Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Crll
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Unified Cell Theory
the biological concept that states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and new cells arise from existing cells
Importance of Surface Area
A high surface area to volume ratio is important to cells. When the surface area is greater than volume, there is more plasma membrane relative to the inside of the cell. This allows for materials to be transported as efficiently as possible into, out of, and around the cell
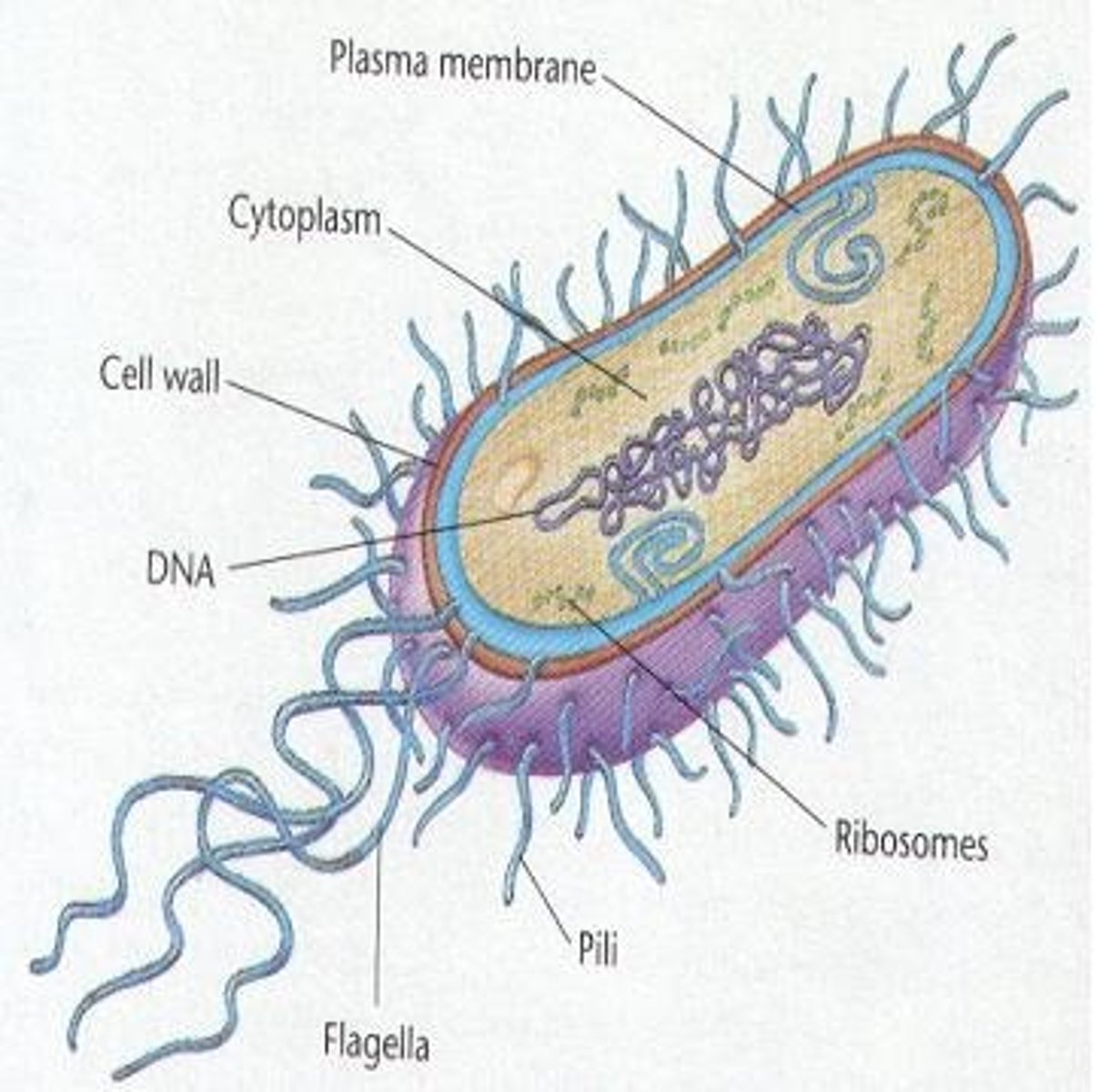
Prokaryotic cell
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles; includes achaea and bacteria
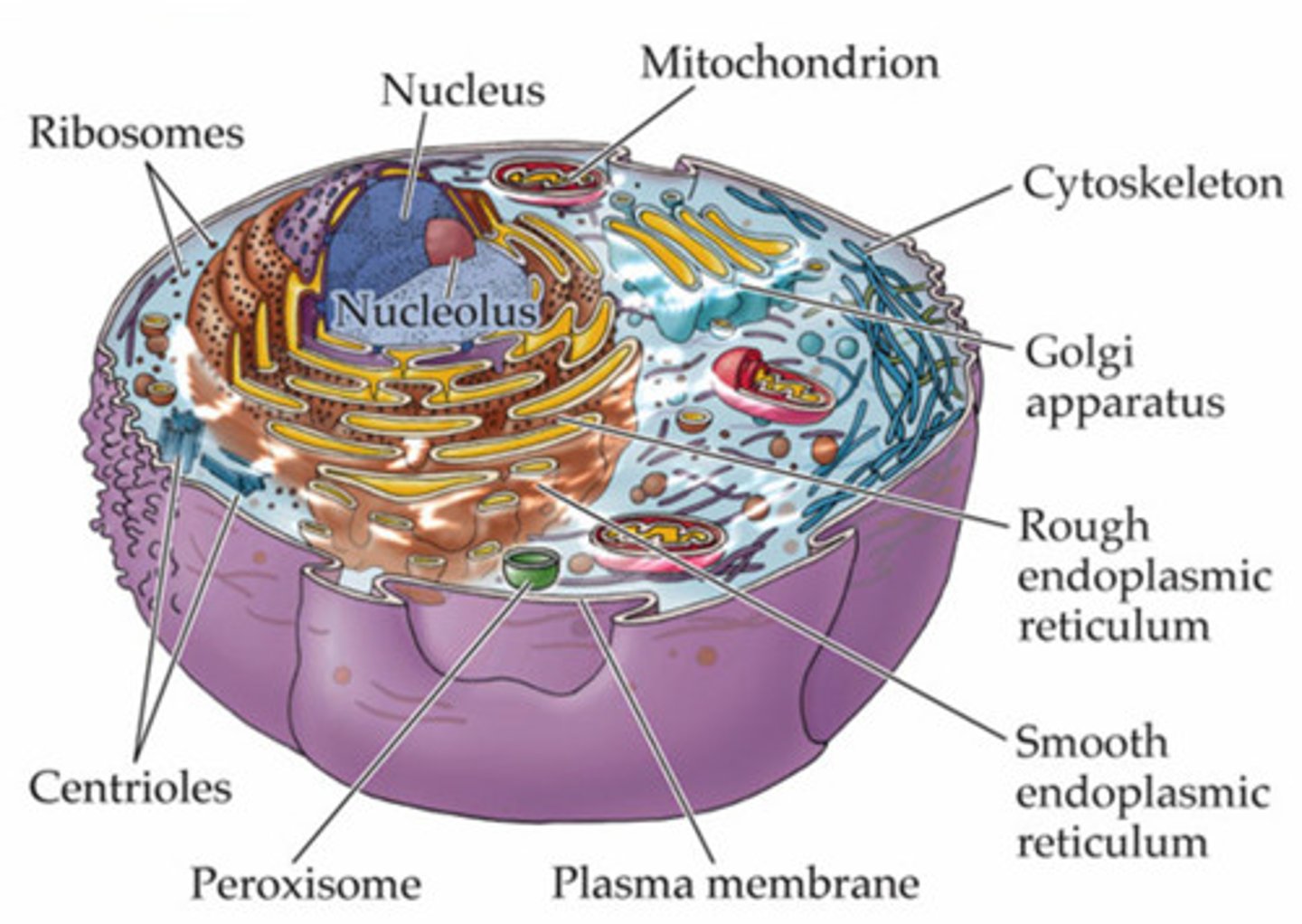
Eukaryotic Cell
A cell containing a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles
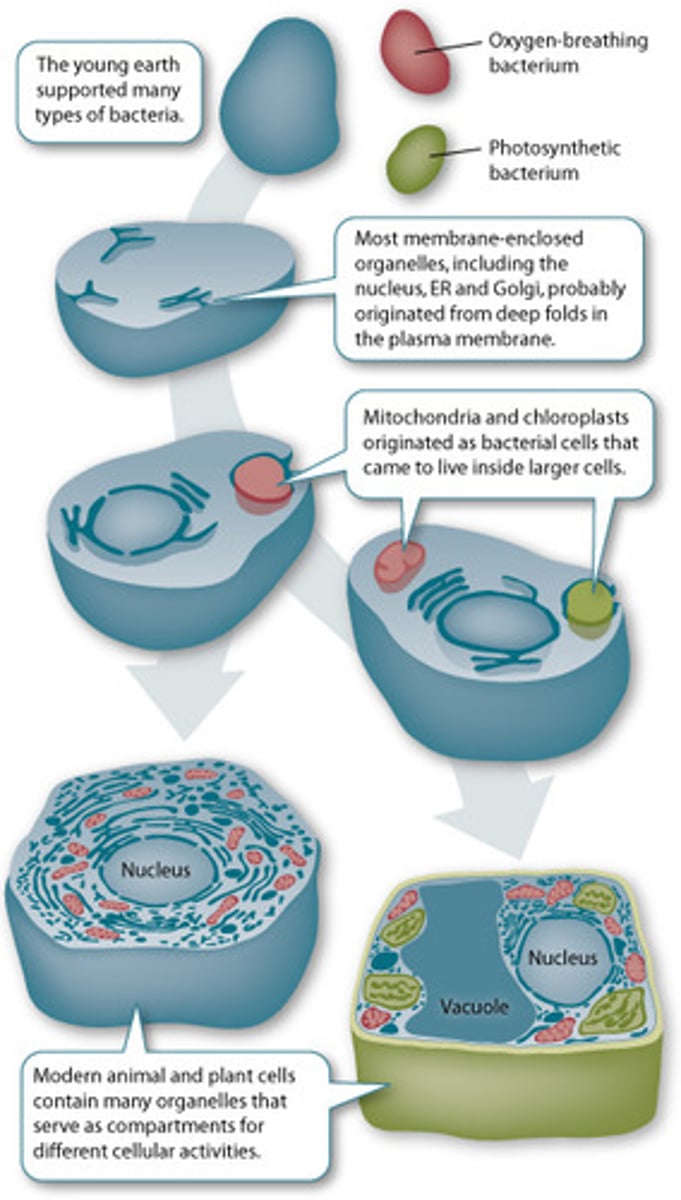
Endosymbiosis Theroy
the idea that the mitochonria and chloroplasts were once free living and were engulfed by other prokaryotic cells.
