SBI4U - Animal and Plant Cell Review
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the two main types of cells?
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Out of the two main types of cells; which one can I find in bacteria and archaea?
Prokaryotic
Out of the two main types; which one can I find in plants, humans, fungi, and Protista cells?
Eukaryotic
What are the characteristics of Prokaryotic cells?
They are microscopic/unicellular (small and only have one cell -> humans have many cells)
They have no-membrane bound organelle
They have no nucleus
What are the characteristics of a Eukaryotic cell?
Mutli-celluar
Has a nucleus
Complex internal structure
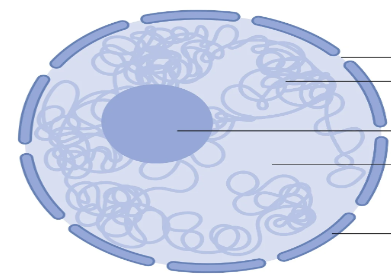
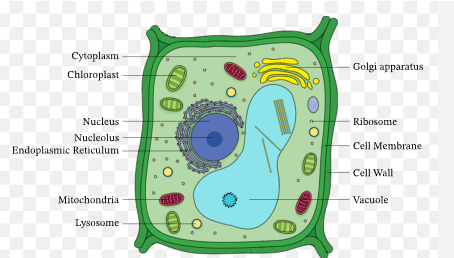
Define a nucleus
It’s the command center of the cell, contains DNA codes for the cells function and it’s surrounded by the nuclear envelope
Inside it contains the nucleolus that look like worms, those contain RNA to make ribosomes
Define a Ribosome
Ribosomes are the cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. They can be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
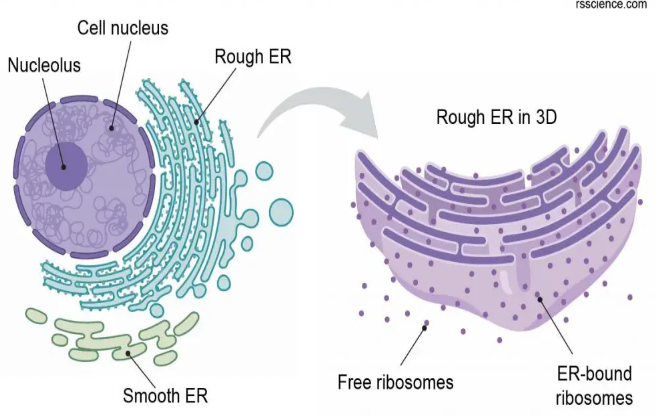
Define the Endoplasmic Reticulum
There are two types - Rough and Smooth
Rough ER’s are covered in ribosomes, make (synthesize) and package proteins to the Golgi Apparatus
Smooth ER’s make phospholipids and other macromolecules - most of the time lipids - to be sent to other parts of the cell
Define the Vesicles
The Vesicles is a saclike organelle that transports or stores substances within a cell
Define the Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi Apparatus is a stack of membrane bound sacs and tube
It receives vesicles from the ER and finishes packing them for excretion on the outside
Define the Cell Membrane
