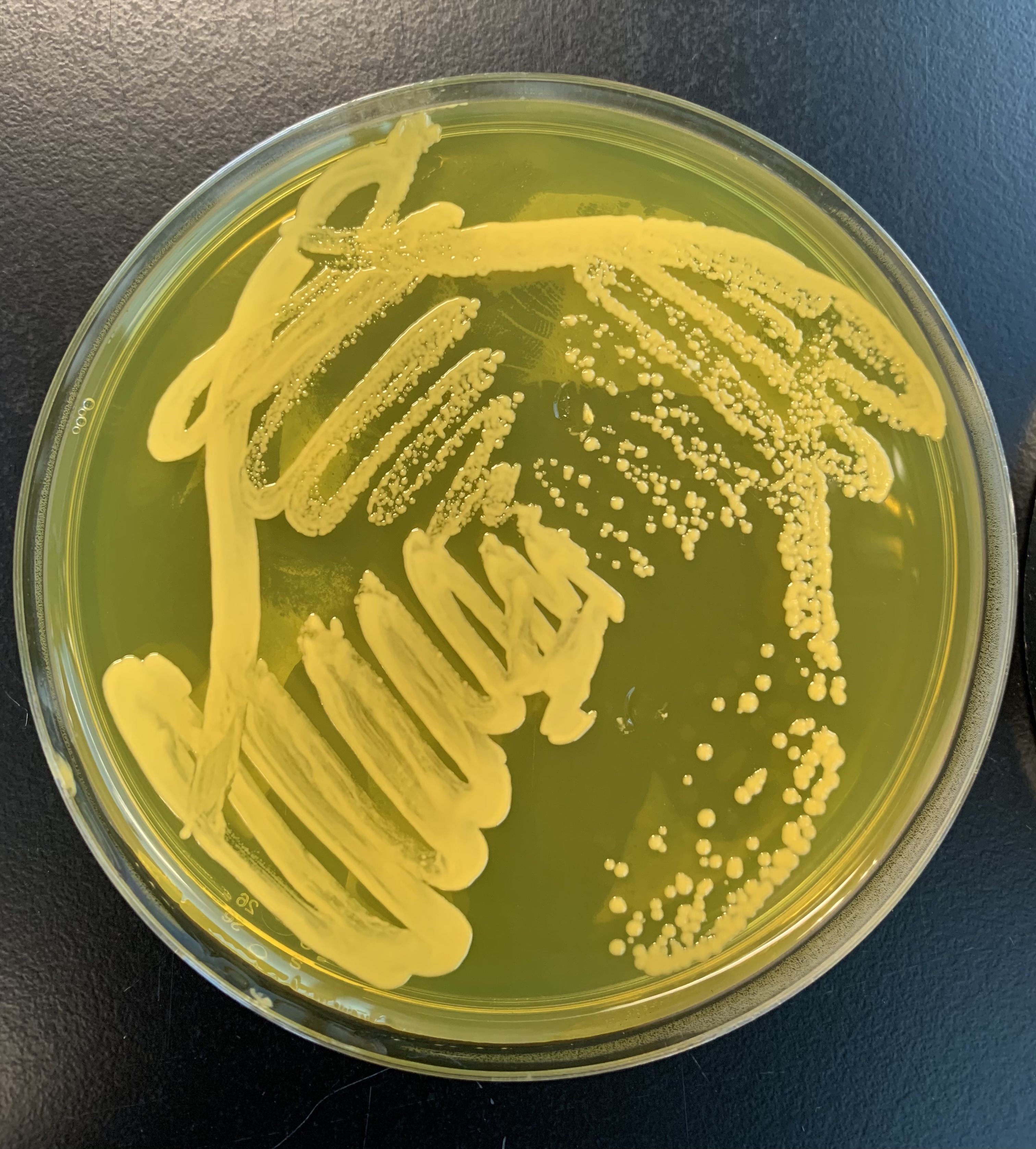
What does a positive test of the MSA Salt Agar test indicate?
Positive Test indicates that the bacteria is pathogenic.
If it is acidic, this means that is it pathogenic because acidic products were formed.
What does a negative test of the MSA Salt agar plate indicate?
