Physics II Lesson 11: Thermodynamics Part I
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is the difference between Heat (Q) and Specific Heat (c)?
Heat (Q) is the overall change in heat for a substance.
Specific Heat (c) is the degree to which a given substance's temperature will increase based on the amount of heat added. It is the ease with which a substance will heat up.
The Specific Heat (c) for water is equal to 4186 J/kg⋅C. What does that mean?
It means that it would take 4186 J of heat energy (Q) to raise the Temperature of 1kg of water by 1°C.

What equation can be used to relate heat (Q) and Specific Heat (c)?
Q = mc∆T
Q = Heat
m = Mass
c = Specific Heat
∆T = Change in Temperature (in C or K)
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
How much Heat is absorbed when 423 grams of Copper (c = .385 J/g⋅C) goes from 22.3°C to 44.4°C (in kJ)?
(A) 3.599
(B) 35.99
(C) 359.9
(D) 3599
(A) 3.599 kJ
Q = mc∆T
Q = (423)(.385J/g⋅C)(22.1°C)
Q = approx. 4000 (actual: 3599 J)
Remember to convert to kJ!
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What equation allows you to determine the amount of energy required to cause a phase change in a certain amount of a substance?
Q = mL
Q = Heat
m = Mass
L = Latent Heat of Fusion (or Vaporization)
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
You have 4.3 kg of water (c = 4186 J/kg⋅C; L = 2260 J/kg). How much Heat would it take to convert all of the water into vapor if the current temperature of the water is 53.7°C?
(A) 1,423
(B) 843,109
(C) 1,423,675
(D) 2,143,896
(B) 843,109
Qtotal = Qheat + Qphase
Qtotal = mc∆T + mL
Qtotal = (4.3)(4186)(100-53.7) + (4.3)(2260)
Qtotal = (approx. 800,000 (actual: 833,390.74)) + (approx. 9,000 (actual: 9,718))
Qtotal = (approx. 809,000 (actual: 843,108.74))
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
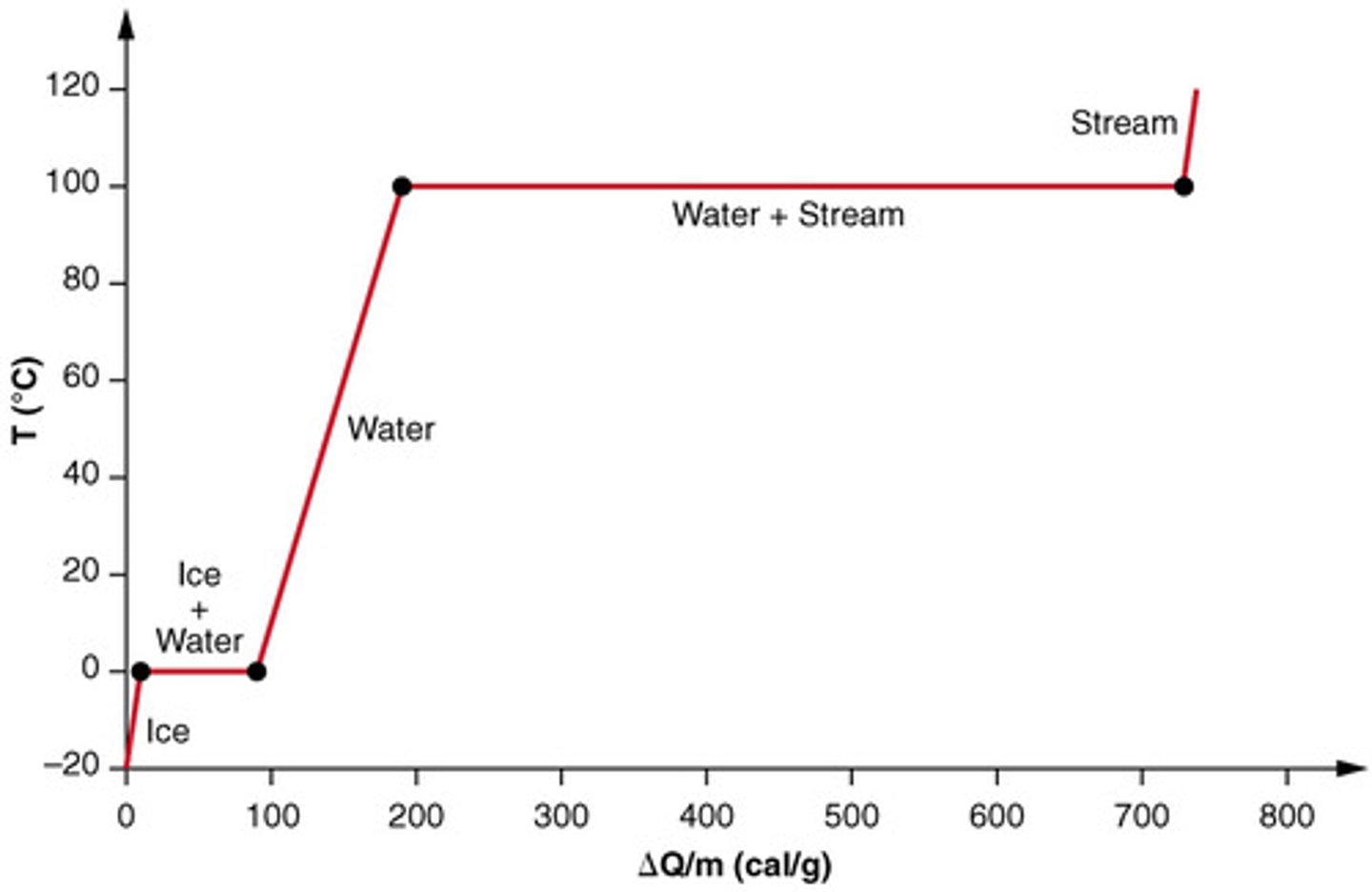
Draw a diagram of Q (x-axis) and T (y-axis) as you heat up ice from -20°C to 120°C.
The 0th Law of Thermodynamics states that if A is in Thermal Equilibrium with B and B is in Thermal Equilibrium with C; therefore, C must be in thermal equilibrium with:
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
(A) A
The 0th Law of Thermodynamics states that if A is in Thermal Equilibrium with B and B is in Thermal Equilibrium with C; therefore, C must be in thermal equilibrium with A.
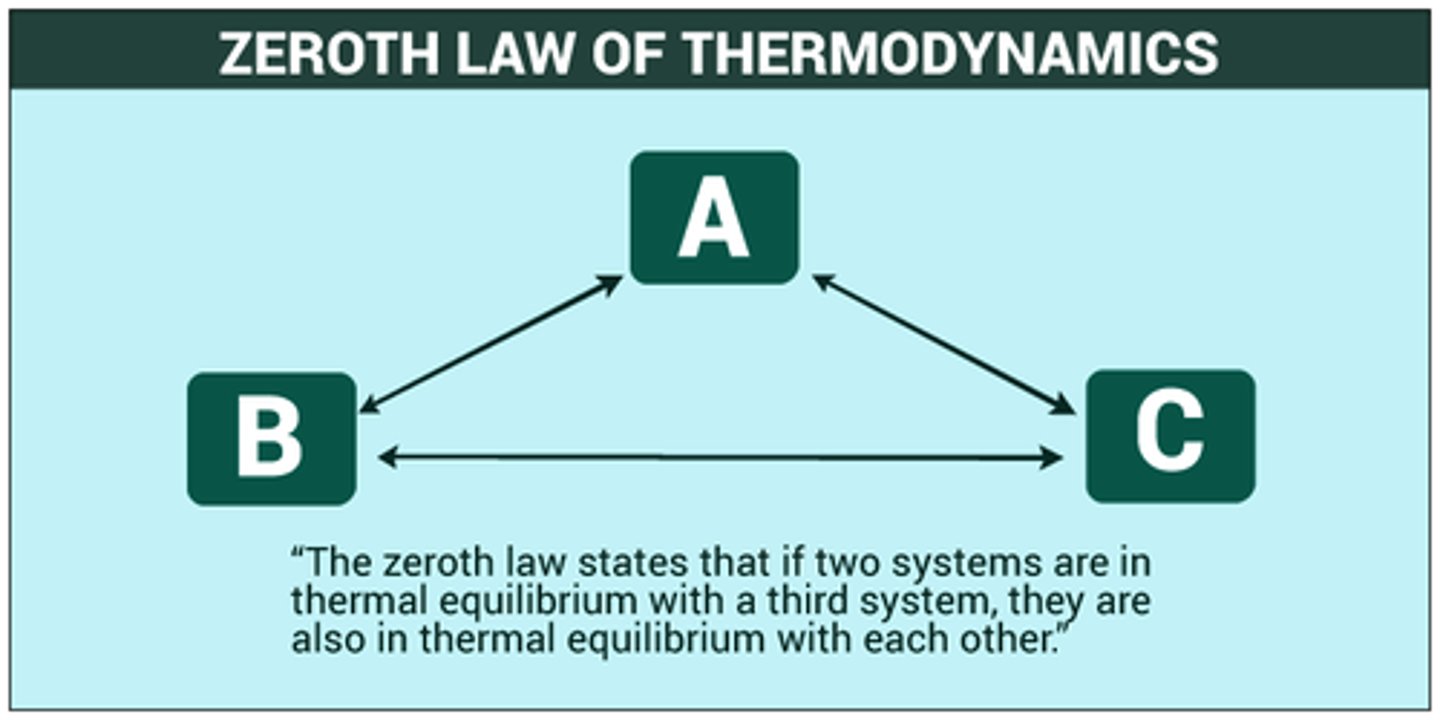
CRB Which of the following statements about the 0th Law of Thermodynamics are true?
