alkenes
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
what are alkenes?
unsaturated hydrocarbons (at least 1 C=C bond)
what is the general formula of an aliphatic alkene with 1 C=C bond?
CnH2n
first 3 members of the alkene homologous series:
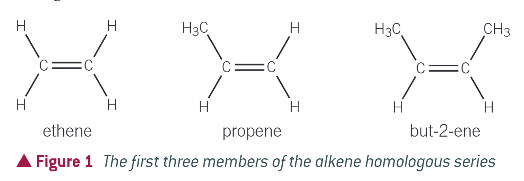
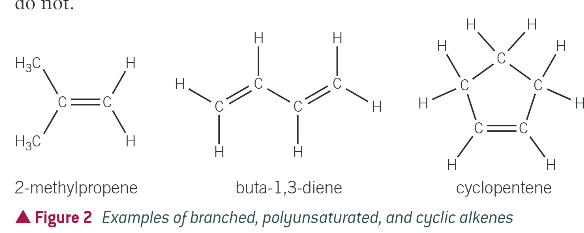
what are different ways/ types of alkenes?
branched alkenes (follow formula)
alkenes with more than 1 double bond (dont follow formula)
cyclic alkenes (dont follow formula)
each carbon atom has…
4 electrons which can form bonds
in a carbon atom in a bond bond:
¾ of the electrons are used in 3 sigma bonds (one to other carbon atom of double bond and 2 to the other atoms bonded to it)
1 electron on each carbon atom is in a p-orbital, and a pi bond is formed by the sideways overlap of the 2 p orbitals, one from each carbon atom of the double bond
where is the pi electron density concentrated?
above and below the line joining the nuclei of the bonding atoms
what does the pi bond do to the 2 carbon atoms?
locks them in position and prevents them from rotating around the double bond, making the geometry of the alkenes different from that of the alkanes, where rotation is possible
diagram to show the formation of the C=C bond in ethene:
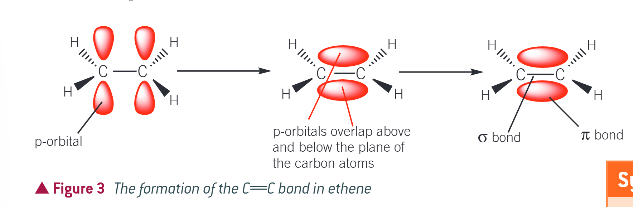
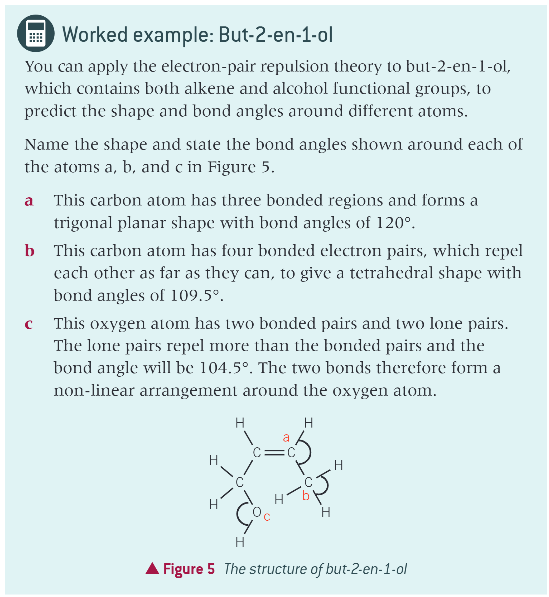
what is the shape around each of the carbon atoms in the double bond?
trigonal planar
why is it trigonal planar?
