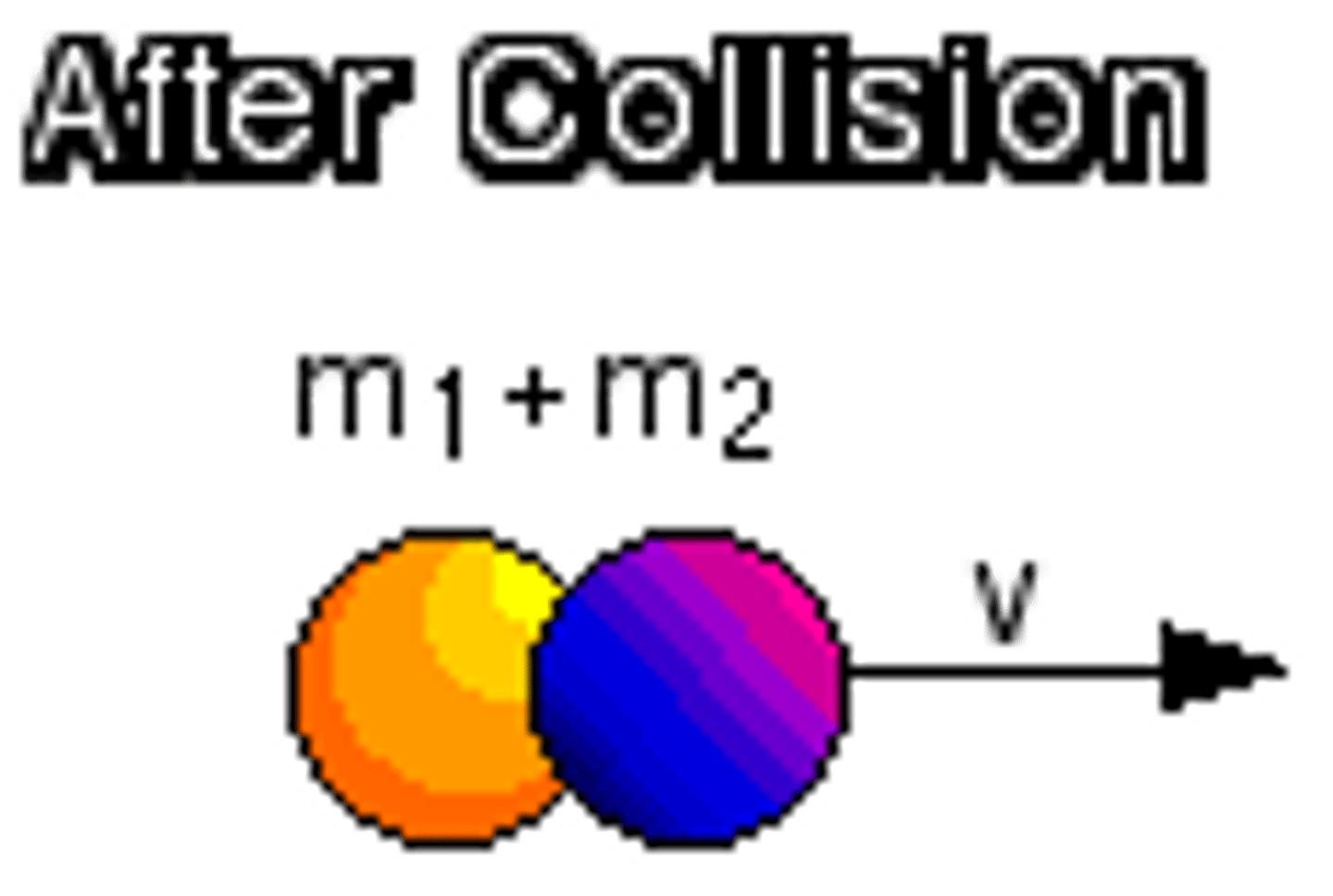Physics 1 - Lesson 5: Work and Energy
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 1 Lesson 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Lesson 5: Work and Energy
Lesson 5: Work and Energy
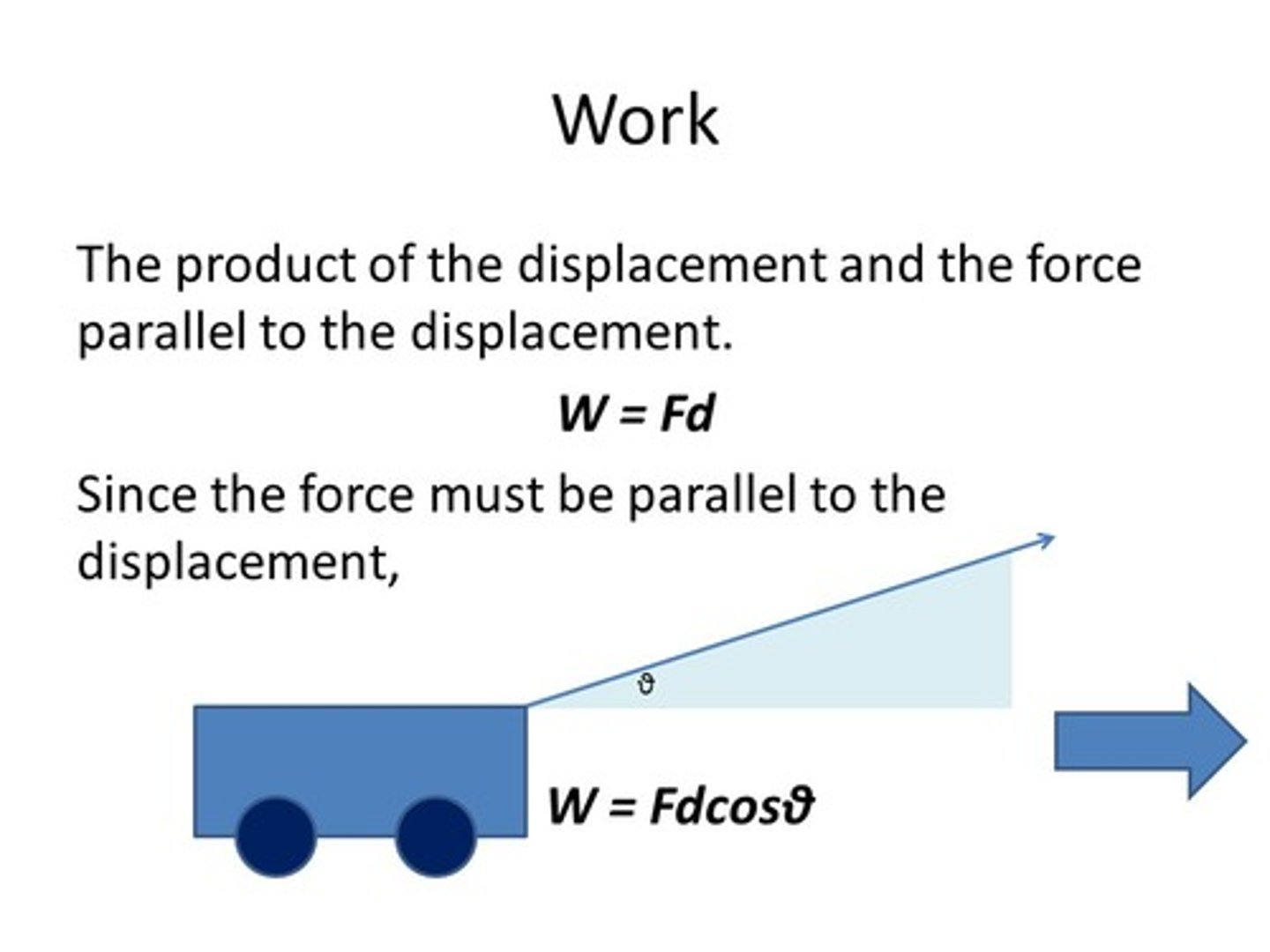
What is the equation for work in terms of force?
