Transdermal Drug Delivery: Principles and Applications
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Transdermal Drug Delivery
Method delivering drugs through skin to bloodstream.
Topical Drug Delivery
Method delivering drugs to local skin tissue.
Systemic Absorption
Drug absorption into systemic circulation.
Ideal Drug Characteristics
Specific properties for effective transdermal delivery.
Dose Deliverable
Maximum dose for transdermal delivery, < 10 mg/day.
Aqueous Solubility
Required solubility for transdermal drugs, > 1 mg/ml.
Lipophilicity
Optimal range for transdermal drugs, 101 < Ko/w < 105.
pH of Saturated Solution
Ideal pH range for transdermal drugs, pH 5-9.
Molecular Weight
Ideal weight for transdermal drugs, < 500 Da.
Melting Point
Ideal melting point for transdermal drugs, < 200°C.
Bioavailability
Extent and rate at which active drug is absorbed.
First-Pass Metabolism
Liver metabolism reducing drug bioavailability.
Short t1/2 Drugs
Drugs with short half-lives, e.g., nitroglycerin.
Rotigotine
Only marketed drug developed for transdermal delivery.
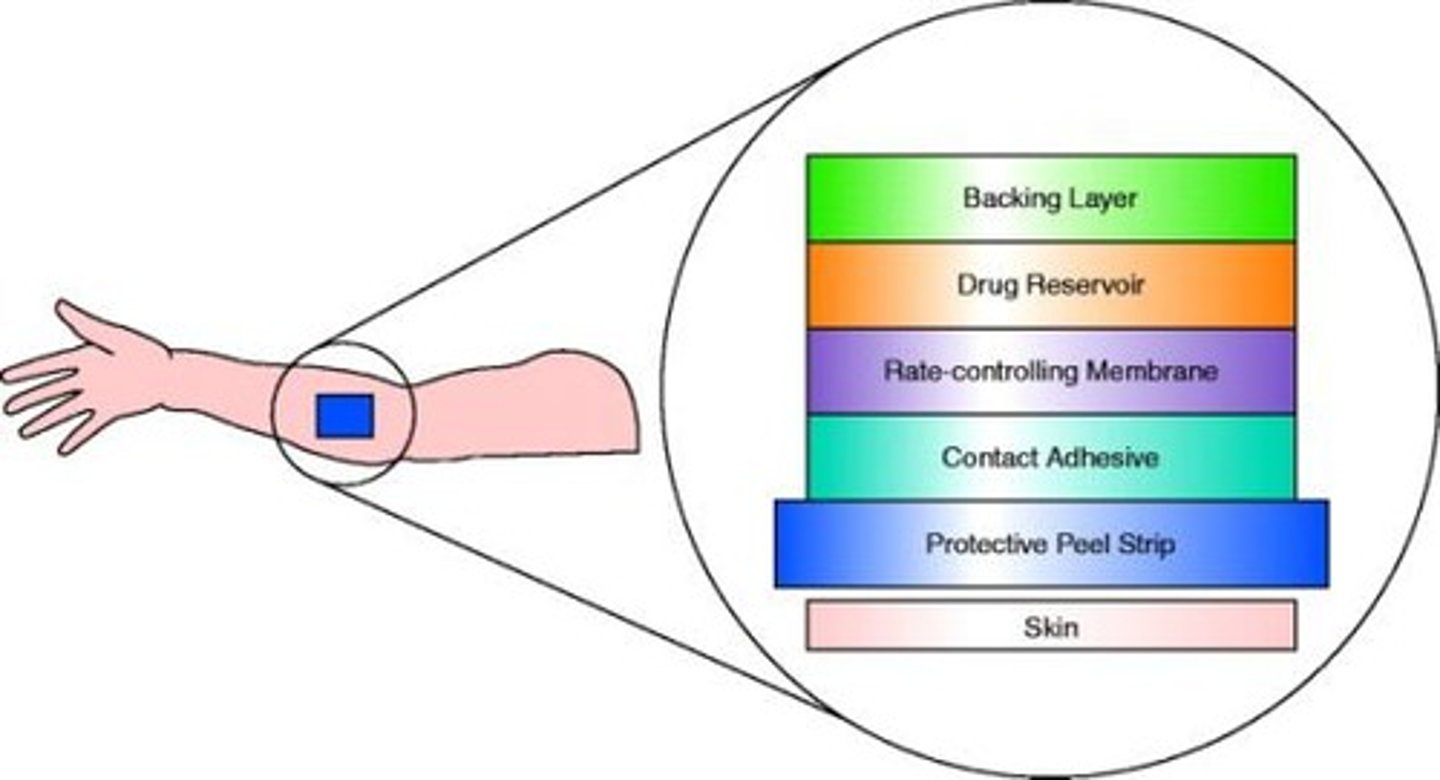
Transdermal Patch Components
Ingredients in patches for effective drug delivery.