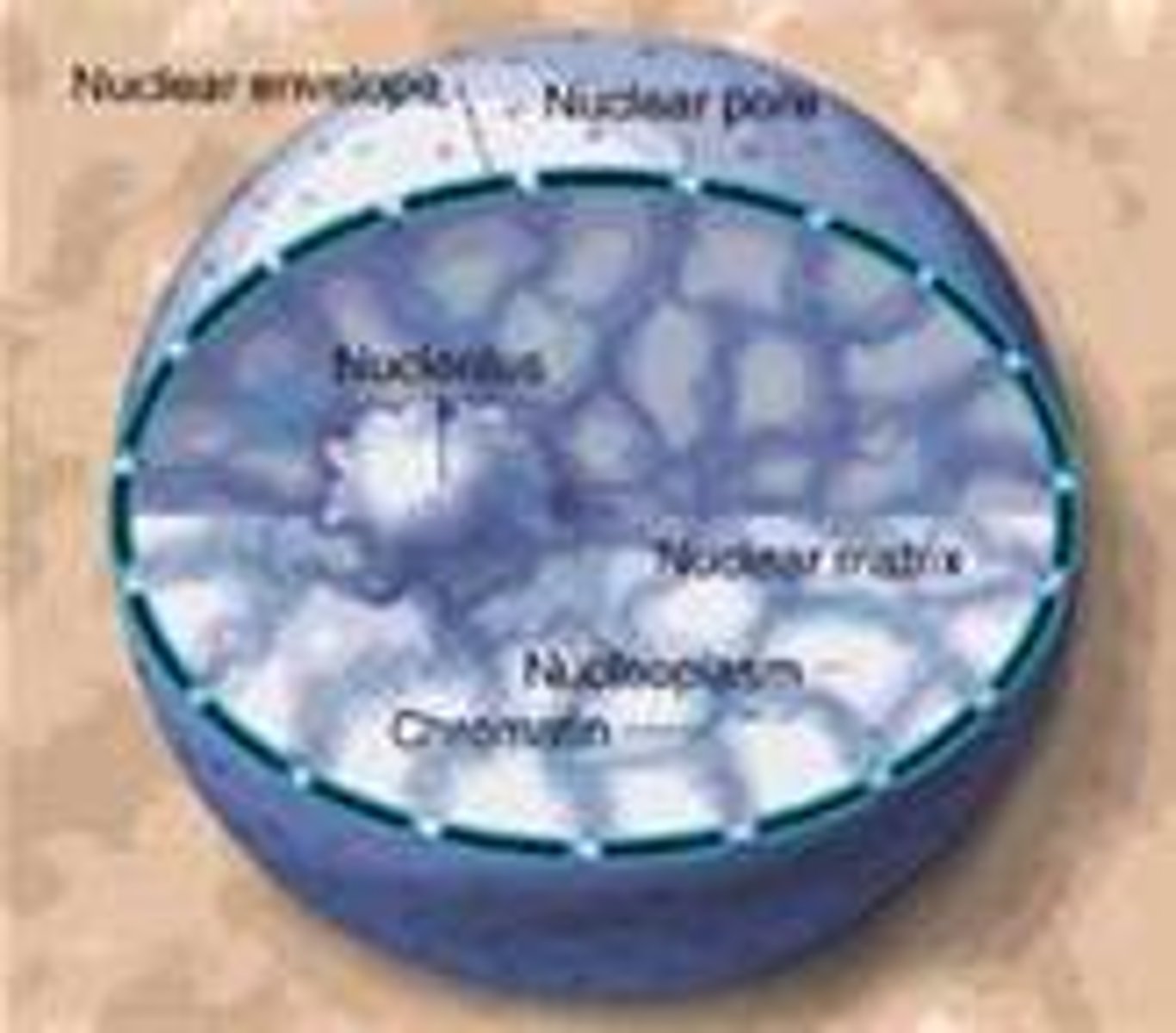
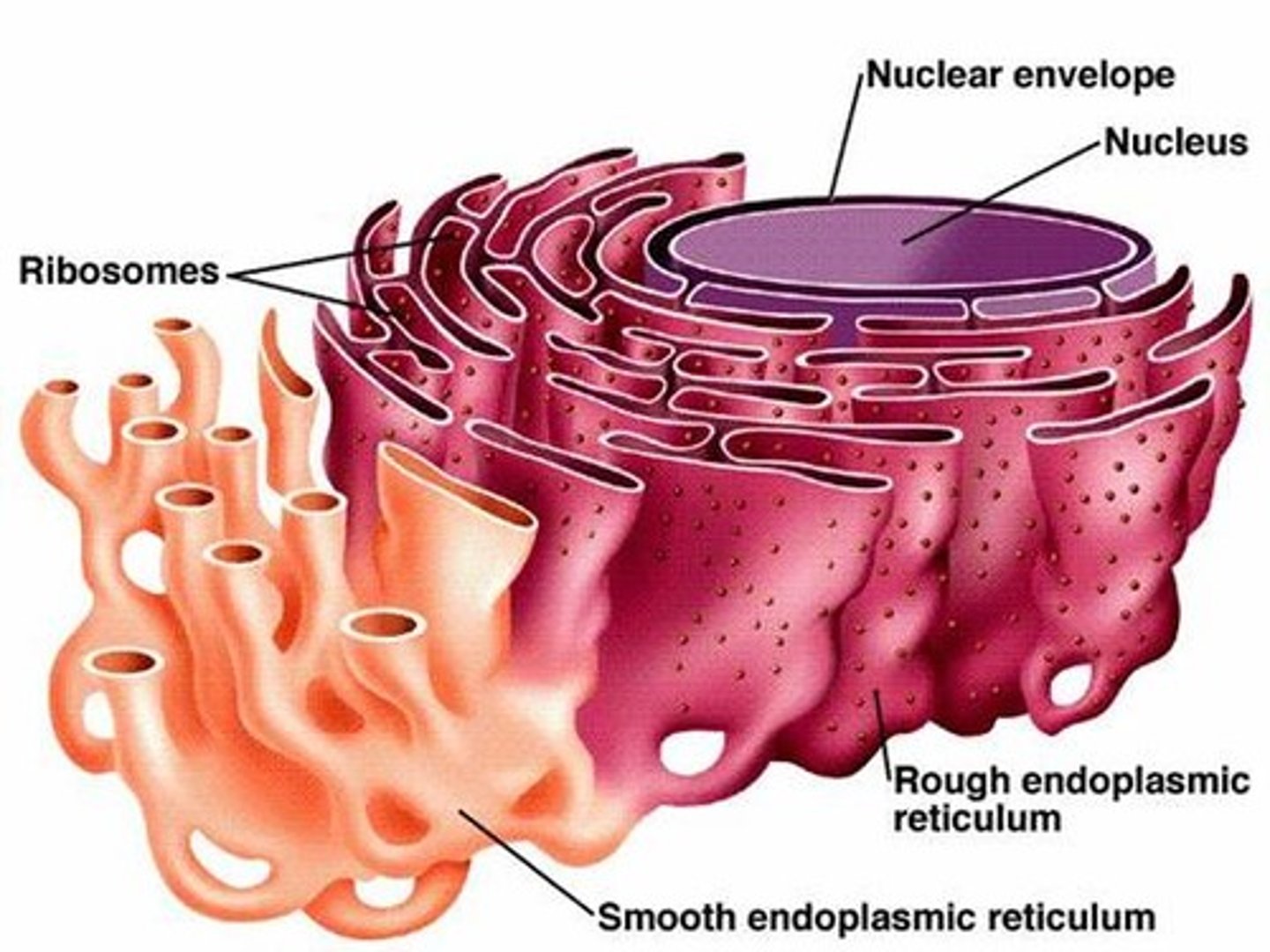
Nucleus
A cell organelle that houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosome and proteins
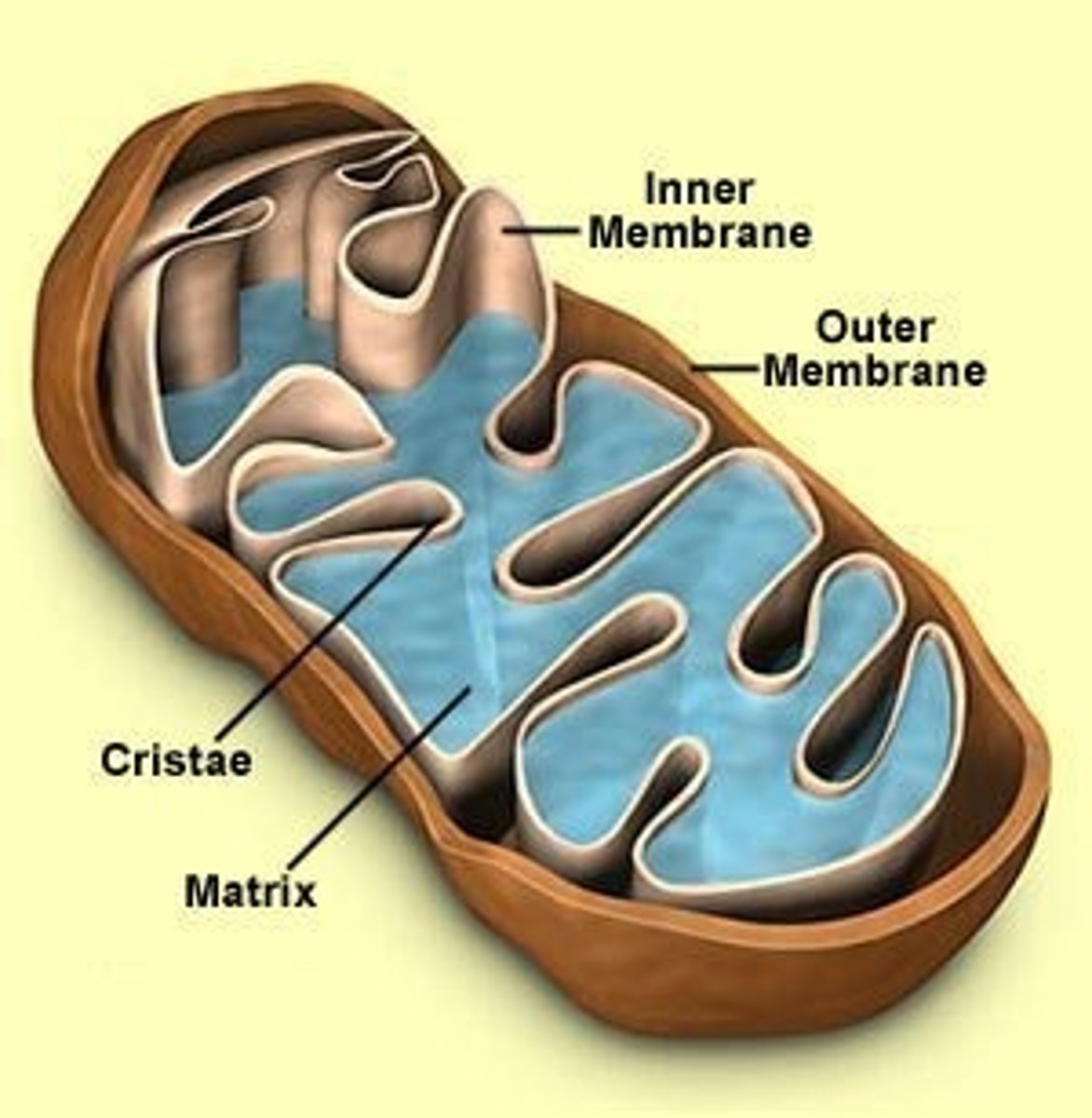
Mitochondria
in eukaryotic cells, the cell organelle that is