Chapter 9 - Intelligence, and Psychological Testing
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Intelligence
Measures general mental ability/intellectual potential.

Aptitude
Specific abilities/potential
Achievement
Measures knowledge

Standardization
Procedures used to give score the test - always done the same.
Test norms
Information about how a score relates to other sources… tells you to compare to others.
Percentile Scoring
The % of people who scored at or below your score
Reliability
Refers to the consistency of the test
Correlation Coefficient
Can be used to measure the strength of the relationship between test and retest
Split-half Reliability
Compare two halves of an exam

Validity
The ability of a test to measure what it was designed to measure
Content Validity
The degree to which the content on a test matches the subject covered.
Criterion Related Validity
A measure of validity by measuring test scores with another independent criterion
Construct Validity
The extent to which there is evidence that a test measures a particular hypothetical construct questions?
Sir Francis Galton
Heredity Genius who believes that intelligence comes from heredity from the nature vs nurture correlation
Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon
Studied studies w/learning disabilities (1905)
Lewis Terman
Stanford-Binet Test
Average of 100
Still used today
David Weschler
Weschler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
Iq was too verbal IQ and performance IQ (nonverbal)
Normal distribution of scores
Mental Age
A measure based on child’s ability compared to the mental ability of a typical child of a certain age.

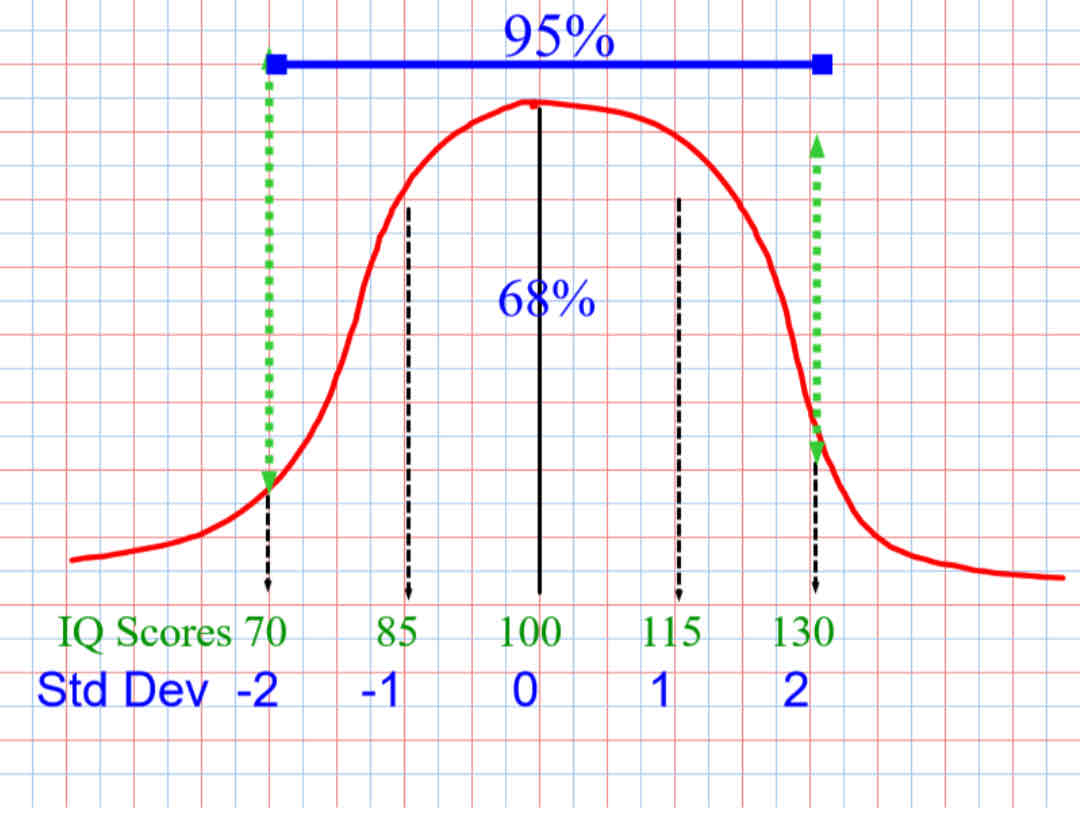
Which side is declared for gifted genus?
The right
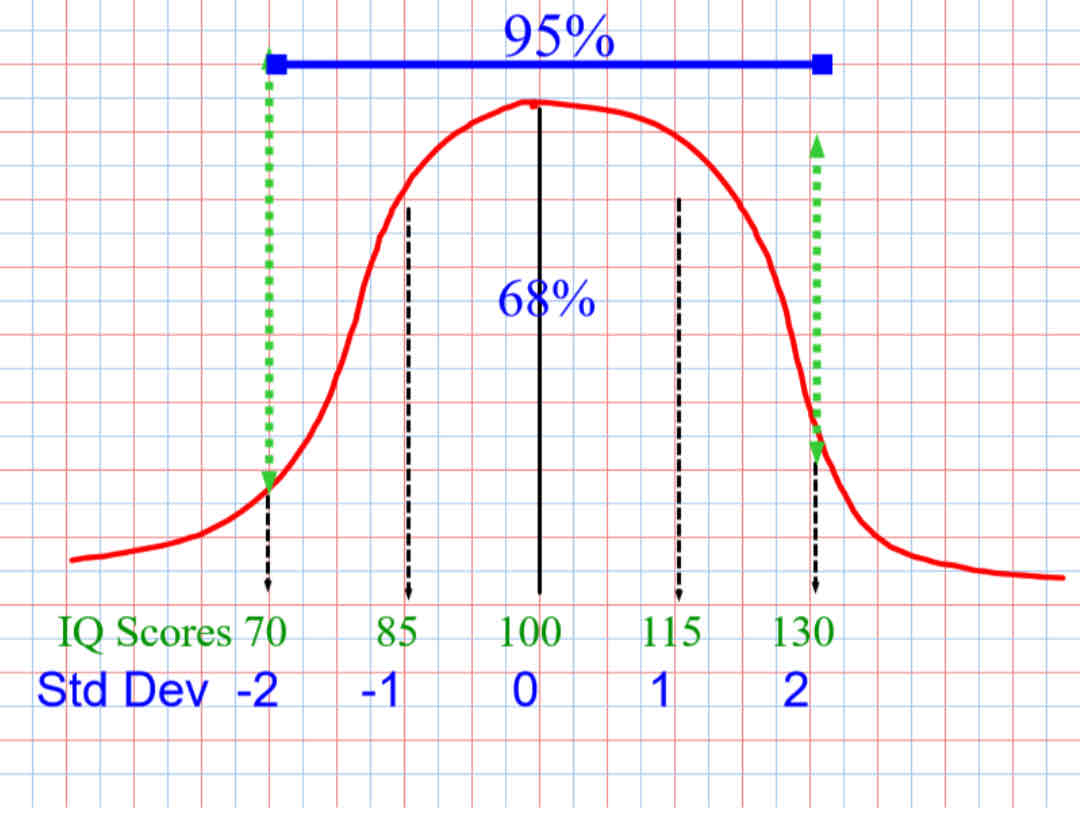
Which side is for the intellectual disabilities
The left
Average IQ is
100
100 = ?
100 = 50%
1 standard deviation is
15
How is the percentage between the green lines?
95%
Giftedness characteristics
Defined by an IQ but other characteristics are used.
Gifted individuals are usually above average in physical, mental and social/emotional features.
Stereotype - Profoundly gifted (above 80) may be socially isolated

