ROTC MS1 Final
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
React to Near Ambush
Situation: enemy firing and mass casualty
Actions on: Element under fire returns fire and charges enemy
React to Contact
Situation: Element moving in wedge formation, take contact
Actions On: Element taking contact sets up line of support by fire, Others flank enemy
Break Contact
Situation: currently in actions on, decide to retreat (due to many factors such as mass casualty)
Actions on: Bounding away till away from enemy
List ten branches in the army
aviation, infantry, signal corps, finance corps, ordnance corps, air defense artillery, corps of engineers, chemical corps, military intelligence, medical corps, quartermaster corps, armor, field artillery, military police
define and specify the uniqueness of a decisive point
A point that can continue or stop a mission
Gain advantage
Geographic location, structure, key event
Mission dependent
Troop leading procedures (TLPs)
1. Receive the Mission:
Leaders receive the initial mission or task from a higher headquarters.
2. Issue a Warning Order:
A preliminary order is issued to prepare subordinates for the upcoming mission.
3. Make a Tentative Plan:
A preliminary plan is developed based on the information available at the time.
4. Initiate Movement:
Subordinate elements begin preparing for the mission, including gathering equipment and personnel.
5. Conduct Reconnaissance:
The leader gathers more information about the area of operation and the situation.
6. Complete the Plan:
The plan is finalized, incorporating the results of the reconnaissance and any new information.
7. Issue the Order:
The complete plan is issued to subordinates in the form of an operations order (OPORD).
8. Supervise and Refine:
The leader supervises the execution of the plan, making necessary adjustments to ensure success.
6 war fighting functions
Command and control
Movement and maneuver
Intelligence
fires
Sustainment
Protection
characteristics of the offense
Audacity
Bold and accept risk
Concentration
Concentrate all weapons
Surprise
Attacking at a time, place, or manor that is not expected by the enemy
Tempo
Speed and rhythm of attack to disrupt enemy plans
Keeps the initiative
What are offensive operations
Movement to contact
Attack
Exploitation
Pursuit
key principles of defensive operation
Prepared Positions: Defenders establish fortified positions to maximize their defensive strength and leverage terrain.
Security: Maintaining a security perimeter prevents enemy reconnaissance and disrupts their ability to plan and execute attacks.
Disruption: Defenders employ tactics to disrupt enemy formations and plans, making them more vulnerable.
Mass: Concentrating forces at key points to overwhelm the enemy.
Concentration: Focusing firepower and other resources on the most critical areas.
Flexibility: The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and enemy tactics
define and specify the uniqueness of mission command
Army’s approach to command and control empowers subordinate decisions and centralized execution
Mission command is a military leadership philosophy centered on empowering subordinate decision-making within a commander's intent, focusing on decentralized execution and adaptable responses to changing situations. Its uniqueness lies in its ability to foster initiative, adapt to uncertainty, and enable rapid action while maintaining control and achieving desired outcomes.
positions of an infantry rifle squad
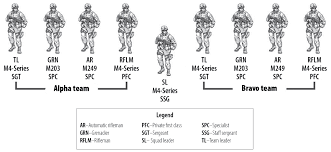
Unit symbols
Infantry
Armor
Recon
Field artillery
Engineer
Aviation