lysosomes, vacuoles, quick flashcards
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is the structure of a lysosome
membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
their enzymes work best in acidic environment inside the lysosome
what is the function of a lysosome
fuses with the food vacuole and digests the contents
also use enzymes to recycle the cell’s own contents through autophagy
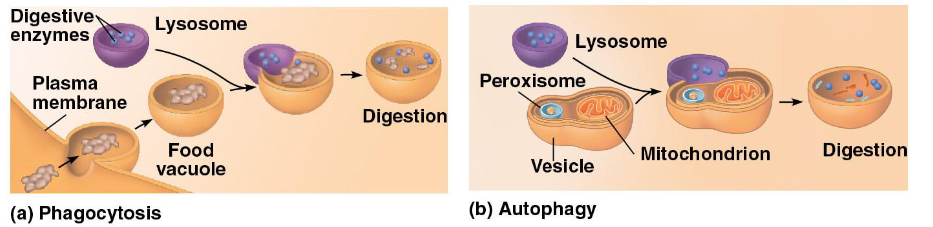
how do cells protect themselves from self digestion
pH controlled mechanisms → hydrolases only work in acidic pH
bulky protective structure of lysosomal components → protected from cleavage by high level of glyosylation
an H+ATPase in the membrane pumps H+ into the lysosome, maintaining its lumen at an acidic pH
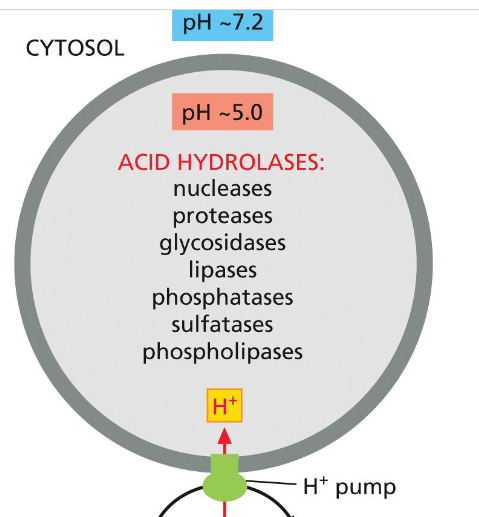
what is phagocytosis
engulfing solid particles
used by unicellular protists and some specialized cells in multicellular eukaryotes (eg macrophages)
what is autophagy
damaged organelles are wrapped in a double membrane autophagosome, which fuses with a lysosome to digest and recycle the contents
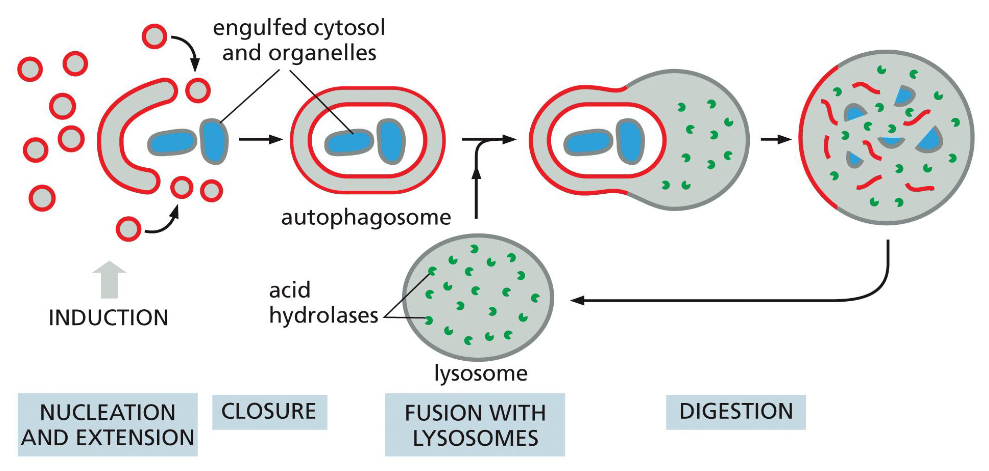
what is nonselective autophagy regulated by
by nutrient availabilty
eg degrades cytosolic proteins and organelles
what is selective autophagy regulated by
by receptors that recruit cargo to the autophagosome membrane
eg mitophagy selectively degrades mitochondria
what is tay sachs disease
a lipase is missing
leads to accumulation of lipids in the brain as the lipids cannot be digested
what is inclusion cell disease
almost all lysosomal enzymes are missing due to them being secreted
leads to inclusions of undigested material in the cell
leads to multi organ disfunctions
what are vacuoles
large vesicles derived from the ER and golgi apparatus
what do vacuoles do
food vacuoles - formed by phagocytosis in animal cells
contractile vacuoles - pump excess water out of cells, found in protists
central vacuoles - in plant cells, have sap, is a repository of inorganic ions, major role in growth of plant cells and maintains turgor
digestive vacuoles - are plant lysosomes
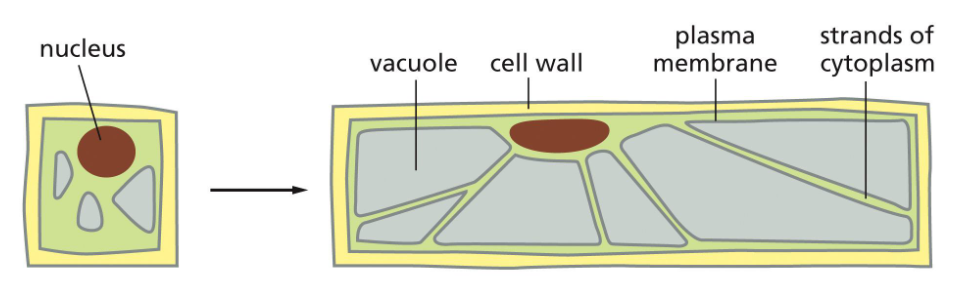
how do plant cells grow w/o increasing volume of cytoplasm
storing more water in the vacuole instead of making more cytoplasm
the cytosol is pushed to the edges of the cell, supported by actin filaments
what are peroxisomes
specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane
have enzymes that remove hydrogen atoms and transfer them to oxygen, forming hydrogen peroxide
also contains catalse which converts this to water
what do peroxisomes do
some use oxygen to break fatty acids into smaller molecules, eventually used for fuel for respiration
in the liver, they detoxify alcohol and other harmful compounds
what are glyoxysomes
are in the fat-storing tissues of plant seeds
convert fatty acids to sugar to feed the emerging seedling
what is X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD)
defective peroxisomal enzyme = unable to break down very long chain fatty acids
fatty acids accumulate, damaging the myelin sheath in the nervous system. nerves cannot conduct impulses properly
leads to neurological symptoms and paralysis
what is used to treat ALD
mix of rapeseed and olive oil
reduces the levels of very long chain fatty acids
must be used with low fat diet