AP Biology unit 7
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Oogenesis
Egg production
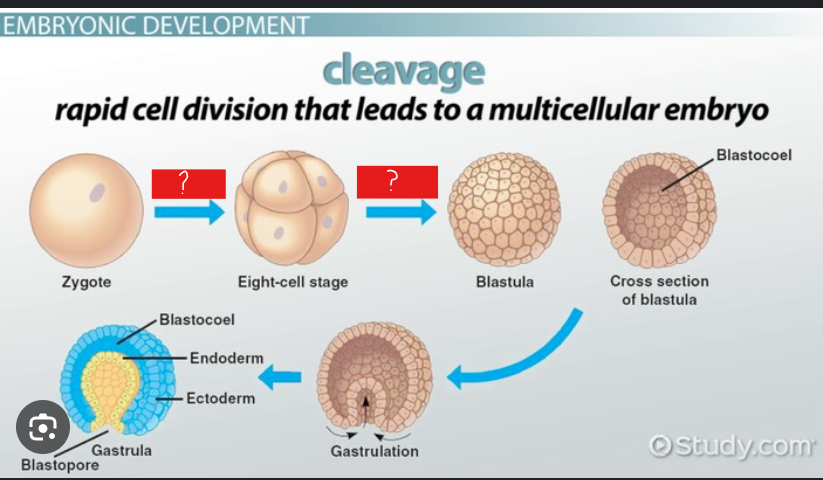
cleavage
a series of mitotic divisions whereby the enormous volume of egg cytoplasm is divided into numerous smaller, nucleated cells.
differentiation
process in which cells become specialized in structure and function
morphogenesis
The process by which an organism takes shape and the differentiated cells occupy their appropriate locations.
differential
gene expression results from genes being regulated differently in each cell type
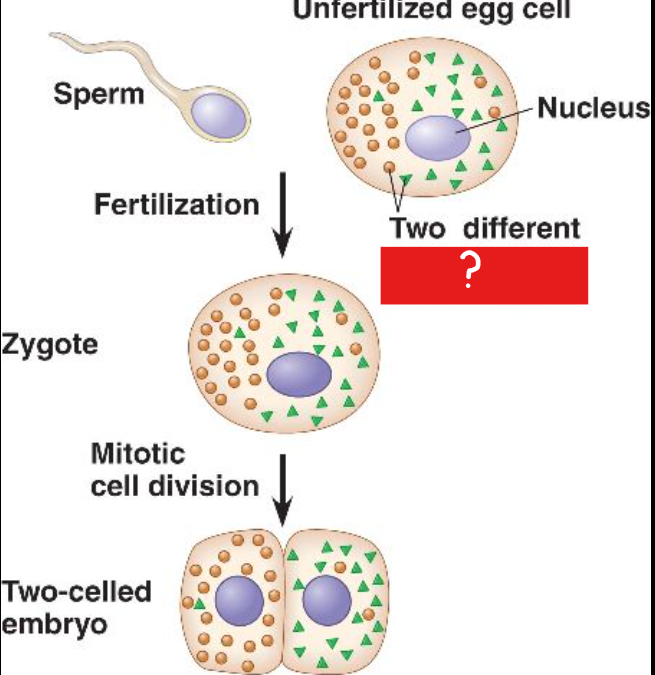
Cytoplasmic determinants
Maternal substances in egg that influence the course of early development.
cytoplasmic determinants
As the zygote divides by mitosis, the resulting cells contain different ___ ___, which lead to different gene expression
induction
signal molecules from embryonic cells cause transcriptional changes in nearby target cells
morula, blastula
zygote--> ___ ---> ____
morula
solid ball of cells
blastula
hollow ball of cells
zygote
fertilized egg
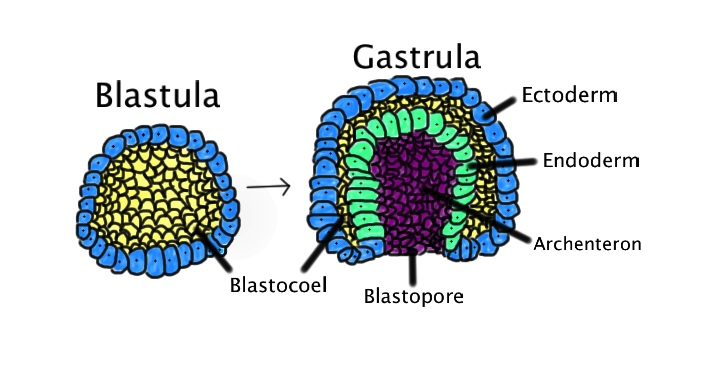
gastrulation
In animal development, a series of cell and tissue movements in which the blastula stage embryo folds inward, producing a three layered embryo, the gastrula.