responsible for carrying out cellular respiration, resulting in the production of ATP (energy)
Ribosomes
Responsible for protein synthesis
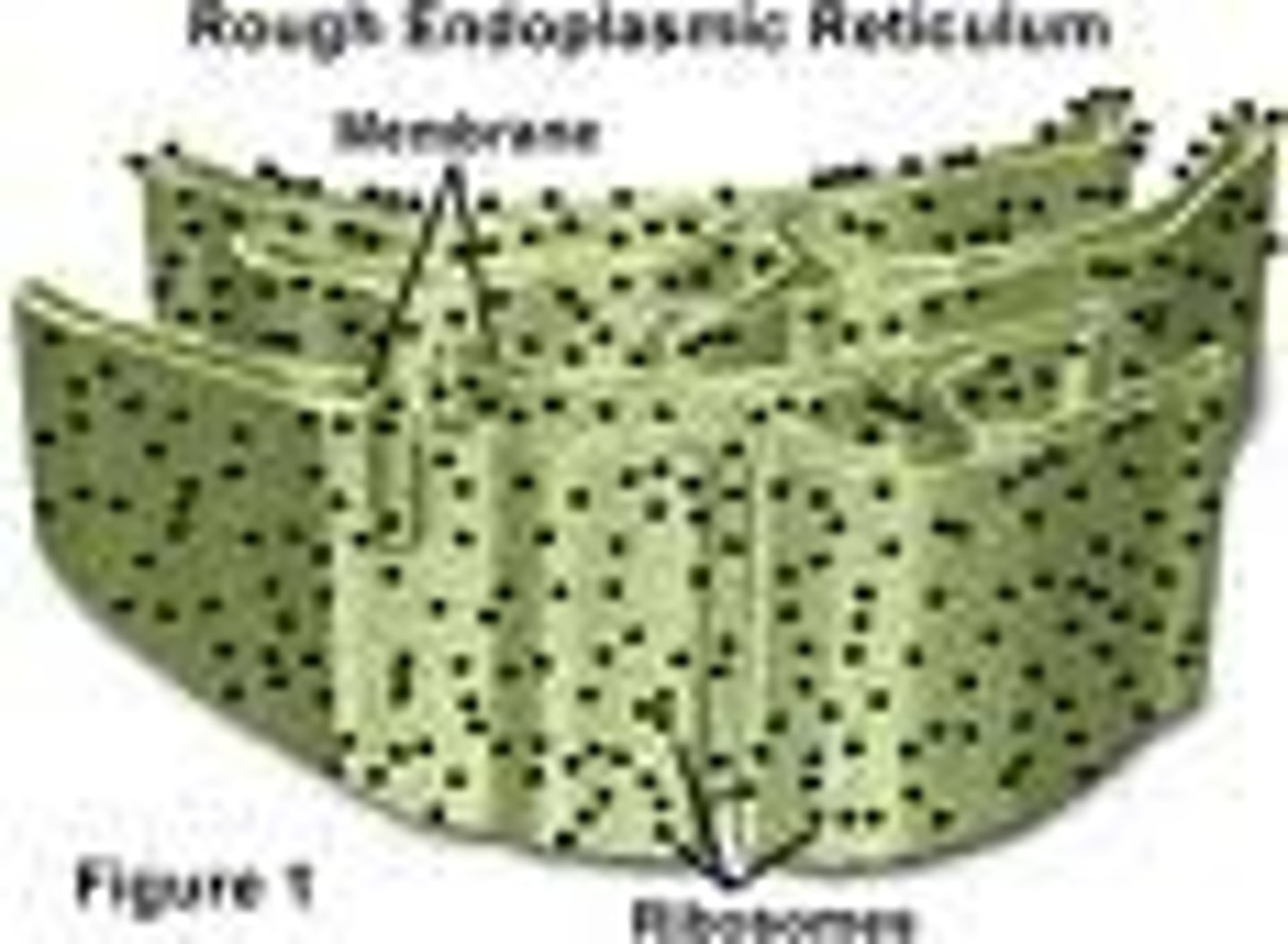
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The region of the endoplasmic reticulum that’s studded with