P1B - Organisation 2
1/109
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Tissue
Group of cells w similar structure and function
Organ
Group of tissues working together for a specific function.
e.g stomach has muscle and glandular tissue, releasing enzymes.
Organ system
Groups of organs which work together to form organisms.
Main food nutrients + the type of molecule they are
All are large molecules. Too large to be absorbed into blood. Must be digested.
carbohydrates (starch)
protein
lipids (fats)
Digestion
Large food molecules broken down into small molecules by enzymes.
Small molecules can then be absorbed into blood.
These digestion products are used by the body to build new carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Some glucose produced is used in respiration.
1st: Mouth function
food is chewed.
saliva enzymes begin digesting starch into smaller sugar molecules.
2nd: Oesophagus function
food passes through oesophagus into stomach
3rd: Stomach function
enzymes begin digestion of proteins
has hydrochloric acid, helping the enzymes
food spend several hours inside
churning action of muscles turns food to fluid, increasing SA for enzymes to digest
4th: small intestine function
when fluid’s inside, pancreas releases enzymes that continue starch and protein digestion, and begin lipid digestion.
liver releases bile, speeding up lipid digestion. bile neutralises acid released from stomach
small intestine walls release enzymes to continue lipid and protein digestion
small food molecules produced are absorbed into blood by diffusion or AT
5th: large intestine function
water from fluid is absorbed into blood
faeces
V1 digestive system
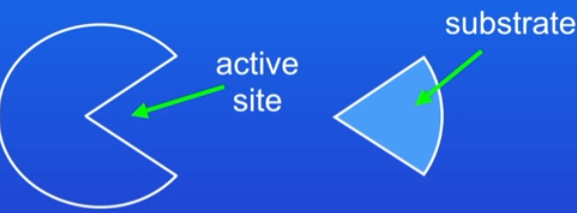
Enzyme
catalyse chemical reactions
large protein molecules and have groove on surface (active site)
active site is where substrate attaches
enzyme process and conditions
active site and substrate MUST fit perfectly, attaching
enzyme breaks down substrate into products
not a perfect substrate fit = enzyme can’t break it down
enzymes are specific (lock and key theory)
protein enzyme and where its located
proteases
stomach
pancreatic fluid
small intestine
protein structure and digestion steps
long chains of chemicals called amino acids:
when digesting proteins, protease convert them back to individual amino acids, which are then absorbed into the blood.
when absorbed by body cells, they join in a diff order to make human proteins
Carbohydrate enzymes, and specific e.g location
carbohydrases
amylase in saliva and pancreatic fluid
starch (carbohydrate) structure and digestion steps
Chain of glucose molecules:
broken down by amylase (carbohydrase)
when carbs like it are digested, produce simple sugars
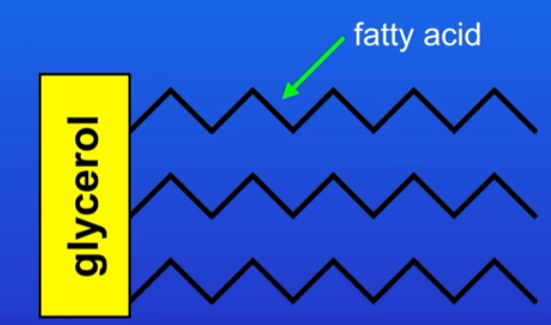
lipid structure and digestion steps
Molecule of glycerol attached to 3 molecules of fatty acids.