I. This establishes Temperature as a Phase Function.
II. This establishes Temperature as a fundamental property of matter
III. For Thermal Equilibrium to occur, the objects must be in contact and heat must pass.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(B) II only
Each of the following statements about the 0th Law of Thermodynamics are true:
I. This establishes Temperature as a State Function.
II. This establishes Temperature as a fundamental property of matter
III. For Thermal Equilibrium to occur, the objects must be in contact, meaning that heat is able to pass, but no heat actually will pass.
CRB Which of the following is NOT one of the three mechanisms that Heat Transfer can use?
(A) Conduction
(B) Radiation
(C) Ionization
(D) Convection
(C) Ionization
The 3 mechanisms that Heat Transfer can use are Conduction, Convection and Radiation.
CRB Which of the three mechanisms of Heat Transfer relies upon energy that is carried by electromagnetic waves, and can occur over long distances?
(A) Conduction
(B) Radiation
(C) Ionization
(D) Convection
(B) Radiation
Radiation is when the thermal energy is carried by electromagnetic waves before heat transfer, and can occur over long distances.
CRB Which of the three mechanisms of Heat Transfer relies upon transfer caused by the motion of a fluid?
(A) Conduction
(B) Radiation
(C) Ionization
(D) Convection
(D) Convection
Convection relies upon the movement of fluids for Heat Transfer to occur.
CRB Which of the three mechanisms of Heat Transfer relies upon the actual collisions of molecules from different objects?
(A) Conduction
(B) Radiation
(C) Ionization
(D) Convection
(A) Conduction
Conduction relies upon the actual collisions of molecules from different objects for heat transfer to occur.
CRB A convection oven uses heating elements to convert electrical energy to thermal energy, and then the movement of air in the oven can disperse that energy while it is pre-heating. Then, I put my meatloaf in and the air particles bombard the pan and meatloaf, increasing its temperature and cooking the meatloaf! Which mechanisms of heat transfer were used here?
I. Convection
II. Conduction
III. Radiation
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
Convection was used when pre-heating the oven, and the heat transfer was mediated by hot air flowing away from the heating element.
Conduction was used when the air particles collided with the pan and meatloaf, increasing the temperature of the meatloaf.
When energy is added to a gas particle, the energy can be manifested in all the following ways except for which one?
(A) Translational Kinetic Energy
(B) Rotational Kinetic Energy
(C) Thermal Kinetic Energy
(D) Vibrational Kinetic Energy
(C) Thermal Kinetic Energy
When energy is added to a gas particle, the energy can be manifested in the three following ways:
(1) Translational Kinetic Energy
(2) Rotational Kinetic Energy
(3) Vibrational Kinetic Energy
How does the Internal Energy (U) of a gas relate to these three energies?
Internal Energy (U) = Translational Kinetic Energy + Rotational Kinetic Energy + Vibrational Kinetic Energy
The First Law of Thermal Dynamics describes how the Internal Energy of a gas can be changed. What equation exemplifies this law?
∆U = Q + W
∆U = Internal Energy of the gas
Q = Heat added to gas
W = Work done on the gas
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB True or false? Work is a transfer of mechanical energy out of a system into the environment.
False. Work is a transfer of mechanical energy into or out of a system, which goes from or to the environment.
CRB When talking about Thermodynamics, it is important to clarify what the System is and what the Surroundings/Environment are. Compare the two.