3 regions of electron density around each of the carbon atoms
the 3 regions repel each other as far apart as possible, so the bond angle around each carbon is 120
all of the atoms are in the same plane
worked example of bond shape: but-2-en-1-ol
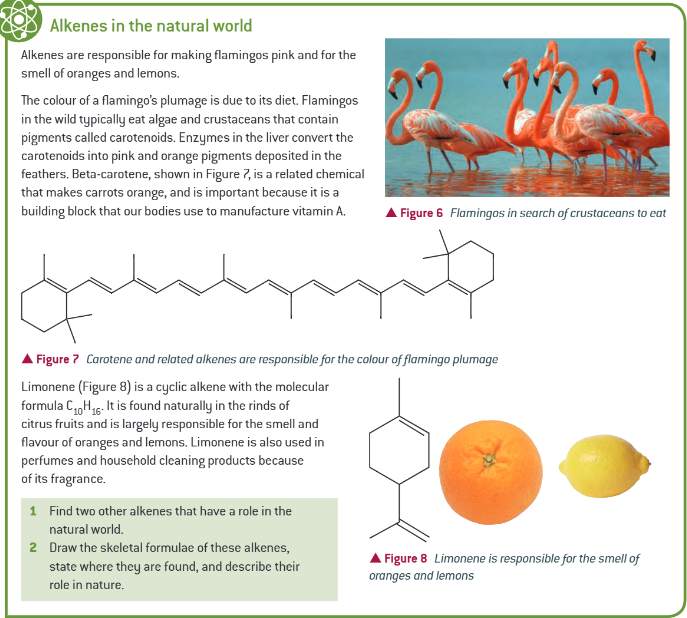
extra info: alkenes in the natural world
what are stereoisomers?
same structural formula but a different arrangement of the atoms in space
what are the 2 types of stereoisomerism?
E/Z isomerism
optical isomerism
where does E/Z isomerism only occur?
in compounds with a C=C double bond
where can optical isomerism occur?
wider range of compounds, like alkanes with no functional groups
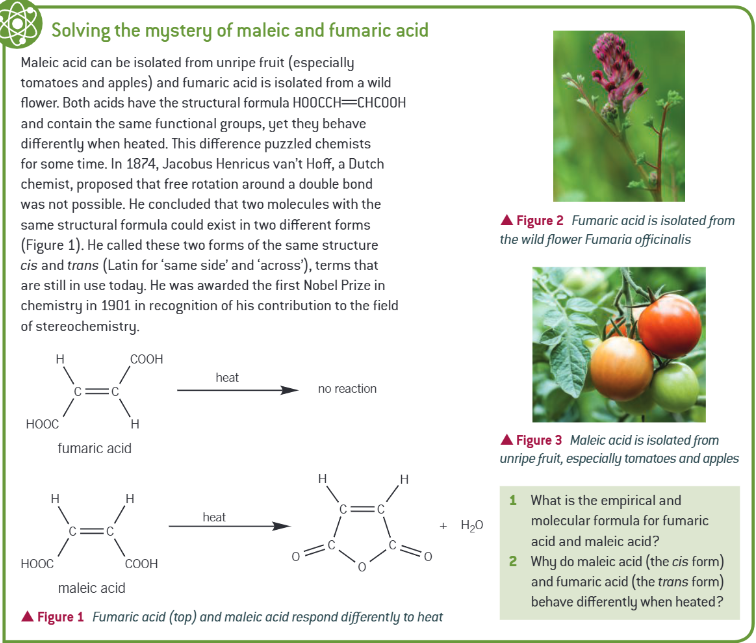
extra info: maleic and fumaric acid:
why does stereoisomerism around double bonds arise?
rotation about the double bond is restricted and the groups attached to each carbon atom are therefore fixed relative to each other
why is the bond and position so rigid?
the position of the pi bonds electron density above and below the plane of the sigma bond
what will be the case if a molecule has E/Z isomerism?
there will be a C=C bond
there will be different groups attached to each carbon atom of the double bond
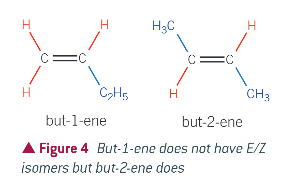
example:
But-1-ene has 2 hydrogen atoms attached to the left carbon: therefore doesnt satisfy conditions
But-2-ene has a methyl group and a hydrogen atom on each of the carbon atoms of the double bond, so has E/Z isomers
carry of of example with skeletal formula:
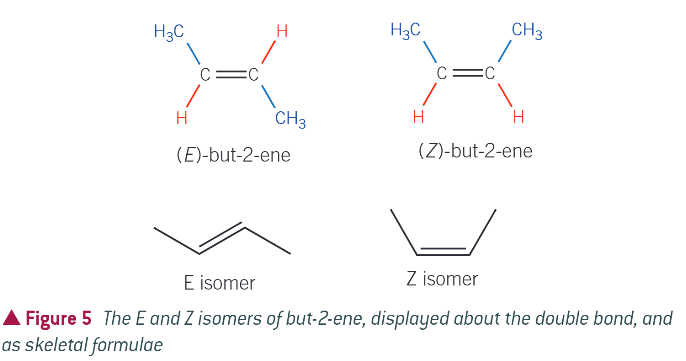
what is cis trans isomerism?
