Lab F: Fischer Esterification
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Fischer Esterification Reaction
Carboxylic acid and alcohol (reagent)
Acid catalyst (H2SO4)
Reversible reaction
Ester and water (product)
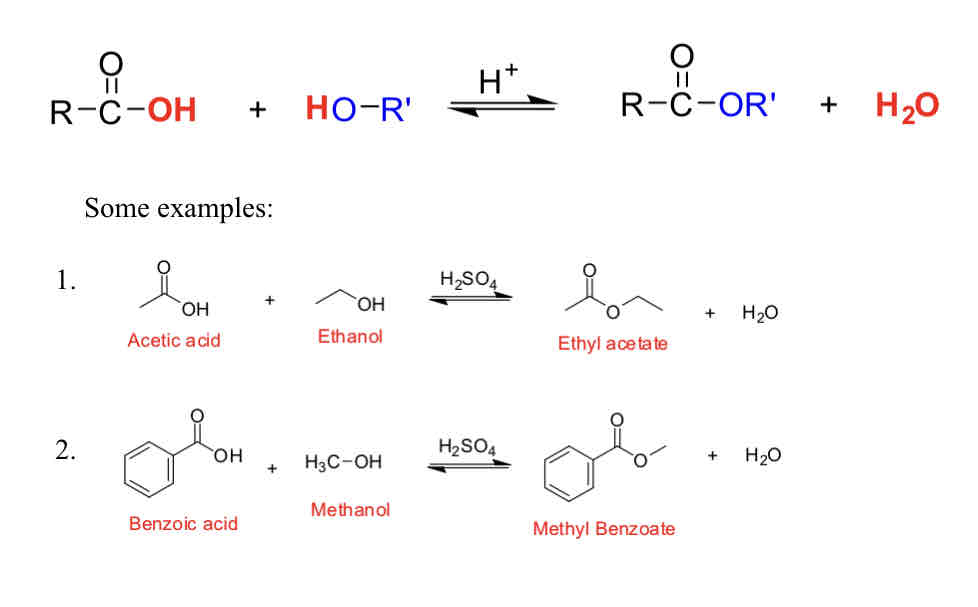
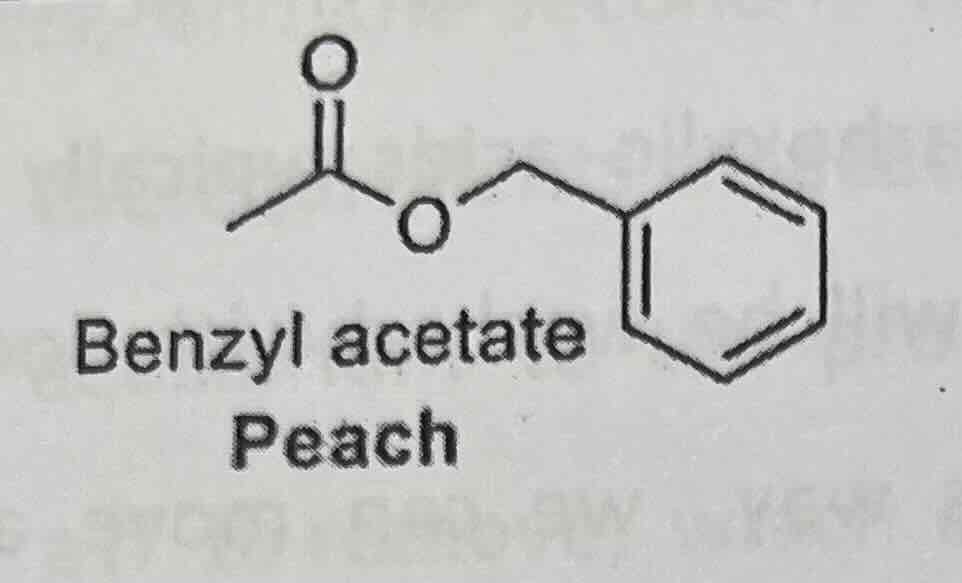
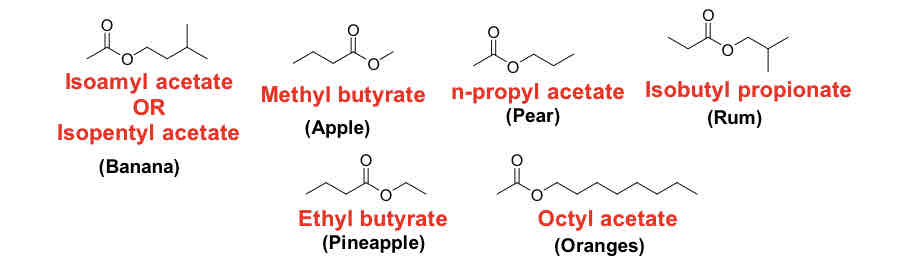
Examples of esters
**isoamyl acetate or isopentyl acetate (banana)
Have pleasant fruity odors
Used as flavoring agents
General method for preparation of Esters
Reflux
Extractions
Simple distillation
** acid catalyzed reaction, acid is regenerated and is never consumed
Why is it impossible to obtain 100% yield?