ribosomes and engages in protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The region of the endoplasmic reticulum that’s not studded with ribosomes and engages in lipids synthesis and detoxifies chemicals
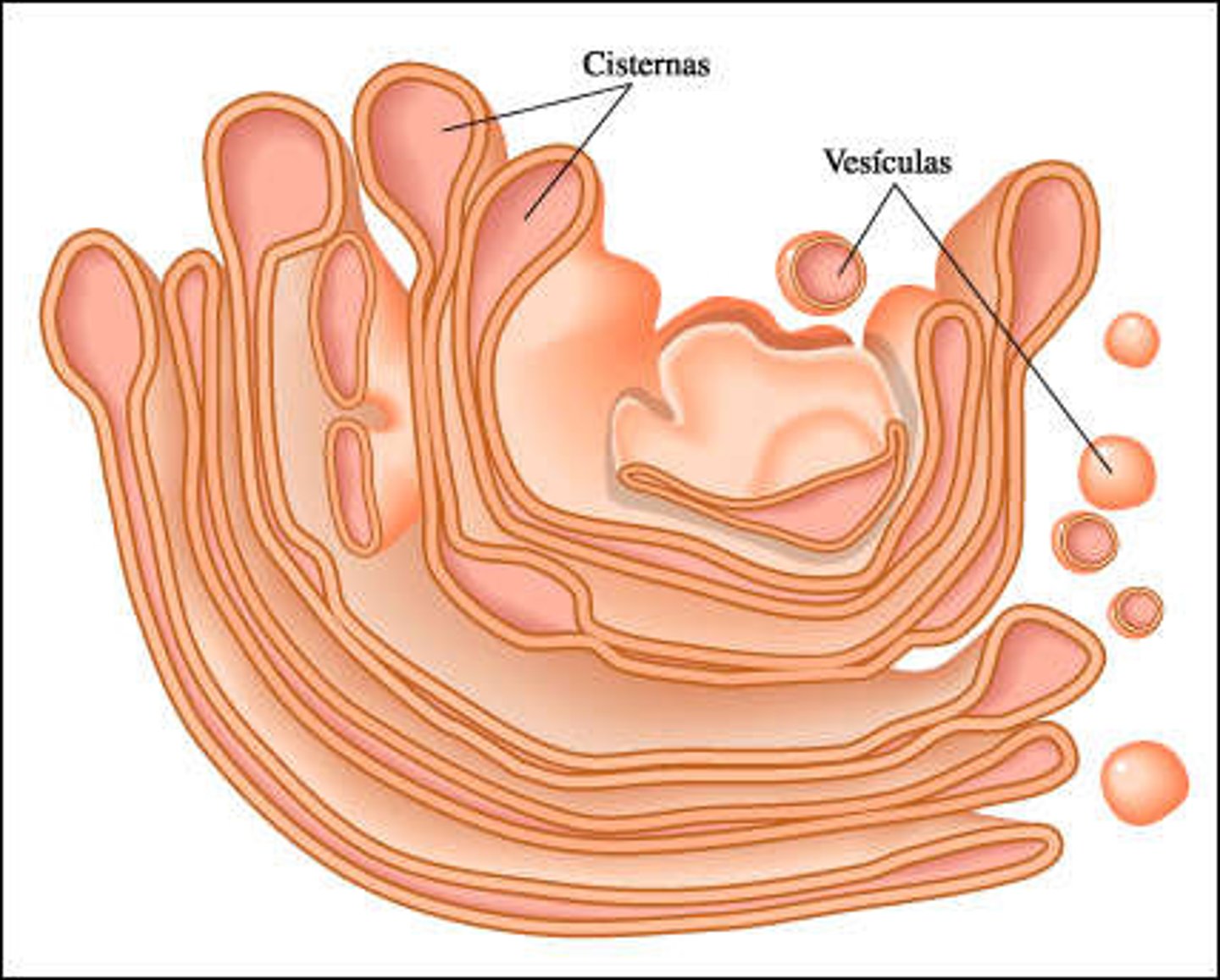