Work = Force x Distance
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
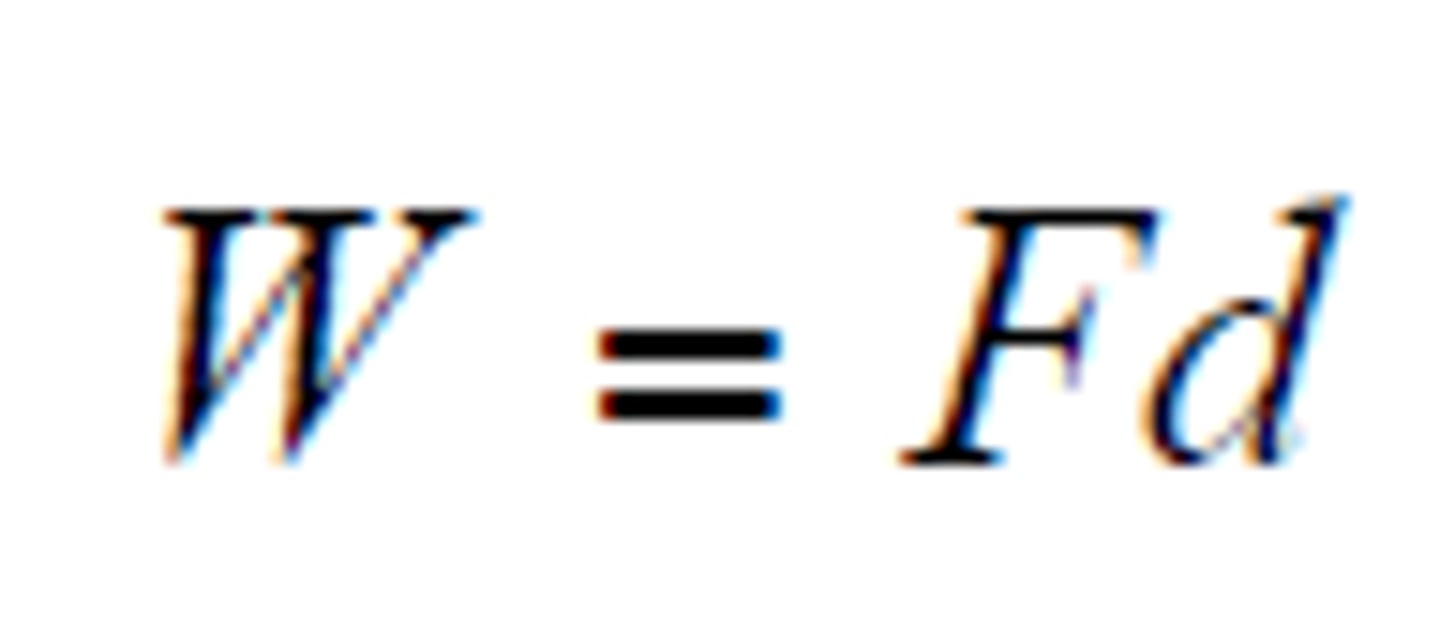
CRB There will also be some instances where the constant force and the displacement are not in the same direction. In this case, what is the equation for Work?
Work = Force x Distance x cosθ
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB True or false? If there is an obtuse angle between Force and Displacement, then the Work done by the force must be negative.
True. If there is an obtuse angle between Force and Displacement, then the Work done by the force must be negative.
This is because the cosine of the angle is negative!
If Johnny pushes a box with a force of 21.24 N over a distance of 10.76 m, how much work has Johnny done to the box (in J)?
(A) 165.9
(B) 228.5
(C) 302.6
(D) 452.1
(B) 228.5
Work = Force x Distance
Work = 21.24 N x 10.76 m
Work = approx. 200 (actual: 228.5)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB In the previous example, how much work was done by the Normal Force? How much work was done by Gravity? Explain.
There was no vertical displacement due to the Normal Force or Gravity. Because there was no displacement, the work done by these forces is 0!
What is the equation for kinetic energy in terms of velocity?
Kinetic Energy = (1/2)mv^2
m = mass
v = velocity
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
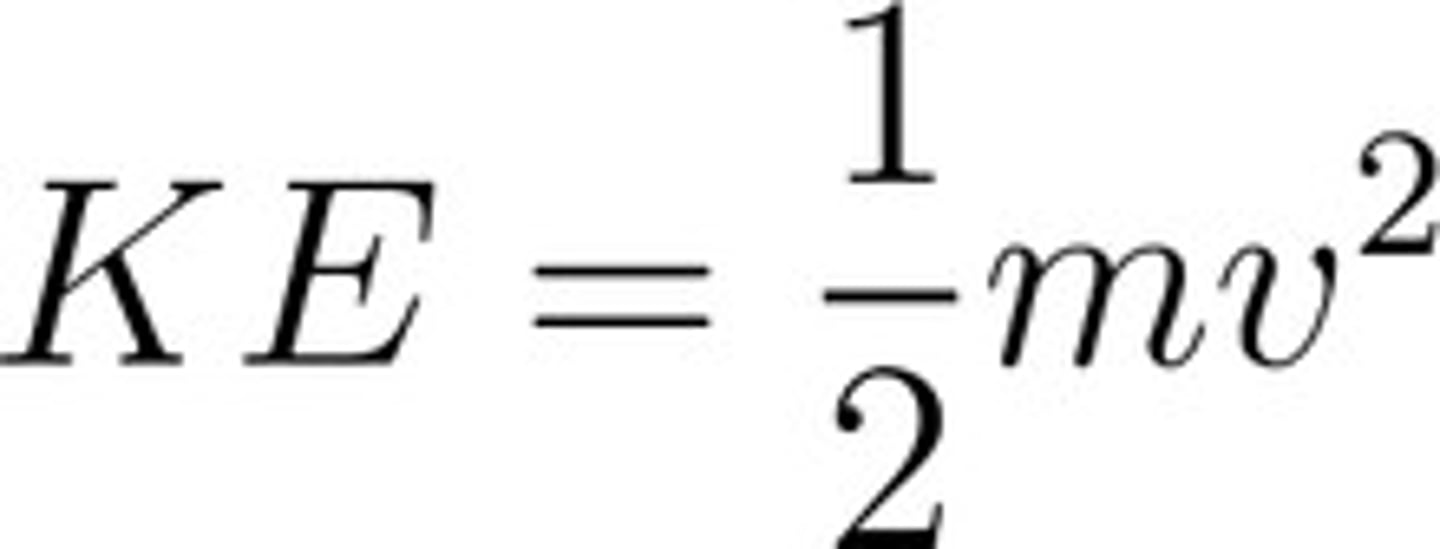
Johnny does 209.87 J of work to a box of mass 4.04 kg that was sitting still on frictionless ice. What is the velocity of the box (in m/s)?