The reaction is reversible and will strive to be at equilibrium, need to drive reaction forward:
Remove water
Excess reagent (glacial acetic acid)
Refluxing for 50 min (increase rate)
Glacial acetic acid
Has little water and looks like ice at room temperature
Excess amounts because cheaper reagent
Bp 118
Hazards
Glacial acetic acid: flammable (2), health (3), corrosive
Sulfuric acid: corrosive, health (3)
Fischer esterification reflux schematic
Heating mantle on ring stand
• no stir plate
• plug into VARIAC on bottom right of hood and cord wrapped around metal bar under white bar
RB flask flush on mantle with 2 boiling stones
Clamped RB flask cover with foil
Condenser
• CHWS on bottom (water in)
• CHWR on top (water out)
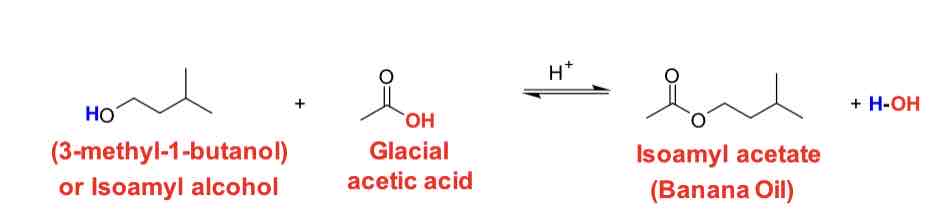
Scheme 1: synthesis of isopentyl acetate
3-methyl-1-butanol (isoamyl alcohol) and glacial acetic acid
H2SO4
Isopentyl acetate (isoamyl acetate) and water
Why use boiling stones in Fischer and not Diels Alder?
boiling stones smoothes boil and avoid bumps - violent boils will spill out of condenser