digested by the enzyme lipase
produces glycerol and fatty acids
lipids enzyme and location
lipase
in pancreatic fluid and small intestine
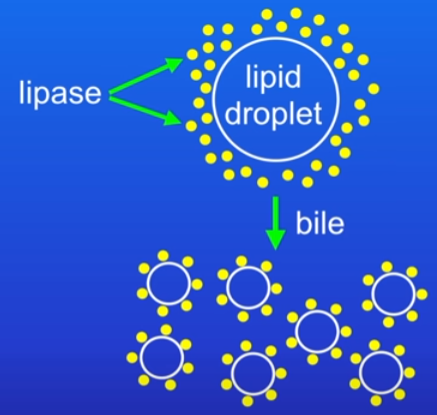
bile’s purpose + creation and storage place
made in liver, stored in gall bladder
speeds up digestion of lipids but NOT an enzyme
converts large lipid droplets into smaller droplets
bile emulsifies the lipid = increasing lipid droplet SA = increased lipid breakdown rate by lipase
bile’s pH and purpose for pH
alkaline, neutralising the stomach acid = alkaline conditions in small intestine
this increases rate of lipid digestion by lipase
V2 digestive enzymes
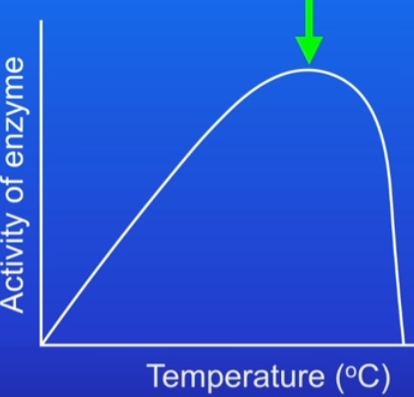
temp effect on enzyme
increase temp = enzyme activity increases
because enzyme and substrate are moving faster, so more collisions/sec happen between them
Optimum temp = at a certain temp, enzymes work at fastest possible rate
max frequency of successful collisions between both
temp is usually 37C - body temp
Temp past optimum = activity rapidly decreases to zero
at high temp, enzyme molecule vibrates and active site changes
no longer perfect fit = active site has denatured = can’t catalyse
pH effect on enzyme
enzyme has an optimum pH = activity is maximum
each one has a specific optimum pH (protease better in acidic, lipase in alkaline)
if made more acidic/alkaline = activity is zero
active site denatures if conditions are too acidic/alkaline
V3 - effect of temp and ph on enzyme activity
RP5: effect of pH on amylase
One drop of iodine solution into each well of a spotting tile.
1st test tube - 2cm³ starch solution, 2nd - 2cm³ amylase solution, 3rd- 2cm³ pH 5 buffer solution (controls the pH)
Place all into water bath at 30C. Leave for 10 mins to reach correct temperature
Combine all 3 into one test tube, mix w stirring rod, return immediately to water bath and start stopwatch.
After 30 secs, transfer 1 drop of solution to a well using a stirring rod
iodine should turn blue-black, showing that starch is present
Take a sample every 30 seconds, stop when iodine remains orange
starch is no longer present (reaction is completed)
record time for this in our results
Repeat entirely several times using diff pH buffers, 6,7,8.
RP5: pH effect on Amylase ISSUES
only taking samples every 30 secs = only have approximate time for complete reaction
address by taking sample every 10 secs
time for iodine not going blue-black is not always obvious - colour change is gradual, some wells may have a bit of blue-black mixed w orange, so hard to see when reaction has finished
ask several people to look and decide
V4 RP5: effect of pH on amylase
RP4: food tests setup
safety goggles must be worn due to harmful work chemicals
take food sample, grind with distilled water using mortar and pestle = paste
transfer to beaker, and add more distilled water. stir so chemicals in the food dissolve in water
filter to remove suspended food particles
RP4: starch test
2cm³ of food solution into a test tube
few drops of iodine solution (orange)
present, iodine = blue-black, not = stays orange
RP4: sugars test
2cm³ of food solution into a test tube
10 drops Benedict’s solution (blue) in test tube
put test tube into beaker w half-filled water from kettle
leave for 5 min
present = benedict changes colour
colour gives idea of amount of sugar present but NOT exact
green = small amount
yellow = more sugar
brick-red = a lot of sugar
ONLY works w certain “reducing sugars” (glucose). Doesn’t work w “non-reducing” (sucrose).
RP4: protein test
2cm³ of food solution into a test tube
add 2cm³ of biuret solution (blue)
present = biuret is purple/lilac
RP4: lipids test
during the setup DO NOT FILTER the solution
lipid molecules can stick to filter paper
2cm³ of food solution into a test tube
few drops of distilled water and ethanol.
ethanol = highly flammable. no flames around.