Eminece
Those achieving eminece make a genius contribution to society
Intellectual Disability Characteristics
(Formerly known as Mental Retardation) - Subaverage mental ability with issues with adaptive skills. Cutoff IQ = 70 or 75
Mild
51-70 (6th grade) - most intelligent abilities are mild
Moderate
36-50 (4th grade)
Severe
20-35 (limited speech)
Profound
0-20 (no speech)
Prevalence
21.5% with most (85%) in mild category
Causes of intellectual disabilities
Organic - “nature” from birth
Unknown - often times related to environment
Heredity (Nature)
IQ are similar from biological parents which heritability ratio accounts for 50 - 80%
Environment(Nurture)
When an adoptive child gets their iq from their adopted parent.
Generation Effect
IQ scores are rising from generation to generation that has an adjusted scale overtime. Scaled to be an average of 100
Reaction Range
genetically determined limits (low and high) on traits. About 25 points in IQ
Genetics
Differences explained by genetics/very problematic due to group is genetically superion
Field Analogy
Both sail and seed matter/environment genetic matter
Socioeconomic
Link between SES and IQ
Stereotype threat
failure based on demographics
Emotional investment and test vulnerability
“It is not how intelligent you are, it is how you are intelligent” meaning
People have different intelligences
Howard Gardner
Multiple Intelligences
Logical/mathematical
Ability to reason

Linguistic
Verbal Skills

Musical
Connection to music

Spatial (visual)
Mental manipulation of space

Bodily-kinesthetic
Movement

Interpersonal
With others socializing and working with others

Intrapersonal
Self

Naturalist
Connected to nature

Sternberg’s Facets of Intelligence
A cognitive focus on intelligence
Analytical Intelligence
Abstract reasoning, evaluation and judgement
Creative Intelligence
Ability to generate new ideas

Practical Intelligence
Dealing with everyday problems with knowledge, not explicitly taught