ZOOLONE Module 01-06 (Long Exam 1)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/207
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unifying Themes in Biology, The Animal Cell, Membrane Transport, Cellular Respiration, Cell Cycle, Introduction to Genetics
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
1
New cards
Evolution
- process of change that has transformed life on Earth
- results in an organism’s adaptations to its environment
- results in an organism’s adaptations to its environment
2
New cards
Order
Evolutionary adaptation
Regulation
Reproduction
Response to the environment
Growth and development
Energy Processing
Evolutionary adaptation
Regulation
Reproduction
Response to the environment
Growth and development
Energy Processing
7 Properties of Life
3
New cards
Organization, Information, Energy and matter, Interactions, & Evolution
5 Unifying Themes of Biology
4
New cards
Organization
Biosphere, Ecosystem, Communities, Population, Organism, Organs and Organ Systems, Tissues, Cells, Organelles, Molecules
5
New cards
Emergent properties
- result from the arrangement and interaction of parts within a system
- can characterize non-biological entities as well
- allows a system to be fully functional if everything falls to their perfect places
- can characterize non-biological entities as well
- allows a system to be fully functional if everything falls to their perfect places
6
New cards
Reductionism
a theory that refers to:
the reduction of complex systems to simpler components that are more manageable to study
the reduction of complex systems to simpler components that are more manageable to study
7
New cards
Systems Biology
analysis of the interactions among the parts of a biological system
8
New cards
Structure and Function
- organism’s basic unit of ___ = cell
- lowest level of organization that can perform activities required for life
- lowest level of organization that can perform activities required for life
9
New cards
Information: DNA
Genes encode info for building molecules & are units of inheritance
10
New cards
Genomics
the study of genes within and between species
11
New cards
Proteomics
the study of whole sets of proteins encoded by the genome (proteomes)
12
New cards
"High-throughput" technology
tools that can analyze many samples very rapidly
13
New cards
Bioinformatics
use of computational tools to store, organize, and analyze huge volume of data
14
New cards
Formation of interdisciplinary research teams
groups of diverse specialists
15
New cards
Energy (and matter)
- input of ___ from the sun and the transformation of ___ one form to another
- when used to perform work, some is lost to surroundings as heat
- usually enters as light, exits as heat
- when used to perform work, some is lost to surroundings as heat
- usually enters as light, exits as heat
16
New cards
Interactions
- ___ between the components of the system ensure smooth integration of all parts
- ___ of organisms and environment affect each other
- ___ of organisms and environment affect each other
17
New cards
Positive Feedback
type of feedback wherein a reaction causes another reaction
(ex. contractions during childbirth)
(ex. contractions during childbirth)
18
New cards
Negative Feedback
type of feedback wherein the system brings the organism to its original state & maintain homeostasis
(ex. change in body temp)
(ex. change in body temp)
19
New cards
Taxonomy
branch of biology that names & classifies species into groups of increasing breadth
20
New cards
Levels of Classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
21
New cards
Binomial Nomenclature
Genus species
22
New cards
3 Domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
23
New cards
Kingdoms under Domain Eukarya
Animalia, Plantae, Fungi
24
New cards
Darwin's observation
- individuals in a population vary in their traits, many of which are heritable
- more offspring are produced than survive, and competition is inevitable
- species generally suit their environment
- more offspring are produced than survive, and competition is inevitable
- species generally suit their environment
25
New cards
Darwin's conclusion (Natural Selection)
- individuals are best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce
- over time, more individuals in a population will have advantageous traits
- over time, more individuals in a population will have advantageous traits
26
New cards
Tree of Life
“unity in diversity” arises from “descent with modification”