special case of E/Z isomerism
what is this special case?
molecules must have a C=C bond and each carbon must be attached to 2 different groups, however in cis trans, one of the attached groups on each carbon atom of the double bond must be the same
eg. cis tans isomers of but-2-ene:
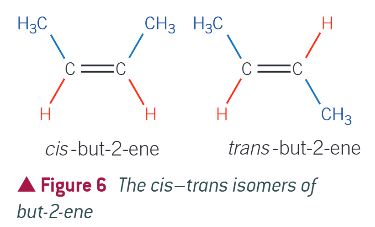
cis:
same atom on the same side of molecule (hydrgoen)
trans:
same atoms diagonally opposite each other (hydrgoen)
is cis Z or E isomerism?
Z
is trans Z or E isomerism?
E
when can the cis trans system of naming only be used?
when one of the substituent groups on each carbon atom in the double bond is the same
what is the naming system called when it cant be classified as cis or trans?
Cahn-Ingold-prelog nomenclature
CIP rules:
atoms attached to each carbon atom in a double bond are given a priority based on their atomic number
if the groups of higher priority are on the same side of the double bond, the compound is Z isomer
if the groups of higher priority are diagonally placed across the double bond, the compound is E isomer
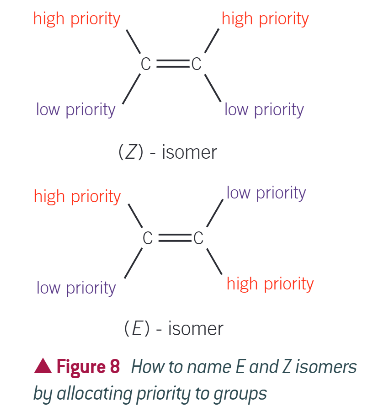

worked example: group priorities in 2-bromo-1-chloropropene

worked example: group priorities at point of difference

why are alkenes much more reactive than alkanes?
the presence of a pi bond
where are these pi electrons?
on the outside of the double bond, so the pi electrons are more exposed than the electrons in the sigma bond, breaking more easily and undergoing addition reactions to become an alkane
data to show why a pi bond breaks and the sigma bond remains when alkenes react:

what addition reactions do alkenes undergo?
hydrogen with nickel catalyst
halogens
hydrogen halides
steam with nickel catalyst
what do these addition reactions do to the alkene?
break the pi bond and add a small molecule across the double bond
what is hydrogenation?
when an alkene is mixed with hydrogen and passed over a nickel catalyst at 423K, forming an alkane
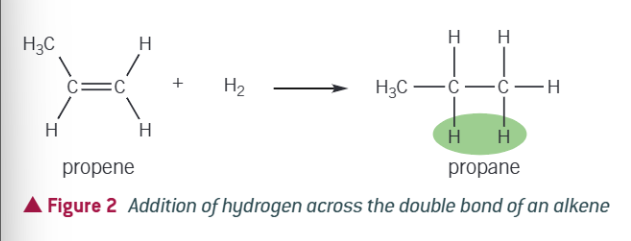
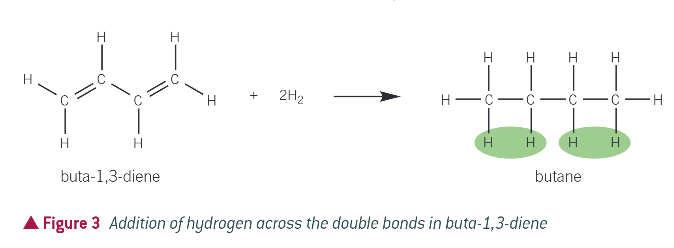
what will be needed if there is 2 double bonds?