It indicates that it is not pathogenic and doesn’t produce acidic products.
What does a positive and negative test for Coagulase production indicate?
Positive
Solid Media
this means that it has COAGULASE, and increases it virulence.
Negative
Liquid Media
Does not have COAGULASE .
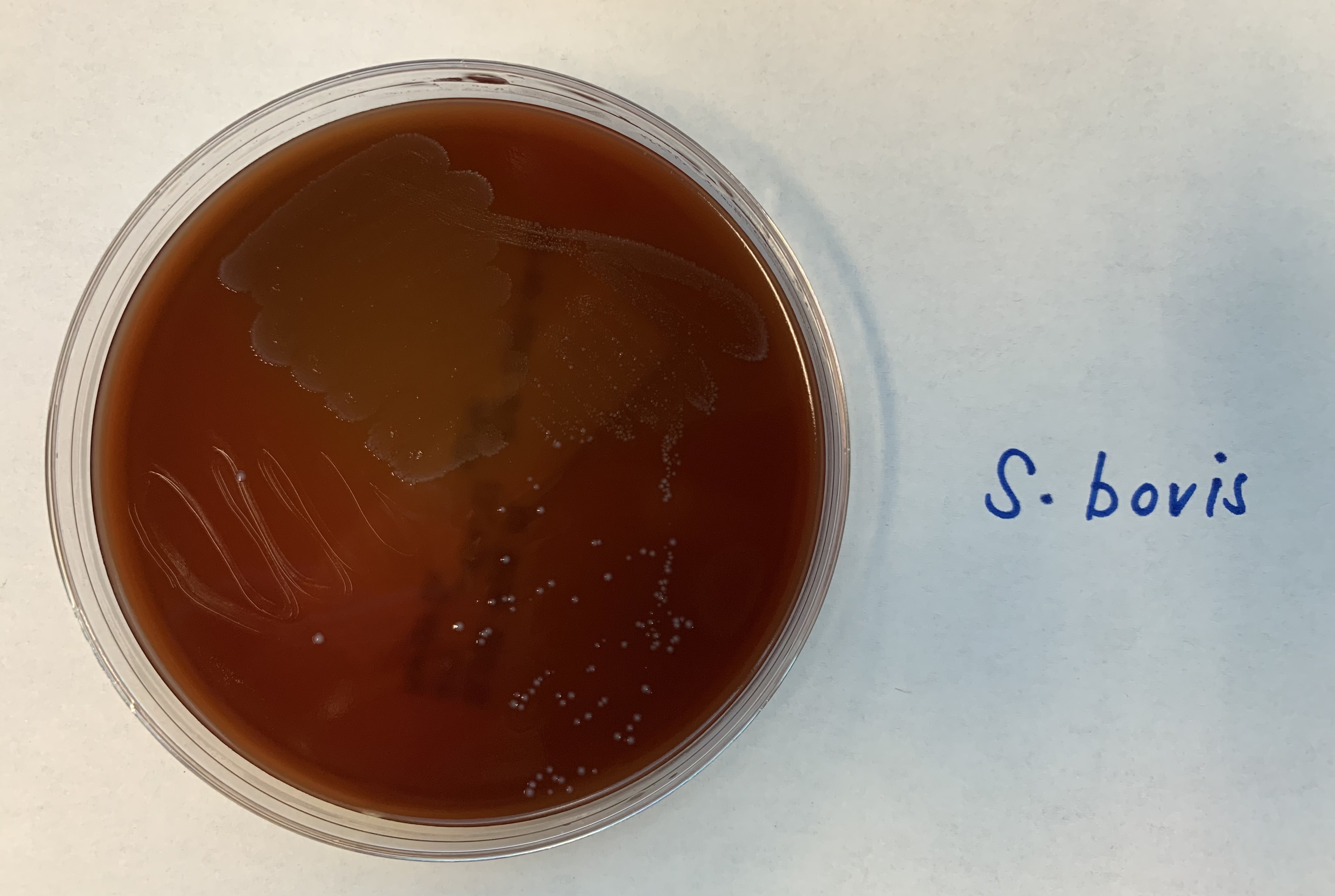
This is an Alpha Hemolysin Test, what does this test indicate?