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of stacks of membranous that sort and process lipids and proteins for distribution
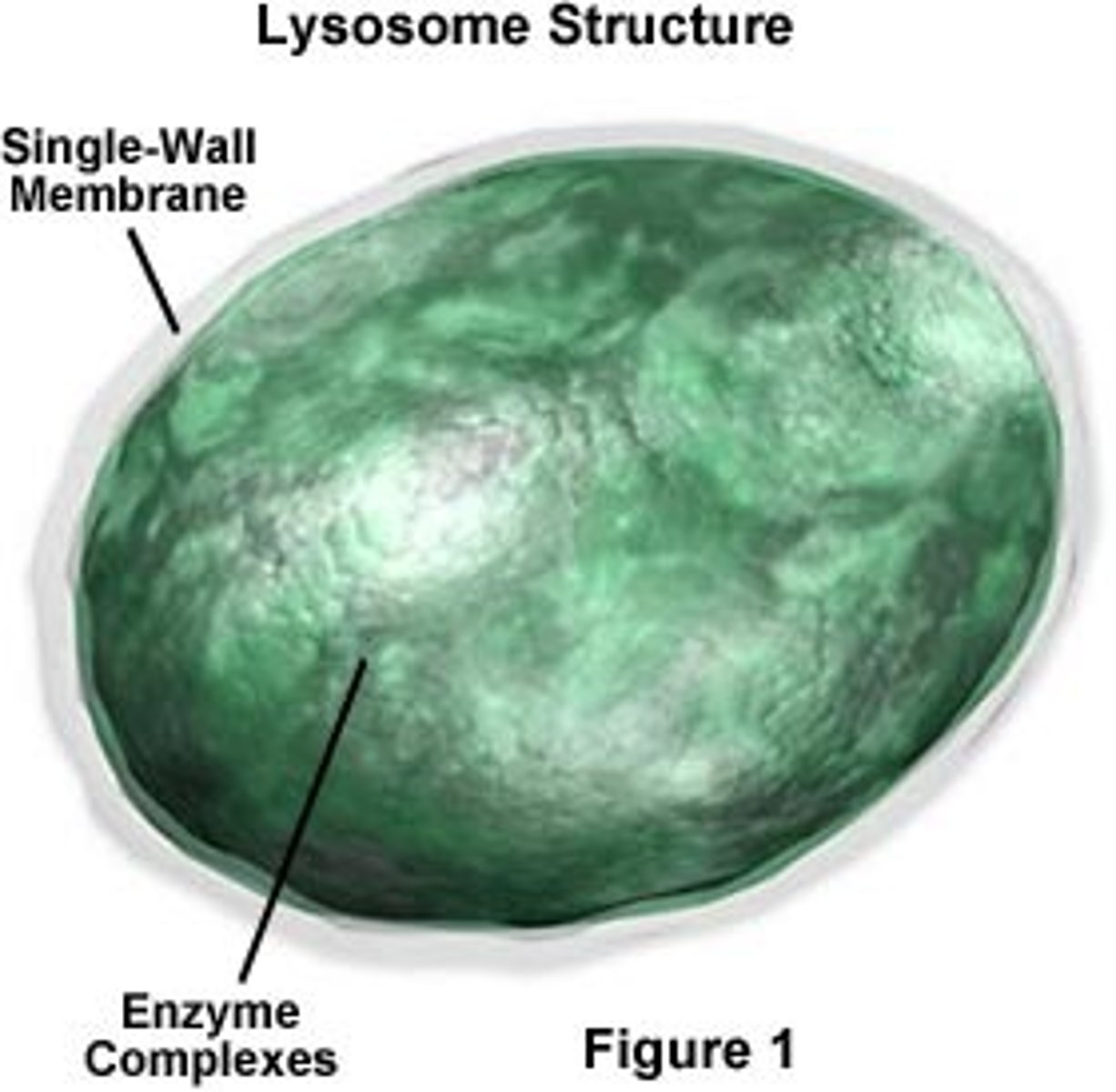
Lysosome
An organelle in an animal cell contains digestive enzymes that can break down proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides
