2 Implant (Final): IMPLANT-SUPPORTED FIXED RESTORATIONS
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
• preservation of tooth structure on the teeth adjacent to the edentulous
area
• avoiding tooth hypersensitivity that can accompany tooth preparation
• avoiding the potential need for root canal treatment when teeth are
prepared for fixed partial denture (11% may require RCT)
• improved access for oral hygiene
• enhanced gingival response
• fewer complications with single dental implants compared with fixed
partial dentures
Reasons for selecting a single implant crown over a 3-unit FPD:
true
t/f: The survival of three-unit TFDPs and ISCs over 15 years was not statistically different when replacing posterior teeth, but ISCs survived significantly better when replacing anterior teeth.
true
t/f: the complication rates between TFDPs and ISCs were similar
false
t/f: the economic burden between TFDPs and ISCs were similar
TFDPs
Which has the higher economic burden, TFDPs and ISCs?
retaining teeth through periodontal care
Which is more cost effective, retaining teeth through
periodontal care and both initial root canal treatment and root canal retreatment OR tooth extraction and rehabilitation with a single implant?
external abutment connection interface
A implant w/ a coronal surface w/ an external hexagon:
internal abutment connection interface
A implant w/ a coronal surface of the implant has a core that
is threaded or tapered or has a polygonal design:
engaging
refers to presence of anti-rotational features of the implantabutment connection mechanism:
false
t/f: multiple unit (splinted) restorations are at more risk than single unit restorations
internal or external
Today anti-rotational features can be either:
single tooth restorations
What type of restorations always require ENGAGING
(antirotational) connections?
abutment supported, cement retained FPD
ID the type of implant fixed partial denture:
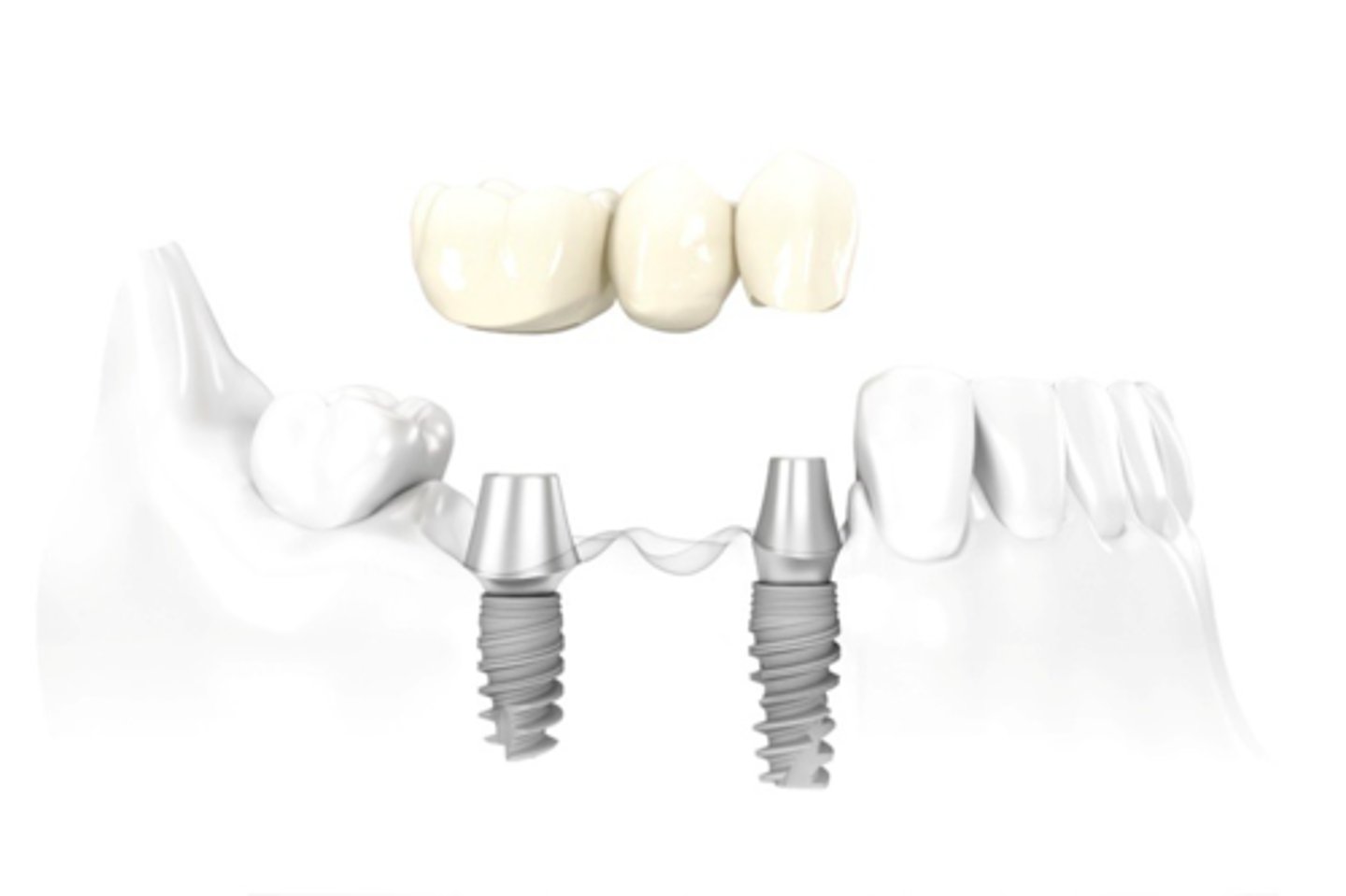
abutment supported, screw retained FPD
ID the type of implant fixed partial denture:
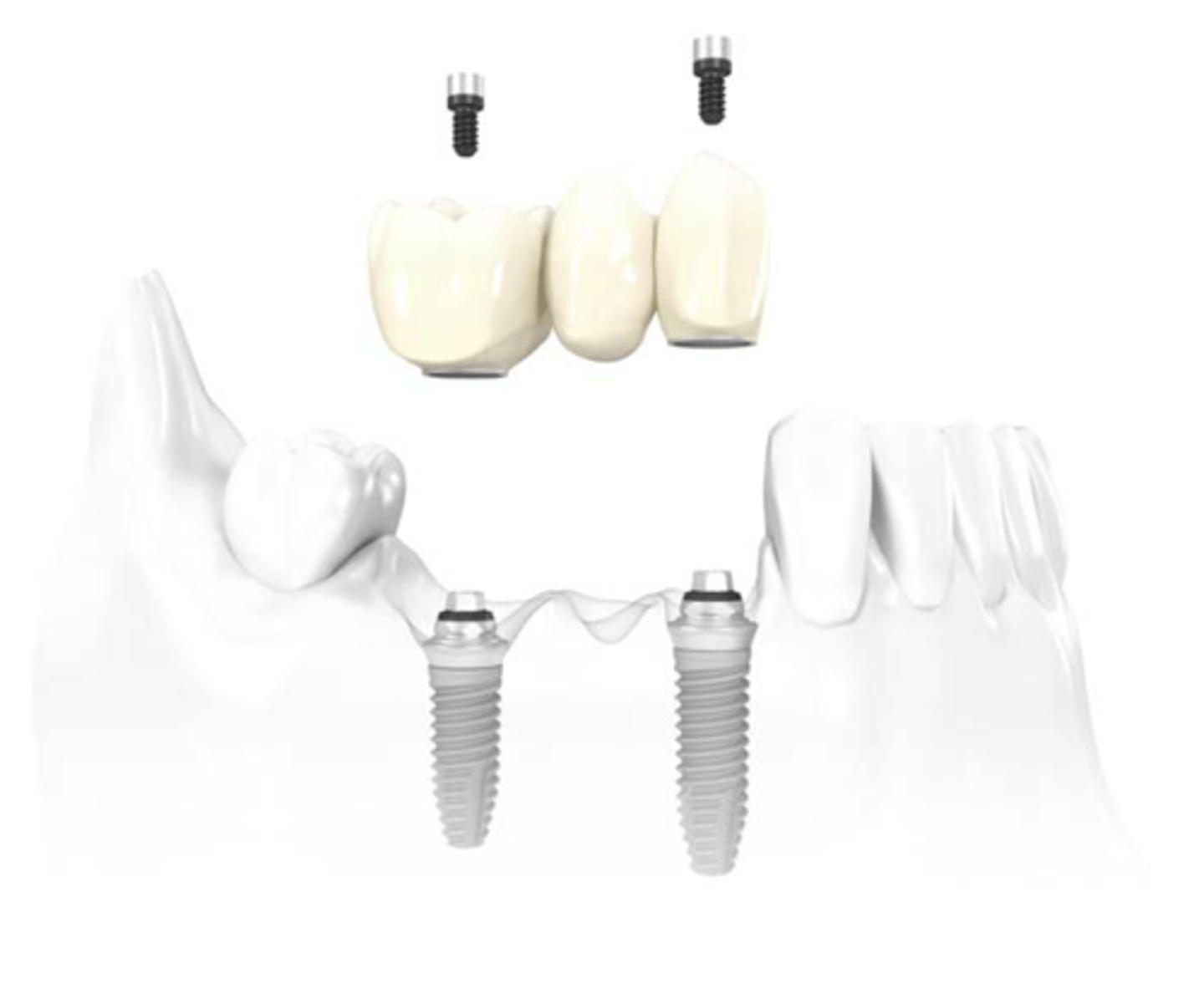
implant supported, screw retained FPD
ID the type of implant fixed partial denture:
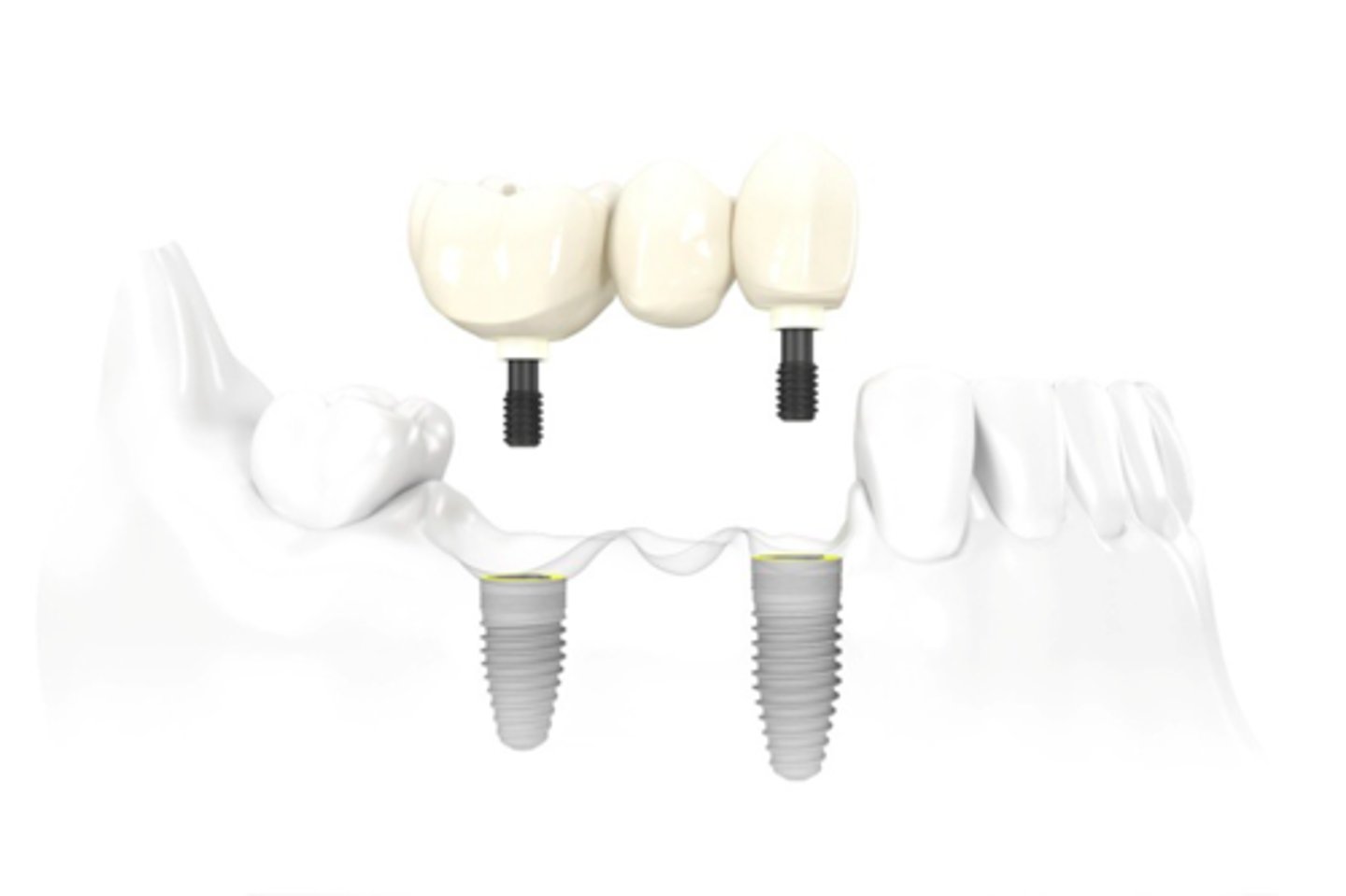
healing abutment
Implant component placed at stage-two surgery to guide
periodontal soft tissue healing prior to definitive prosthetic restoration:
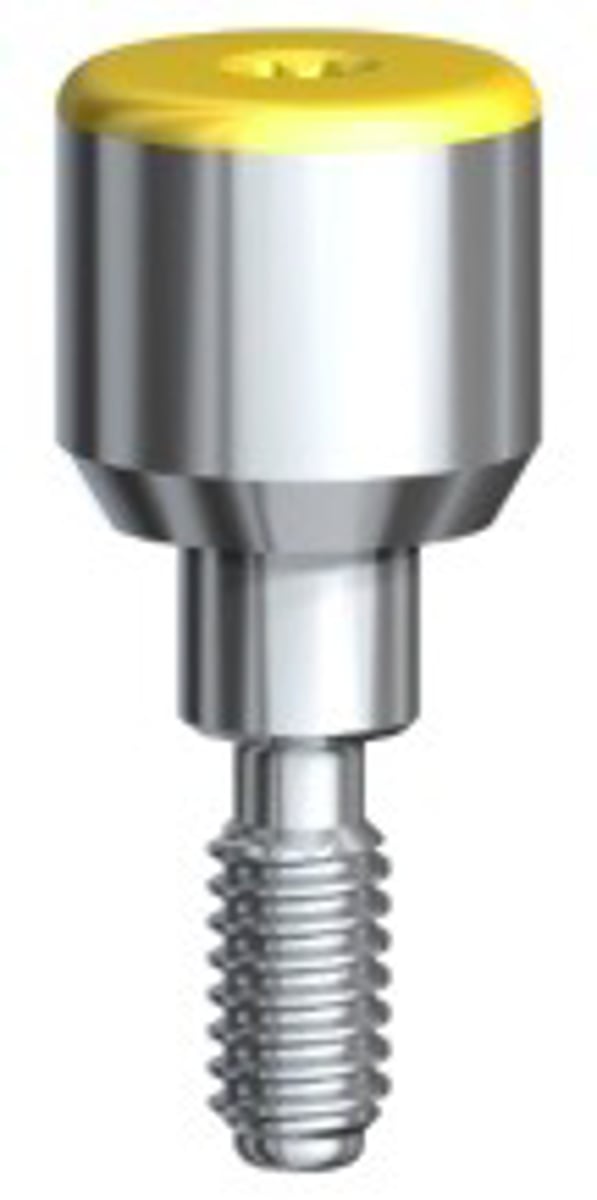
non-anatomical
ID the type of healing abutment:

anatomical