27
New cards
Subdisciplines of Zoology
Anatomy, Cytology, Ecology, Embryology, Genetics, Histology, Molecular Biology, Parasitology, Physiology, Systematics
28
New cards
Specialization in Zoology
Entomology, Helminthology, Herpetology, Ichthyology, Mammalogy, Ornithology, Protozoology
29
New cards
Cells
- fundamental unit of life
- can be seen using microscope
- can be seen using microscope
30
New cards
Light Microscope
- a type of microscope with visible light passing through a specimen and then through the glass lenses
- can magnify up to about 1000x the size of the actual specimen
- can magnify up to about 1000x the size of the actual specimen
31
New cards
Electron Microscope
- a type of microscope used to study subcellular structures
32
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
type of electron microscope that focuses the electron beams on the surface of the specimen
33
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
type of electron microscope that is used to study internal structures of cells
34
New cards
Cell Fractionation
- process that takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from another
- enables scientists to determine the function of each organelles
- enables scientists to determine the function of each organelles
35
New cards
Centrifugation
the process of separating organelles of different densities inside a test tube by the use of a centrifuge
36
New cards
Prokaryotic Cell
type of cell:
NO true nucleus
LACKS nuclear membrane
genetic material in nucleic region
NO membrane-bound organelles
cytoplasm is bound by plasma membrane
NO true nucleus
LACKS nuclear membrane
genetic material in nucleic region
NO membrane-bound organelles
cytoplasm is bound by plasma membrane
37
New cards
Eukaryotic Cell
type of cell:
with true nucleus
bounded by nuclear envelope
genetic material within nucleus
contains cytoplasm with cytosol and membrane-bound organelles
with true nucleus
bounded by nuclear envelope
genetic material within nucleus
contains cytoplasm with cytosol and membrane-bound organelles
38
New cards
Basic Features of All Cells
Plasma Membrane, Cytosol, Chromosomes, Ribosomes
39
New cards
Plasma Membrane
organelle:
- selective barrier that allows a sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell
- bi-layer of phospholipids
- selective barrier that allows a sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell
- bi-layer of phospholipids
40
New cards
Nucleus
organelle:
- information central
- contains most of the cell’s genes
- most conspicuous organelle
- information central
- contains most of the cell’s genes
- most conspicuous organelle
41
New cards
Nuclear envelope
organelle:
- encloses nucleus
- separates nucleus from cytoplasm
- encloses nucleus
- separates nucleus from cytoplasm
42
New cards
nuclear membrane
part of nucleus:
- a double membrane
- each membrane consists of a lipid bilayer
- a double membrane
- each membrane consists of a lipid bilayer
43
New cards
nucleolus
- located within nucleus
- may vary in numbers
- the site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
- may vary in numbers
- the site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
44
New cards
Nuclear pores
part of nucleus that regulates entry and exit of molecules
45
New cards
nuclear lamina
- lines nuclear envelope
- maintains shape of nucleus
- composed of proteins
- maintains shape of nucleus
- composed of proteins
46
New cards
Ribosomes
organelle:
- protein factories
- complexes made of ribosomal RNA & protein
- carries protein synthesis in cytosol and outside the ER
- protein factories
- complexes made of ribosomal RNA & protein
- carries protein synthesis in cytosol and outside the ER
47
New cards
Endomembrane System
system in a cell that:
- regulates protein traffic & performs metabolic functions
- made up of:
- nuclear envelope
- endoplasmic reticulum
- golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- vacuoles
- plasma membrane
- regulates protein traffic & performs metabolic functions
- made up of:
- nuclear envelope
- endoplasmic reticulum
- golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- vacuoles
- plasma membrane
48
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
organelle:
- biosynthetic factory
- accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
- continuous with the nuclear envelope
- biosynthetic factory
- accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
- continuous with the nuclear envelope
49