Diels Alder product physically similar to boiling stones, inaccurate yield
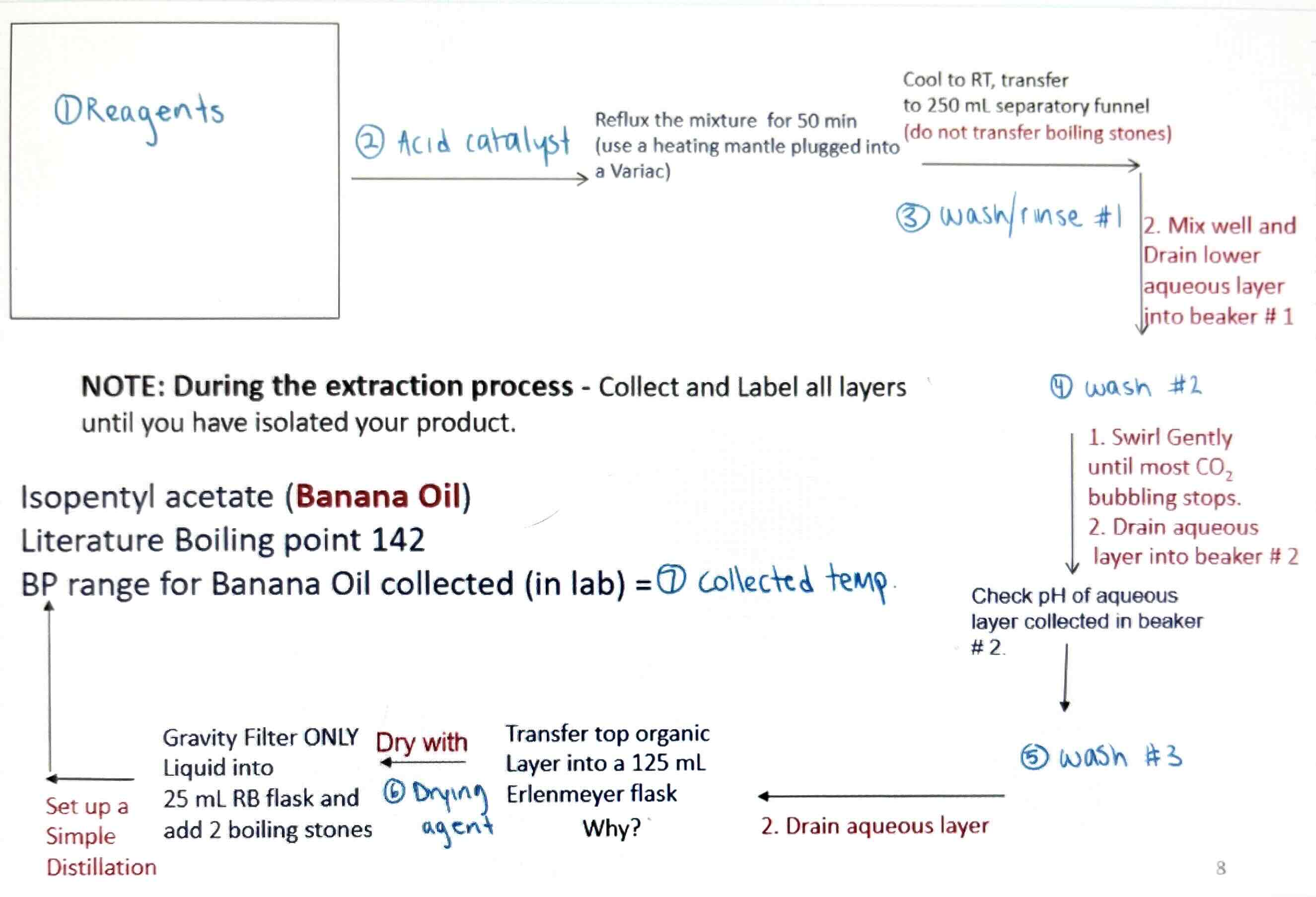
Flow chart of Fischer Esterification Reaction
15mL 3-methyl butanol and 20mL Glacial acetic acid
2mL conc. H2SO4
50mL cold water and 10mL to rinse
25mL 5% NaHCO3 solution
25mL water and 5mL NaCl solution
Anhydrous CaCl2 pellets
125-138
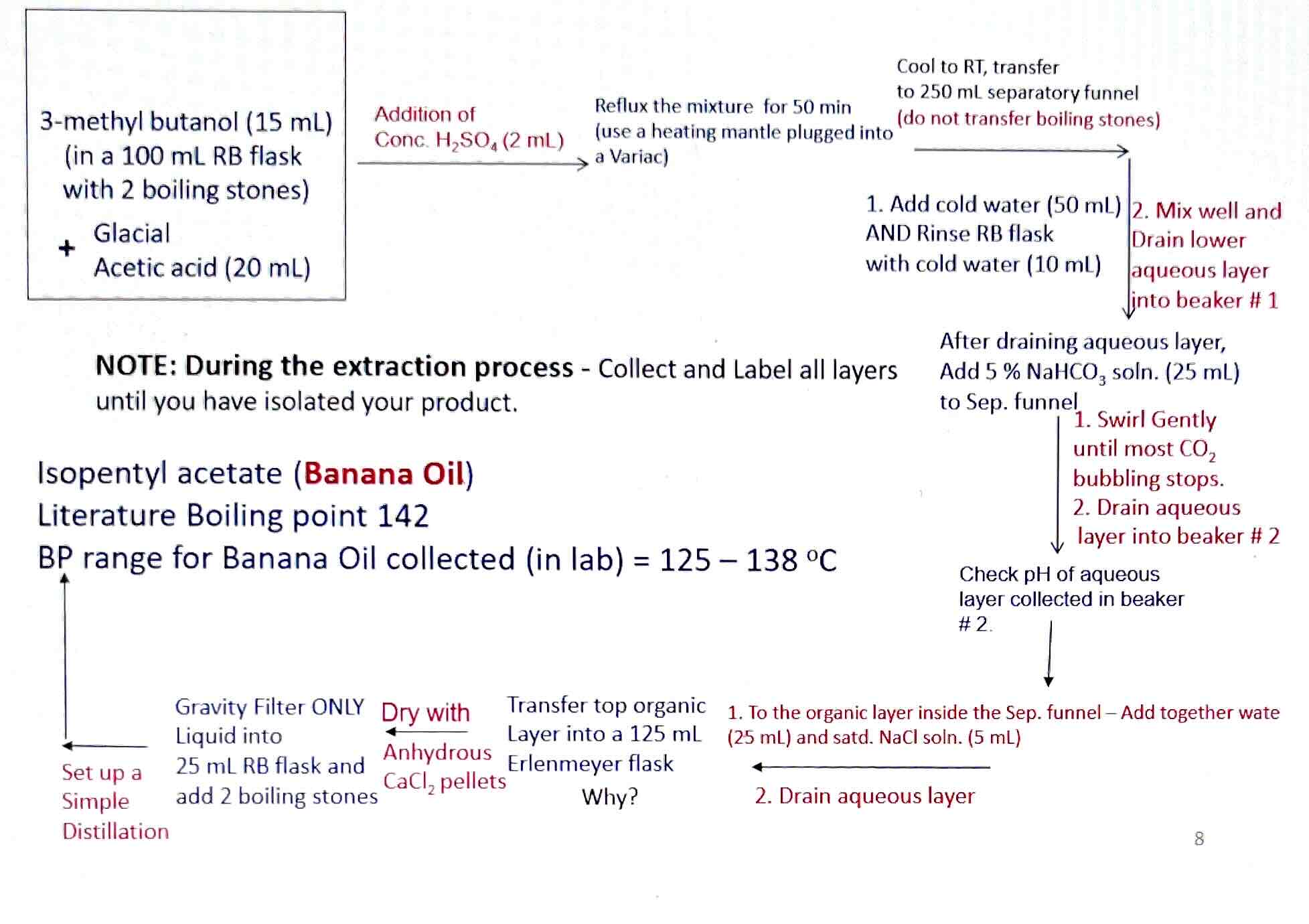
Why use water for the first wash?
Cool the reaction
Draw out acid catalyst
Create an aqueous layer
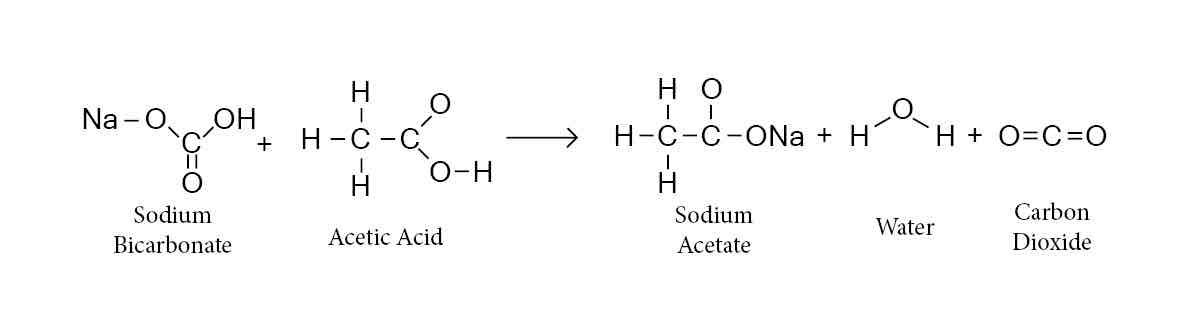
Why use bicarbonate (NaHCO3) for the second wash?