The System is the group of objects (or single object) that you are considering, whereas the Surroundings/Environment are all of the objects and forces outside of the system.
CRB Compare Heat (Q) and Temperature (T) in terms of thermal energy.
Heat is the Transfer of thermal energy between a system and its environment, whereas Temperature is the macroscopic features of having different thermal energy levels (i.e. a high temperature feeling "hot" and having high thermal energy).
CRB Fill in the blanks: If ____________ is increasing the thermal energy in the system, then the temperature of that system is _______________.
(A) Kinetic Energy, Increasing
(B) Kinetic Energy, Decreasing
(C) Heat, Increasing
(D) Heat, Decreasing
(C) Heat, Increasing
If Heat is increasing the thermal energy in the system, then the temperature of that system is Increasing.
CRB Within a system, which of the following are possible?
I. Energy increases without the Surroundings changing
II. Energy is Destroyed
III. Energy is transformed from one form to another
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) III only
According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, Energy cannot be Created (I) nor Destroyed (II), only transformed from one form to another.
CRB When energy goes from the system to the environment caused by friction or air resistance, in what form does that energy enter the environment?
(A) Nuclear
(B) Rotational
(C) Thermal
(D) Chemical
(C) Thermal
When energy goes from the system to the environment caused by friction, that energy enters the environment as thermal energy.
45.3 J of work is done on a certain gas, and gains 32.6 J of heat from its surroundings. By how much did its Internal Energy change?
(A) -77.9
(B) -12.7
(C) 12.7
(D) 77.9
(D) 77.9
∆U = ∆Q + ∆W
∆U = 32.6 + 45.3
∆U = 32.6 + 45.3
∆U = 77.9
Note that work done on a gas adds energy to the system, whereas work done by a gas subtracts energy from the system.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