ID the type of healing abutment:
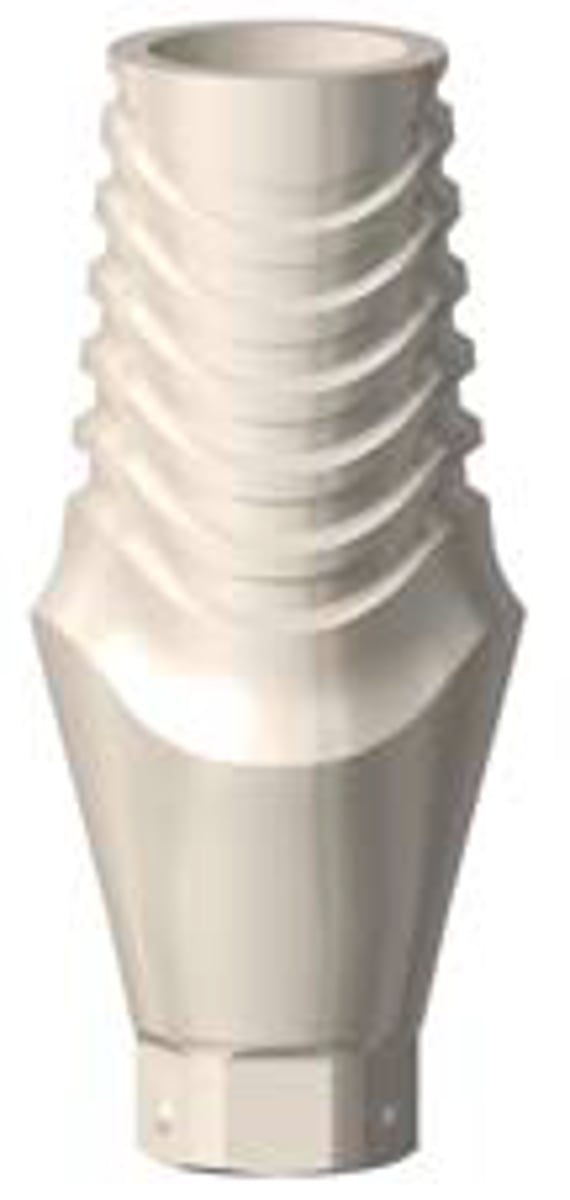

impression coping
in traditional implant impressions, the implant location is picked up via _______
scan body
in digital implant impressions, the implant location is picked up via _______
impression coping
• any device that registers the position of the dental
implant or dental implant abutment relative to adjacent
structures;
• most such devices are indexed to assure reproducible
three dimensional location
closed tray / transfer technique
ID the technique:
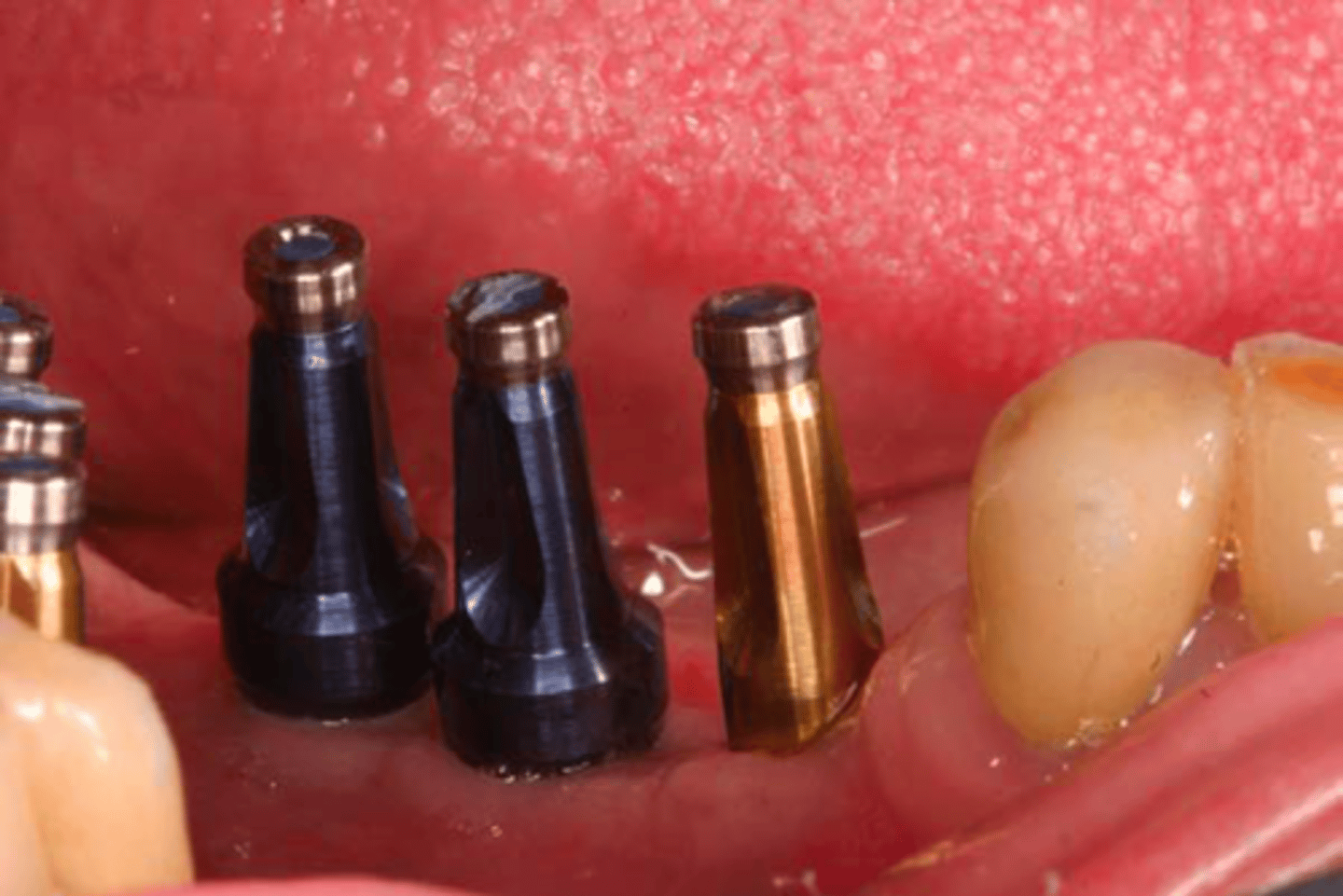
closed tray / transfer technique
ID the technique:
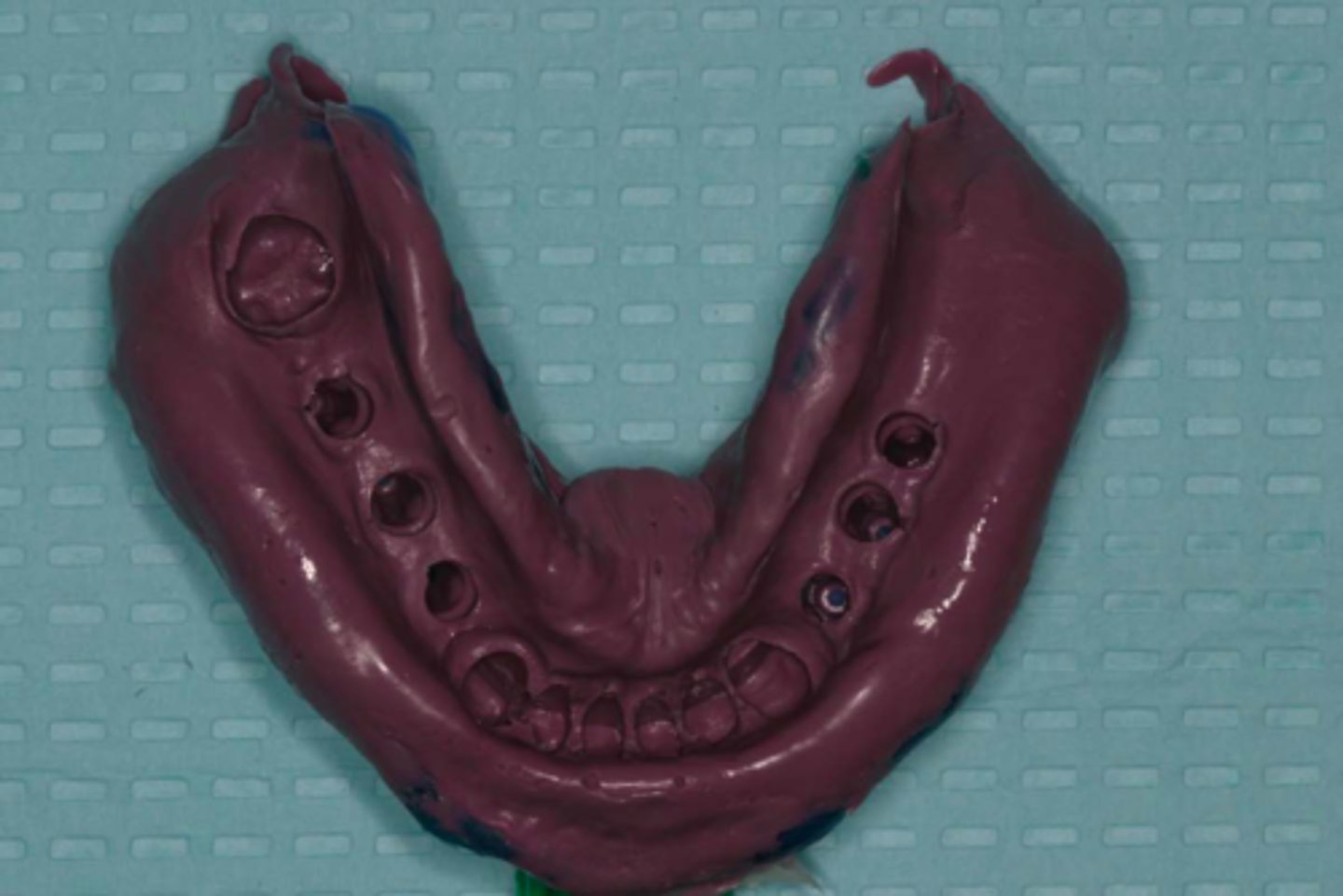
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID the technique:
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID the technique:
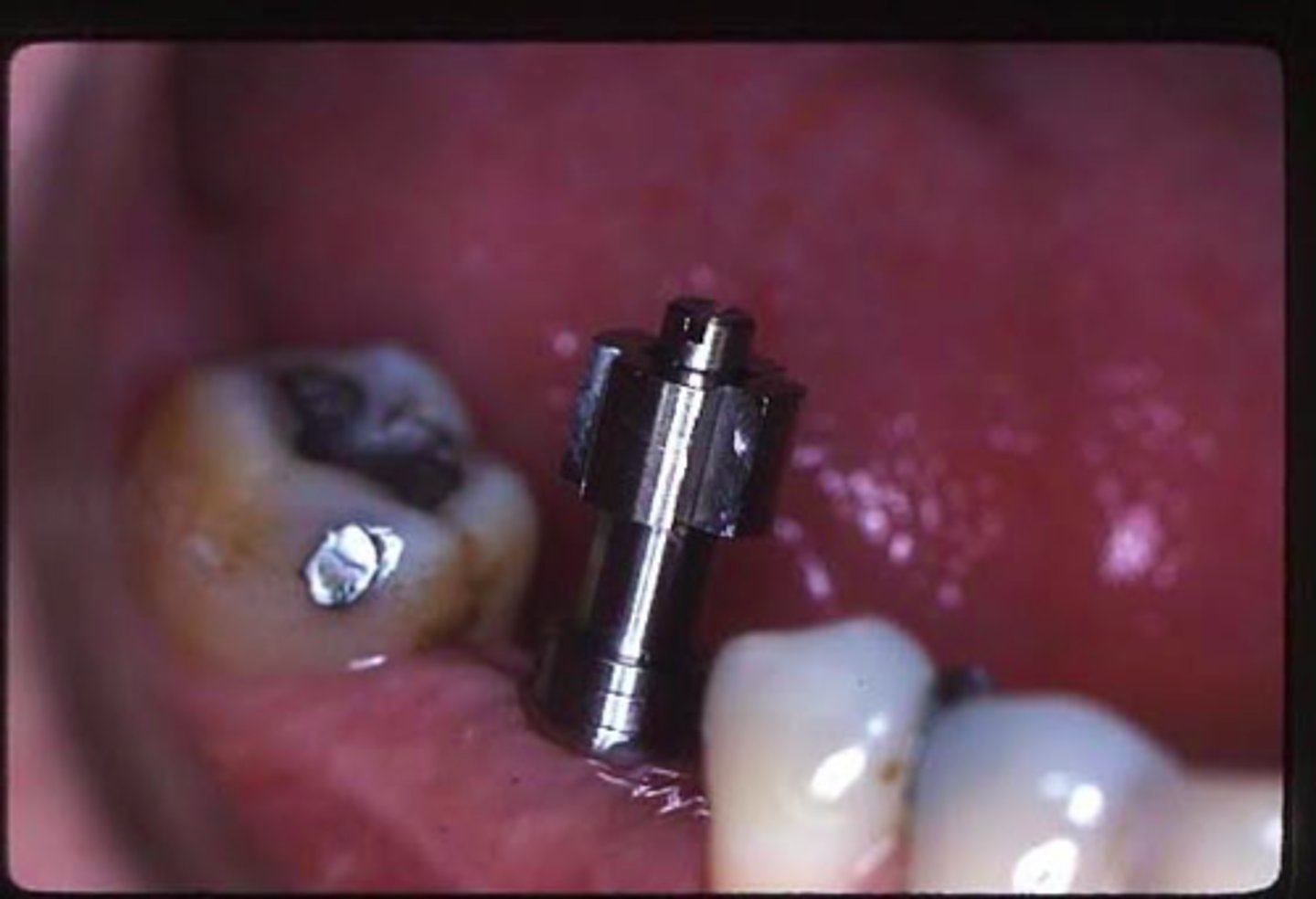
closed tray / transfer technique
ID the technique on the patient's left:
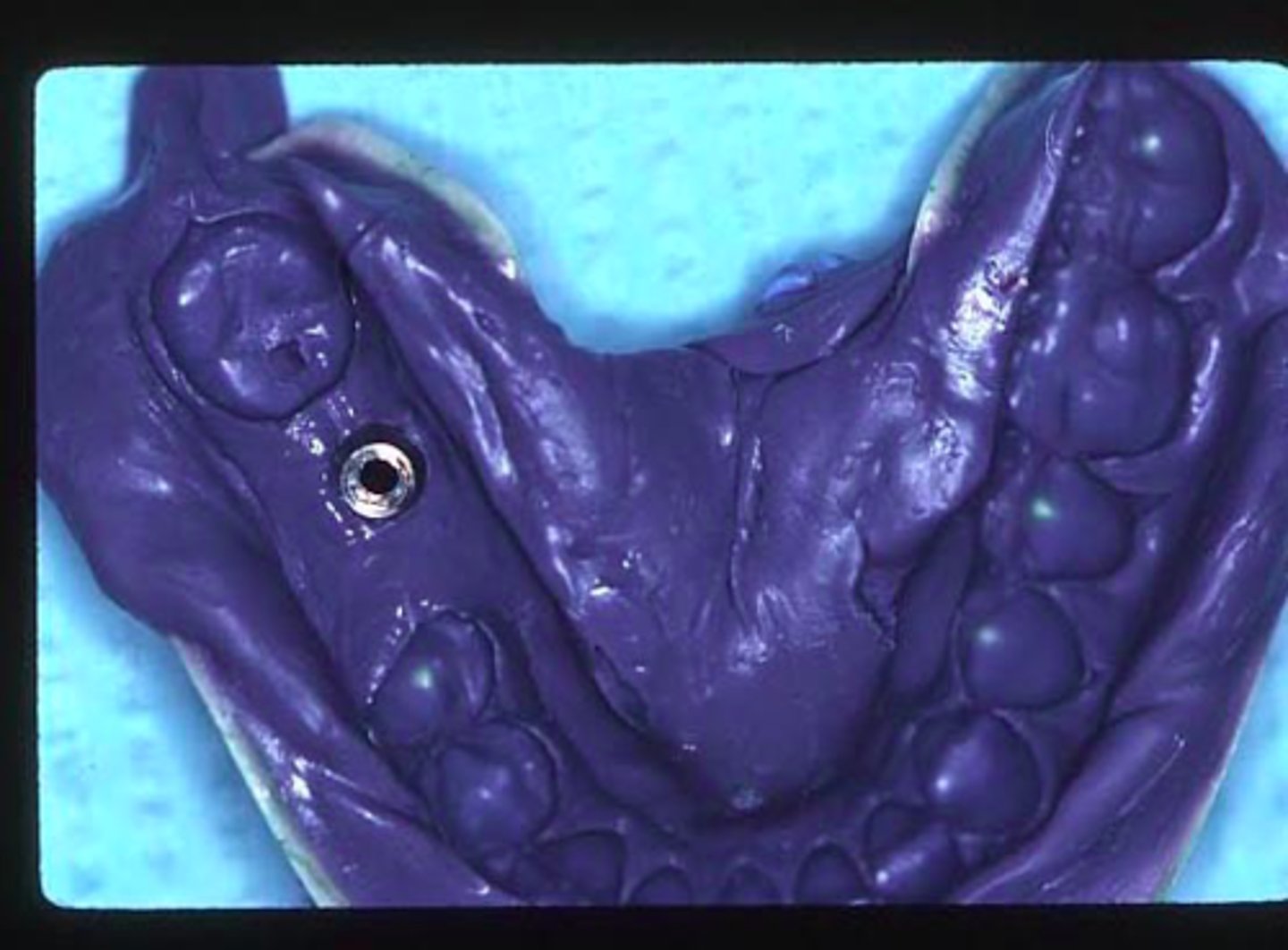
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID the technique on the patient's right:
implant replica
ID the part:
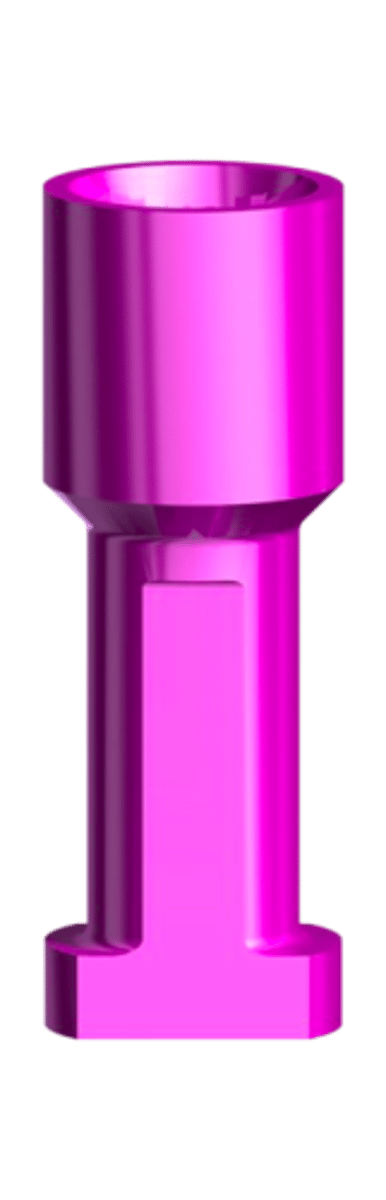
implant replica/analog
-replica of the implant that is embedded in
the working cast
• has same platform and connection
mechanism as the implant
• used during fabrication of the implant
prosthesis
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID which technique the following quality belongs to:
• reduces the effect of the implant angulation
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID which technique the following quality belongs to:
-removes the concern for replacing the coping back into its respective space in the impression
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID which technique the following quality belongs to:
-there are more parts to control when
fastening
open tray/ pick-up technique
ID which technique the following quality belongs to:
-there may be some rotational movement of the impression coping when securing the implant analog
closed tray / transfer technique
ID which technique the following quality belongs to:
- better for pts with limited mouth opening
closed tray / transfer technique
ID which technique the following quality belongs to:
- better for pts w/ gag reflexes
• limited mouth opening
• gag reflex
• if impression of natural teeth are to be
made at the same time with the implant(s)
• less number of implants
What are some indications for the closed tray / transfer technique?
