Topic 1: Introduction to Business management
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A business is a decision-making organization involved in the process of using inputs to produce goods and/ or to provide services
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Difference between a good and a service
Goods are physical products, such as smartphones, clothes, books and food. Services are intangible products, such as haircuts, public transport, education and healthcare.
What is an entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is the individual who plans, organizes and manages a business and its operations, taking on financial risks in doing so.
What is HRM
The human resources (HR) department is responsible for managing the personnel of the organization. This includes roles such as human resource planning, organizational structures, management and leadership, motivation and demotivation and dealing with industrial/employee relations
What do Finance and acounts do
The finance and accounts department is responsible for managing the organization's money, ensuring compliance with legal requirements (such as filing of corporate taxes)
What do the marketing department do
The marketing department of a business is responsible for identifying and satisfying the needs and wants of customers. It is ultimately in charge of ensuring that the firm's products sell
What do operation management do
This functional area of a business is responsible for the process of converting raw materials and components into finished goods, ready for sale and delivery to customers.
State some challenges of starting a business
Lack of finance, Unestablished customer base, Cash flow problems, Marketing problems etc
These opportunities to start a business can be remembered by the mnemonic GET CASH
Growth, Earnings, Transferance/inheritance, challenge, Autonomy, Security, Hobbies
Distinction between the private and the public sectors
private sector are owned and controlled by private individuals and businesses, rather than by the government.
Organizations that operate in the public sector are under the ownership and control of the government.
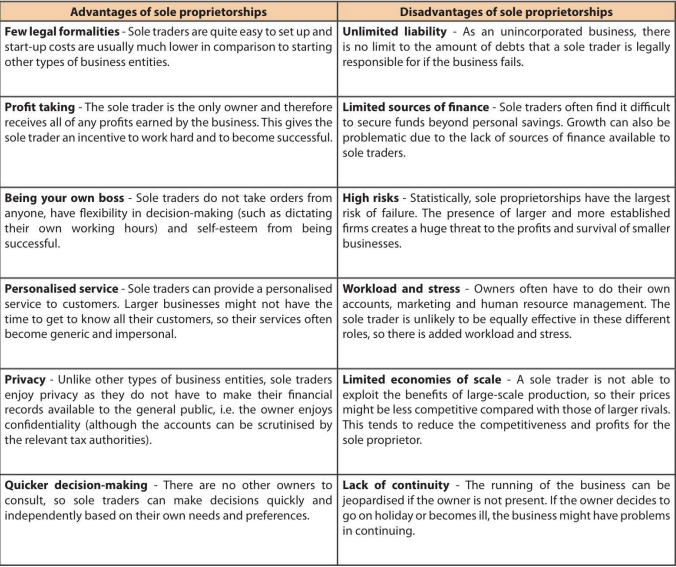
What is a sole trader + advantages and disadvantages
A sole trader (or sole proprietor) is an individual who owns his/her personal business.
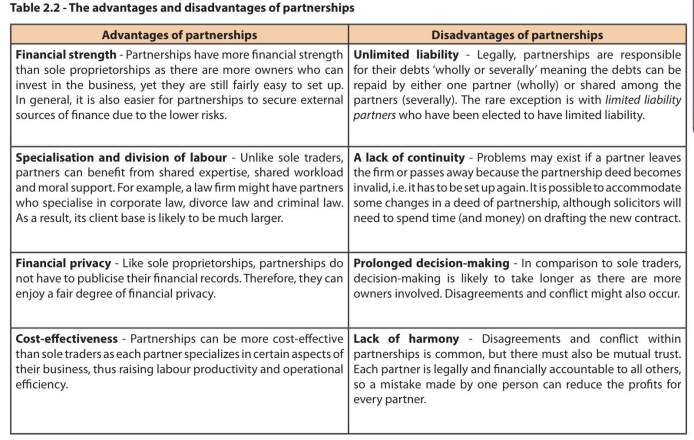
What is a partnership + advantages and disadv