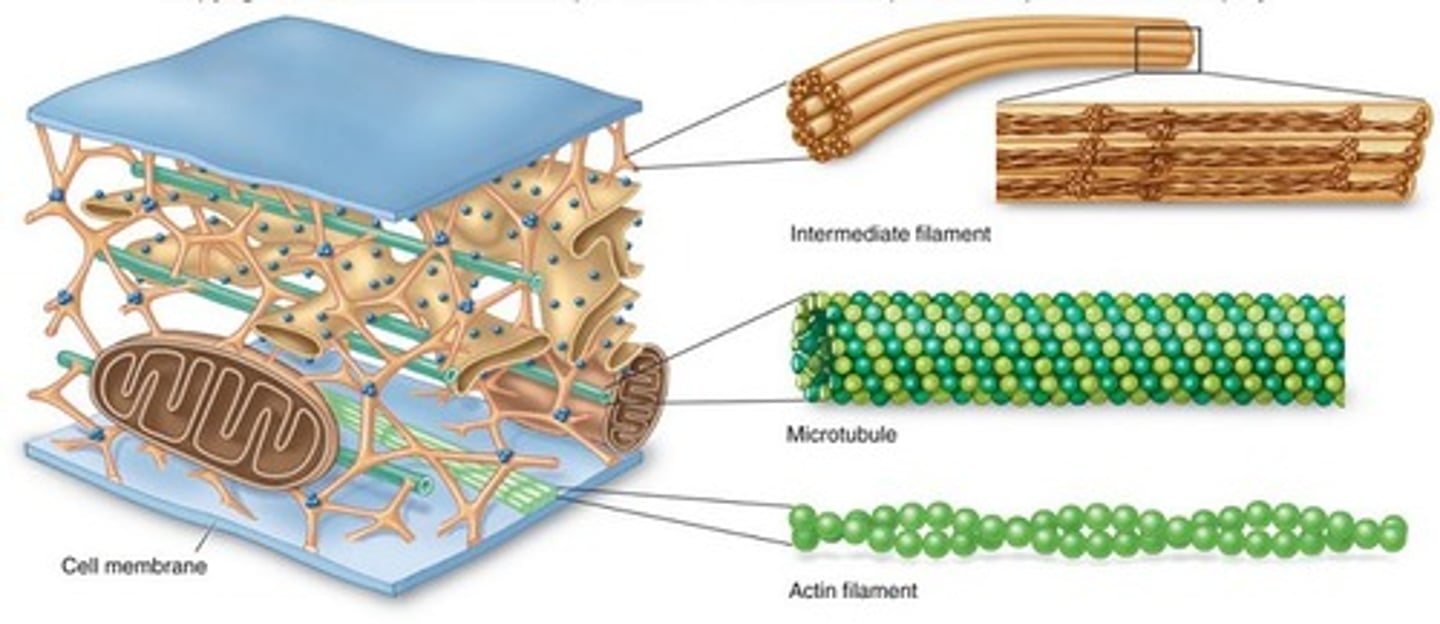
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers that helps the cell maintain its shape, secures organelles in their place, allows cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enables the unicellular organisms to move
Cilia