- 4 or more implants
- angulation over 15 degrees
What are some indications for the open tray/ pick-up technique?
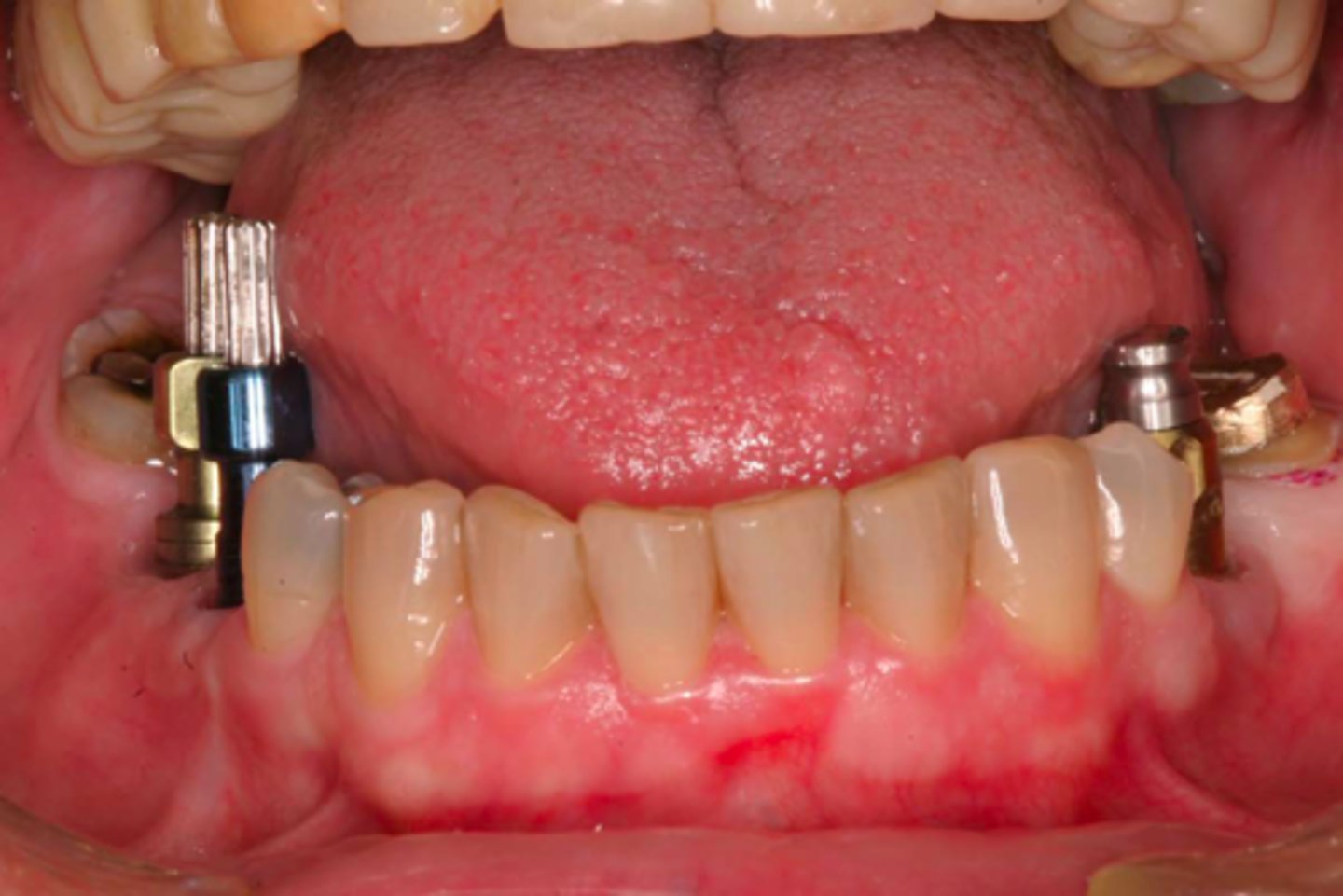
open tray/ pick-up technique
Which impression technique should be used here?
open tray/ pick-up technique
An _________ will reduce the effect of
the implant angulation
verification jig/index
what can you use to verify the accuracy of a multiunit implant bridge?
verification jig/index
ID the method:
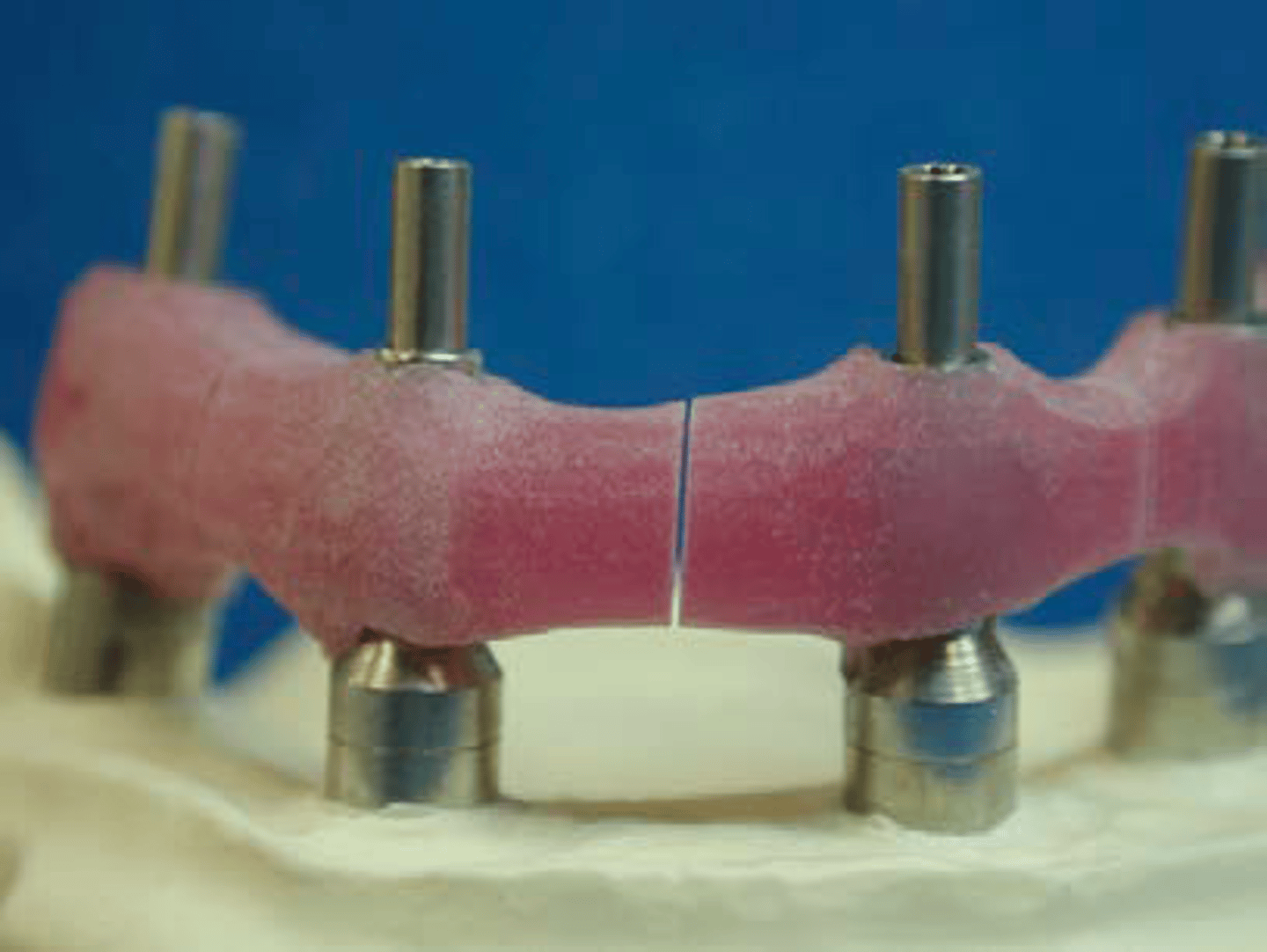
scan body
ID the part:
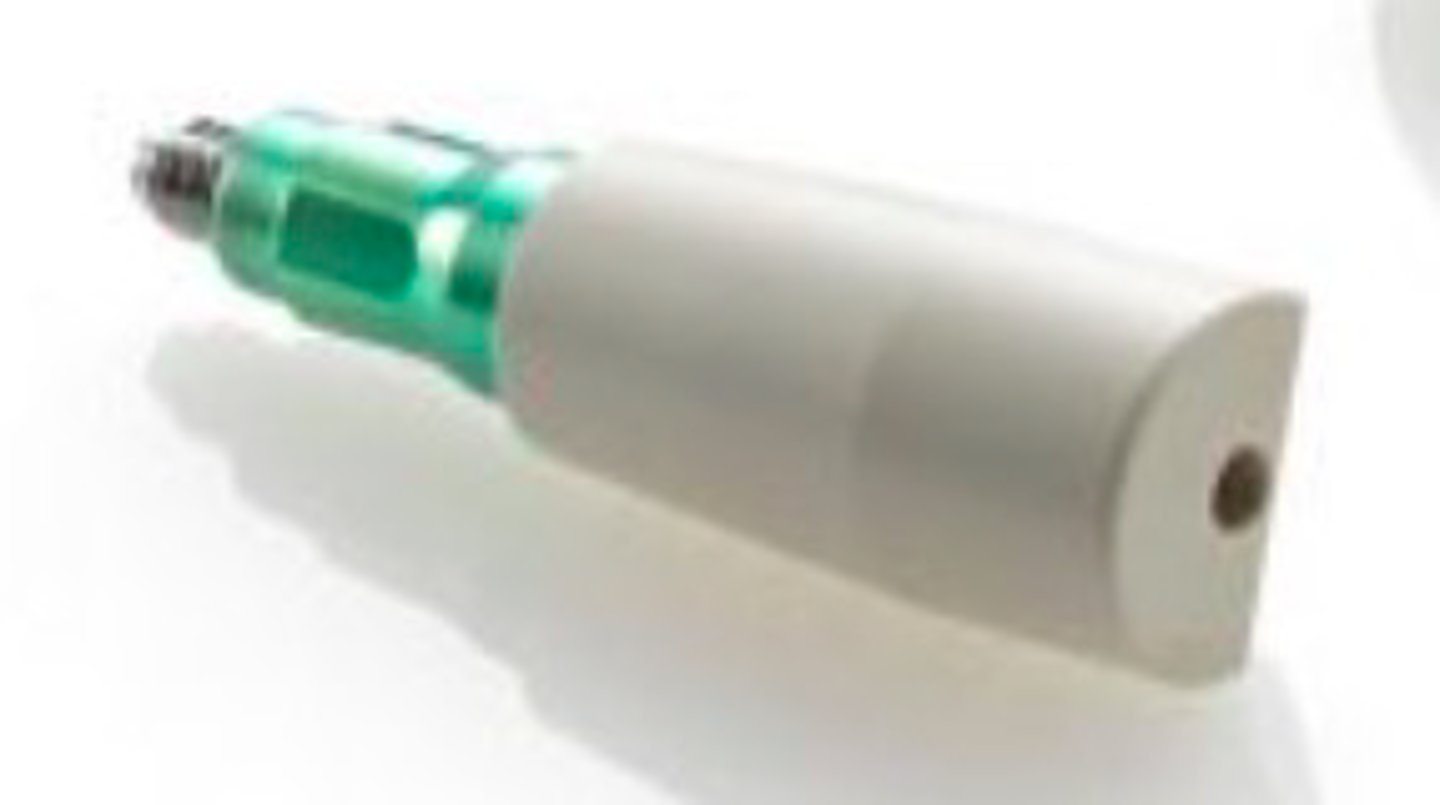
scan body
• serves the same purpose in digital design that the
impression coping serves in the traditional impression and
model technique
• all are secured on the implant with screws
Standard Tessalation Language
digital scans are read and stored in ______ format
Digital Imaging and Communication In Medicine
CBCTs are read and stored in ______ format
• Complete arch scans (particularly for mandible) may not be
possible or accurate
• Scans for removable prosthesis may not be possible or
accurate
• High initial/ acquisition cost
• Learning curve
What are some disadvantages of digital implant scans:
• Real-time imaging
• Easy repeatability
• Step-by-step imaging of relevant segments
• No need to disinfect and clean impressions or
impression trays
• Chairside analysis
• Rapid communication and availability
• Archivability
• Material savings
• Chairside CAD/CAM option
• Color selection
• Shorter over all treatment time
• More comfortable for the patient
• Easy bite registration
What are some advantages of digital implant scans:
engaging temporary abutment
ID the part:
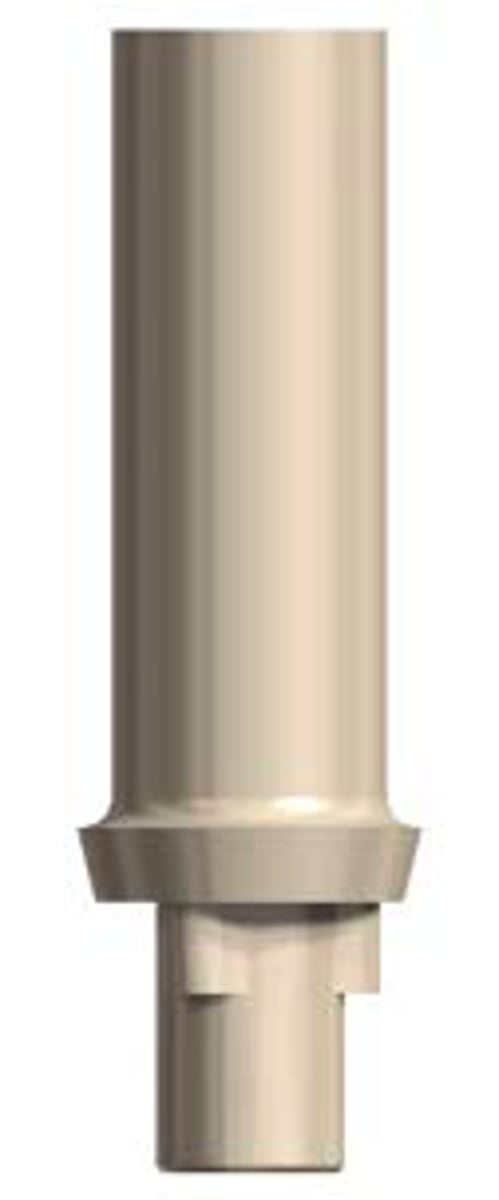

non-engaging temporary abutment
ID the part:
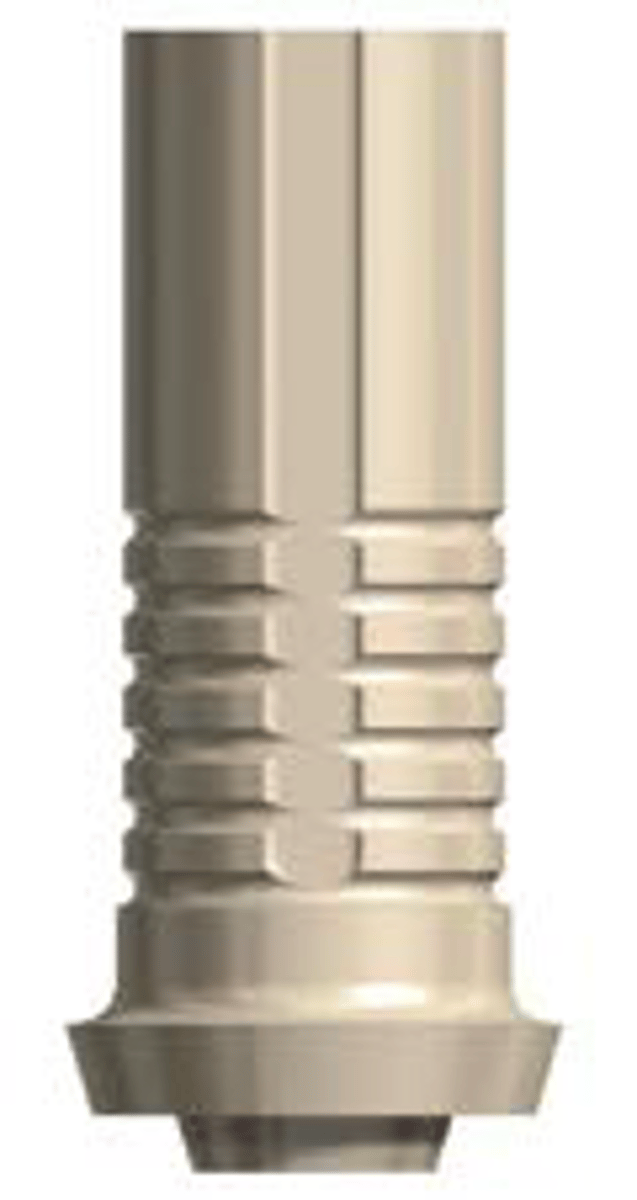

- cement
- screw
What are the 2 types of retention for an implants