2 molecules of hydrogen per molecule
extra reading: focus on margarine:

what halogens do alkenes undergo rapid addition at room temp with?
bromine and chlorine
example: bromination of propene
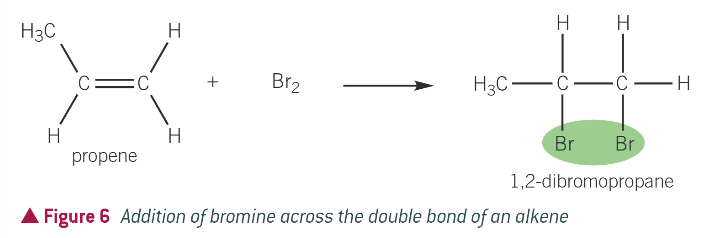
how can you test for unsaturation?
add bromine water (orange)
if alkene (unsaturated), the orange colour will disappear as it forms an alkane
if not alkene, solution will remain orange, indicating no C=C bond

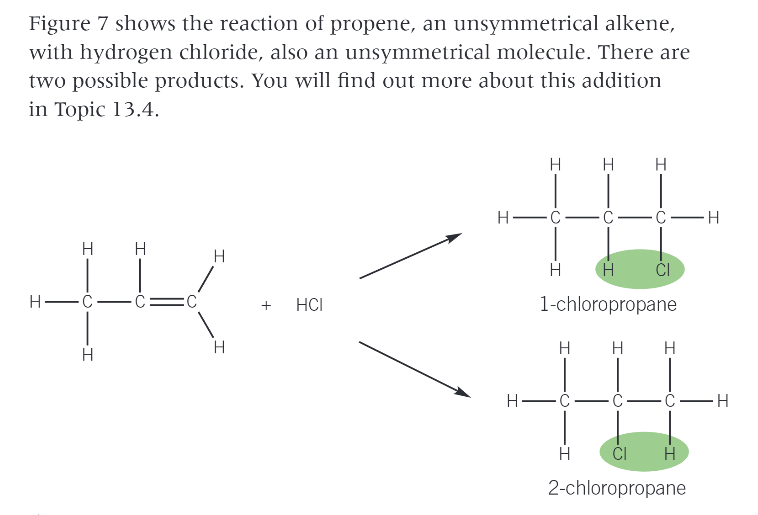
what forms when you react an alkene with a gaseous hrdrogen halide?
haloalkane
when does the reaction take place if the alkene is..
a gas?
a liquid?
gas: when the 2 gases mix
liquid: when a hydrogen halide is bubbled through the alkene
eg. reaction of propene with hydrogen chloride
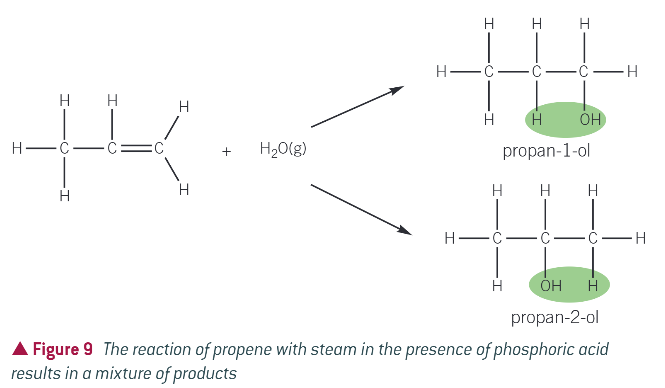
what forms when you react an alkene with steam?
an alcohol
what catalyst must be present?
phosphoric acid catalyst
what is this hydration widely used with?
ethene to become ethanol
example:
what is electrophilic addition?
addition reactions to form saturated compounds
what does the double bond in an alkene represent?
a region of high electron density due to the presence of the pi electrons
what does this region of high electron density do?
attract eletrophiles
what is an electrophile?