New cards
Smooth ER
type of ER that:
- lacks ribosomes
- synthesizes lipids
- metabolizes carbs
- detoxifies drugs & poisons
- stores calcium ions
- lacks ribosomes
- synthesizes lipids
- metabolizes carbs
- detoxifies drugs & poisons
- stores calcium ions
50
New cards
Rough ER
type of ER that:
- is studded with ribosomes (secrete glycoproteins)
- distributes transport vesicles
- is the membrane factory for the cell
- is studded with ribosomes (secrete glycoproteins)
- distributes transport vesicles
- is the membrane factory for the cell
51
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
organelle:
- shipping and receiving center
- made up of flattened membranous sacs (Cisternae)
- functions:
- modifies products of the ER
- manufactures certain macromolecules
- sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
- shipping and receiving center
- made up of flattened membranous sacs (Cisternae)
- functions:
- modifies products of the ER
- manufactures certain macromolecules
- sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
52
New cards
Lysosome
organelle:
- digestive compartments
- membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
- enzymes work best in its acidic environment
- hydrolytic enzymes and ___'s membranes are made by the RER and transferred by GA for further processing
- digestive compartments
- membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
- enzymes work best in its acidic environment
- hydrolytic enzymes and ___'s membranes are made by the RER and transferred by GA for further processing
53
New cards
Phagocytosis
type of endocytosis:
- "cellular eating"
- process in which lysosomes digest food from the food vacuole
- cell engulfs a particle in the vacuole
- vacuole fuses with a lysosome to digest the particle
- "cellular eating"
- process in which lysosomes digest food from the food vacuole
- cell engulfs a particle in the vacuole
- vacuole fuses with a lysosome to digest the particle
54
New cards
Autophagy
process in which lysosomes break down damaged organelles
55
New cards
Vacuoles
organelle:
- digestive maintenance compartments
- large vesicles derived from ER & GA
- digestive maintenance compartments
- large vesicles derived from ER & GA
56
New cards
Food Vacuole
type of vacuole:
- formed by phagocytosis
- from plasma membrane
- formed by phagocytosis
- from plasma membrane
57
New cards
Contractile Vacuole
type of vacuole:
- found in freshwater protists
- pump excess water out of cell
- found in freshwater protists
- pump excess water out of cell
58
New cards
Central Vacuole
type of vacuole:
- found in mature plant cells
- NONE in animal cells
- hold organic compounds and water
- found in mature plant cells
- NONE in animal cells
- hold organic compounds and water
59
New cards
Mitochondria and Chloroplast
Pair of organelles that:
- both change energy from one form to another
- have similarities with bacteria:
- double membranes, contain free ribosomes
- both change energy from one form to another
- have similarities with bacteria:
- double membranes, contain free ribosomes
60
New cards
Mitochondria
organelle:
- sites of cellular respiration
- metabolic process that uses oxygen to generate ATP
- chemical energy conversion
- smooth outer membrane & inner membrane folded into Cristae
- inner membrane creates 2 compartments: intermembrane space & mitochondrial matrix
- sites of cellular respiration
- metabolic process that uses oxygen to generate ATP
- chemical energy conversion
- smooth outer membrane & inner membrane folded into Cristae
- inner membrane creates 2 compartments: intermembrane space & mitochondrial matrix
61
New cards
Chloroplast
organelle:
- found in plants and algae
- sites of photosynthesis
- found in plants and algae
- sites of photosynthesis
62
New cards
Endosymbiont Theory
a theory that basically shows ancestry of mitochondria and chloroplast
ancestor eukaryotic cell > engulfed a prokaryotic cell > engulfed cell > endosymbiont > mitochondria > chloroplast
ancestor eukaryotic cell > engulfed a prokaryotic cell > engulfed cell > endosymbiont > mitochondria > chloroplast
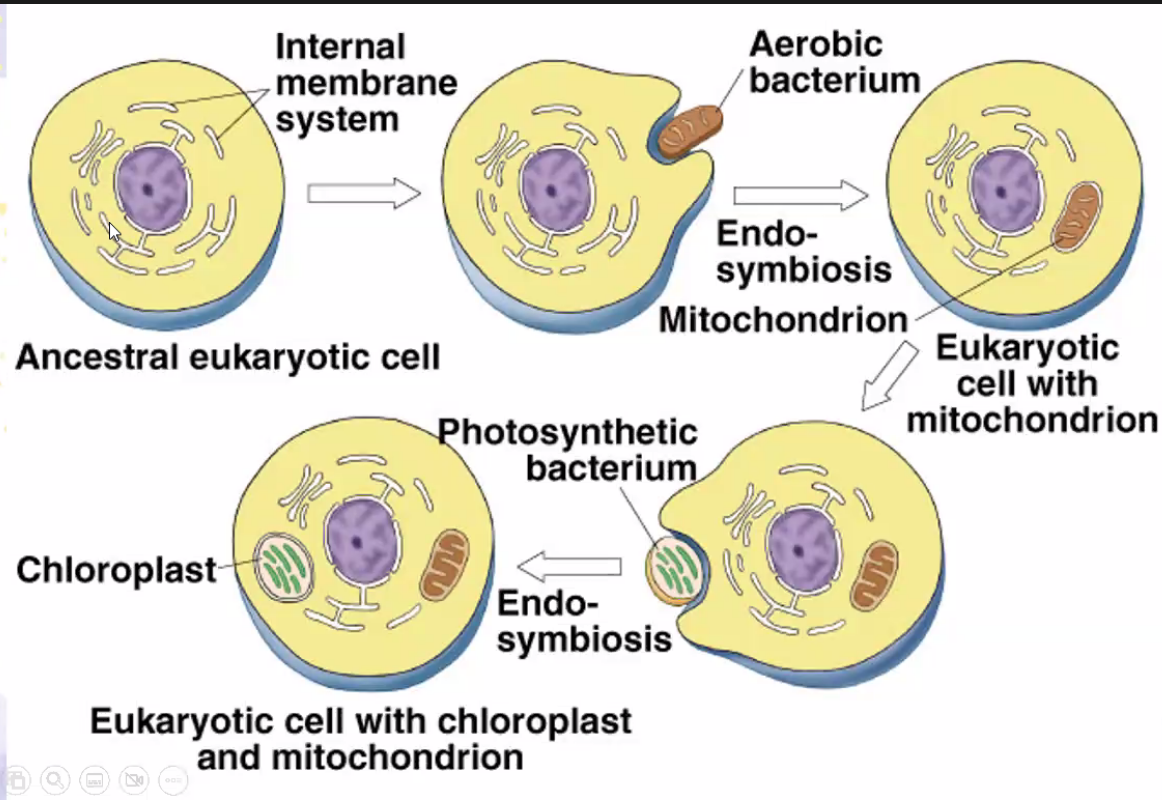
63
New cards
Peroxisomes
organelle:
- specialized metabolic compartments
- produce hydrogen peroxide and convert to water
- unknown relationship with other organelles
- specialized metabolic compartments
- produce hydrogen peroxide and convert to water
- unknown relationship with other organelles
64
New cards
Cytoskeleton
organelle:
- network of fibers that organizes structures & activities in the cell
- help support the cell and maintain its shape
- 3 types: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments:
- network of fibers that organizes structures & activities in the cell
- help support the cell and maintain its shape
- 3 types: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments:
65
New cards
microtubules
type of cytoskeleton:
- thickest of the 3 cytoskeleton compartments
- hollow tubes
- functions: cell motility, chromosome movement, & organelle movement
- centrosome has a pair of centrioles, each with 9 triplets of ___ arranged in a ring
- seen in cilia & flagella
- thickest of the 3 cytoskeleton compartments
- hollow tubes
- functions: cell motility, chromosome movement, & organelle movement
- centrosome has a pair of centrioles, each with 9 triplets of ___ arranged in a ring
- seen in cilia & flagella
66
New cards
Dynein
motor protein that drives the bending movements of a cilium or flagellum
67
New cards
Microfilaments
type of cytoskeleton:
- actin filaments
- thinnest
- functions:
- changes in cell shape
- muscle contraction
- cell motility
- division of animal cells
- actin filaments
- thinnest
- functions:
- changes in cell shape
- muscle contraction
- cell motility
- division of animal cells
68
New cards
Intermediate filaments
type of cytoskeleton:
- fibers w diameters in a middle range
- fibrous proteins coiled into cables
- function:
- anchorage of nucleus and some organelles
- formation of nuclear lamina
- fibers w diameters in a middle range
- fibrous proteins coiled into cables
- function:
- anchorage of nucleus and some organelles
- formation of nuclear lamina
69
New cards
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
- alternative to cell wall for animal cells
- made of glycoproteins (collagen, proteoglycans, & fibronectin)
- bind to receptor proteins (integrins) in plasma membrane
- made of glycoproteins (collagen, proteoglycans, & fibronectin)
- bind to receptor proteins (integrins) in plasma membrane
70
New cards
Tight Junctions
type of cell junction:
- member of neighboring cells pressed together
- prevents leakage of extracellular fluid
- “glue”
- member of neighboring cells pressed together
- prevents leakage of extracellular fluid
- “glue”
71
New cards
Desmosomes
type of cell junction:
- anchoring junctions
- fasten cells together into strong sheets
- “sewn together”
- anchoring junctions
- fasten cells together into strong sheets
- “sewn together”
72
New cards
Gap junctions
type of cell junction:
- "communicating junctions"
- provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
- "communicating junctions"
- provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
73
New cards
Phospholipids
- most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane
- amphipathic (hydrophilic head & hydrophobic tails)
- exist as a stable boundary between 2 aqueous compartments
- amphipathic (hydrophilic head & hydrophobic tails)
- exist as a stable boundary between 2 aqueous compartments
74
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model
a model:
- another term for plasma membrane
- fluid structure w/ various proteins embedded in it (NOT randomly distributed)
- constantly move with the flow yet not displaced
- another term for plasma membrane
- fluid structure w/ various proteins embedded in it (NOT randomly distributed)
- constantly move with the flow yet not displaced
75
New cards
Fluidity of the Membrane
- phospholipids can move within the bilayer
- mostly drift laterally
- rare for it to flip-flop transversely across the membrane
- mostly drift laterally
- rare for it to flip-flop transversely across the membrane
76
New cards
Peripheral protein
type of membrane protein that is bound to the surface of the membrane
77
New cards
Integral protein
type of membrane protein that penetrates hydrophobic core
78
New cards
Transmembrane protein
type of integral protein that spans the membrane
79
New cards
6 Major Functions of Membrane Proteins
Transport
Enzymatic activity
Signal transduction
Cell-cell recognition
Intercellular Joining
Attachment to cytoskeleton & ECM
Enzymatic activity
Signal transduction
Cell-cell recognition
Intercellular Joining
Attachment to cytoskeleton & ECM
80
New cards
Formation of Proteins
steps:
1. Formed in ER
2. carried to GA for segregation and packing into a trans phase vesicle
3. vesicle will go to plasma membrane to release proteins
1. Formed in ER
