Water balance + Hydrographs
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How can the balance of a river level be described?
Dynamic (constantly changing). This means river levels rise and fall depending on precipitation.
Explain surplus in a river.
Precipitation is greater than evapotranspiration
The soil refills with water (soil moisture recharge)
The soil becomes saturated (soil moisture surplus)
Explain deficit in a river.
Evapotranspiration is greater than precipitation
The soil dries out (soil moisture utilisation)
The soil becomes fully dry (soil moisture deficit)
In what season does deficit in rivers usually occur?
Summer.
In what season does surplus in rivers usually occur?
Winter.
What does a water balance graph look like?
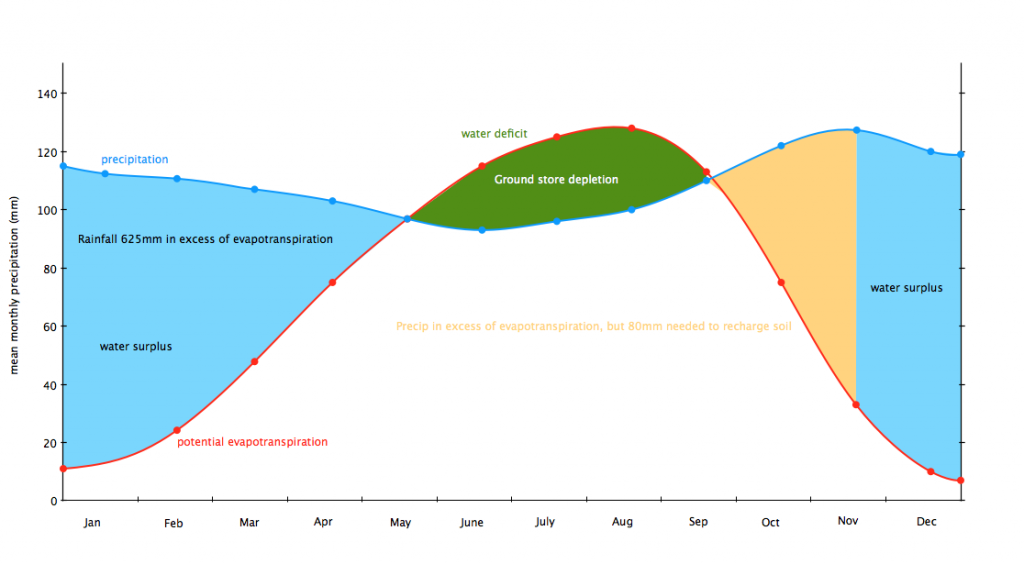

What is the other name for water balance?
Water budget.
What is the equation to find precipitation?
Precipitation = streamflow + evapotranspiration ± change in storage
What is a hydrograph?
A graph used to display changes in different factors during and after a storm event.
Define baseflow.
The level of the water in a river when it doesn’t rain.
Define discharge.
The volume of water in a river.
What is one Cumec equal to?
1 m³s^-1
What is the rising limb?
The period of time when river discharge is rising (on a hydrograph).
What is the falling limb?
The period of time where river discharge is falling (on a hydrograph).
What is peak rainfall?
The highest precipitation during a storm event.
What is peak discharge?
The highest discharge during a storm event.
What is lag time?
The time between peak rainfall and peak discharge.
What is bank full discharge?
The level of discharge where a river’s banks are completely full.
What is storm flow?
The amount of water produced by a storm event.
What is a flashy hydrograph?
A hydrograph with a high peak discharge and a short lag time, which usually results in a flood.
What is a subdued hydrograph?
A hydrograph with a low peak discharge and a long lag time, which usually results in little to no flooding.
Flood Hydrograph:
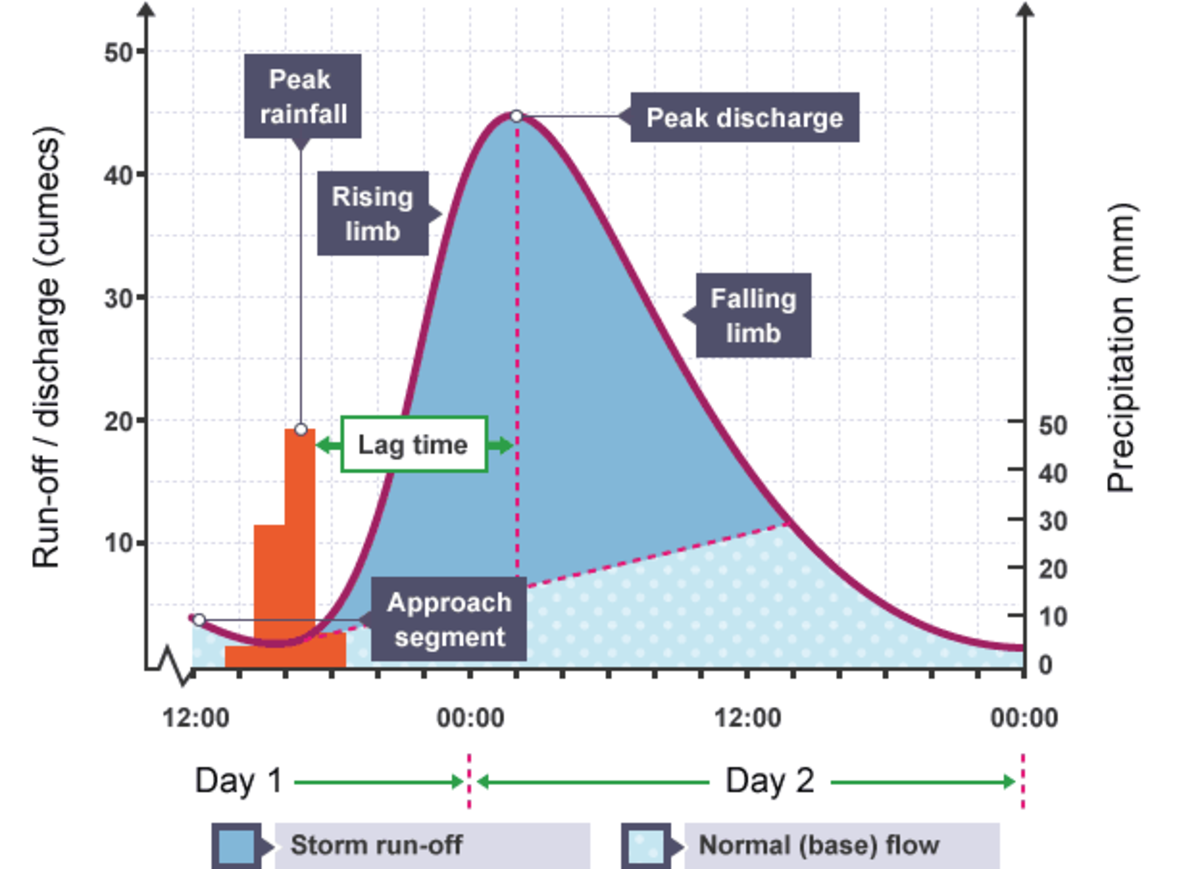

How does gradient affect lag time and discharge?
Water flows and the river quicker with a steeper gradient
Therefore, drainage basins with steeper sides have flashier hydrographs
Water moves quicker both in throughflow and overland flow
What is antecedent rainfall?
Rainfall that occurs before a storm event.
How does antecedent rainfall affect lag time and discharge?
If the drainage basin is already saturated, there is a lower infiltration capacity
This causes an increase in overland flow
Overland is the fastest transfer of water overall, so lag time is significantly reduced
This results in a flashy hydrograph
How does the soil/rock type affect lag time and discharge?
Impermeable rock causes increased overland flow and reduced throughflow and infiltration
This leads to a flashy hydrograph
Surfaces baked hard or frozen behave similarly to impermeable rock types
Drainage basins underlain by porous rocks such as sandstone have more subdued hydrographs