an atom/ group of atoms that is attracted to an electron rich centre and accepts an electron pair. Usually a positive ion/ molecule containing an atom with delta pos charge
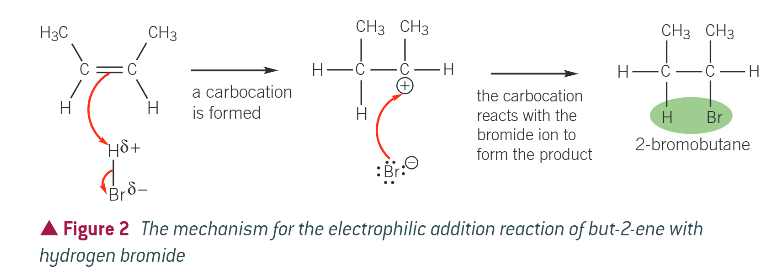
EXAMPLE FOR ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION: but-2-ene and hydrogen bromide
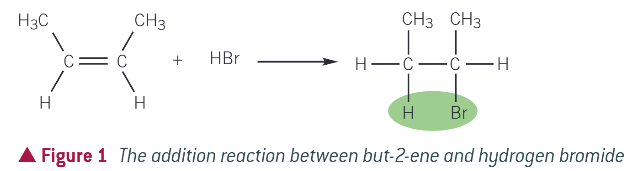
mechanism for reaction:
bromine is more electronegative than hydrogen, so hydrogen bromide is polar and contains the dipole H+-Br- (delta)
the electron pair in the pi bond is attracted to the partially positive hydrogen atom, causing the double bond to break
a bond form between the hydrogen atom of the H-Br molecule and a carbon atom that was a part of the double bond
the H-Br bond breaks by heterolytic fission, with the electron pair going to the bromine atom
a bromide ion (Br-) and a carbocation are formed. A carbocation contains a positively charged carbon atom
in the final step the Br- ion reacts with the carbocation to form the addition product
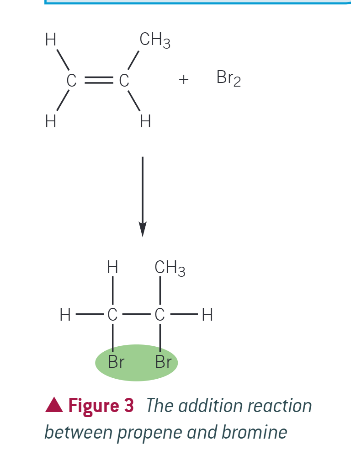
EXAMPLE FOR ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION: propene and bromine
HBr is polar, so the electrophilic addition is easy to see, but non polar molecules (Br) can also be used. it forms a single addition product
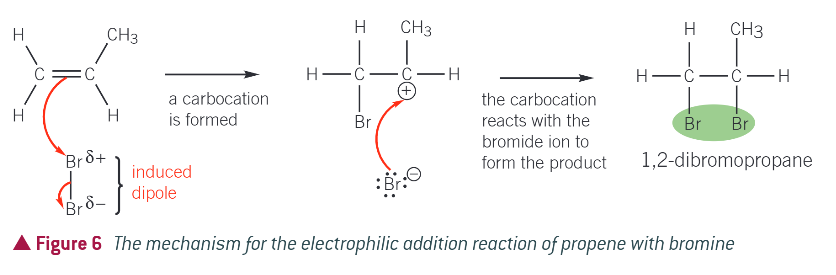
mechanism for reaction:
bromine is a non polar molecule. when bromine approaches an alkene, the pi electrons interact with the electrons in the Br-Br bond
this interaction causes polarisation of the Br-Br bond, with one end of the molecule becoming Br+ and the other Br- (induced dipole)
the electron pair in the pi bond is attracted to the Br+ end of the molecule, causing the double bond to break
a bond has now been formed between one of the carbon atoms from the double bond and a bromine atom
the Br-Br bond breaks by heterolytic fission with the electron pair going to the Br- end of the molecule
a bromide ion and carbocation forms
in the final stage the Br- ion reacts with the carbocation to form the addition product of the reaction
what did Markownikoff state about when a hydrogen halide reacts with an unsymmetrical alkene?
the hydrogen of the hydrogen halide attaches itself to the carbon atom of the alkene with the greater number of hydrogen atoms and smaller number of carbon atoms
what is a primary carbocation?
the pos charge is on a carbon atom at the end of a chain, only attached to 1 other carbon
what is a secondary carbocation?