2. carried to GA for segregation and packing into a trans phase vesicle
3. vesicle will go to plasma membrane to release proteins
81
New cards
Transport Proteins
type of protein that allows passage of hydrophilic substance across membrane
82
New cards
Channel proteins
type of transport protein that is a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules can use as a tunnel
83
New cards
Aquaporin
type of channel protein that facilitates the passage of water
84
New cards
Carrier Protein
type of transport protein that bind molecules & change shape to shuttle them across membrane
85
New cards
Diffusion
type of membrane transport:
- movement of solutes from high to low concentration
- WITHOUT any energy investment
- tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space
- follow concentration gradient
- reach equilibrium
- movement of solutes from high to low concentration
- WITHOUT any energy investment
- tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space
- follow concentration gradient
- reach equilibrium
86
New cards
Osmosis
type of diffusion:
- diffusion of water across selectively permeable membrane
- low to high solute concentration
- until both sides are equal
- diffusion of water across selectively permeable membrane
- low to high solute concentration
- until both sides are equal
87
New cards
Tonicity
ability of surrounding solution to cause a cell to lose or gain water
88
New cards
Isotonic
type of solution wherein:
- the solute concentration is the same as inside the cell
- NO net movement
- the solute concentration is the same as inside the cell
- NO net movement
89
New cards
Hypertonic
type of solution wherein:
- solute concentration is greater outside the cell
- cell lose water
- becomes shriveled
- solute concentration is greater outside the cell
- cell lose water
- becomes shriveled
90
New cards
Hypotonic
type of solution wherein:
- solute concentration is less than the inside of cell
- cell gains water
- may swell or burst
- solute concentration is less than the inside of cell
- cell gains water
- may swell or burst
91
New cards
Osmoregulation
- control of solute concentrations and water balance
- needed for organisms that have problems with hypertonic or hypotonic environments
- present in freshwater & saltwater fish
- needed for organisms that have problems with hypertonic or hypotonic environments
- present in freshwater & saltwater fish
92
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
type of membrane transport:
- uses transport proteins to speed up passive movement
- uses transport proteins to speed up passive movement
93
New cards
Ion channel
type of transport protein:
- facilitates diffusion of ions
- some are known as gated channels
- open and close in response to a stimulus
- facilitates diffusion of ions
- some are known as gated channels
- open and close in response to a stimulus
94
New cards
Active Transport
type of transport:
- AGAINST concentration gradient
- requires energy (ATP)
- allows cell to maintain concentration gradients that differ than their surroundings
- uses specific proteins
- AGAINST concentration gradient
- requires energy (ATP)
- allows cell to maintain concentration gradients that differ than their surroundings
- uses specific proteins
95
New cards
Membrane Potential
- voltage difference across a membrane
- created by differences in the distribution of positive and negative ions across a membrane
- created by differences in the distribution of positive and negative ions across a membrane
96
New cards
Electrochemical Gradient
- 2 combined forces: chemical & electrical forces
- drive the diffusion of ions across a membrane
- drive the diffusion of ions across a membrane
97
New cards
Electrogenic Pump
pump wherein:
- transport protein that generates voltage across the membrane
- help store energy that can be used for cellular work
- transport protein that generates voltage across the membrane
- help store energy that can be used for cellular work
98
New cards
Sodium-Potassium pump
major electrogenic pump for animal cells
99
New cards
Proton Pump
major electrogenic pump for plants, fungi, and bacteria
100
New cards
Cotransport
type of transport:
- coupled transport by a membrane protein
- 2 different transports at once
- when active transport of a solute indirectly drives transport of other substances
- coupled transport by a membrane protein
- 2 different transports at once
- when active transport of a solute indirectly drives transport of other substances