• in situations of minimal interarch space
• to avoid a cement margin and the possibility of cement residue
• when retrievability is of importance
• in the esthetic zone, to facilitate tissue contouring and
conditioning in the transition zone (emergence profile)
What are some indications for a screw retained implant:
• For short-span prostheses with margins at or above tissue level to simplify
fabrication procedures
• To enhance esthetics when the screw access hole is visible or in cases of
malposition of the implant
• When an intact occlusal surface is desirable
• To reduce initial treatment costs
What are some indications for a cement retained implant:
prefabricated abutment
this type of abutment is:
- frequently titanium
- mostly engaging
- mostly used for cement type
- less expensive
- measured from platform to gingival margin
prefabricated abutment
ID the part:
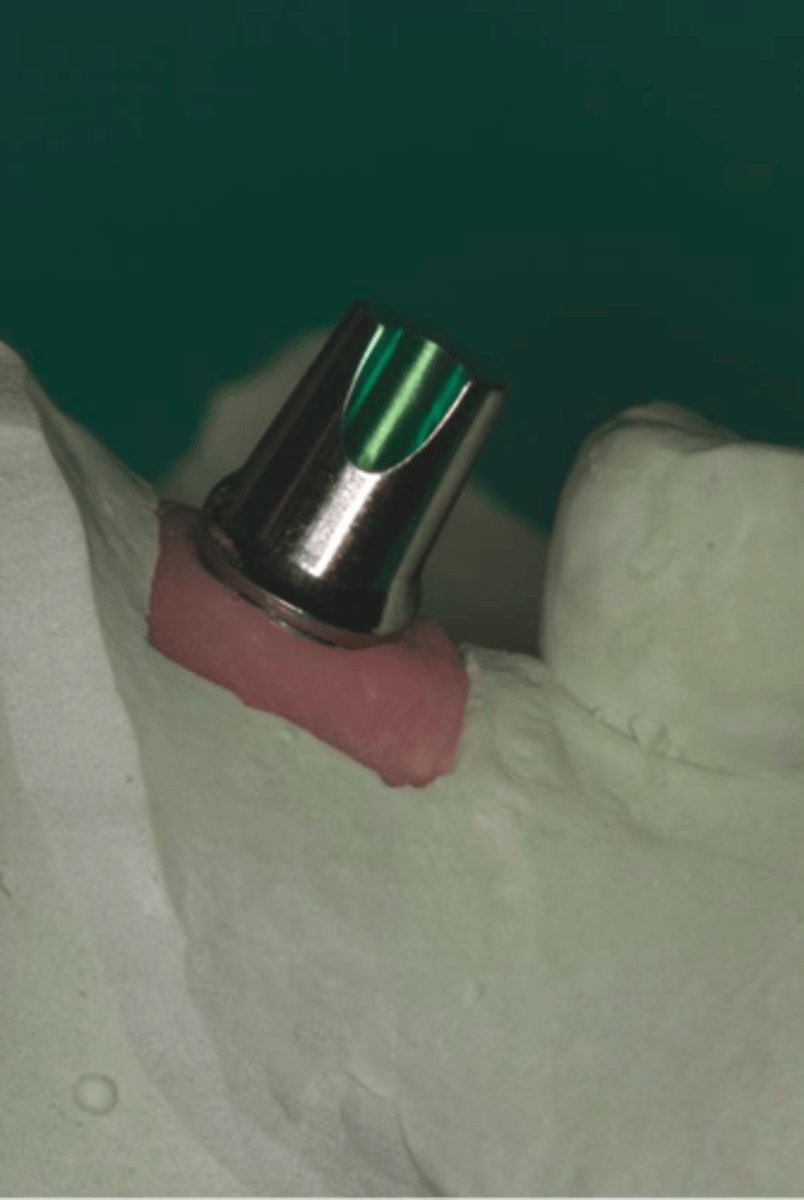

prefabricated abutment
_________abutments do not alter emergence profile, since
their cross section is round and the resulting tissue profile is
round.
custom abutment
this type of abutment is:
• most frequently for cement type restorations
• can be made of cast gold alloy, titanium or ceramic
• all should be 'engaging' type for single unit restorations
• more expensive than prefabricated cement type abutments
• better esthetics (emergence profile)
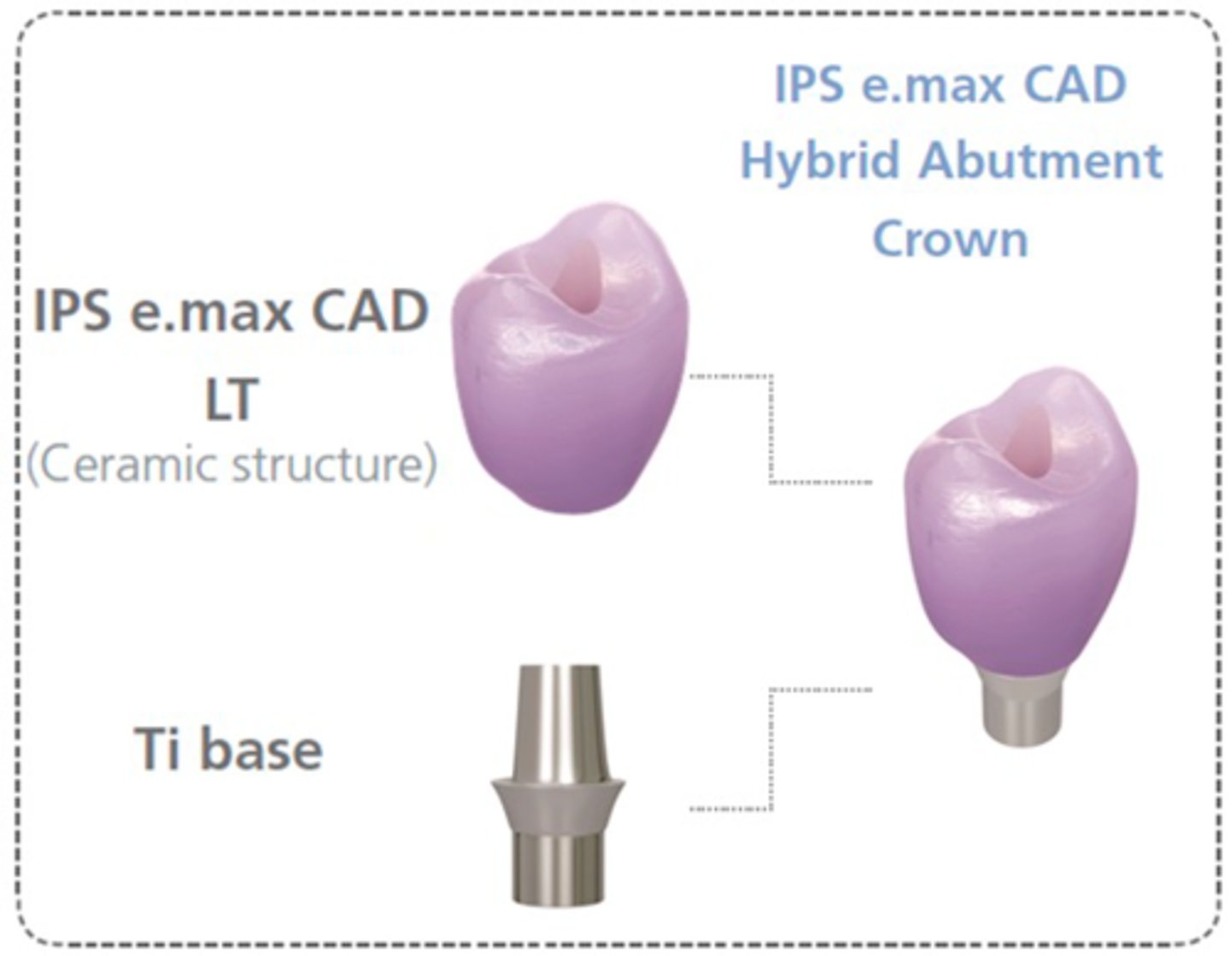
hybrid abutment
this type of abutment is an individually milled ceramic (lithium disilicate or Zr abutment) which is luted to the Ti base
-shape, emergence profile and esthetic properties of this
abutment can be ideally adjusted with the design software
Angulated screw channel (ASC)
• by Nobelbiocare in 2016
• TUSDM predoctoral clinic started 2019
• Only for conical implant abutment connection mechanism
• Ceramic restorations or abutments on titanium inserts
