circle theorems
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
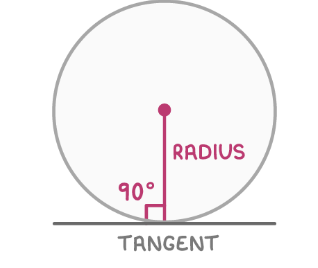
Tangents meet the radius
The radius drawn to a tangent is always perpendicular to the it, forming a 90° angle.
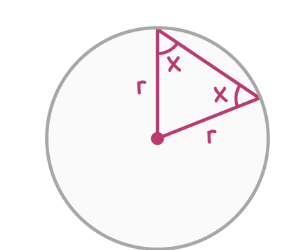
Joining two radii
Two radii can be connected to form an isosceles triangle. The angles at the base of the triangle are always idntical
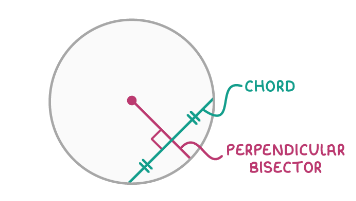
Perpendicular bisectors of chords
A chord is a line which joins two points on the circumference of a circle. A line which is drawn at 90° to a chord, halfway along its length, will always pass through the centre of the circle.
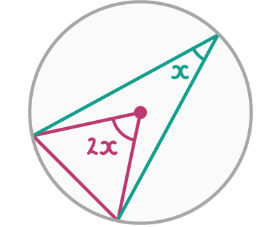
The angle at the center and the angle at the circumference
The angle at the centre that subtends the same arc is always double the angle at the circumference.
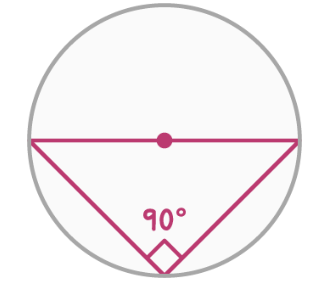
The angle in a semicircle
The angle opposite the hypotenuse is always 90°
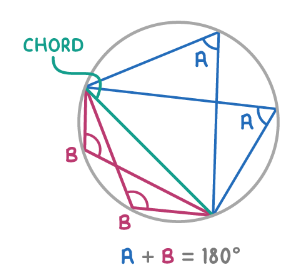
Angles in the same segment
A chord separates a circle into two segments. Angles in the same segment are equal. Angles in opposite segments add to 180°.
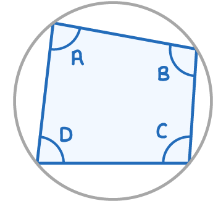
Cyclic quadrilaterals
The opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral sum to 180°
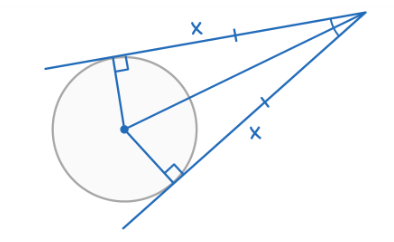
Tangents from a single point
Two tangents to a circle from an external point are always equal in length. A line from the centre of the circle to the external point, will bisect the angle between the two tangents.
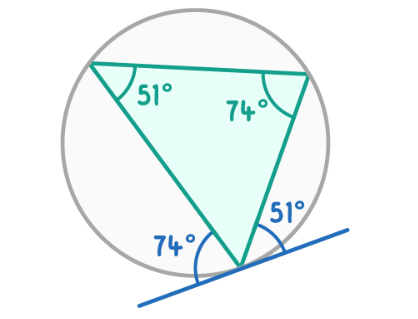
Angles in alternate segments
The angle between a tangent and a chord at the point of contact is equal to the angle in the alternate segment.