Patient Counseling
Guidelines for safe use of transdermal formulations.
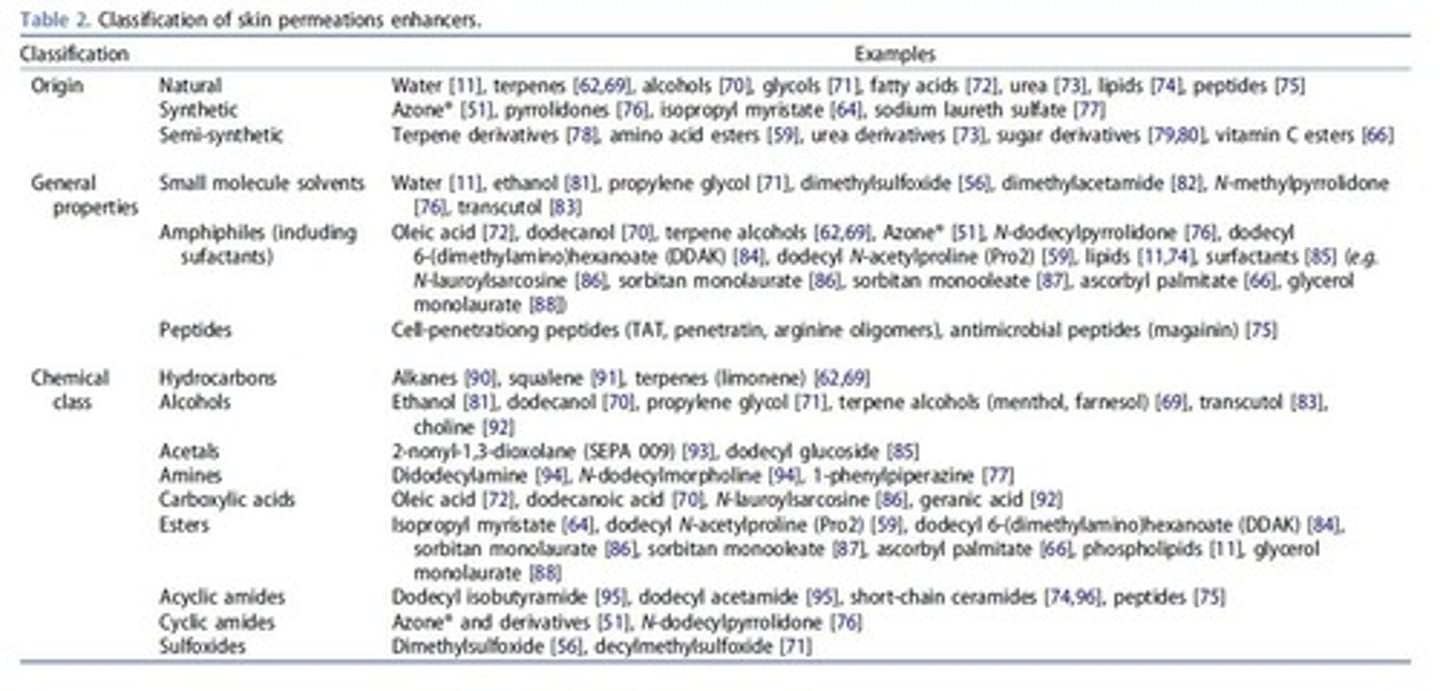
Permeation Enhancers
Substances improving drug absorption through skin.
