unit 6 - molecular genetics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:17 PM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
Nitrogenous Base
A molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties of a base. The binding of these base pairs forms the structure of DNA .
2
New cards
Adenine
A chemical compound that is used to make one of the building blocks of DNA. Bonds with thymine or uracil.
3
New cards
Guanine
A chemical compound that is used to make one of the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Bonds with cytosine.
4
New cards
Cytosine
A chemical compound that is used to make one of the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Bonds with Guanine.
5
New cards
Thymine
A chemical compound that is used to make one of the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Bonds with adenine.
6
New cards
Uracil
A chemical compound that is used to make one of the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Bonds with adenine.
7
New cards
Double helix
A term used to describe the physical structure of DNA.
8
New cards
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Forms the structural framework of nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA. This is composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups, and defines directionality of the molecule.
9
New cards
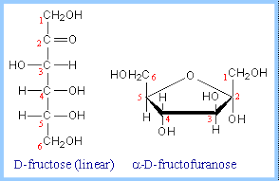
Carbon labeling (primes)
the numbering of ring carbons then continues in a direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise)
10
New cards
DNA
The molecule inside cells that contains the genetic information responsible for the development and function of an organism. Double Helix
11
New cards
RNA
a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides
12
New cards
Complementary base pairs
Hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of the molecule together. These pair up with each other in a consistent way,
13
New cards
Chargaff’s Rule
states that in the DNA of any species and any organism, the amount of guanine should be equal to the amount of cytosine and the amount of adenine should be equal to the amount of thymine.
14
New cards
Antiparallel
A term used to describe the opposite orientations of the two strands of a DNA double helix; the 5' end of one strand aligns with the 3' end of the other strand.
15
New cards
Nucleotide bonding (5’ to 3’ or vice versa)
to the orientation of nucleotides of a single strand of DNA or RNA. specifically refer to the 5th and 3rd carbon atoms in the deoxyribose/ribose sugar ring.
16
New cards
Histone
A type of protein found in chromosomes. These bind to DNA, help give chromosomes their shape, and help control the activity of genes. Enlarge. Structure of DNA.
17
New cards
Nucleosome
a section of DNA that is wrapped around a core of proteins
18
New cards
Semiconservative replication
the two strands of DNA unwind from each other, and each acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. This results in two DNA molecules with one original strand and one new strand.
19
New cards
Helicase
enzyme that separates double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied.
20
New cards
DNA Polymerase
enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA.
21
New cards
Primase
enzyme that creates a primer on a DNA strand by adding RNA nucleotides to the strand according to the DNA template sequence.
22
New cards
Primer
a short nucleic acid sequence that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis.
23
New cards
Ligase
for sealing any breaks in the sugar-phosphate backbone of the strand, sealing Okazaki fragments (the glue)
24
New cards
Okazaki Fragments
short sections of DNA formed at the time of discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand during replication of DNA, need to be sealed by ligase
25
New cards
Leading Strand
a single DNA strand that, during DNA replication, is replicated in the 3' – 5' direction (same direction as the replication fork). DNA is added to this continuously, one complementary base at a time.
26
New cards
Lagging Strand
a single DNA strand that, during DNA replication, is replicated in the 5′ – 3′ direction (opposite direction to the replication fork). DNA is added to this in discontinuous chunks called 'okazaki fragments'.
27
New cards
Telomerase
progressive synthesis of telomeric DNA repeats (TTAGGG) at the 3′ ends of linear chromosomes, thereby reversing the loss of DNA from each round of replication.
28
New cards
mRNA
Role is to carry protein information from the DNA in a cell's nucleus to the cell's cytoplasm (watery interior), where the protein-making machinery reads it’s sequence and translates each three-base codon into its corresponding amino acid in a growing protein chain. (messenger)
29
New cards
tRNA
type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome. serves as a link (or adaptor) between the mRNA molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein
30
New cards
rRNA
a major constituent of ribosomes. It ensures the proper alignment of the mRNA and the ribosomes during protein synthesis and catalyzes the formation of the peptide bonds between two aligned amino acids during protein synthesis. (ribosomal)
31
New cards
Transcription
the process by which a cell makes an RNA copy of a piece of DNA. This RNA copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information needed to make proteins in a cell.