Remove excess glacial acetic acid
COOH can be deprotonated pka~5
Acetic acid into sodium acetate salt (polar)
Sodium acetate salt has greater solubility in the aqueous layer (drained)
Generates CO2, vent to prevent loss in yield
Why use brine (NaCl) and water for third wash?
Addition of water removes any leftover acetic acid after wash #2 and create an aqueous layer
Addition of brine initiates the drying process by removing excess water from organic layer
Why transfer the organic layer into a 125mL Erlenmeyer flask?
The sloped slides prevent evaporation of organic layer during gravity filtration with CaCl2
Why collected isopentyl acetate (banana oil) below literature bp?
Literature bp = 142C
Thermometers are poorly calibrated at temperatures over 100C, so product distilled from 125-138C
Purification techniques
Recrystallization
Thin layer chromatography
Extraction for immiscible liquids
Simple distillation for miscible liquids
Why do a simple distillation to purify?
Separate liquids where bp differ by greater than 100C at 1atm
Miscible liquids
Distillation: technique where liquid is vaporized by heating its bp, then recommended back to a liquid
Why do a simple distillation to purify?
Purifying isopentyl acetate from trace isopentyl alcohol (bp<125)
Differ by 13C (less than 100C) but fractional distillation will lose a large amount of material to column holdup with sufficient number of theoretical plates
Small amount left due to driving equilibrium (excess reagent and removing product)
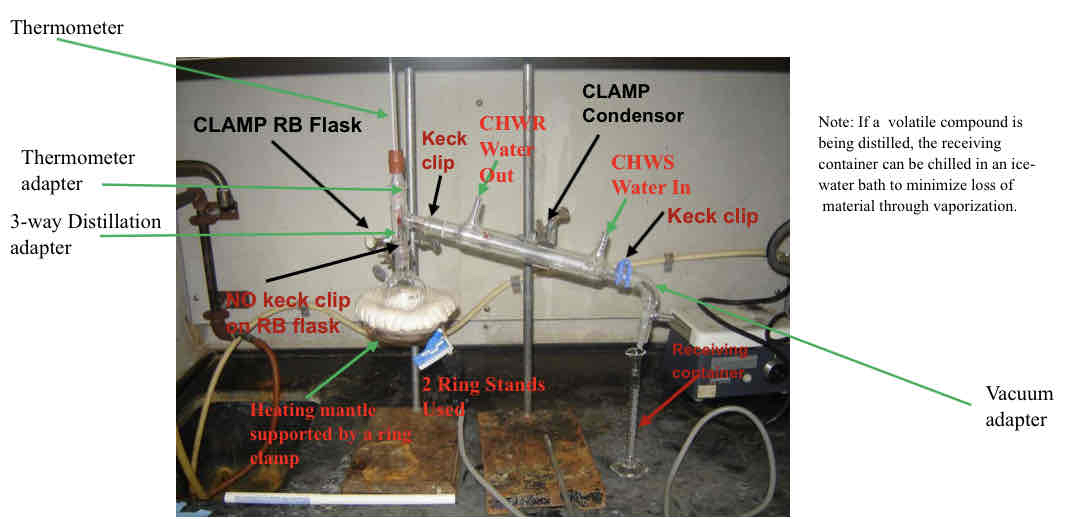
Simple distillation schematic
2 ring stands used
Heating mantle supported by ring clamp
RB flask flush against heating mantle clamped with 2 boiling stones
3 way distillation adapter with thermometer adapter
• thermometer bulb position below junction for accurate readings
Keck clip between 3 way adapter and condenser
Condenser clamped to 2nd ring stand
• CHWS toward the vacuum adapter (bottom)
• CHWR toward the RB (top)
Keck clip between condenser and vacuum adapter
Vacuum adapter to receiving container (vial)
Why do not distill to dryness?
Small amount of residue will prevent overheating and breaking the flask, and the formation of pyrolytic tars that are difficult to wash out
How to minimize loss of material through vaporization if volatile compound is being distilled?