As the Internal Energy of a gas increases, what happens to the temperature of the gas?
As the Internal Energy of a gas increases, the temperature of the gas also increases.
CRB Which of the following would increase the energy in the system? Which would increase the energy in the surroundings?
- Work done on a system
- Work done by a system
- Heat into a system
- Heat out of a system
Increasing the energy of the system:
- Work done on a system
- Heat into a system
Increasing the energy of the surroundings:
- Work done by a system
- Heat out of a system
The area under the curve on a PV diagram is equal to what? What equation does this relate to?
The area under the curve on a PV diagram is equal to work according to the relationship W = P∆V where:
W = Work done to/by the gas.
P = Pressure
∆V = Change in Volume
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
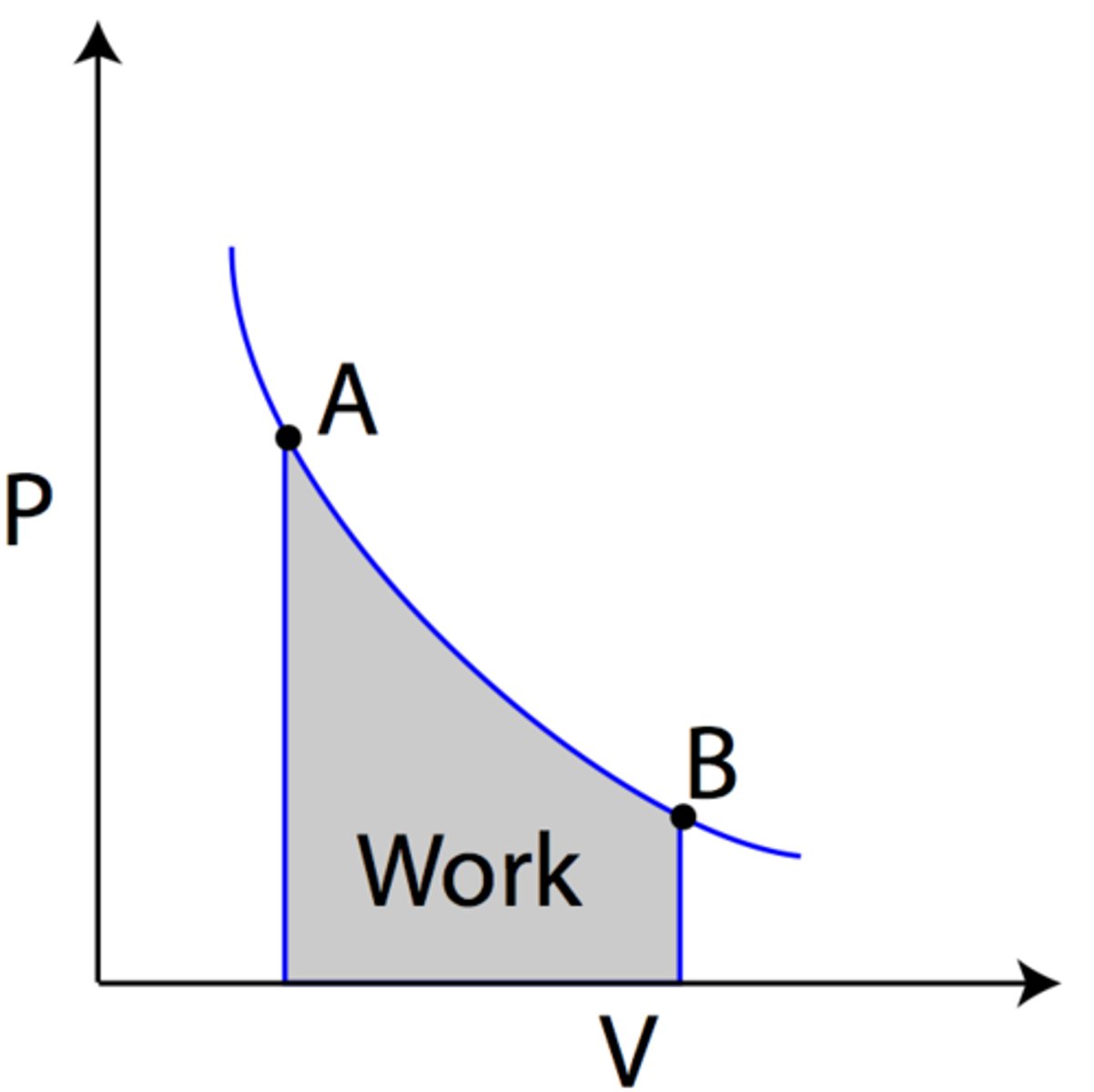
CRB Fill in the blanks: According to most conventions, W is positive if work is done ____________ the system, and is negative if work is done _____________ the system.
(A) By, On
(B) On, By
(C) By, By
(D) On, On
(B) On, By
According to most conventions, W is positive if work is done On the system, and is negative if work is done By the system.
You look at a PV diagram and notice that the pressure increases from 12.5 atm to 34.6 atm while the Volume decreases from 55.6 L to 35.4 L. Can we use the W = -P∆V equation to solve for the work done? Explain.
No, the W = -P∆V equation cannot be used here because this equation only works for isobaric systems. Since both pressure and volume are changing here, the work could only be found by integrating or estimating the area under a PV curve on a graph.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
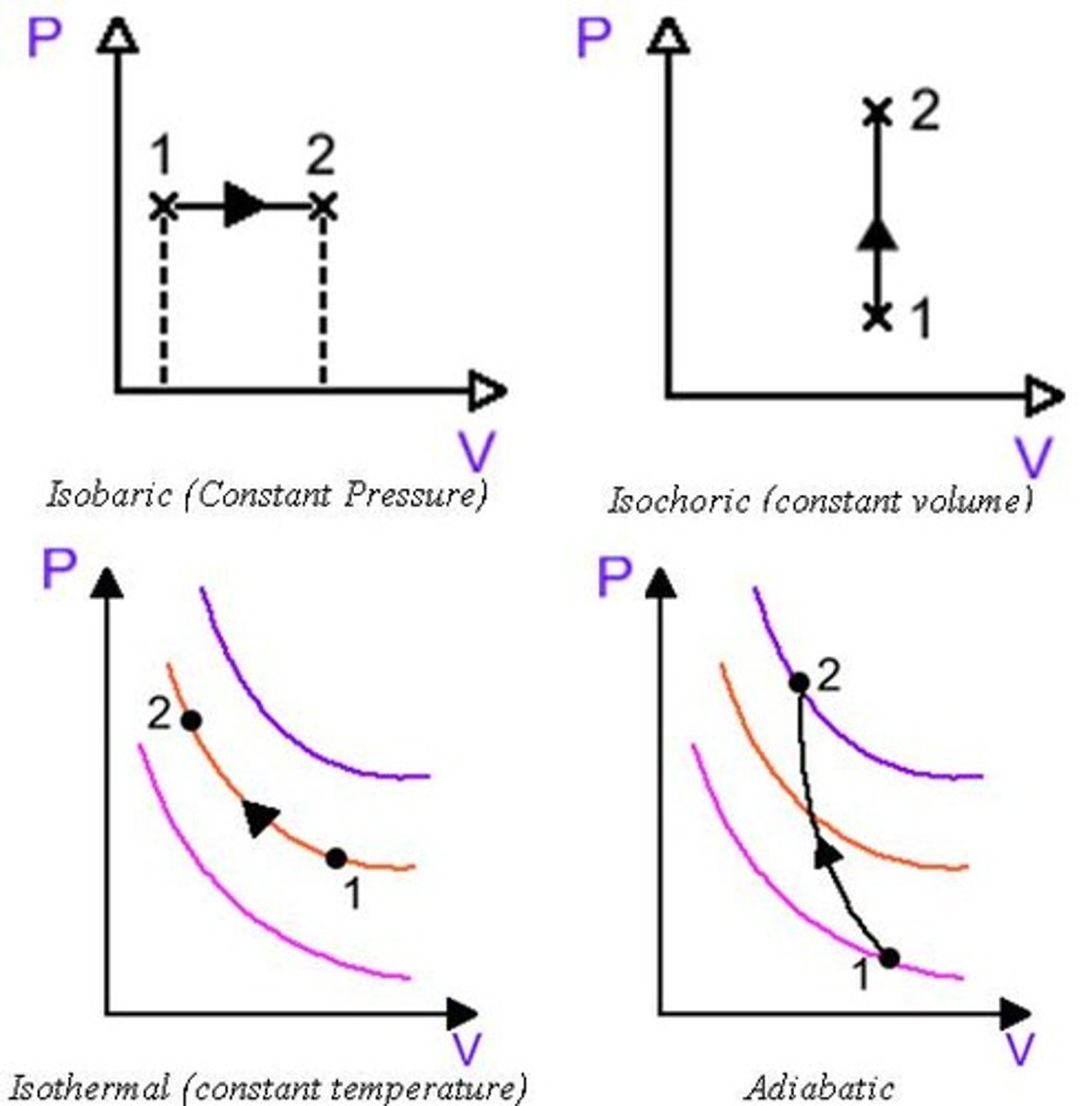
Draw the PV diagram for the four main process types:
(1) Isobaric
(2) Isochoric
(3) Isothermal
(4) Adiabatic
CRB True or false? When the temperature of all materials increase, there is a tendency for the materials to want to expand, which is called Thermal Expansion.