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
the 3 cell layers that gastrulation establishes
ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
endoderm
the inner germ layer that develops into the lining of the digestive and respiratory systems
neurulation
formation of notochord and neural tube, develop into backbone and brain and spinal cord
Organogenesis
organ formation that takes place during the first two months of prenatal development
Placenta
organ that nourishes the fetus
determination
The point during development at which a cell becomes committed to a particular fate due to cytoplasmic effects or to induction by neighboring cells.
epigenetics
the study of influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
gene
determination is at the ___ level
apoptosis
programmed cell death
pattern formation
The development of a spatial organization of tissues and organs.
Positional information
The molecular cues that control pattern formation, tells a cell its location relative to the body axes and to neighboring cells
homeotic genes
Genes that determine basic features of where a body part is.
maternal effect genes
encode cytoplasmic determinants that initially establish the axes of the body of Drosophila
egg polarity
maternal effect genes are also called _ ___ genes
Bicoid
'Two Tailed', a defect in an embryo that results in two posterior structures (two tails, no head)
morphogens
establish an embryo's axes and other features of its form
totipotent
Stem cells with the potential to differentiate into any type of cell.
nuclear transplantation
A technique in which the nucleus of one cell is placed into another cell that already has a nucleus or in which the nucleus has been previously destroyed.
enucleated
the condition where a cell does not contain a nucleus
stem cell
unspecialized cell that can give rise to one or more types of specialized cells
pluripotent
Cells that are capable of developing into most, but not all, of the body's cell types
acquired traits
Skills that you learn to do or develop during your life time
Charles darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)
selective breeding
The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation
charles darwin's ideas
natural selection: variation exists, overproduction of offsping, competition, differential survival and reproduction
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
variation
Any difference between individuals of the same species.
overproduction
organisms produce more offspring than can survive
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
differential survival
the belief that only the organisms best adapted to existing conditions are able to survive and reproduce.
differential reproduction
Phenomenon in which individuals with adaptive genetic traits produce more living offspring than do individuals without such traits.
fossil record
information about past life, including the structure of organisms, supports transition species
anatomical record
homologous and vestigial structures, embryology and development
molecular record
comparing DNA and protein structure
artificial selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits; human caused evolution
vestigial structures
remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species.
homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
analogous structures
Body parts that share a common function, but not structure; no evolutionary relationship
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
parallel evolution
Two related species that have made similar evolutionary adaptations after their divergence from a common ancestor
vestigial organs
organ that serves no useful function in an organism
comparative embryology
the study of the similarities and differences in the embryos of different species
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
gene pool
collection of alleles in the population
allele frequency
Number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of alleles in that pool for the same gene
genetic drift
A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection
predation selection
acts on both predator and prey: behaviors, camouflage and mimicry, speed, defenses (physical and chemical)
physiological selection
Acting on body functions (disease resistance, protection from injury, etc.)
sexual selection
A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates.
founder effect
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population
bottleneck
process in which a large population declines in number, then rebounds but with a limited gene pools
founder effect and bottleneck
two examples of genetic drift
founder effect
the ___ ___ skews the gene pool of the new population
industrial melanism
darkening of populations of organisms over time in response to industrial pollution
allopatric isolation
The process of speciation that occurs in geographic isolation
sympatric isolation
two subpopulations become reproductively isolated within the same geographic area
allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
ecological isolation
species occur in the same area, but they occupy different habitats and rarely encounter each other
mechanical isolation
Morphological differences can prevent successful mating
gametic isolation
Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize eggs of another species
hybrid breakdown
Hybrid is fertile, but when they breed the next generation is sterile.
gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly but steadily
Punctuated Equilibrium
Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change
stromatolites
Oldest known fossils formed from many layers of bacteria and sediment.
endosymbiosis
A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes.
cleavage
cytoplasmic determinants
morula
blastula
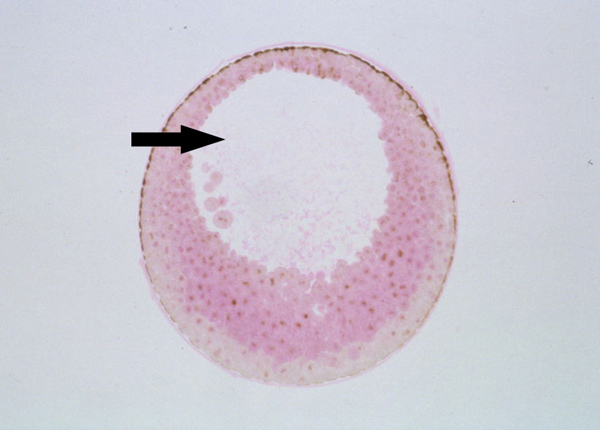
gastrulation