• Screw access hole can be up to 25 degree off long-axis
• Uses special screw and screw driver
Angulated screw channel (ASC)
ID the part:
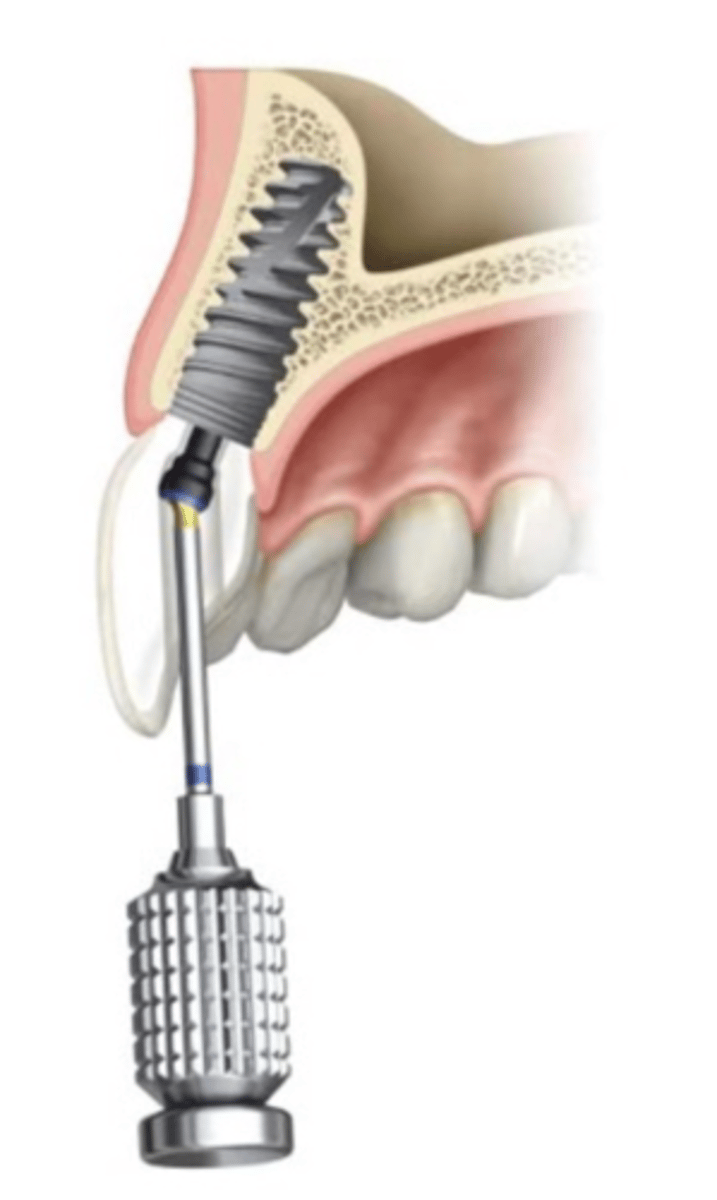
screw-retained single unit restorations
ID the type of restoration:
Always
– secured directly onto the implant (implant supported)
– involve
• a CAD/CAM (Zr, Alumina, Lithium disilicate) or cast custom
abutment (Porcelain does not bond very well to Titanium)
• an engaging abutment
UCLA abutment
-Prosthetic implant component developed as a
plastic castable pattern that can be modified
by adding wax for custom shape and
dimensions (lost wax technique)
• This is a foundation for creating a cast-tocustom
option
• The component is screw retained directly into
the implant, which circumvents the
attachment screw.
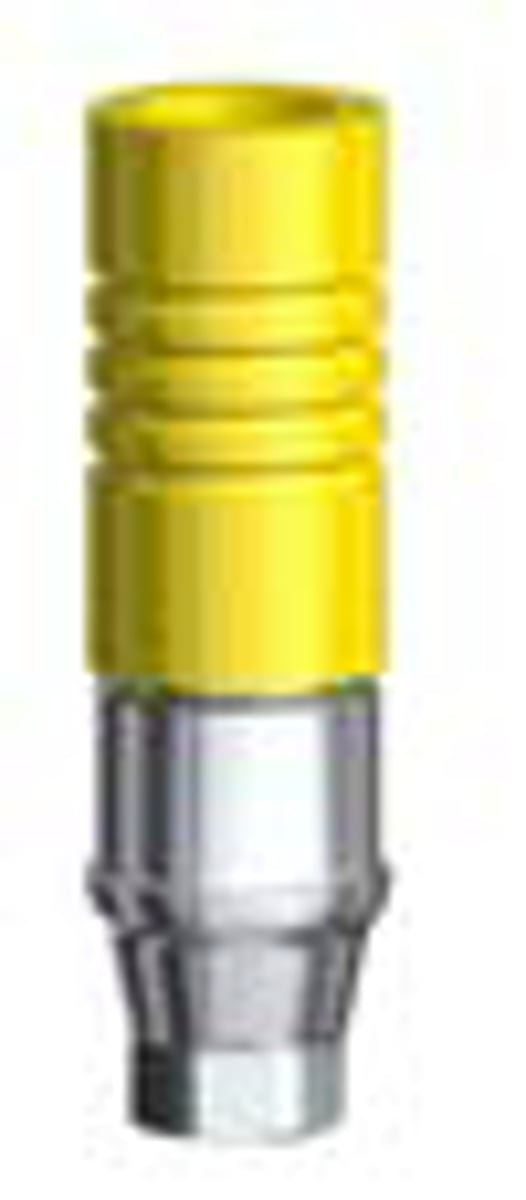

implant-supported ceramic crown *monolithic
• combines abutment and
monolithic crown in one piece
• an efficient two-in-one solution
made of lithium disilicate or
zirconia which is directly luted to
a Ti base
• Good for non-esthetic areas for
patients who do not exhibit
parafunctional activity
Multiunit abutments
Used for splinted crowns or FPDs:

implant
Use ____ support if implants are <3 mm subgingival and parallel to each other
abutment
Use ____ support if implants are placed very subgingival and/or not parallel to each other
abutment
cement-retained multiple unit restorations are ALWAYS ________ supported
Position
Angulation
Interocclusal Distance
Tissue depth/Contour
What does PAIT stand for?
1. Make implant-level soft tissue cast
2. Mount cast
3. Cover implant with aluminum foil
4. Set up missing tooth to ideal form and position
5. Duplicate a wax up cast
6. Fabricate a clear thermoplastic template
7. Attach guide pin(s) to the implant
8. Retrofit and make access hole to facilitate