gently shake - present = white cloudy emulsion
v5 - RP4: food tests
small intestine adaptations for rapid diffusion rate
5m = very large SA for absorption
millions of villi cover inside = increase SA for absorption
microvilli on villi = increase SA even more
villi have very good blood supply = bloodstream rapidly removes digestion products = increases conc gradient
villi have thin membrane = short diffusion path + molecules that can’t be diffused are absorbed by AT
V6 - Absorption in the Small Intestine
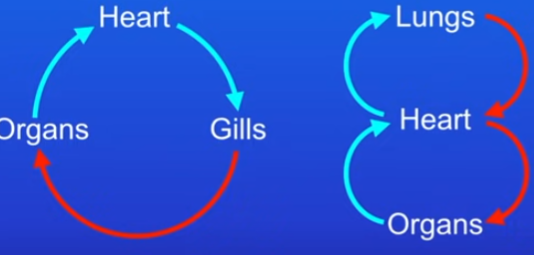
Fish vs Human circulatory system
fish - single: oxygenated from gills to organs, deoxygenated from organs to heart to gills.
human - double: lungs to heart to organs = oxygenated, organs to heart to lungs = deoxygenated
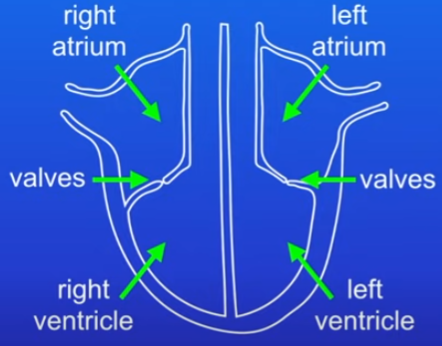
Hearts chambers:
right and left atrium
right and left ventricle
always shown as if your looking at the person
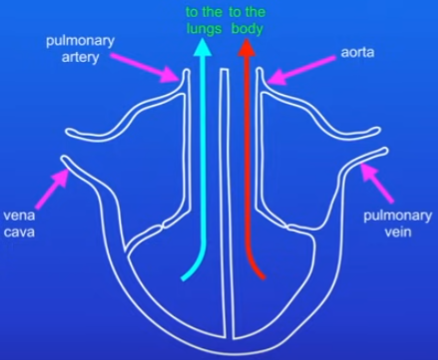
Main vessel in the heart and purpose:
vena cava = brings deoxygenated blood
blood goes through heart to lungs = pulmonary artery
oxygenated blood from lungs to heart = pulmonary vein
blood is pumped from heart to body = aorta
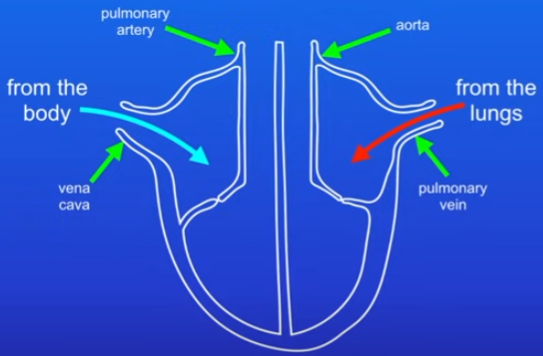
Process of blood flow in heart
blood enters the left and right atrium
atria now contract and blood is forced into ventricles
ventricles now contract and force blood out of the heart
valves stop the blood from flowing backwards into atria when ventricles contract
Left side of heart = thicker muscular wall since it pumps blood round body and needs to give a greater force, right ventricle only to lungs.