Receiving container can be chilled in an ice water bath
Vacuum Distillation
For compounds that either boil at too high a temperature or decompose near their bp
Under vacuum compounds can be distilled at temperatures lower than their atm bp (>200C)
Fractional distillation
Used to separate liquid mixtures where difference in bp < 100C at 1atm
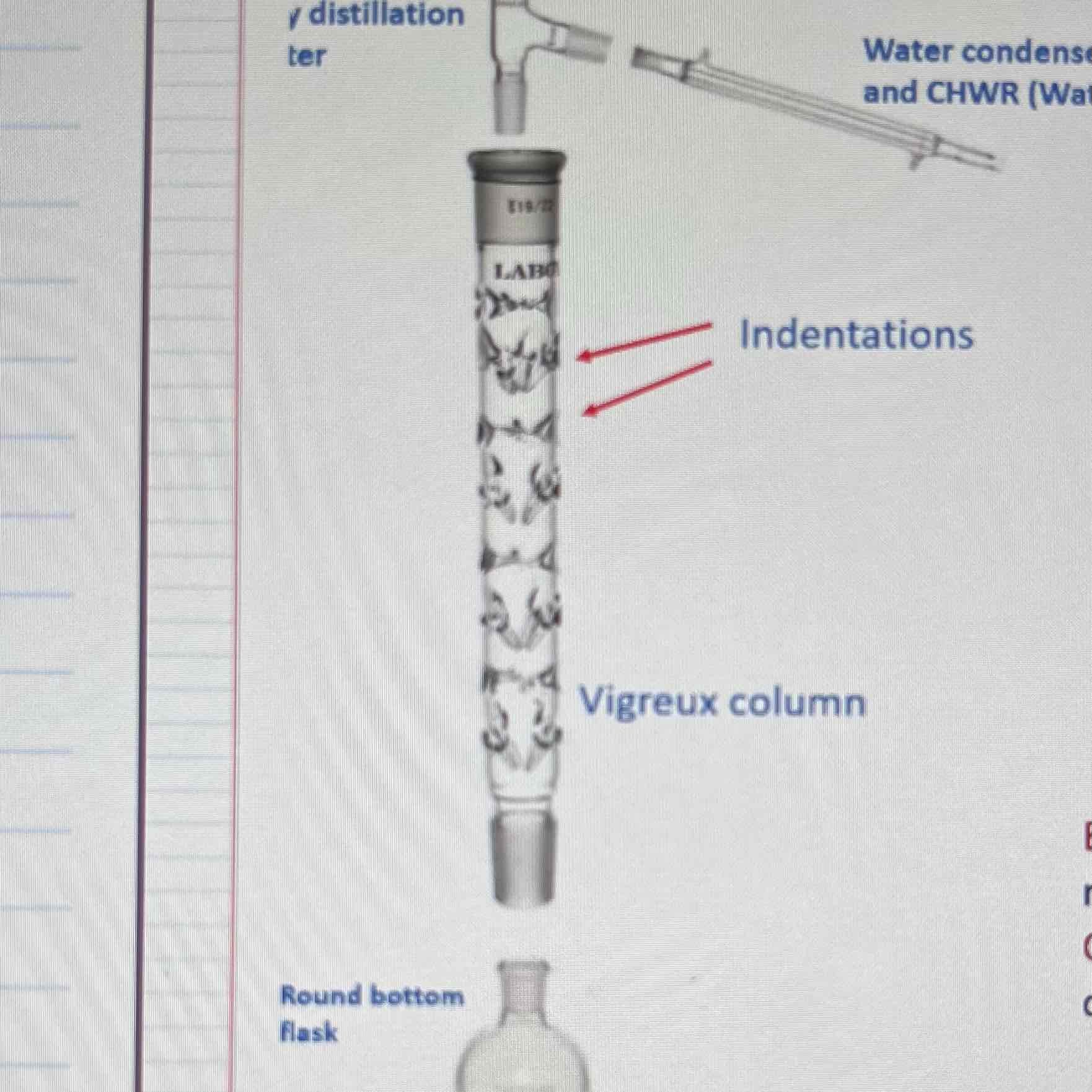
Vigreux column: greater surface area for a number of separate liquid equilibria to occur
Many vaporizations and condensations before distillate is collected
Efficiency is determined by number of theoretical plates
Several simple distillation cycles
Greater loss of product and longer time to distill
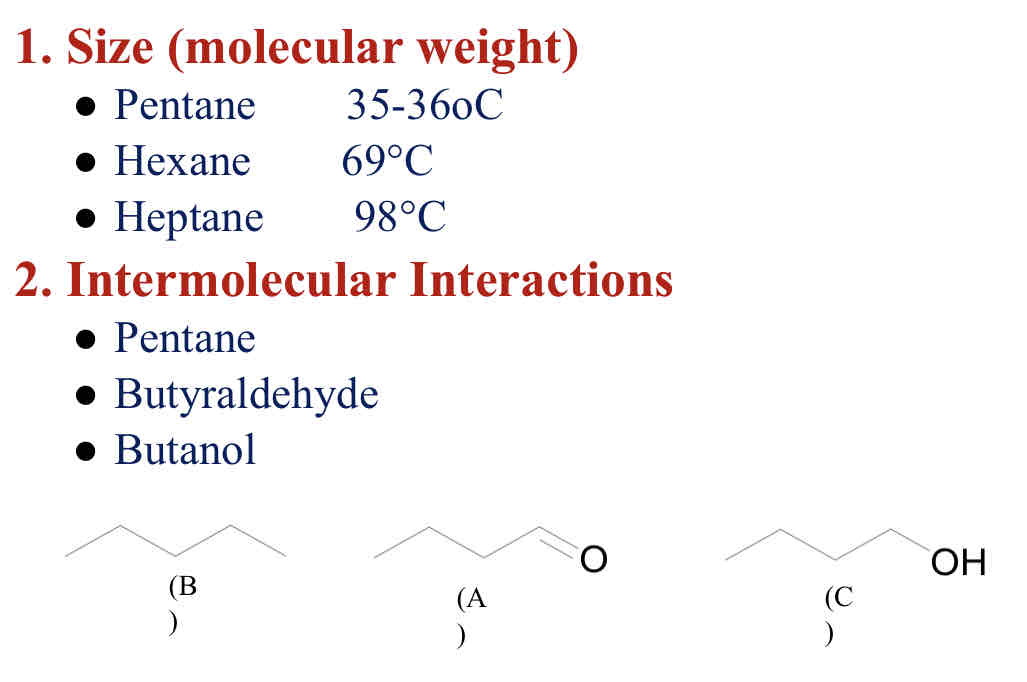
Factors affecting Boiling Points
Increase in size (MW) = higher bp
Increase intramolecular interactions = higher bp
• hydrogen bond (FON)
• dipole
• van der waals
Increase stability = higher bp
Factors affecting Boiling Points
Increase in size (MW) = higher bp
Increase intramolecular interactions = higher bp
• hydrogen bond (FON)
• dipole
• van der waals
Increase stability = higher bp
Why should Keck clips at joints be tight?