seating of the clear template
9. Use PAIT to analyze proper abutment selection
"PAIT" analysis using traditional workflow:
guide pin
-Type of laboratory screw used in the
fabrication of a prosthetic restoration.
• Surgical or restorative adjunctive marker used
to indicate implant angulation or location when
preparing osteotomy sites.
position
the location of the implant in relation to the intended prosthesis:
angulation
- B M L D divergence from the intended path of insertion:
interocclusal space
measure of the distance between the implant platform and the opposing tooth:
tissue depth/contour
measure the distance (BLMD) between the implant platform and the gingival margin:
tissue depth/contour
this PAIT feature determines the collar height of the abutment:
articulating paper (2 types)
-accufilm (thick)
- shimstock (thin)
What two materials should be used to check occlusion for an implant?
framework has to be tried in for passive fit
The Framework try-in/insertion sequence for a cement retained multiple unit implant is similar to single units cement-retained EXCEPT:
one-screw test "Sheffield Test"
By inserting a screw in one end of the
prosthesis and then observing whether the
prosthesis lifts off of other implant or abutment
platforms, the clinician can determine the
presence or absence of movement when that
single screw is tightened, either by clinical or
radiographic visualization of the prosthesis
access holes
Opening in a replacement
tooth's occlusal or lingual
surface of an implant-retained
prosthesis that provides
entrance for abutment or
prosthesis screw placement or
removal.
retrievability, avoid excess (residual) cement
when choosing cementation always think about:
subgingivally
Residual cement increased as margins were located more
____
true
t/f: At 2 - 3mm sugingival, residual cement is 10x as much as at 0 - 1mm