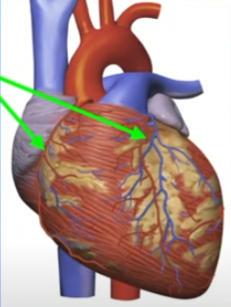
Coronary arteries location and purpose
branch out of aorta and spread out onto heart
provide oxygen to muscle cells of heart = respiration for contraction energy
Pacemaker:
group of cells control resting heart rate in the right atrium
stops working = artificial pacemaker
small electrical device that corrects irregularities in heart rate
V7 - Heart and Circulation
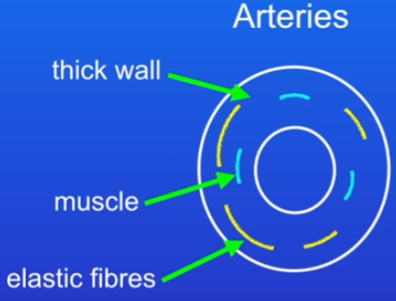
Arteries structure and purpose
carry very high pressure blood from heart to organs
thick muscular walls = withstand very high pressure of blood
blood travels through them in surges w every heart beat = pulse
to cope, elastic fibres stretch when surge passes, and recoil between surges which keeps blood moving
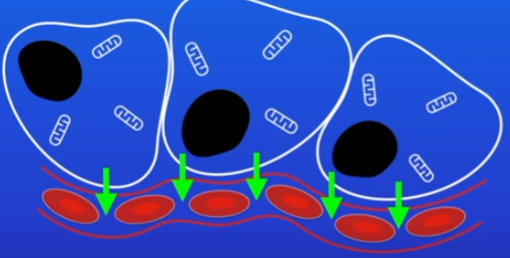
Capillaries structure and purpose
as blood passes through them, substances like glucose and oxygen diffuse from blood to cells
carbon dioxide diffuses from cells back to the blood
very thin walls = very short diffusion pathway = rapid substance diffusion between body and blood cells
Vein purpose and structure
after blood passes organs, goes back to heart by veins
blood travels slowly at low pressure = stop or go backwards
thin wall since blood pressures low
many have valves = stop blood flowing backwards
valves open in correct direction, shut in wrong

V8 - Arteries, veins and capillaries
Blood plasma transports:
the liquid part - transports dissolved substances around the body:
soluble digestion products (glucose) from small intestine to other organs
co2 (made by aerobic respiration) from organs to lungs to be breathed out
urea, the waste product from liver to the kidneys to be excreted in urine
Red blood cells transport:
transport oxygen from lungs to body cells
contain oxygen-carrying molecule haemoglobin
haemoglobin + oxygen —happens in lungs→ oxyhaemoglobin
oxyhaemoglobin —happens in organs→ haemoglobin + oxygen
no nucleus = more haemoglobin room
biconcave disc (centre dimples) = greater SA for rapid oxygen diffusion
White blood cells:
form part of the immune system (e.g making antibodies)
contain nucleus = DNA encodes instructions that they need to do their job
Platelets
tiny fragments of cells - help blood to clot
Donated blood uses in medicine
replace blood lost during injury
some people are given platelets extracted = help clotting
proteins extracted from blood can also be useful (e.g antibodies)
Blood transfusion conditions
donated blood is same as patients type = doesn’t reject and kill patient
in UK blood is screened for infections = low risk of diseases transmitted via blood
v9 - Blood
Cardiovascular diseases
diseases of heart and blood vessels
non-communicable = not infectious, can’t be passed from person to person
Coronary heart disease - cardiovascular disease
layers of fatty material build up inside the coronary arteries = they narrow
body wants to reduce blood flow through them = lack of oxygen for heart
extreme cases = heart attack (starved of oxygen)
Coronary heart disease treatments
statins = drugs that reduce cholesterol blood levels = slows down rate that fatty materials build up in coronary arteries
reduce the risk = effective
unwanted side-effects (e.g liver problems)
Coronary heart disease treatments 2
stent = for almost total blockages
a tube thats inserted to keep it open
blood can flow normally
but doesn’t prevent other regions from narrowing (doesn’t treat underlying causes)
Valve problems - cardiovascular disease
heart valves don’t fully open so heart pumps extra hard to get blood through = heart englarges
OR valves are leaky = weak and tired patient
Solutions of valve problems
Replace with Mechanical Valve made of metal
can last a lifetime
but increase blood clot risk = need anticlotting drugs
Animal valves (pig)
don’t last as long and need replacement
patients don’t need to take drugs
Heart failure problems and solutions
Heart failure is when cardiovascular diseases mean that heart can’t pump enough blood around
Donated heart or heart and lungs
not enough hearts available to treat every patient
patients need drugs to stop heart rejection by bodies immune system
Artificial hearts = temporary solutions while waiting for heart transplant OR to allow damaged heart to rest
increase risk of blood clotting
not long term solution to heart failure
v10 - cardiovascular diseases
Gas exchange in the lungs
air passes into the lungs through a tube called the trachea
rings of cartilage prevent trachea from collapsing during inhalation
trachea splits into 2 smaller tubes called bronchi, 1 to each lung
bronchi subdivide into many smaller tubes called bronchioles
bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli (huge number, microscopic)
alveoli = where gases diffuse in and out of the bloodstream
Alveoli rapid gas exchange adaptations and process
Process: Oxygen in air diffuses into blood stream, co2 diffuses out back into air.