(A) 5.67
(B) 10.19
(C) 16.78
(D) 24.67
(B) 10.19
Work = approx. 210 J
In this example, all of that work is converted to kinetic energy, so
KE = approx 210 J
KE = 1/2 mv^2
209.87 = 4.04/2 V^2
approx. 100 (actual: 103.9) = v^2
v = approx. 10 m/s (actual: 10.19)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What is the equation for gravitational potential energy?
PE = mgh
m = mass
g = acceleration due to gravity
h = height
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
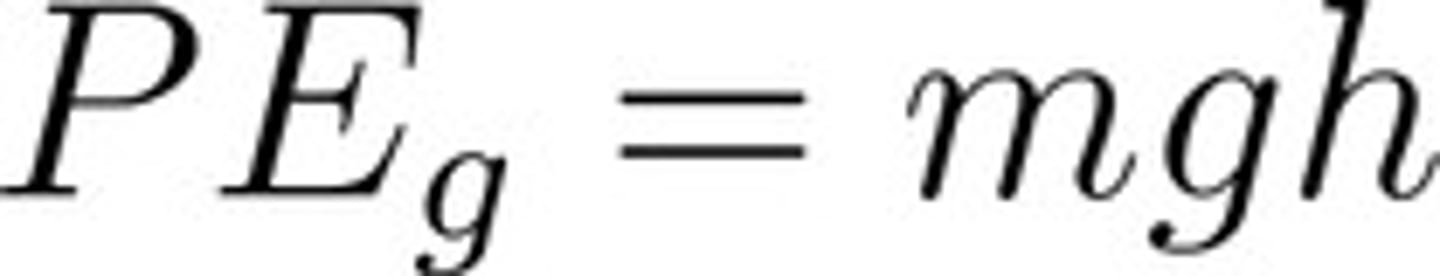
CRB In which of the following scenarios would the gravitational potential energy increase?
I. Increasing the height of the object over the flat ground.
II. Keeping the object at the same altitude, but the ground is much lower (like hovering over a cliff instead of flat ground).
III. Working on a different planet with a larger force of gravity.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following scenarios would increase Gravitational Potential Energy:
I. Increasing the height of the object over the flat ground.
II. Keeping the object at the same altitude, but the ground is much lower (like hovering over a cliff instead of flat ground).
III. Working on a different planet with a larger force of gravity.
CRB In the previous card's second example, the altitude of the object wasn't changing, but rather its reference point as the ground (or 0 potential energy position). What is the proper term for this reference point?
(A) Absolute Height
(B) Relative Height
(C) Base
(D) Datum
(D) Datum
The Datum is the 0 potential energy position, often thought of as the ground.
If a 9.76 kg ball is raised to a height of 10.34 m, what is the potential energy of the ball (in J)?
(A) 675.8
(B) 865.3
(C) 989.0
(D) 1143.6
(C) 989.0
PE = mgh
PE = (9.76)(9.8)(10.34)
PE = approx. 1000 (989.00)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/

CRB True or false? All changes in potential energy are equal to the opposite of work done by gravity (PE = -Wgrav).
False. Changes in potential energy due to gravity are equal to the opposite of work done by gravity (PEgrav = -Wgrav).
What is the Work-Energy principle? (Work in terms of Kinetic energy)
Work = change in kinetic energy
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/

If a box (9.88 kg) is moving at 11.32 m/s and is slowed by friction until the velocity is 4.89 m/s, what is the work done by friction (in J)?
(A) -751
(B) -515
(C) 515
(D) 751
(B) -515
Work = change in kinetic energy
KE = 1/2 mv^2
ΔKE = 1/2 (9.88)(4.89)^2 - 1/2 (9.88)(11.32)^2
ΔKE = (approx. 125 (actual: 118)) - (approx. 600 (actual: 633))
Work done = approx. -475 (actual: -515)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What is the equation for Hooke's law (restorative force of a spring in terms of displacement)?
F = -kx
F = Restorative force
k = spring constant
x = displacement
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/

If a spring is exerting a force of 7.23 N at a displacement of -9.65 m, what is the spring constant for that spring (in N/m)?