A partnership is a for-profit private sector business owned by two or more persons. For ordinary partnerships, the maximum number of owners is 20 ( although this can vary from one country to another)
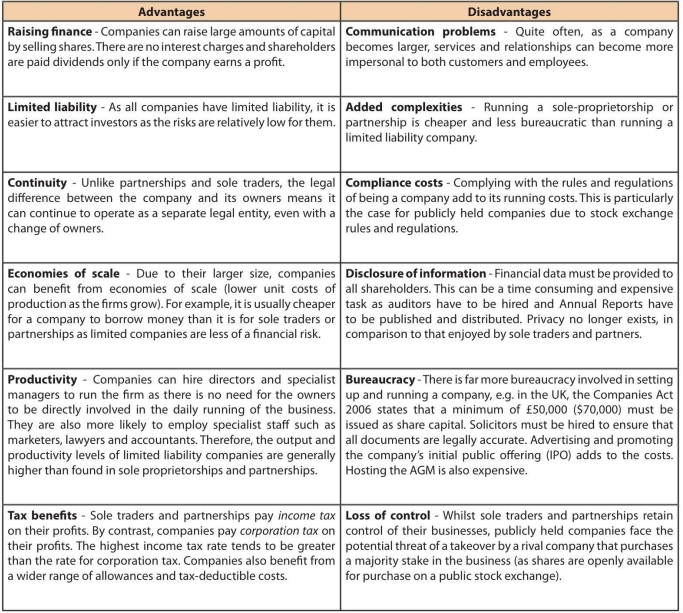
What is an Ltd
Companies are businesses owned by their shareholders. Shareholders are individuals or other businesses that have invested money to provide share capital for a company or corporation.
What to documents must be produced before made
The Memorandum of Association - a relatively brief document outlining the fundamental details of the company, such as its trading name, its main purpose, the registered business address and the amount of share capital invested.
The Articles of Association ( or Articles of Incorporation) - the longer of the two documents, stipulating the internal regulations and procedures of the company, such as the rights, roles and power of the BOD and shareholders.
What is flotation
Flotation is the term used to describe when a publicly held company first sells all or part of its business to external investors (shareholders). This process is known as an initial public offering (IPO).
What is a social entereprise
social enterprises are revenue-generating businesses with social objectives at the core of their operations.
What is a vision statement
outlines an organization's aspirations (where it wants to be) in the distant future.
What is a mission statement
Having a mission means to have a clear purpose. A mission statement tends to be a simple declaration of the underlying purpose of an organization's existence and its core values.
What is an objective
objectives are the goals or targets an organization strives to achieve. They are generally specific and quantifiable (measurable) and are set in line with the organization's mission statement.
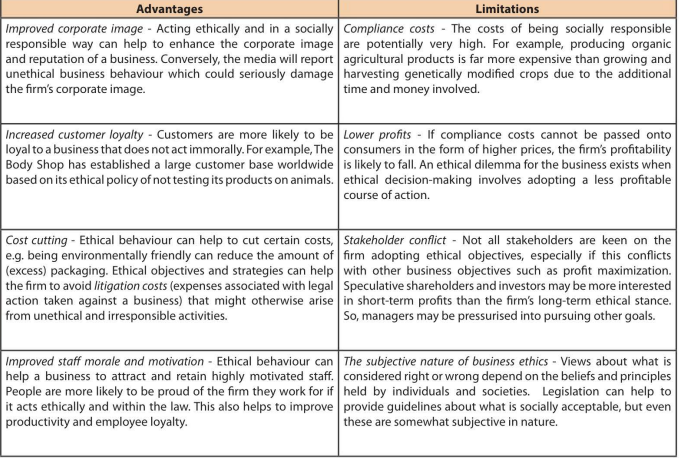
Advantages and lImitations of having ethical objectives and practices
What is a strategy
strategies are the medium to long-term plans of action to achieve the strategic objectives of an organization.
What is coporate social responsibility
corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the conscientious consideration of ethical and environmental practise related to business activity
What is a stake holder
A stakeholder is any individual, group or organization with a direct interest or involvement in the operations and performance of a business.