the pos charge is on a carbon atom with 2 carbon chains attached
example: 2 possible carbocations formed when propene reacts with hydrogen halide
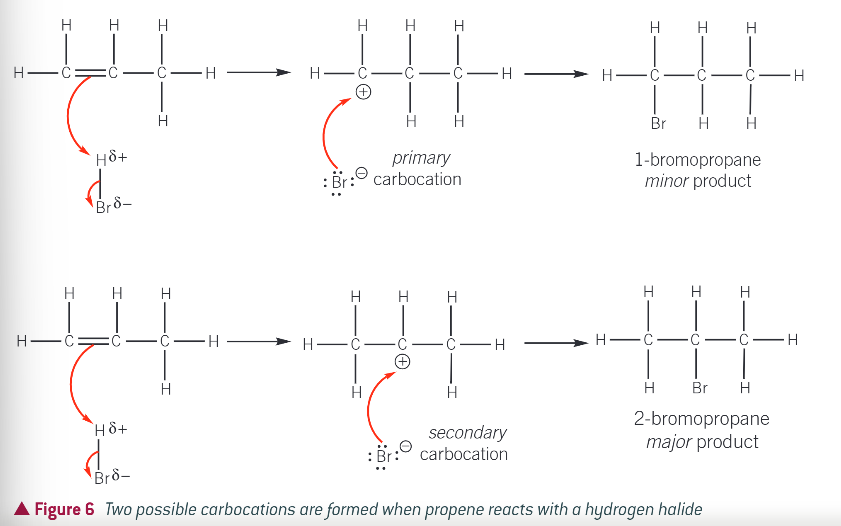
how are carbocations classified?
by the number of alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbom atom
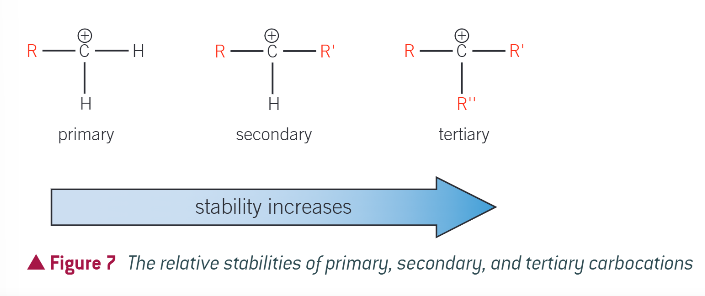
what is the symbol R?
an alkyl group
what is carbocation stability linked to?
the electron donating ability of alkyl groups. each alkyl group donates and pushes electrons towards the positive charge of the carbocation. the positive charge is spread over the alkyl groups
the more alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon atom…
the more the charge is spread out, making the ion more stable
addition of a hydrogen halide to an unsymmetrical alkene forms…
the most stable carbocation
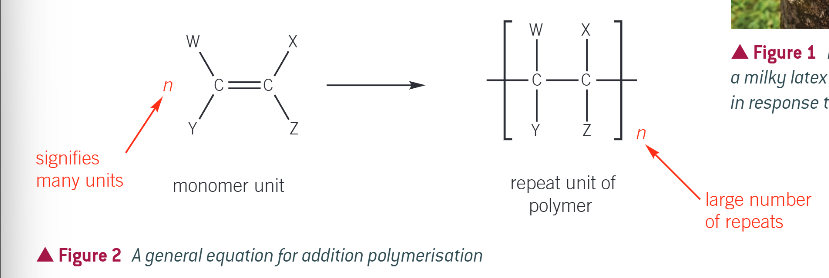
what are polymers?
large molecules formed from thousands of repeating units of smaller molecules (monomers)
what do unsaturated alkenes molecules undergo?
addition polymerisation to produce long saturated chains containing no double bonds
what do the properties of the polymer depend on?
the monomer used
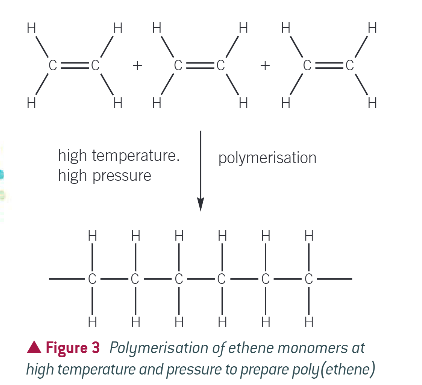
what is industrial polymerisation carried out at?
high temp and high pressure with catalysts
do addition polymers have high or low molecular mass?
high
how are synthetic polymers usually named?
after the monomer that reacts to form their giant molecules (prefix:poly)
general equation for addition polymerisation:
a repeat unit is the specific arrangement of atoms in the polymer molecule that repeats over and over again
the repeat unit is always written in square brackets
after the bracket you place a letter n to show that there is a large number of repeats
how is poly(ethene) made?