(A) .642
(B) .749
(C) .813
(D) .893
(B) .749
Force = 7 N
Displacement = approx. -10 m (actual -9.65 m)
F = -kx
7.23 = -k (-9.65)
k = 7.23/ 9.65
k = approx. .75 (actual: .749)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
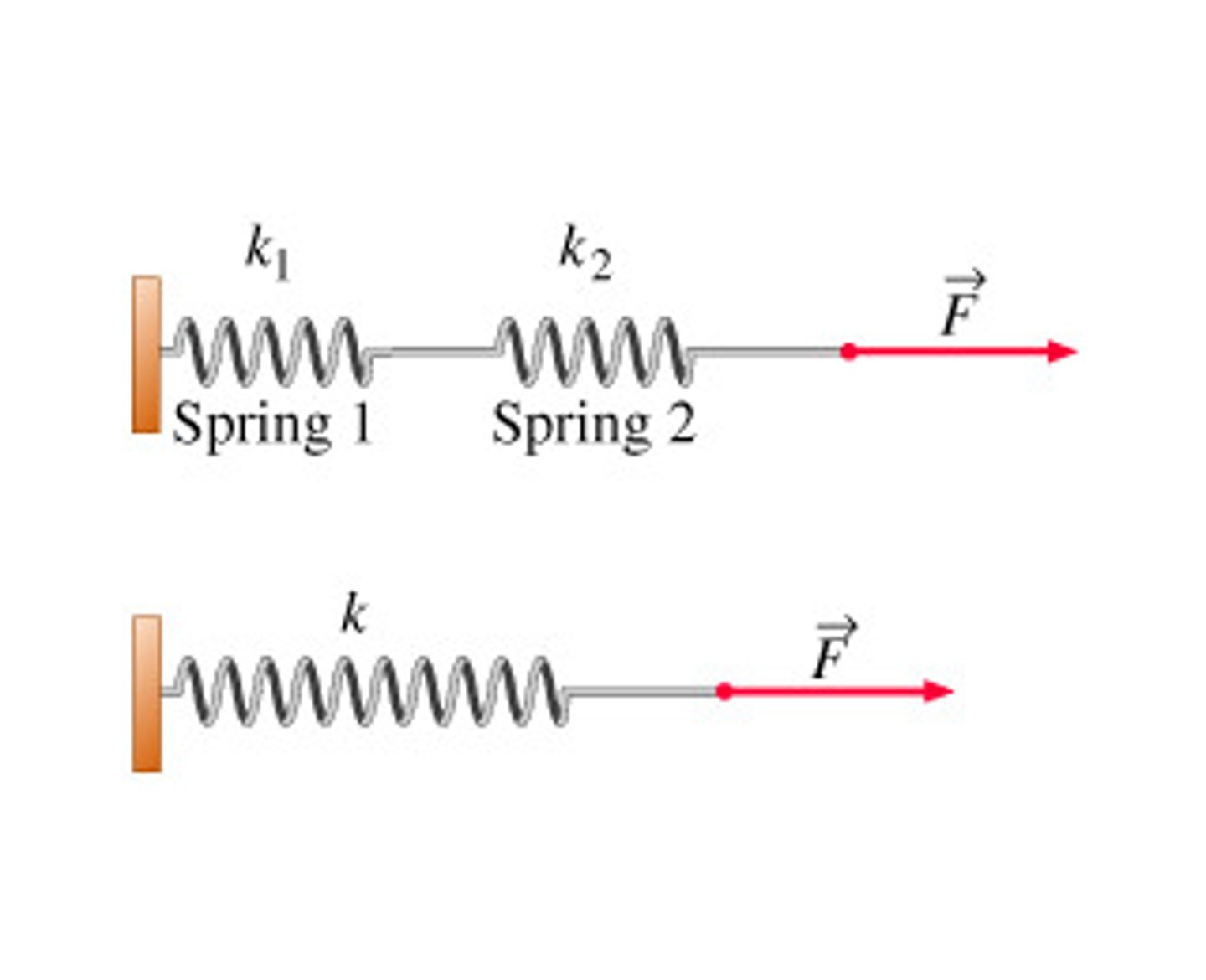
What is the equation for the potential energy of a spring?
PEs = 1/2 k x^2
PEs = Potential energy of a spring
x = displacement
k = spring constant
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/

If a box has a mass of 5.34 kg, and is pushed by a spring for 4.89 m, giving it a velocity of 11.29 m/s, what is the spring constant for that spring (in N/m)?
(A) 14.5
(B) 21.5
(C) 28.5
(D) 43.5
(C) 28.47
KE = 1/2 mv^2
KE = (.5)(5.34)(11.29)^2
KE = approx. 350 J (actual: 340)
KE = PE = 1/2 kx^2
340 J = k(.5)(4.89)^2
k = approx. 30 kg/s^2 (actual: 28.5)
Note: kg/s^2 is equivalent to N/m
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What is the difference between a conservative force and a non-conservative force?
A conservative force conserves mechanical energy, and because of this it doesn't matter what path it takes to calculate work, just the beginning and ending position.
A non conservative force doesn't conserve mechanical energy, and the energy cannot be regained by reversing the process, because of this the path affects the work done.
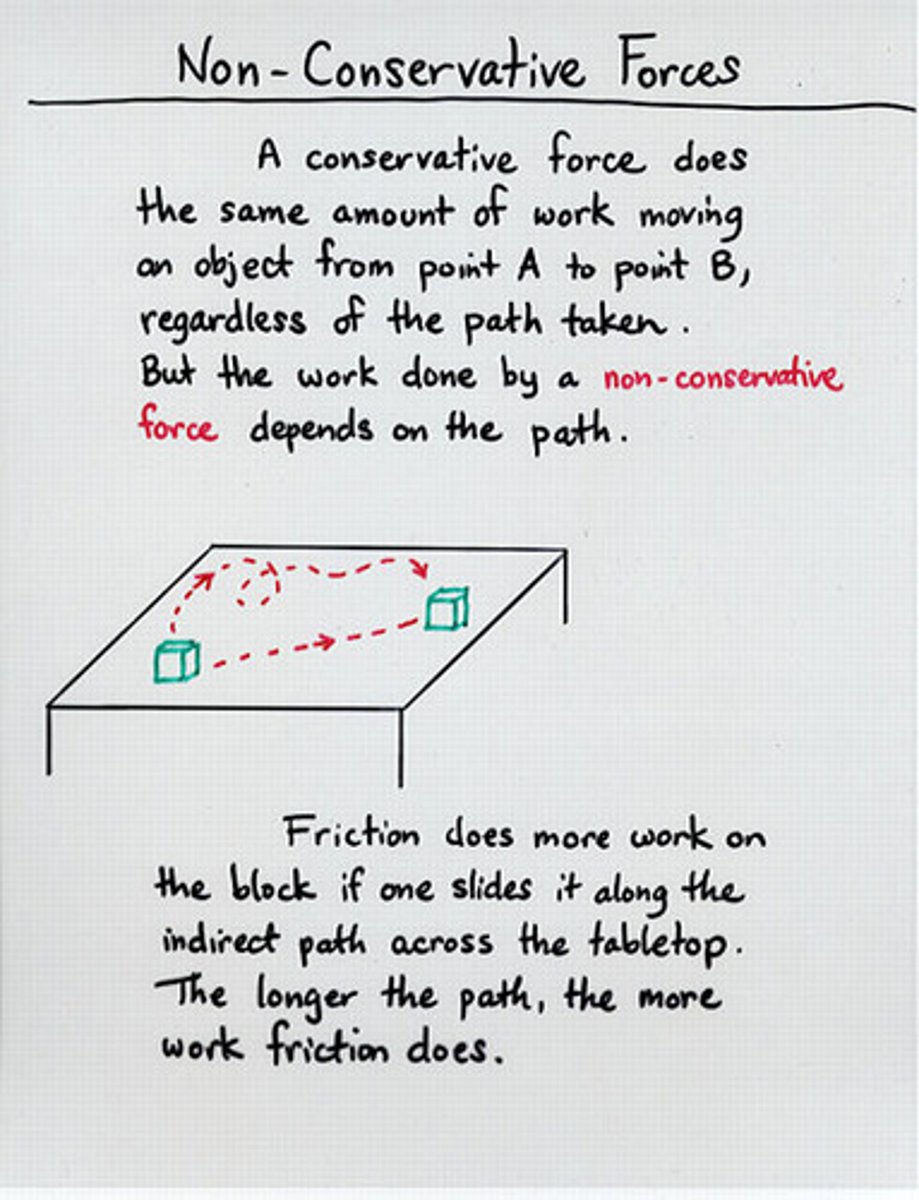
Is Gravitational Force a conservative or non-conservative force? Friction? Force of a Spring? Air Resistance?