What are economies of scale
This refers to lower average cost of production as a firm operates on a larger scale due to an improvement in its productive efficiency
What are diseconomies of scale
Diseconomies of scale are the result of higher unit costs as a firm continues to increase in size. This means that the business becomes outsized and inefficient, so the average cost of production begins to rise
What is internal growth
Internal growth occurs when a business grows organically, using its own capabilities and resources to increase the scale of its operations and sales revenue
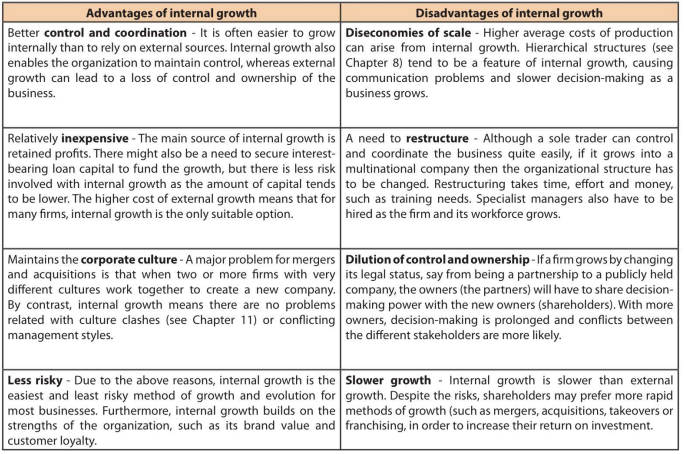
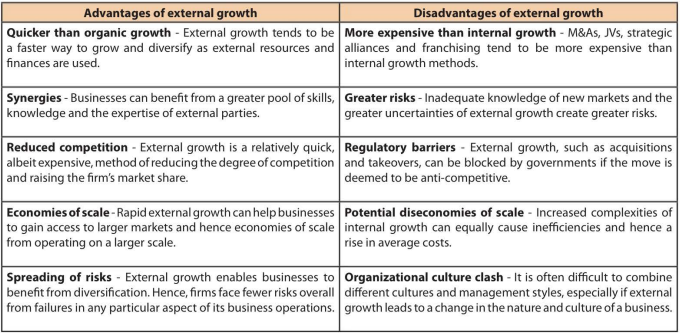
What is external growth
External growth (or inorganic growth) occurs through dealings with outside organizations rather than from an increase in the organization's own business operations.
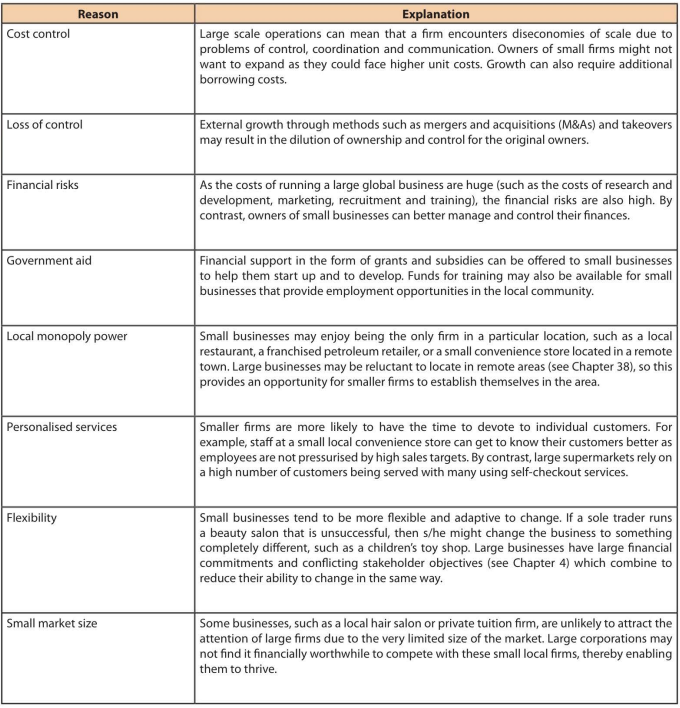
Reasons to stay as a small business
What is a joint venture
A joint venture (JV) occurs when two or more businesses split Joint ventures allow organizations to enjoy similar benefits to mergers and acquisitions but without having to lose their individual corporate identities. The advantages of joint ventures include: the costs, risks, control and rewards of a project. In doing so, the parties agree to set up a new legal business entity. For example, Coca-Cola has a JV with San Miguel by shared ownership of Coca-Cola's bottling plant in the Philippines.
What is an MNC
A multinational company (MNC) is an organization that operates in two or more countries, usually with its head office (or headquarters) based in the home country.
What is Franchising
refers to an agreement between a franchisor selling its rights to other businesses (franchisees) to allow them to sell products under its corporate name in return for a fee and regular royalty payments.