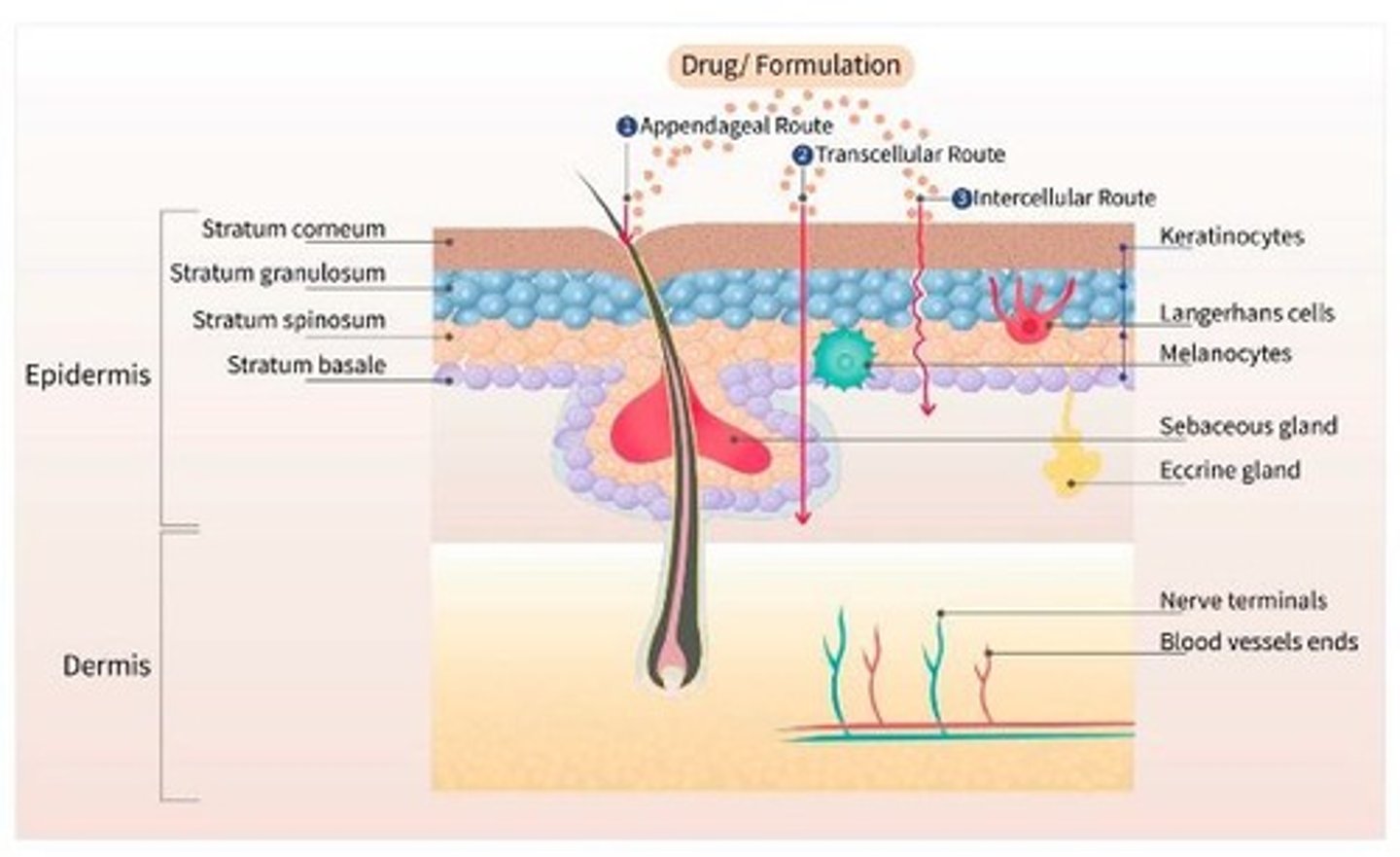
Skin Anatomy
Structure of skin relevant to drug delivery.
Conventional Topical Preparations
Traditional methods for local drug application.
Transdermal Preparations
Formulations designed for systemic drug delivery.
Market Trends
Forecast for transdermal drug delivery market growth.
Challenges in Delivery
Issues affecting reliability of transdermal products.
Steady plasma level
Consistent drug concentration in bloodstream.
Parenteral administration
Drug delivery via injection, bypassing gastrointestinal tract.
Therapeutic effect termination
Ability to quickly stop drug effects.
Patient compliance
Ease of use leading to better adherence.
Potent PK control
Enhanced management of pharmacokinetics for effective dosing.
Transdermal route limitations
Only suitable for potent drugs, not all.
Molecular weight restriction
High molecular weight drugs cannot penetrate skin.
Skin irritants
Drugs causing irritation are unsuitable for patches.
Slow onset action
Delayed therapeutic effects, unsuitable for emergencies.
Patch adhesion issues
Varied skin types affect patch stickiness.
Drug disposal concerns
Residual drug in patches complicates disposal.