False. When the temperature of MOST materials increase, there is a tendency for the materials to want to expand, which is called Thermal Expansion.
There are exceptions to this, like ice decreasing in volume as its temperature increases to form water.
What variables change in the ∆U = Q + W equation for each process?
(1) Isobaric
(2) Isochoric
(3) Isothermal
(4) Adiabatic
(1) Isobaric - W changes due to a change in V.
(2) Isochoric/metric/volumetric - W does not change due to Volume remaining constant.
(3) Isothermal - ∆U remains constant because T remains constant. W and Q also remain constant.
(4) Adiabatic - Q does not change. This is the definition of an Adiabatic process. The change of U is caused solely by a change in W.
CRB In each of the following four types of processes, one variable stays the same in the system. Match each process with its constant parameter.
(1) Isobaric
(2) Isochoric
(3) Isothermal
(4) Adiabatic
(A) Pressure
(B) Temperature
(C) Volume
(D) Heat
(1) Isobaric (A) Pressure
(2) Isochoric (C) Volume
(3) Isothermal (B) Temperature
(4) Adiabatic (D) Heat [constant at 0, there is no heat transfer at all]
CRB True or false? Knowing that Work is the integral of the PV curve, Isobaric processes do no work.
False. Knowing that Work is the integral of the PV curve, Isochoric processes do no work.
This is because there is no change in the volume (x), so there is no area under the curve (really a vertical line).
With an Adiabatic Process, in order to ensure that no heat is lost or gained, you should ____________ the container and change the volume at a very ________ speed.
(A) insulate, fast
(B) insulate, slow
(C) not insulate, fast
(D) not insulate, slow
(A) insulate, fast
With an Adiabatic Process, in order to ensure that no heat is lost or gained, you should insulate the container and change the volume at a very fast speed.
Which has a steeper PV curve? An isotherm or an adiabat?
An adiabat is steeper.