How does vegetation affect lag time and discharge?
More vegetation increases interception
This slows rainwater movement to the ground and river channel
Water is also lost through transpiration, which reduces the final discharge
This creates a subdued hydrograph
How does the amount and intensity of precipitation affect lag time and discharge?
Heavy rainfall in a short time increases discharge
This results in a flashier hydrograph
How does the type of precipitation affect lag time and discharge?
The lag time for snow > the lag time for rain
This is because snow must take the time to melt before entering the channel
If snow melts rapidly, peak discharge could still be high
What defines a high drainage density?
A basin with a high drainage density has a lot of surface streams acting as tributaries to the main river.
How does drainage density affect lag time and discharge?
Basins with a higher drainage density have flashier hydrographs
All the water will arrive at the main river at roughly the same time, increasing peak discharge
How does basin size affect lag time and discharge?
Large drainage basins catch more precipitation
This means they have higher peak discharge
Small basins have shorter lag times because the water doesn’t travel as far
How does deforestation affect lag time and discharge?
Deforestation reduces interception rates, so water hits the ground directly
A lack of roots increases infiltration
This leads to rapid overland flow and flashy hydrographs
Soil exposed by deforestation leads to erosion and sedimentation
This reduces bank full capacity and increases flood risk
How does afforestation affect lag time and discharge?
Afforestation increases interception
Infiltration is decreased by roots
This leads to a more subdued hydrograph
Afforestation is a useful flood preventer
How does agriculture affect lag time and discharge?
Ploughing breaks up topsoil and increases infiltration, and causes a subdued hydrograph
Terracing on hillsides interrupts overland flow and throughflow, and causes a subdued hydrograph
Grass crops increase infiltration, and cause a subdued hydrograph
Furrows can act as tributaries, and cause a flashier hydrograph
Dense animal population compacts the soil, increasing overland flows and causing a flashier hydrograph
How does urbanisation affect lag time and discharge?
Impermeable urban areas reduce infiltration
Many urban developments are on flat flood plains
Vegetation in cities is decreasing
Urban areas cause a flashier hydrograph
How do flood alleviation schemes affect lag time and discharge?
Soft engineering flood management schemes aim to reduce flashiness in a hydrograph
Afforestation increases infiltration and interception
This slows water’s progress to the river and subdues changes in discharge
How does water abstraction affect lag time and discharge?
Water abstraction reduces baseflow
This means more water must reach the channel before it reaches bank full capacity
This reduces flooding, but is more likely to cause, for example, drought