Loose joints will cause product to escape
Positioning of the thermometer bulb
Below the 3-way junction, if placed too high the temperature readings will be low and inaccurate

Using the VARIAC
A variable voltage transformer
Provides voltage adjusted source of alternating current
Higher bp = greater voltage required (start at ~65)
Outlet located BELOW fume hood
Set power = set heat = control reaction rate
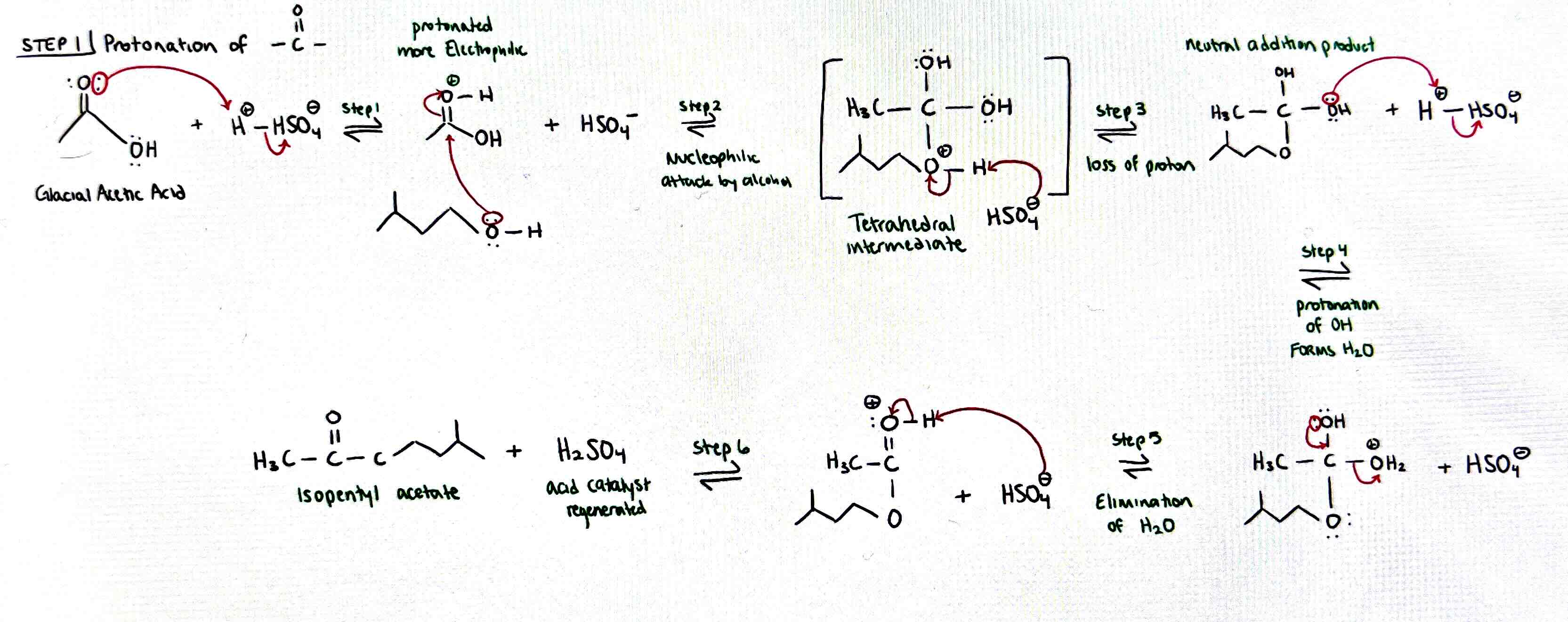
Fischer mechanism
Protonation of glacial acetic acid with H2SO4
• protonated = more electrophilic
Nucleophile (3-methyl-1-butanol) attacks carbonyl
Tetrahedral intermediate O+ deprotonated by HSO4-
Neutral addition product OH protonated by H2SO4 to form H2O+
Elimination of water and forming of double bond
OH+ deprotonated by HSO4-
Final product isopentyl acetate and acid catalyst regenerated
General Procedure
Add 2 boiling stone to 100mL RB flask
Add 15mL 3-methyl-1-butanol, 20mL glacial acetic acid, 2mL H2SO4
Reflux set up (no stir plate) and clamp only RB flask
VARIAC dial to 65 and insulate with foil until solution comes to a boil
Remove foil and reflux for 50 min
Raise clamped RB above heating mantle and cool for 10 min
Transfer to 250mL sep funnel without boiling stones
Add 50mL cold water and rinse RB flask with 10mL
Shake and drain aqueous layer into beaker #1
Add 25mL 5% NaHCO3
Shake and vent, then drain into beaker #2
pH of beaker #2 = orange or green
Add 25mL water and 5mL NaCl
Shake and drain into beaker #1
Drain organic layer into 125 Erlenmeyer flask and add CaCl2
Gravity filtration into 25mL RB flask with 2 new boiling stones (crude ester)
Simple distillation 125-138C
Waste disposal and cleanup
Disassemble simple distillation setup starting from the right
All aqueous waste disposed in “aqueous waste Fischer lab”
CaCl2, gravity paper, boiling stones in biohazard
If any, low boiling distillate into “CHO nonhalogenated”
MP capillary tubes in sharps
Prep glassware for grignard lab by rinsing with acetone
Why is the pH of beaker #2 orange/green (neutral)?
Acid-base neutralizing reaction
OBSERVATION: reflux is deep purple color
OBSERVATION: after extraction the product is yellow
OBSERVATION: final product isopentyl acetate is clear with banana odor
Fischer IR Spectrum