Rapidly done by:
Millions of them = huge SA for lungs
very thin walls = very short diffusion pathway
very good blood supply = once o2 is diffused into blood, it’s rapidly removed = concentration gradient is as steep as possible
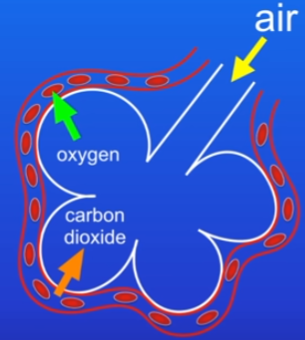
Breathing + gas exchange in the lungs
Breathing = rate of diffusion increases
brings in fresh o2 to alveoli and takes away co2
makes concentration gradients high for these gases
v11 - gas exchange in the lungs
Tumour creation
Mitosis = tightly controlled. Genes in nucleus tell cells when to divide and not.
Changes in these genes = uncontrolled growth and mitosis
Benign tumours
growth of abnormal cells found in one area, usually contained within a membrane
do not invade other parts of the body, stay in one place
Malignant tumours
invade neighbouring tissues and move into the bloodstream = cancer
once in the bloodstream, malignant cells spread to different body parts and form new tumours (secondary tumours)
Cancers linked to genetics
certain breast types
prostate
large intestine
Cancers liked to lifestyle
Smoking - lung cancer
Ultraviolet light - skin cancer
Alcohol - mouth and throat cancer
Substance in our environment that links to cancer
Radon:
radioactive gas that increases risk of lung cancer
releases ionising radiation which damages cell DNA
causes uncontrolled cell division
v12 - cancer
Communicable (CD) and Non (ND) diseases
CD - spread from person to person (e.g measles), spread by pathogens like bacteria or viruses
ND - can’t be passed from person to person. Caused by risk factors (e.g coronary heart disease)
Health, disease interaction and causes
Health - state of physical and mental well-being
Ill health can be caused by CD/ND, poor diet, high stress and other life-situations (e.g working with harmful chemicals)
different types of diseases can interact
Tuberculosis (TB)
Communicable lung disease, fatal
immune system fights TB, but defective immune system (HIV) is more likely to suffer from infectious diseases
e.g one disease increasing risk of another
Human papilloma virus (HPV)
extremely common, mostly harmless
can cause cervical cancer (3000 women/yr in UK)
infects cervix cells
e.g one disease causing another disease
Allergies
body is infected by pathogen, which immune system fights off but the person is then left with an allergy
Asthma or dermatitis
e.g disease triggered by the immune system
Arthiritis
joint condition
difficult to move and live a normal life = isolated and depressed
e.g mental illness triggered by a physical illness
V13 - Communicable and Non diseases
Lung cancer studies, graph and history
epidemiology meaning
Studying patterns of disease to determine risk factors = Epidemiology
1930s: lung cancer rates had a sharp increase
Scientists looked at lifestyle habits to find links (correlation):
more common among smokers = positive correlation
Correlation =! cause. Graph doesn’t prove that smoking causes lung cancer. It only suggests they might be linked.
if x-axis = numbers of years of smoking, you also get a positive correlation
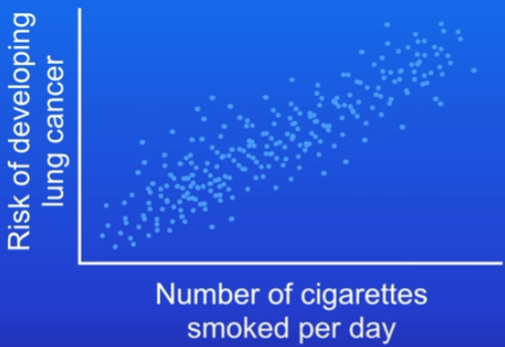
Causal mechanism
Scientists looked at how smoking could cause cancer
Found that smoke has chemicals that damage DNA and increase cancer risk = Carcinogens
Sampling issues
If investigating whether a disease is linked to diet, we want to look at every single person’s diet and then the chances of them developing the disease.
It’s not possible to sample every single person.
Scientists sample a group of people and try to draw conclusions about whole population.