Contains green colonies which means that it does NOT digest IRON. Its pathway is incomplete.
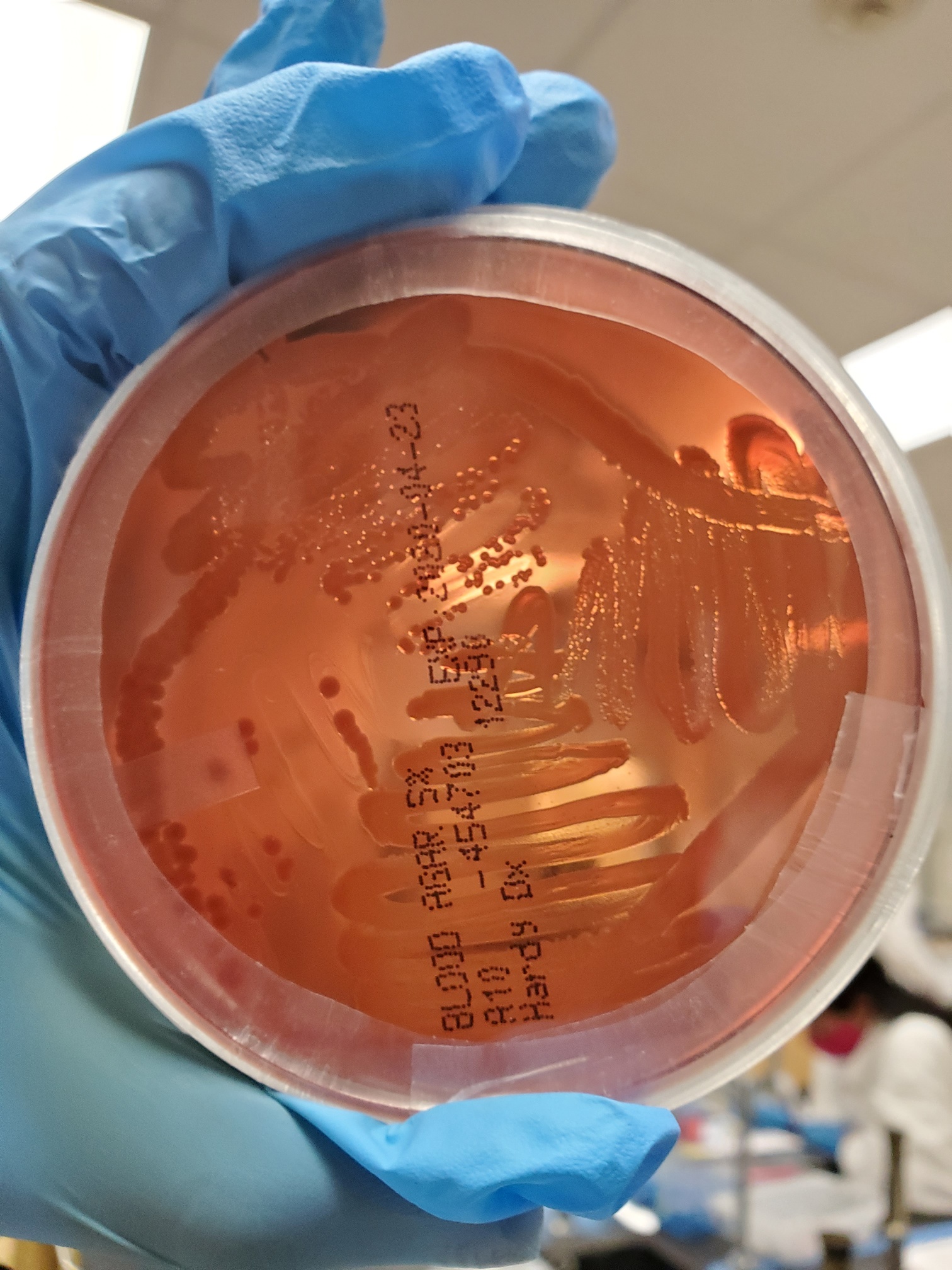
This is a BETA HEMOLYSIN test, what does this indiciate?