heating a large number of ethene monomers at high pressure
applications of poly(ethene):
supermarket bags
shampoo bottles
childrens toys
extra info:history of polyethene
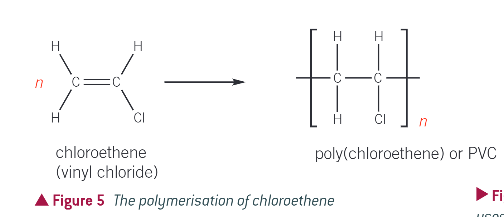
poly(chloroethene) can be prepared to make what?
a polymer that is rigid or flexible
equation for the formation of poly(chloroethene)/ PVC:
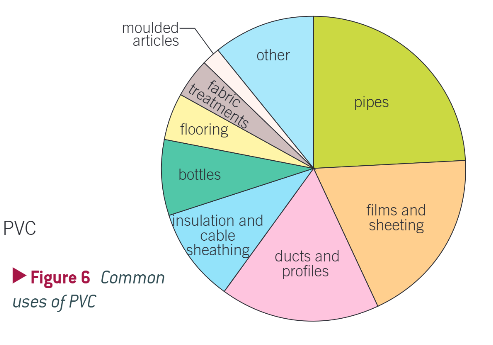
common uses of PVC:
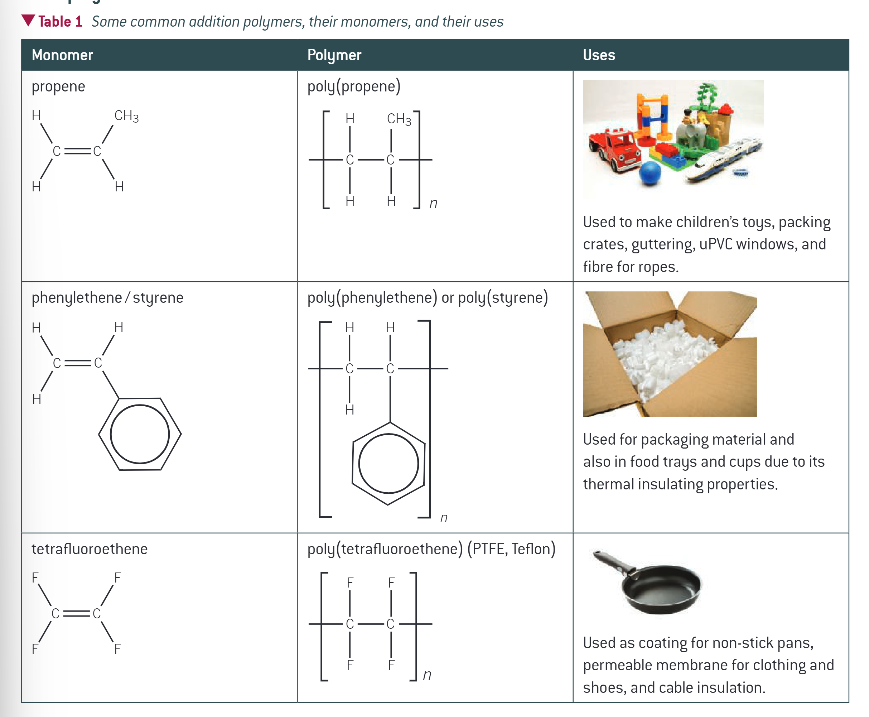
other addition polymers, their monomers and their uses:
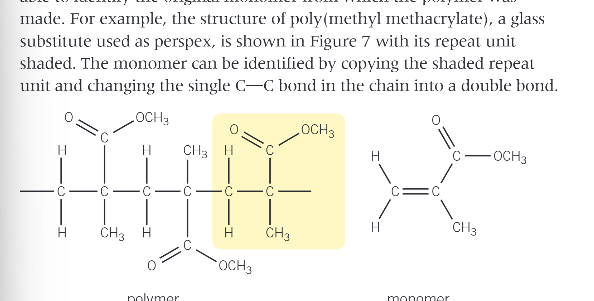
how can you identify monomers from polymer chains?
identify the repeating unit, then change the single C-C bond to a double bond
example of doing this:
environmental concerns:
disposing of waste polymers
recycling
PVC recycling
using waste polymers as fuel
feedstock recycling