Moisture exposure effects
Sweating reduces patch adhesion effectiveness.
Backing layer
Provides flexibility and appearance to the patch.
Drug reservoir
Contains drug with excipients in reservoir systems.
Membrane function
Encloses drug layer, forming a pouch.
Pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA)
Adhesive layer, typically drug-free in reservoir systems.
Release liner
Protective layer removed before patch application.
Permeation enhancer
Substances that improve skin permeability for drugs.
Application site preparation
Skin must be clean, dry, and hair-free.
Patch rotation
Changing application sites to prevent irritation.
Heat exposure precautions
Avoid excessive heat to maintain patch effectiveness.
Crystallization issue
Prolonged storage can cause drug crystallization.
Non-medicated adhesive tape
Used to secure patches for extended wear.
Residual drug delivery
Patches often leave significant drug amounts after use.
Skin irritation causes
Active and inactive ingredients may provoke reactions.
Transdermal Patch
A drug delivery system applied to skin.
Buprenorphine
Used for moderate to chronic pain relief.
Capsaicin
Management of neuropathic pain via patch.
Clonidine
Treats hypertension; available in various doses.
Diclofenac
Short-term pain relief for sprains and bruises.
Estradiol
Hormone therapy for menopause symptoms.
Fentanyl
Reservoir patch for chronic pain management.
Granisetron
Antinauseant for chemotherapy patients.
Lidocaine
Local anesthetic delivered via patch.
Methylphenidate
Treats ADHD; delivered over 9 hours.
Nicotine
Smoking cessation aid via transdermal system.
Nitroglycerin
Treats angina pectoris; various release rates.
Oxybutynin
Antispasmodic for bladder control issues.
Rivastigmine
Used for Alzheimer's disease management.
Selegiline
Antidepressant available in multiple doses.
Scopolamine
Prevents motion sickness via transdermal patch.
Testosterone
Replaces low endogenous testosterone levels.
Iontophoresis
Delivers ionic drugs using electric current.
Heat Effects
Increases drug absorption through skin.
Patch Disposal
Follow specific instructions to prevent reuse.
Patient Consultation
Educate on proper patch application and risks.
MRI Precautions
Metal in patches can cause burns.
Cathode
Electrode that attracts positive ions in iontophoresis.
Anode
Electrode that attracts negative ions in iontophoresis.
Iontophoresis
Technique using electric current to deliver drugs transdermally.
Advantages of Iontophoresis
Noninvasive, minimizes trauma, local action with minimal absorption.
Disadvantages of Iontophoresis
Requires trained professional, potential skin irritation, higher cost.
Electrode Defect
Risk of overdose due to cathode-generated hydroxide.
pH in Iontophoresis
Affects drug ionization; optimal at pH 5 for HCl salts.
Current Density
Must be less than 0.5 MA/cm² to prevent burns.
Extraneous Ions
Compete with drugs, negatively affecting iontophoresis efficiency.
Fentanyl Iontophoretic Patch
Withdrawn in 2009 due to safety concerns after 2006 approval.
Sumatriptan Delivery
Approved in 2013, uses lithium batteries for controlled delivery.
Zecuity
Sumatriptan device, must be removed before MRI.
Electroporation
Experimental method using high voltage pulses to enhance skin permeability.
Phonophoresis
Ultrasound creates microjets to enhance drug delivery through skin.
Microneedles
Tiny needles pierce skin to facilitate drug transport.
Chemical Permeation Enhancers
Substances that temporarily reduce skin barrier permeability.
Skin Irritation
Adverse effect of iontophoresis; can cause discomfort.
Cost Effectiveness
Iontophoresis is more expensive than topical formulations.
Current Intensity
Electric current strength impacting drug delivery safety.
Metal Electrodes
Commonly used electrodes that alter solution pH.
Microjets
High-speed fluid jets created by imploding bubbles in phonophoresis.
Stratum Corneum
Outer skin layer targeted by various drug delivery methods.
Enhancers
Substances that improve drug permeability in skin.
Lipid-protein-partitioning theory
Explains how enhancers affect drug absorption.
Lipid lamellae
Layers of lipids in skin affecting permeability.
Keratin modification
Enhancers alter keratin structure for hydration.
Stratum corneum
Outer skin layer where drugs partition.
USP-NF
United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary.
Apparatus 5
Paddle over disk method for drug release testing.
Apparatus 6
Cylinder method for evaluating drug release.
Apparatus 7
Reciprocating holder for drug release assessment.