Contains see-through zones which means that it digests IRON. Its pathway is complete.
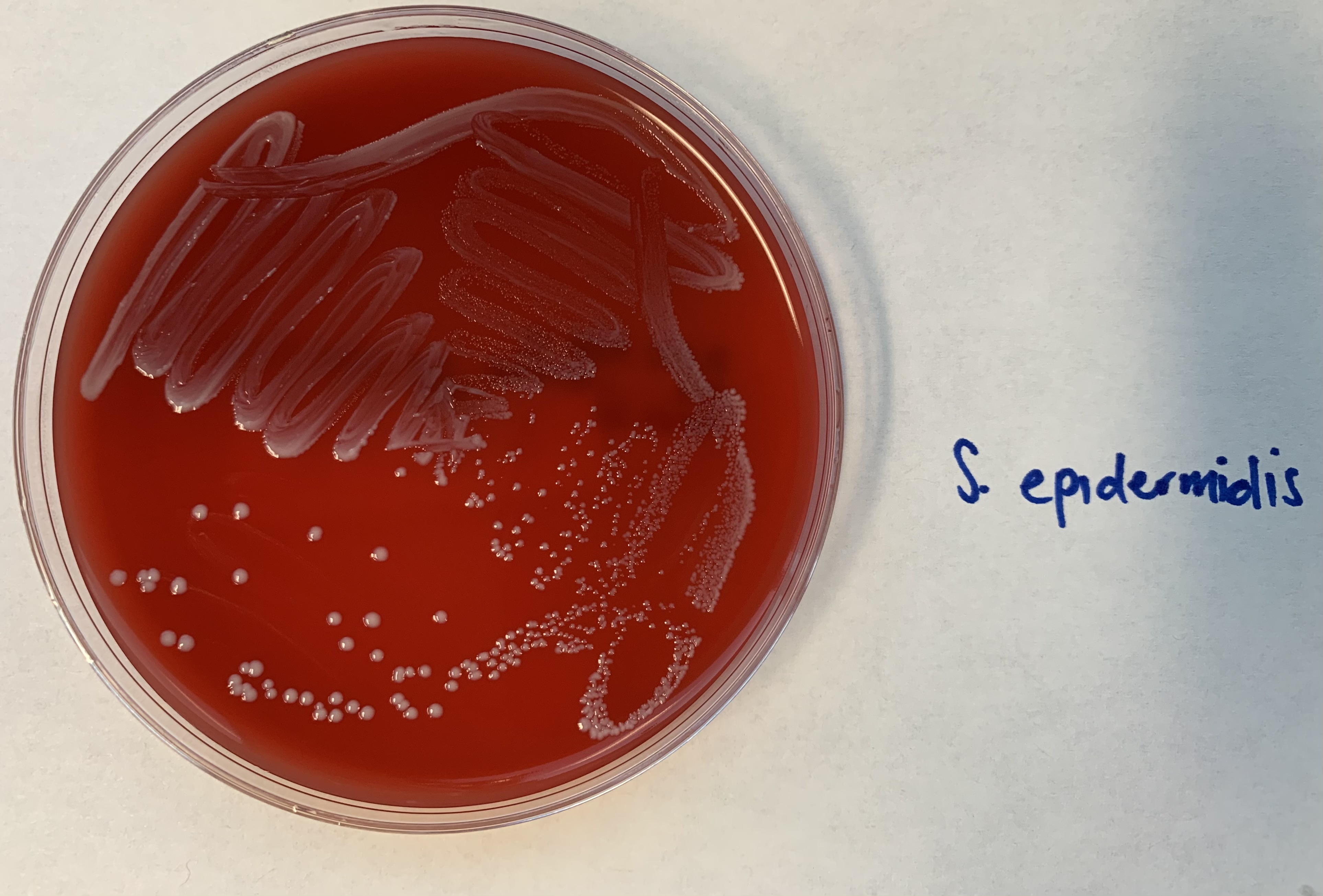
This is a Gamma HEMOLYSIN test, what does this indicate?
The red agar indicates that it only goes after the plasma proteins. Its pathway is incomplete.