32
New cards
Translation
the process by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA (mRNA). amino acids are linked together to form proteins
33
New cards
Elongation (transcription/translation)
Middle stage. transcription - nucleotide bases are added to mRNA strand, it gets longer. translation - amino acids are added to amino acid chain, it gets longer.
34
New cards
Termination (transcription/translation)
End stage. transcription - RNA polymerase transcribes terminator sequence and releases DNA template. translation - ribosome reaches the stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) and protein is released.
35
New cards
Transcription Bubble
A molecular structure formed during DNA transcription when a limited portion of the DNA double helix is unwound. The size of this ranges from 12 to 14 base pairs.
36
New cards
Template/Nontemplate Strand
The template one is the one that RNA polymerase uses as the basis to build the RNA. . The non-template one has the identical sequence of the RNA (except for the substitution of U for T).
37
New cards
Promoter
a region of DNA upstream of a gene where relevant proteins (such as RNA polymerase and transcription factors) bind to initiate transcription of that gene, also defines the direction of transcription and indicate which DNA strand will be transcribed
38
New cards
RNA polymerase
an enzyme that is responsible for copying a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence, duyring the process of transcription. acts as all the other enzymes (primase, ligase, etc) in DNA replication.
39
New cards
Nucleotide cap
Attaches to the 5’ end, protects mRNA from degradation and helps in ribosome binding during translation.
40
New cards
Poly-A tail
Attaches to the 3’ end, 200 adenines, protects mRNA from degradation and helps in ribosome binding during translation.
41
New cards
Intron
The sequence of DNA in between exons that is initially copied into RNA but is cut out of the final RNA transcript and therefore does not change the amino acid code.
42
New cards
Exon
The sequence of DNA present in mature messenger RNA, some of which encodes the amino acids of a protein.
43
New cards
Polypeptide
A substance that contains many amino acids (the molecules that join together to form proteins).
44
New cards
Large Subunit
contains the active site of the ribosome: the site that creates the new peptide bonds when proteins are synthesized.
45
New cards
Small Subunit
In charge of information flow during protein synthesis. It initially finds a messenger RNA strand and, after combining with a large subunit, ensures that each codon in the message is paired with the anticodon in the proper transfer RNA.
46
New cards
Amino Acids
molecules that combine to form proteins
47
New cards
Codons
A sequence of three consecutive nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that codes for a specific amino acid.
48
New cards
Start Codon
the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome (AUG)
49
New cards
Stop Codon
a sequence of three nucleotides (a trinucleotide) in DNA or messenger RNA (mRNA) that signals a halt to protein synthesis in the cell (UAA, UAG and UGA)
50
New cards
A site
a binding site for charged t-RNA molecules during protein synthesis. One of three such binding sites, the first location the t-RNA binds during the protein synthesis process
51
New cards
P site
the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain.
52
New cards
E site
third and final binding site, tRNA goes here after it is empty, meaning that it has transferred its polypeptide to another tRNA (which now occupies the P site).
53
New cards
Initiation step (transcription/translation)
Beginning stage. transcription - RNA polymerase binds to the region called the promoter. translation - initiator tRNA interacts with AUG start codon
54
New cards
Point Mutation
a change in a single base pair of DNA by substitution, deletion, or insertion of a single nitrogenous base.
55
New cards
Silent Mutation
when the change of a single DNA nucleotide within a protein-coding portion of a gene does not affect the sequence of amino acids that make up the gene's protein.
56
New cards
Missense Mutation
a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
57
New cards
Nonsense Mutation
occurs in DNA when a sequence change gives rise to a stop codon rather than a codon specifying an amino acid.
58
New cards
Frameshift Mutation
An insertion or deletion involving a number of base pairs that is not a multiple of three, which consequently disrupts the triplet reading frame of a DNA sequence.
59
New cards
Insertion
A type of genetic change that involves the addition of a segment of DNA
60
New cards
Deletion
A type of genetic change that involves the absence of a segment of DNA.
61
New cards
CRISPR
is a highly precise gene editing tool that is changing cancer research and treatment.
62
New cards
Gene Expression
the process by which the instructions in our DNA are converted into a functional product, such as a protein.