Year 13 Chemistry Mocks
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
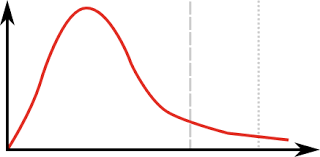
Name the Curve
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
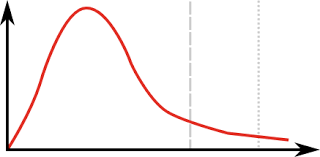
Which line is the mean energy particles have
Line 1
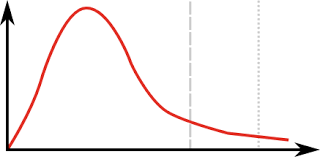
Which line is the activation energy?
Line 2
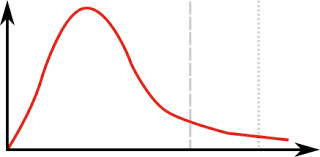
Which point on the graph is the most likely energy of a molecule
Highest peak
Esterification Word Equation
Alcohol + Carboxylic Acid → Ester + Water
Catalyst for Esterification
Sulphuric Acid
Uses for Esters
Food colouring
Solvents
Perfumes
Glues
Plasticisers
Conditions for Ester Hydrolysis
HCl acid catalyst under reflux
Nucleophilic Addition Elimination
Acid Chloride + Alcohol (+Chloride ion from HCl) → Ester (+HCl)
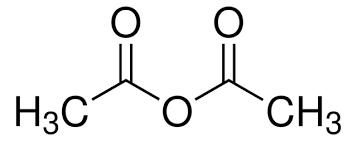
Name the molecule
Ethanoic Anhydride / Acetic Anhydride
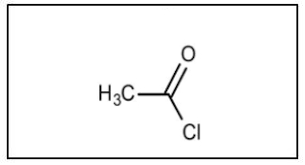
Name the molecule
Ethanoyl Chloride
Industrially why is an acid anhydride preferred over an acid chloride?
No HCl production
Cheaper
Does not react vigorously with water
Thermal Cracking
High temp (1000 degrees celsius)
High pressure (70 atm)
Produces mostly alkenes
Catalytic Cracking
High temp (450 degrees celsius)
Slightly high pressure
Mostly aromatics
Fuel for vehicles
Issue combusting impure hydrocarbons
May contain sulphur impurities which produce SO2 which leads to acid rain
Materials in Flue Gas Desulphurisation
CaO and gypsum
Initiation in Ozone Depletion
O3 + Cl* → ClO* + O2
Propagation in Ozone Depletion
Cl* + O3 → ClO* + O2
ClO* + O3 → Cl* + 2O2
Termination in Ozone Depletion
Cl* + Cl* → Cl2
Requirement for Free Radical production
presence of UV light
Nucleophilic Substitution
Warm Aqueous NaOH
Haloalkane → Alcohol
Base Elimination
Hot Ethanolic NaOH
Haloalkane → Alkene
Ammonia and Nucleophilic Subsitution
Heat with an excess of ethanolic ammonia
Ammonia acts as a nucleophile then a base
Oxidation of Primary Alcohol
Aldehyde → Carboxylic Acid
Oxidation of Secondary Alcohol
Ketone
Oxidation of Tertiary Alcohol
Not easily oxidised
Test for Aldehydes
Tollen’s Reagent - Produces silver mirror
Fehling’s Solution → blue to brick red
Conditions for fermentation of Glucose
Yeast in anaerobic conditions
35 degrees celsius
Equation for fermentation of glucose
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Nucleophilic substitution of alkene to make alcohol
High Yield / High Atom Economy
High temp and pressure
Fast
Uses Crude oil
Fermentation of glucose to produce alcohol
15% alcohol in water
Low temp and pressure
Slow
Carbon neutral
Electrophilic Addition: Addition of Sulphuric Acid
Ethene + Sulphuric acid → Ethanoyl Hydrogen Sulphate
Dehydration of Alcohols
Cold water, Warm Ethanoyl Hydrogen Sulphate
Ethane carbocation + Water → Ethanol + Sulphuric acid
Properties of Short Branched polymers
More flexible and less strong
They can not pack as closely together
Weakened Van Der Waals’ Forces
Positive Inductive Effect
The more alkyl groups connected to a carbocation, the more stable it is making it the major product
Alkyl groups push electrons towards the positive cation
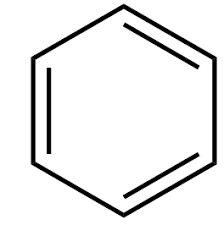
Name the structure
Kekule’s Structure
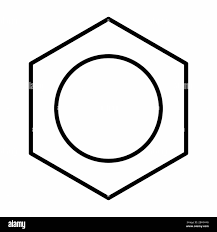
Name the structure
Delocalised Electron Structure
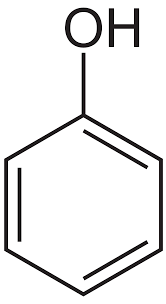
Name the structure
Phenol
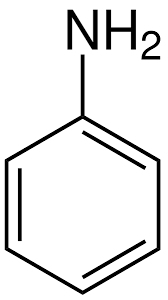
Name the structure
Phenylamine
Friedel-Crafts Acylation Catalyst
AlCl3
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Methanoyl Chloride + AlCl3 → Methanoyl Carbocation + AlCl4+
Benzene + Methanoyl Carbocation + AlCl4+ → Benzene Acetate + HCl + AlCl3
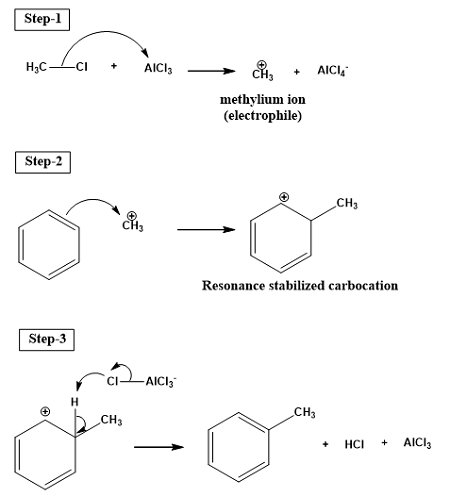
Why is adding an acetyl group to benzene useful?
It weakens it making it easier to modify
Conditions of Nitration Benzene
Heat with Concentrated HNO3 and H2SO4
Temperature must be below 55 degrees celsius
Why must the temperature be low for the nitration of benzene
To prevent multiple substitutions
What is Nitrobenzene used for
Making dyes
Making pharmaceuticals
Making explosives
Test for Alcohols
Add acidified potassium dichromate for oxidation (orange → green)
Use fractional distillation to remove the product
Test product for aldehyde or ketone
Test for Carboxylic Acids
Reacts with carbonate ion (CaCO3) to effervesce and produce CO2