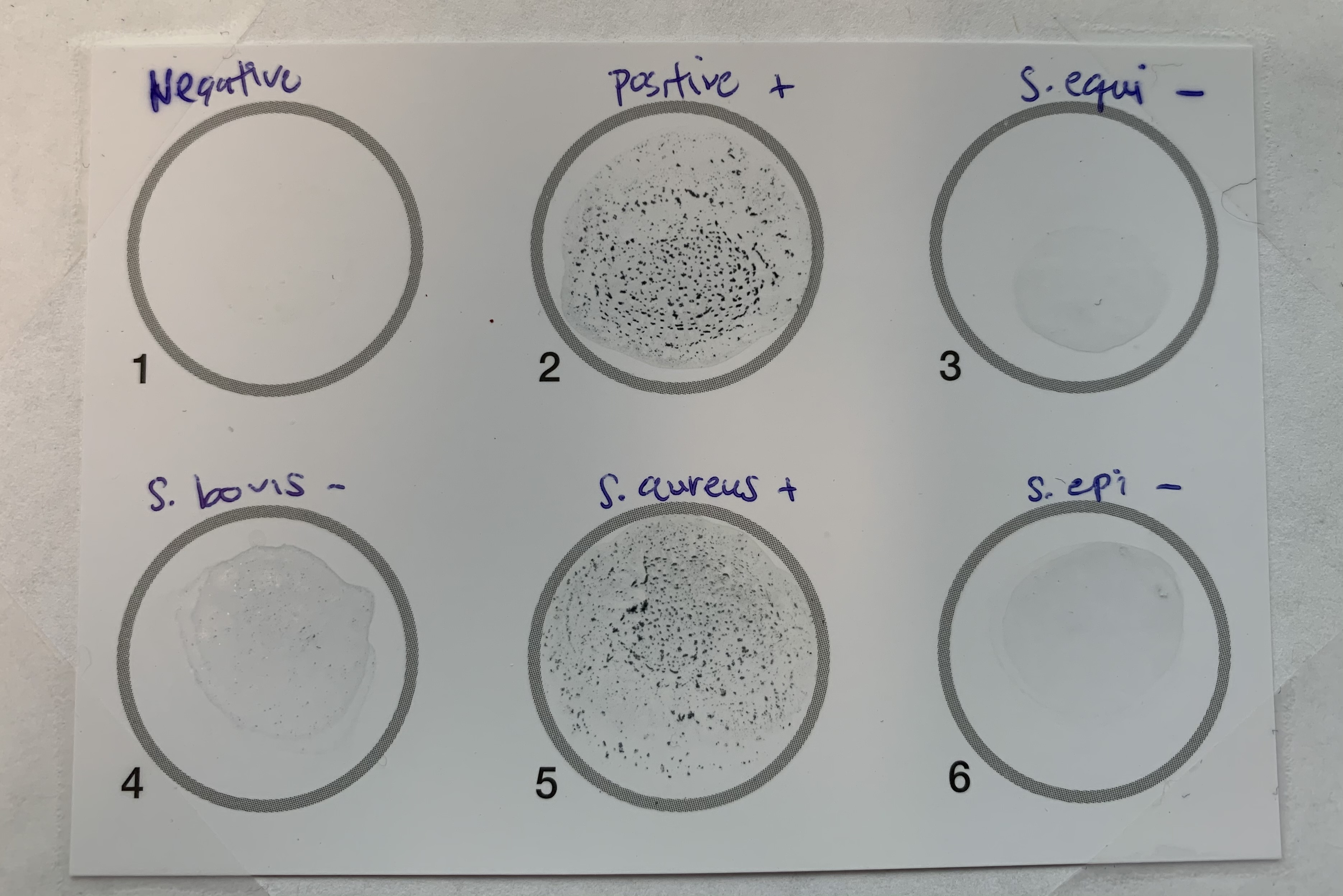
This is a Latex Agglutination Test, what does this indicate?
Positive
Clumps
There is coagulase
negative
No clumps
There is no coagulase.