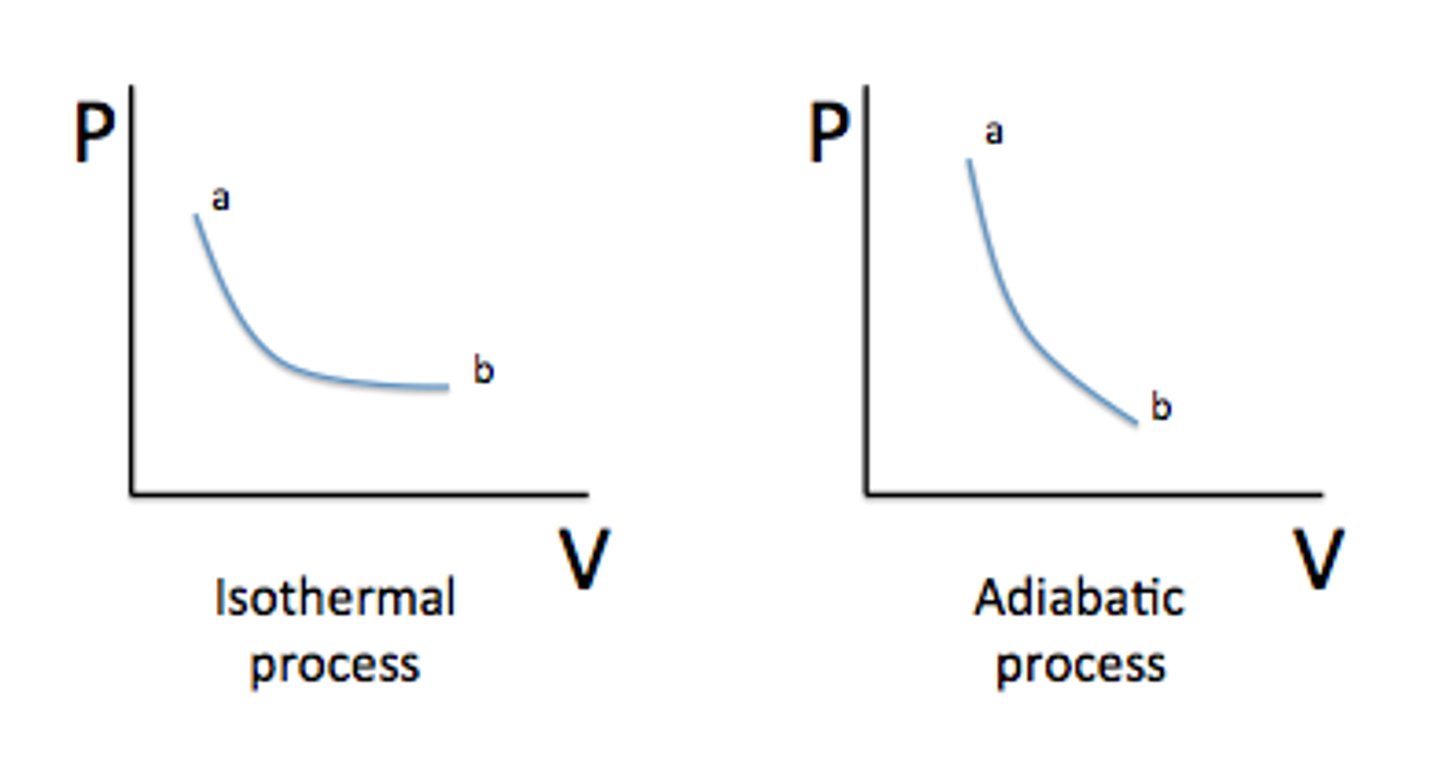
CRB Thermodynamic Cycles occur when a series of reversible processes occurs to an ideal gas. Draw a cycle that has both Adiabatic Expansion and Compression, along with Isothermal expansion and compression.
CRB Recall that Systems are a portion of the universe (an object or some group of objects) we could observe. Which of the following types of Systems cannot exchange energy or matter with its surroundings?
(A) Isolated System
(B) Closed System
(C) Open System
(D) Both A and B
(A) Isolated System
An Isolated System is not capable of exchanging energy or matter with their surroundings.
CRB Compare Open and Closed Systems in terms of what they are capable of exchanging with their surroundings.
An Open system is able to exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings. A Closed system is only able to exchange energy, but not matter, with its surroundings.