Conservative: Gravitational force, Force of a Spring
Non-conservative: Friction, Air Resistance
CRB If you are told the total work that Friction or Air Resistance has on an object, would you be able to trace its path? Why or why not?
Although these are non-conservative forces and we know that the total work done is dependent on the path, simply knowing the amount of work done is not sufficient to determine what path the object took.
CRB True or false? When you are dealing with Conservative Forces, you can treat the force and path of object as independent and assign any arbitrary path to the object.
Why would or wouldn't this be true for Non-Conservative
True. When you are dealing with Conservative Forces, you can treat the force and path of object as independent and assign any arbitrary path to the object.
CRB Why couldn't Non-Conservative Forces be assigned any arbitrary paths and be treated independently like Conservative Forces?
For Non-Conservative Forces, there are other factors that influence the work done, which is why they are path-Dependent (not Independent!) and cannot have arbitrary paths applied.
What is the equation for power in terms of work?
Power = Work / Time
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
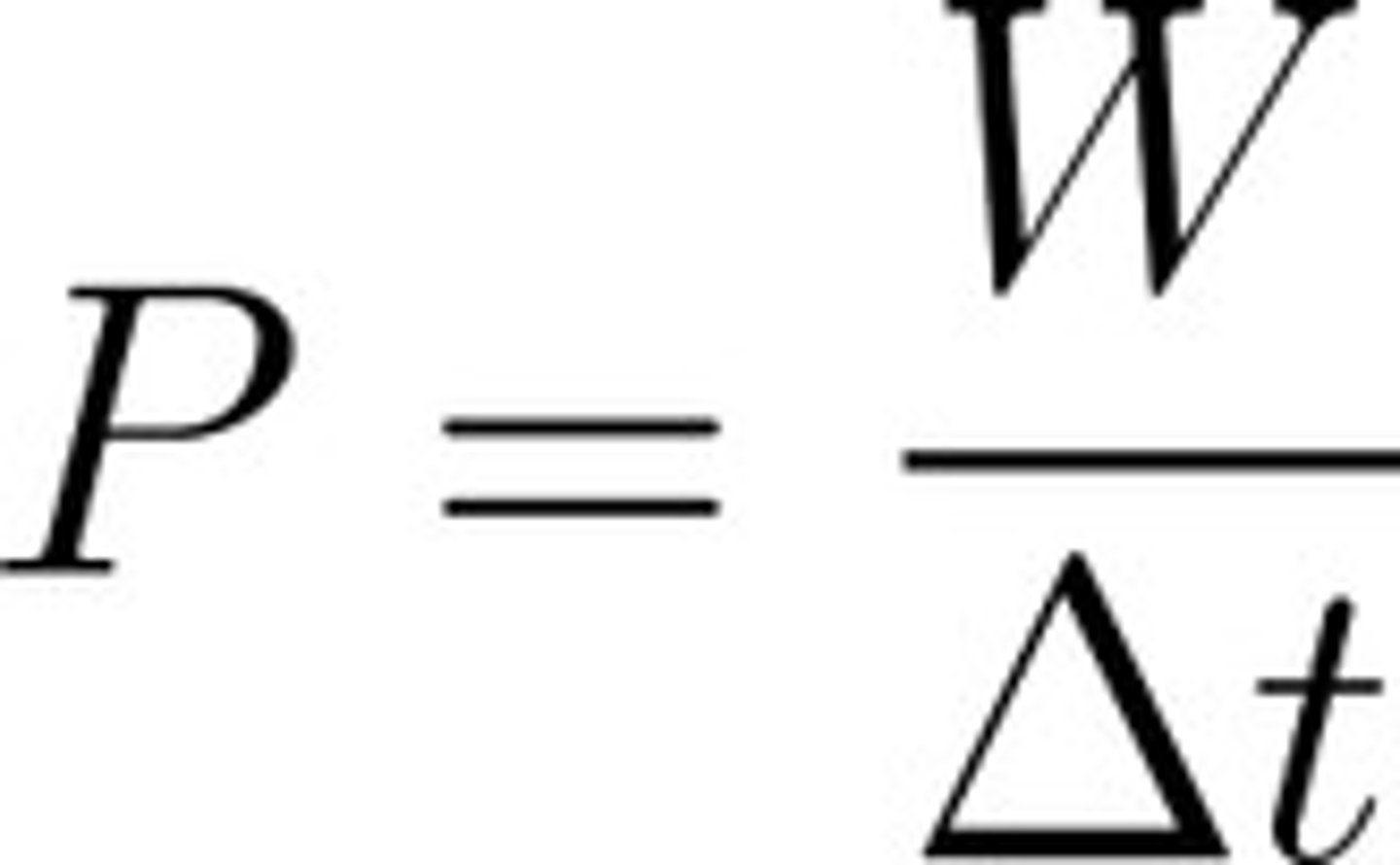
How much power does it take to lift a 96.57 kg weight 1.34 m into the air in 7.25 seconds?