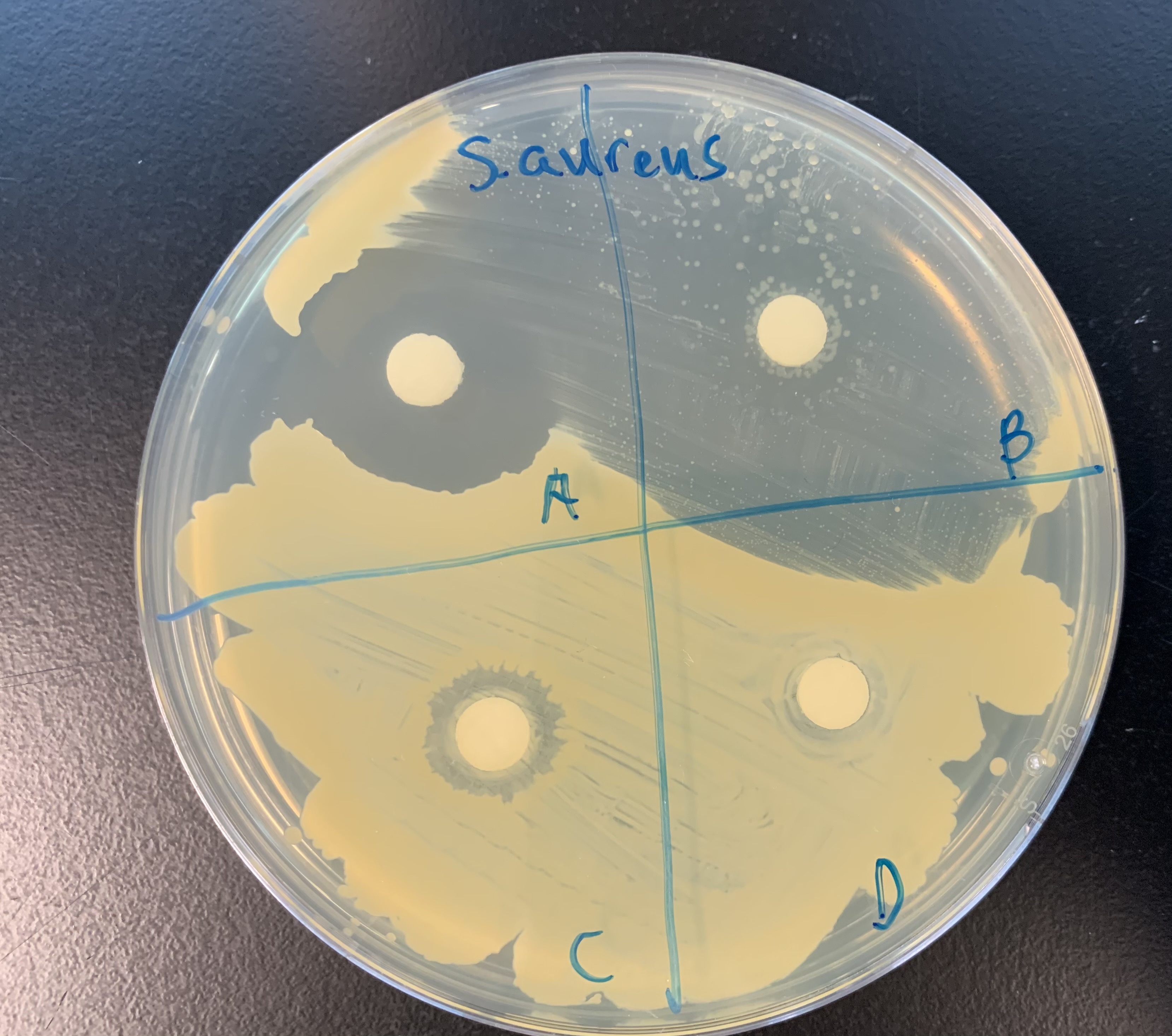
This is a Zone of Inhibition Test, what does this indicate?
Increase in Diameter - Effective at inhibiting growth
Decrease in Diameter - Not effective at inhibiting growth
If the hydrolysis of starch is positive, it indicates the presence of what enzyme?
Amylase.
If a microorganism can hydrolyze gelatin, it will convert it to
amino acids.