Biased sample
Biased sample
Sample from only one town may not represent the entire population, so we can’t use these for conclusions about whole country.
might exercise less than average OR
exposed to certain pollution only found in that town
Avoiding bias
large sample
random
cannot draw conclusions from a small or non-random sample
v14 - correlating risk factors
ND examples
Not person to person or pathogens:
cardiovascular diseases
type 2 diabetes
most cancers
Risk factors for cardiovascular diseases
high fat, low veg diet increases certain types of cholesterol levels in the blood
this increases the rate that fatty materials build up in arteries
high salt diet increases blood pressure
increasing the risk of developing this
smoking increasing risk
regular exercise decreases risk
Risk factors for lung disease and cancer
smoke has chemicals that damage DNA and massively increase cancer risk = Carcinogens
smoking also increases risk of other lung diseases; emphysema
both lead to very poor quality of life
Smoking when pregnant
increases miscarriage risk and premature death
leads to birth with low body-mass
Drinking alcohol when pregnant
fetal alcohol syndrome = learning difficulties and other mental/physical problems
Drinking alcohol on adults
excessive = increase risk of liver cirrhosis/cancer
brain - addiction and memory loss
Type 2 diabetes and how risk factors interact
struggle to control their blood glucose levels
can lead to blindness
may need limb amputation
obese = higher risk. Risk factors can interact; excess alcohol can lead to obesity
v16 - Lifestyle and disease
Leaf def and tissues
A plant organ that contains different tissues:
upper and lower epidermis
waxy cuticle
stomata
guard cells
palisade mesophyll
spongy mesophyll
xylem
phloem
Epidermal cells function and location
top and bottom of the leaf are covered by a layer of very thin cells
epidermis protects the leaf’s surface
upper epidermis
transparent = light can pass through to the photosynthetic cells bellow
covered with waxy cuticle
lower epidermis
has tiny pores called stomata
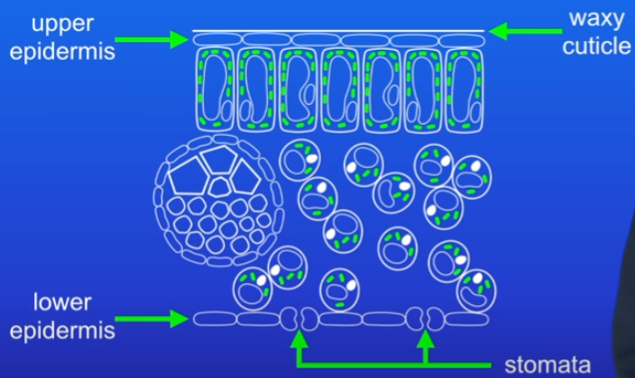
Waxy cuticle
cover the upper epidermis with a thin layer of oily material
reduces the evaporation of water from the surface = prevents from drying out
Stomata
on the lower epidermis
allow co2 to enter the leaf and oxygen to leave
help control water vapour amount that passes out
guard cells on either side
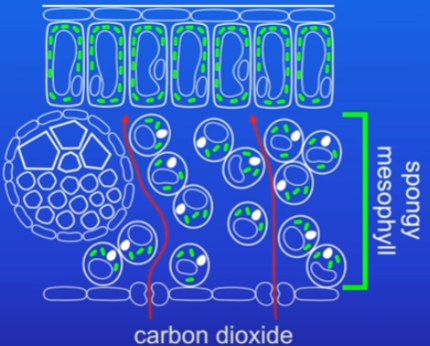
Palisade mesophyll
palisade cells are packed full of chloroplasts (contain chlorophyll, absorbs light needed for photosynthesis) where photosynthesis takes place
underneath there is spongy mesophyll
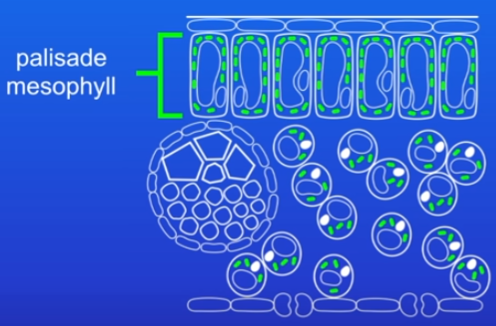
Spongy mesophyll
full of air spaces which allow co2 to diffuse from stomata through it to the palisade cells
other way round for o2 - palisade to spongy to stomata