(A) 97.65
(B) 174.92
(C) 302.65
(D) 425.43
(B) 174.92
Work Done = PE = mgh
PE = (96.57)(9.8)(1.34) = approx. 1000 J (actual: 1268.16)
Power = work/time
Power = 1268.16 J / 7.25 s
Power = approx. 200 J/s (actual: 174.92)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
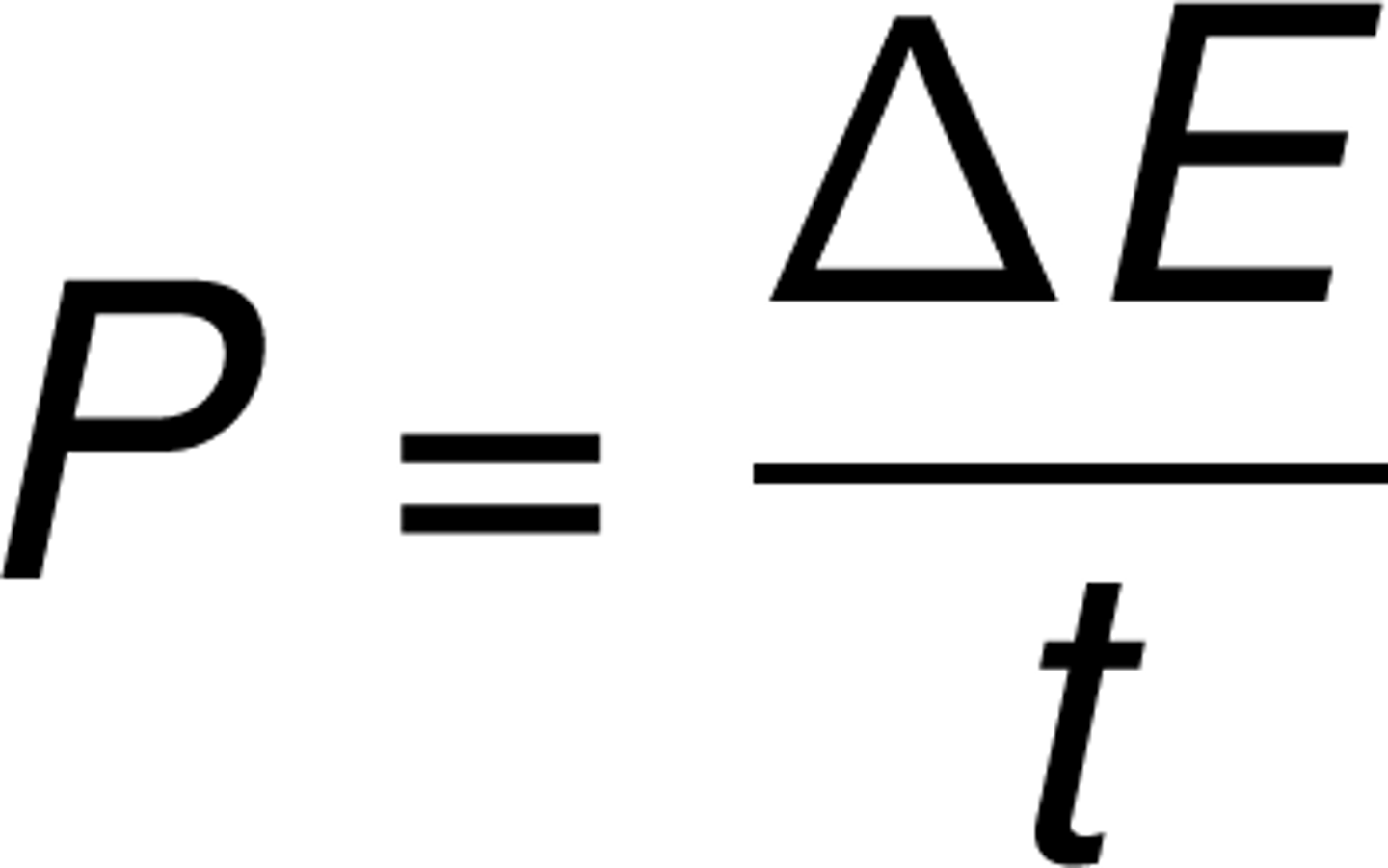
CRB Say that Arnold Schwarzenegger's biceps have the power of 500W. How long would he have to contract his muscles to do 1250J of work?
(A) 2.5 seconds
(B) 7.5 seconds
(C) 2.5 minutes
(D) 7.5 minutes
(A) 2.5 seconds
Power = work/time
Work = Power x Time
1250= (500)(Time)
Time = 1250/500 = 2.5 seconds
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What is the equation for instantaneous power in terms of velocity?
Power = Force x Velocity
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
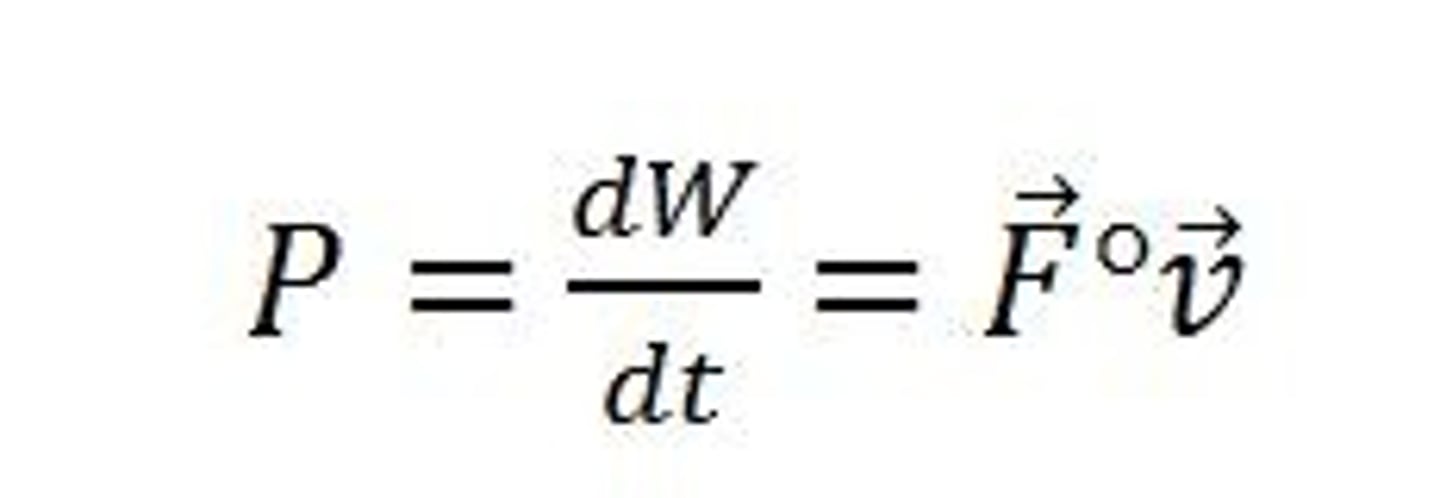
If a car is moving 28.76 m/s and the engine is applying a force of 114.89 N, what is the power output of the engine at that moment (in W)?
(A) 2164.32
(B) 2597.65
(C) 3304.24
(D) 4587.92
(C) 3304.24
Power = Force x Velocity
Power = (114.89)(28.76)
Power = approx. 3000 J/s (actual: 3304.24)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB What is the equation for Total Mechanical Energy E?
E = KE + PE
KE- Kinetic Energy
PE- Potential Energy
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB In which of the following scenarios would you be able to calculate the appropriate variable?
I. Given Gravitational Potential Energy and Elastic Potential Energy, find Kinetic Energy.
II. Given Kinetic Energy and Mechanical Energy, find Elastic potential Energy.
III. Given total Potential Energy and Mechanical Energy, find Kinetic Energy.
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) I and III only
(B) III only
In the following scenario, you would be able to find the asked-for variable:
Given total Potential Energy and Mechanical Energy, find Kinetic Energy.
I. You have no Mechanical Energy.
II. You have no way to differentiate between Elastic and other forms of Potential Energy
CRB What is the Conservation of Total Mechanical Energy Equation in its general form? How would you write it out using Kinetic and Potential Energy?
In its general form:
Einitial = Efinal
See image for other form.
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB True or False? Conservation of Total Mechanical Energy claims that any forces acting on objects will not affect the total Mechanical Energy of the system.
False. Conservation of Total Mechanical Energy claims that any Conservative Forces acting on objects will not affect the total Mechanical Energy of the system.