A short, hair-like structures that extends from the plasma membrane that move a cell or substances through its surroundings or move fluid over the cell's surface
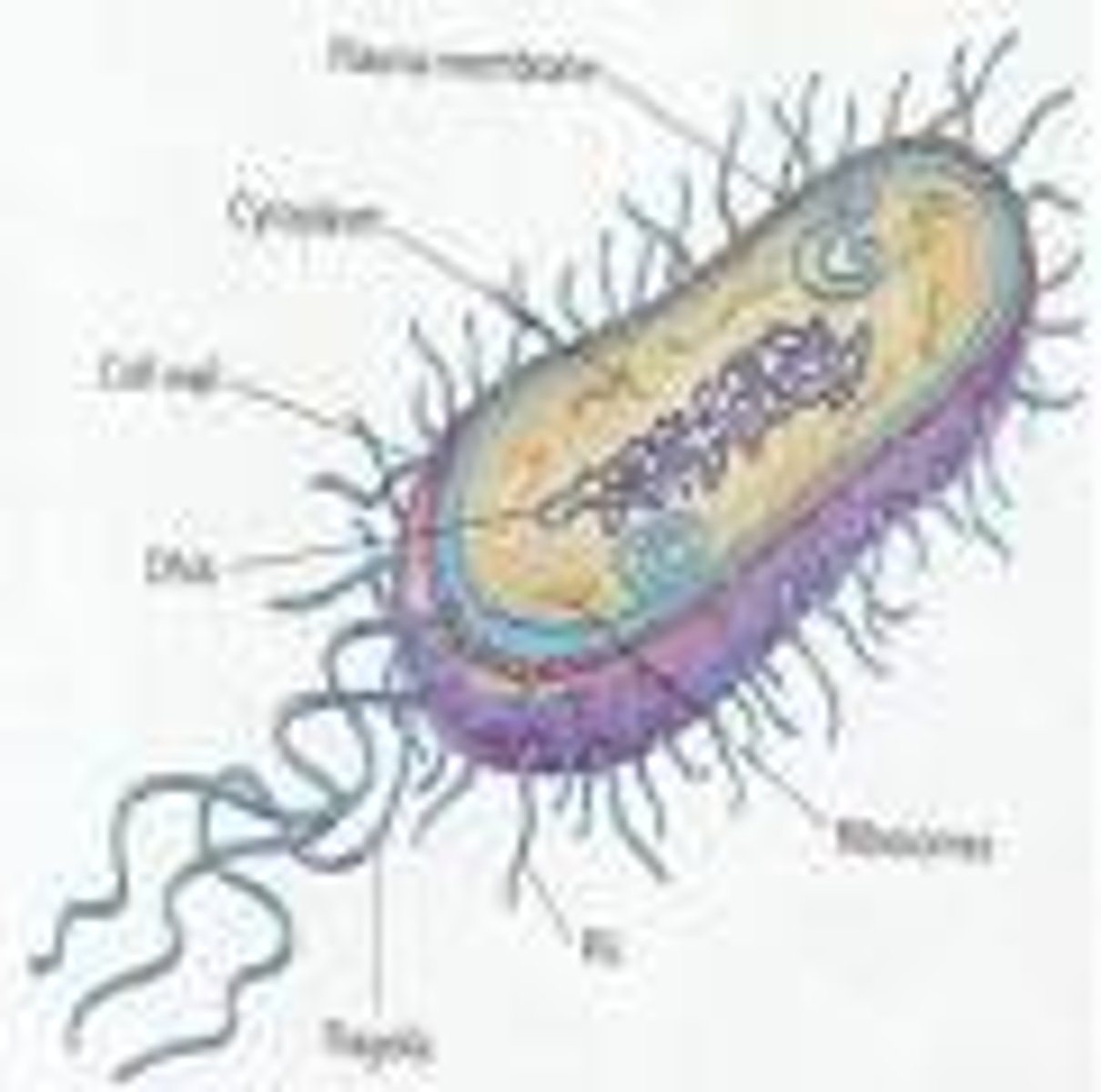
Flagella
A long, hair-like appendage specialized for locomotion in an extension of plasma membrane.