If a microorganism can ferment carbohydrates, what end products are produced?
Pyruvic acid, ATP, and CO2
The pH indicator used in the fermentation of carbohydrates is____, and turns _____ under acidic conditions.
Phenol Red and turns to Yellow.
Name the 2 Reagents used in the Reduction of Nitrates Test.
DAN and Sulfuric Acid.
Catalase converts hydrogen peroxide into
Oxygen bubbles and water.
The indicator used in the production of carboxylases is?
Brom Cresol Purple.
The Decarboxylase test is done under aerobic or anaerobic conditions?
Anaerobic conditions.
A positive test for urease would change the pH indicator to what color?
Hot pink.
What 3 tests can be done with the SIMS reactions?
production of hydrogen sulfide
production of indole
motility test
The substrate used in the MR-VP Test can be converted
Substrate: Glucose
Converted to ATP and Pyruvic acid in MR
Converted to ATP, AMC, Organic acids and alcohols in VP.
The reagent used for the VP test is
Alpha Napthol
Potassium Hydroxide Creatine.
MSA is plate is considered both a selective and differential media plate, why is that?
Selective
Staph grows because this is a high salt concentration
Differential
Distinguishes between pathogenic and nonpathogenic.
Can a staphylococcus organism that is found to be pathogenic, also be considered virulent?
No, pathogenic doesn’t mean virulent.
Pathogenic means that it can cause disease.
Virulent is the degree of how dangerous a pathogen can be.
What two tests can be done for the presence of coagulase?
#26 Rabbit Plasma Test
Coagulase Production
#27 Latex Agglutination
What tests can be used to determine virulence?
Coagulase
Latex Agluttination
Hemolysin
In the Litmus milk test, an Apple juice/Consistency means that
Peptonization
acidic products
Reduction
losing color
Fermentation means
acidic products
peptonization means
complete hydrolysis.
Breaks down both proteins in milk
Alkalinization means
Incomplete hydrolysis, only breaking down one protein.
Gas production only happens
during FERMENTATION reactions.
White hard curd with fissures indicates
White caused by
Reduction
Fissures caused by
Gas Production
Hard Curd caused by
Ferment
Rennet Curd indicates
Soft Curd
only happens during Peptonization
Leucolitmus indicates
Bleached milk
Reduction
Blueberry Shake indicates
Alkanization only.
incomplete hydrolysis
Pink milk indicates
Fermentation only.
White hard curd indicates
Reduction and fermentation.
Grape juice indicates
Peptonization,
Pink hard curd
Fermentation only.
Nitrate is reduced to ______, during the Reduction of Nitrates Test.
Nitrite. KNO3 → KNO2
What are the tests that are pH dependent?
Decarboxylase
Urea Test
Red blood cells are broken down in
Alpha and Beta Hemolysis
Partial breakdown of the hemoglobin occurs in
Alpha Hemolysis
Iron is broken down in
Beta hemolysis
Complete breakdown of hemoglobin occurs in
Beta hemolysis
Breakdown of plasma proteins occurs in
Gamma and Beta hemolysis.
Obligate Aerobe grows in
Tall and Slant
Obligate anaerobes grow in
Thioglycollate
Facultative Anaerobe grows in
Tall, slant, thioglycollate.
Microaerophile grows in
Thioglycollate only on top and in the tall on the stab line.
The ammonium phosphate test products what 2 positive end products?
ammonia and phosphoric acid.
What is the pH indicator used in ammonium phosphate?
Brom cresol purple.
What color will Brom Cresol Purple change to in acidic conditions due to the ammonia phosphate test?
Yellow acidic products
A positive test for sodium citrate would be
Turbidity
What is the Medium for Hydrolysis of starch?
Agar plate
Substrate: Starch
What is the medium for Hydrolysis of Gelatin?
Gelatin
Substrate: Gelatin
What is the medium for fermentation of carbs?
Phenol + protein both
Substrate: Glucose, mannitol, sucrose, sucrose.
What is the medium for all litmus milk tests?
Litmus milk
What is the medium for Reduction of Nitrates?
Nitrate broth
Substrate: KNO3 Potassouim Nitrate