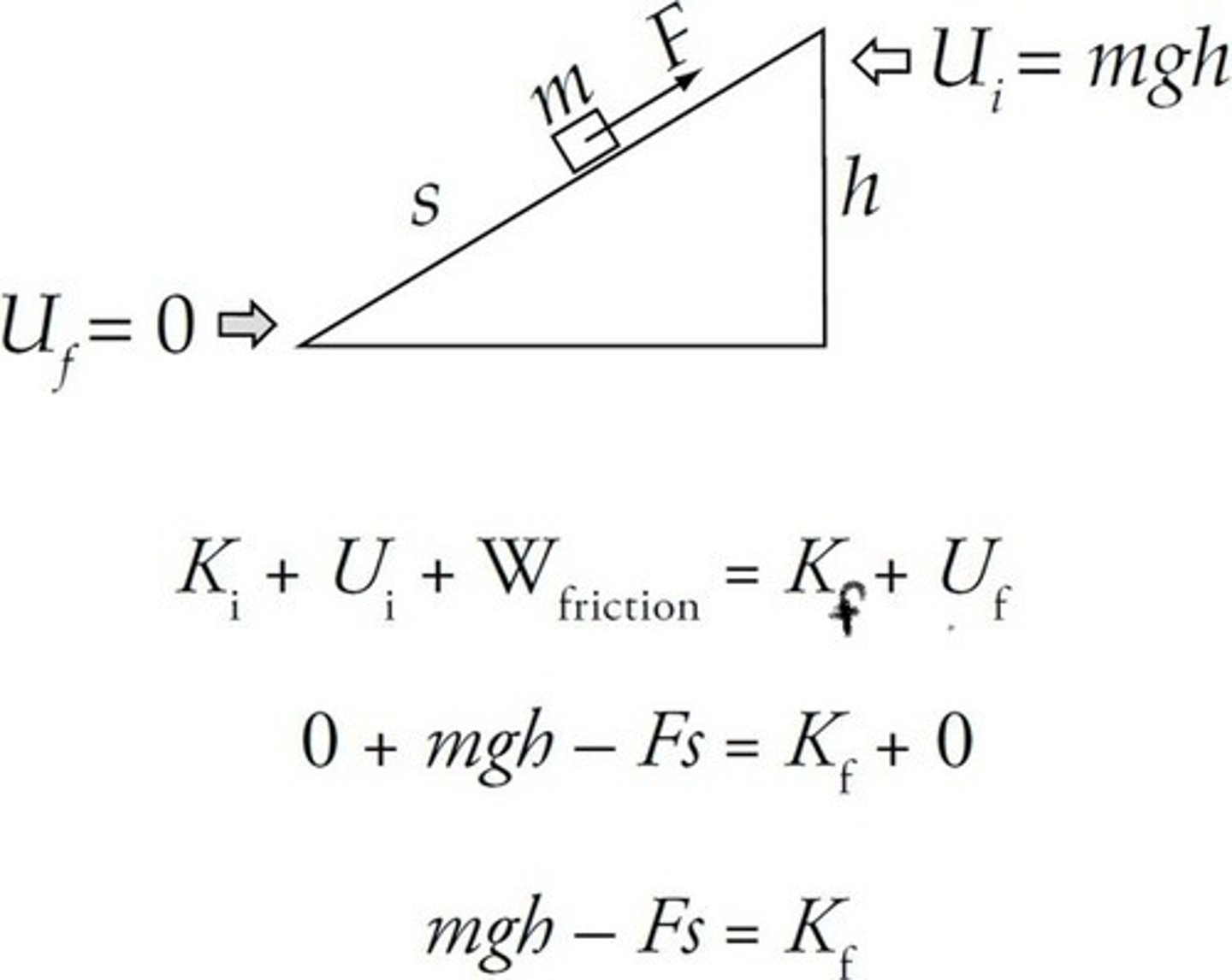
CRB If the Non-Conservative Force of Friction is acting on an object, then how would you write out the Conservation of Mechanical Energy Equation?
Note: Any Non-Conservative force could be in the place of friction here.
What is the equation for mechanical advantage in terms of force in and out?
MA = Fout/Fin
Fin = Force in
Fout = Force out
MA = Mechanical Advantage
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB True or false? The equation for Mechanical Advantage could also be written MA= (Resistance Force) / (Effort Force)
True. The equation for Mechanical Advantage could also be written MA= (Resistance Force) / (Effort Force)
What is the equation that relates the forces in and out when dealing with mechanical advantage in terms of distance of forces from a fulcrum?
f1 x d1 = f2 x d2
F1 = force 1
d1 = distance from force 1 to fulcrum
f2 = force 2
d2 = distance from force 2 to fulcrum
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
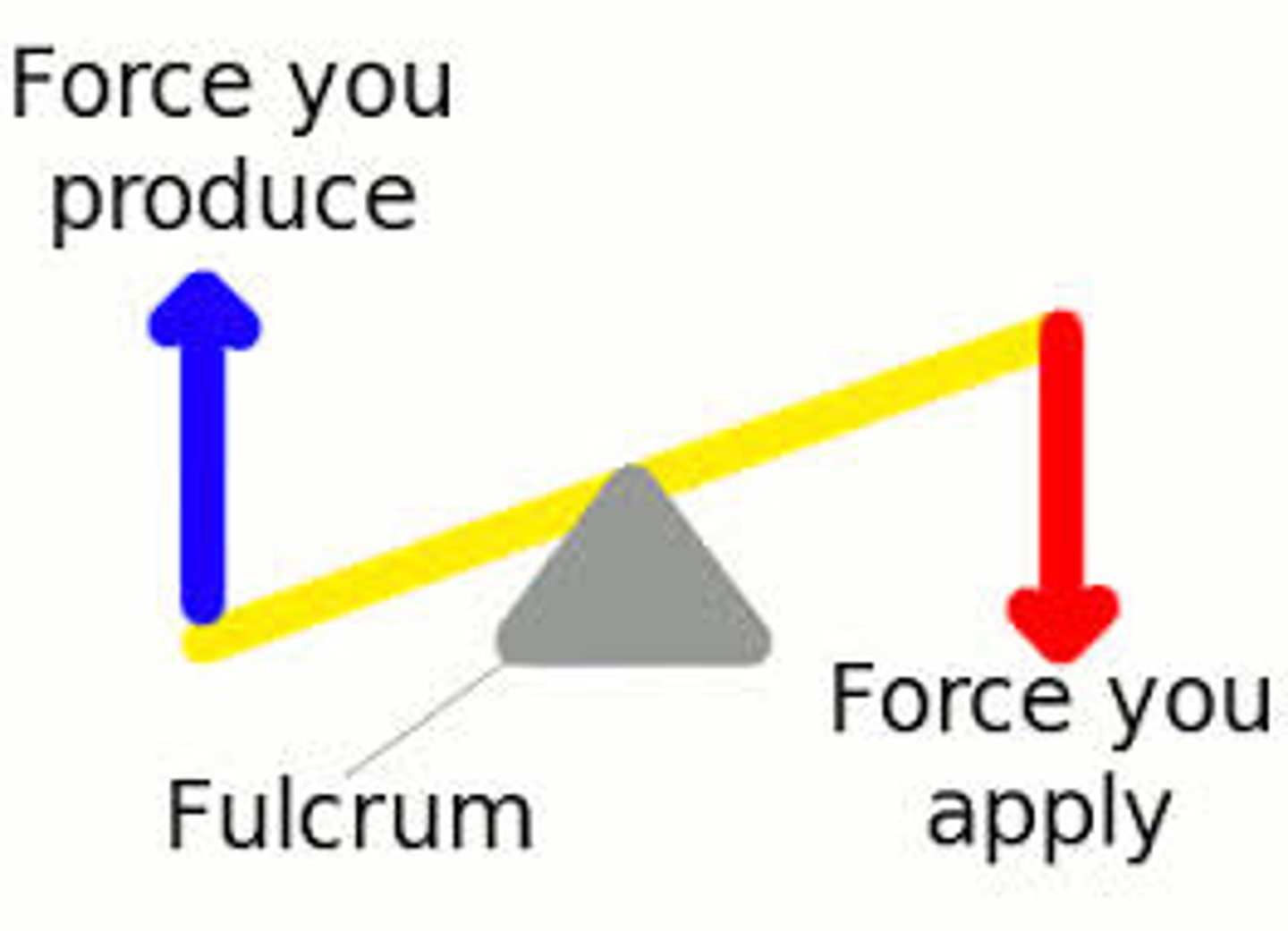
If a 18.77 N box is sitting on one end of a lever at a distance of 1.32 m from the fulcrum, how much force must be applied to at a distance of 4.35 m from the fulcrum to raise the box?