The security guard of the cell - regulates what enters and exists the cell and separates the interior and exterior of the cell
Define the Fluid Mosaic Structure
It is what the Cell Membrane is made of
It is made out of a Phospholipid Bilayer containing proteins, carbs, and cholesterol
Define the Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell! It provides the cell energy through breaking down glucose (found in wheat) and makes it into energy via ATP
Have their own DNA
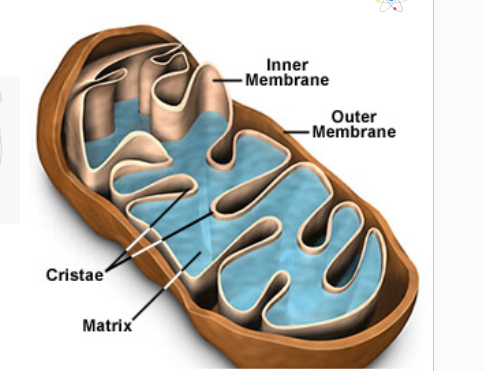
What are all the parts of the Mitochondria
Intermembrane space, Matrix, and Cristae
Recall: I (Intermembrane space) Make (Matrix) Cell (Cristae)
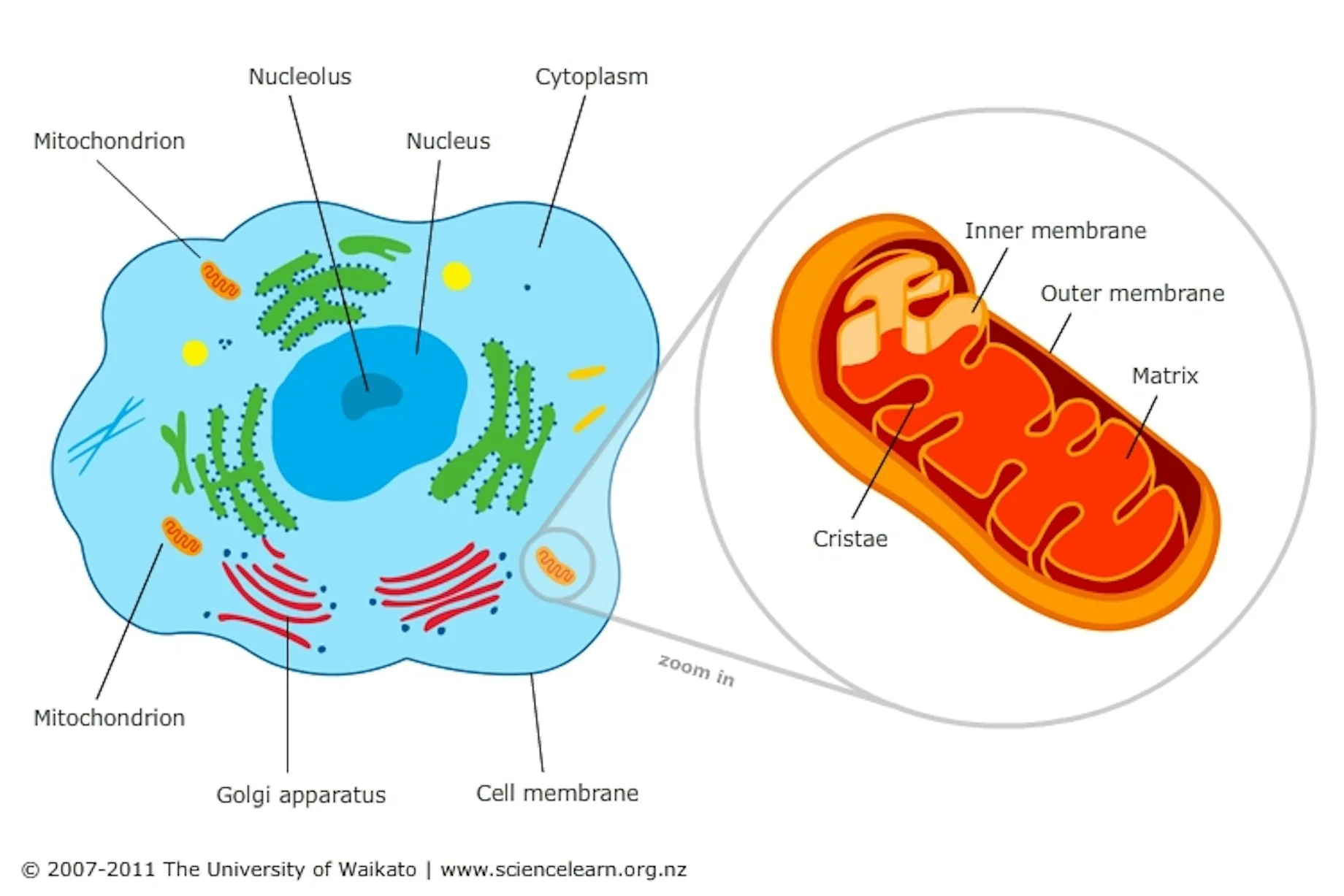
Define the Intermembrane Space
The space between the inner and outer part of the cell
Define the Matrix
Interior aqueous part
Define the Cristea
The folds in the inner part of the Mitochondria \
Define a Cilia
Hairlike structures creating a wave motion
Define a Flagellum
Whiplike tail use for movement (is the tail part of Cilia)
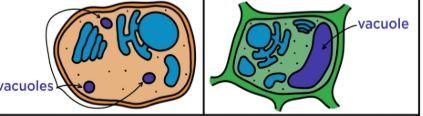
Define a Vacuole
Stores water, food, toxin/waste
Larger in plant than animal cells
Define Lysosomes
Found only in animal cells, they contains digestive enzymes to break down waste and worn out cell parts
Define Centromeres
They are cylindered organelles that produce spindle fibers during cell division
Only found in animal cells
Define Chloroplast
It technically performs photosynthesis, but it just where it takes place
It has it’s own DNA
What does the Chloroplast look like in a plant cell?
The small round things
What are the three things the Chloroplast consists of
Stroma (fluid within), Thylakoid membrane (disks), Grana (stacks of thylakoids)
Some (Storma) Tiny (Thylakoid membenrae) Green (Garna)
Define the Cell Wall
Protects cell walls and allows the cell to pass through pores
Also adds strength to the cell