(A) 3.43
(B) 4.89
(C) 5.70
(D) 7.42
(C) 5.70
f1 x d1 = f2 x d2
18.77 x 1.32 = 4.35 x f2
f2 = approx. 6 N (actual: 5.70)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
CRB Related to the idea of Mechanical Advantage is the Efficiency of converting our output to input. Write out the equation for Efficiency.

What is the difference between work and moment when dealing with mechanical advantage?
Both work and moment are equal to distance times force, but with work the force is in the same direction as the distance, with moment the distance is perpendicular.
CRB Unrelated to Moment, what is the equation for Momentum?
p = mv
p = Momentum
m = Mass
v = Velocity
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
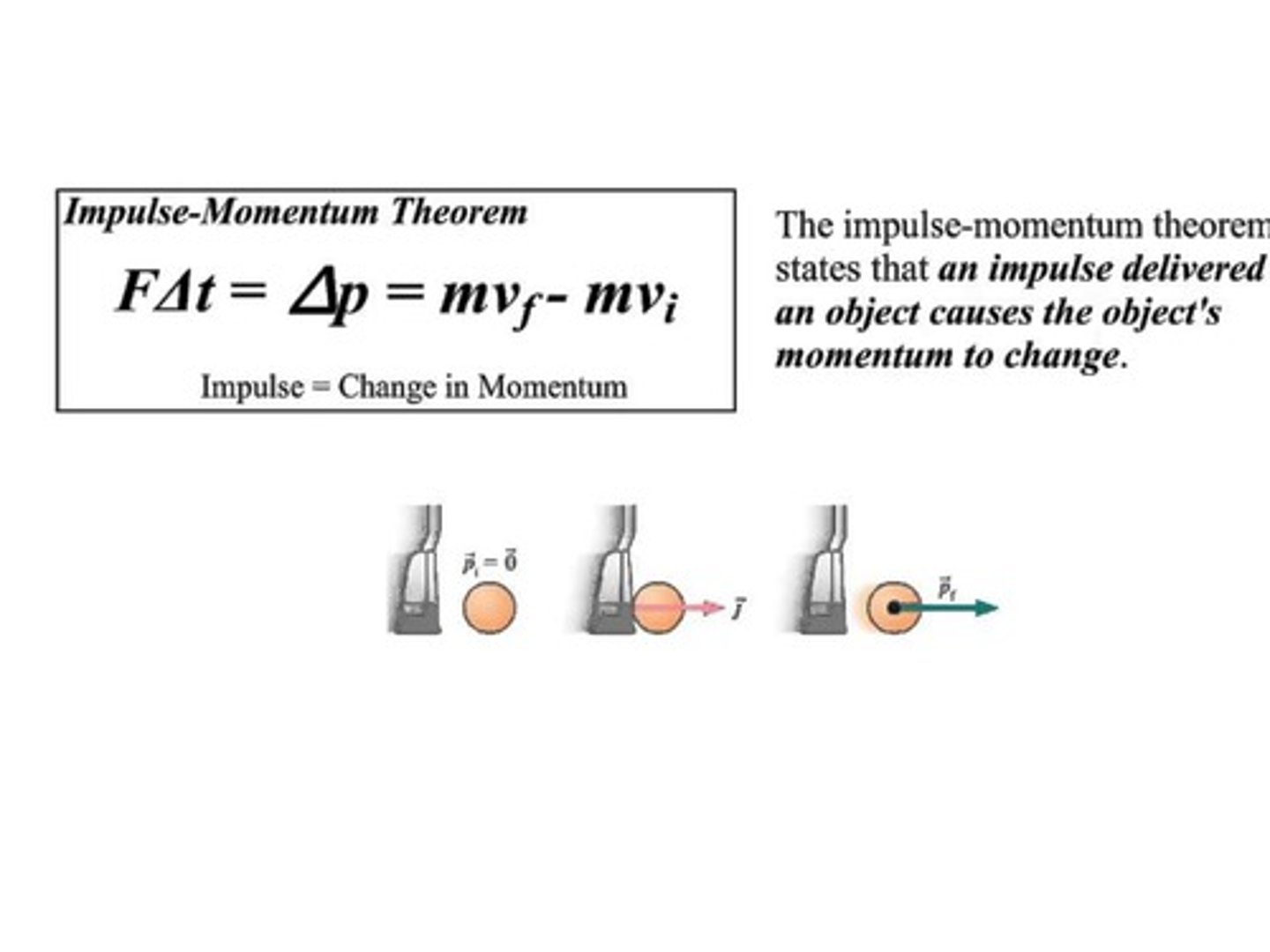
CRB There is an Impulse-Momentum Theory that relates changes in momentum of an object to Forces and Time. Write out this equation.
CRB There is also a Conservation of Momentum, based on the fact that the force exerted by one object onto the second is equal and opposite to the force exerted by the second object on the first. Which of Newton's Laws is this based upon?
(A) First Law
(B) Second Law
(C) Third Law
(D) I will go review Newton's Laws and come back to this!
(C) Third Law
Newton's Third Law is based on equal and opposite reactions, so this should make sense.
CRB Compare Angular and Linear Momentum.
Linear Momentum is what has been already discussed in these cards, p=mv.
Angular momentum is similar to torque, in the way that it relates to some reference point, and could be written L=lmv, with l being related to torque's lever arm.
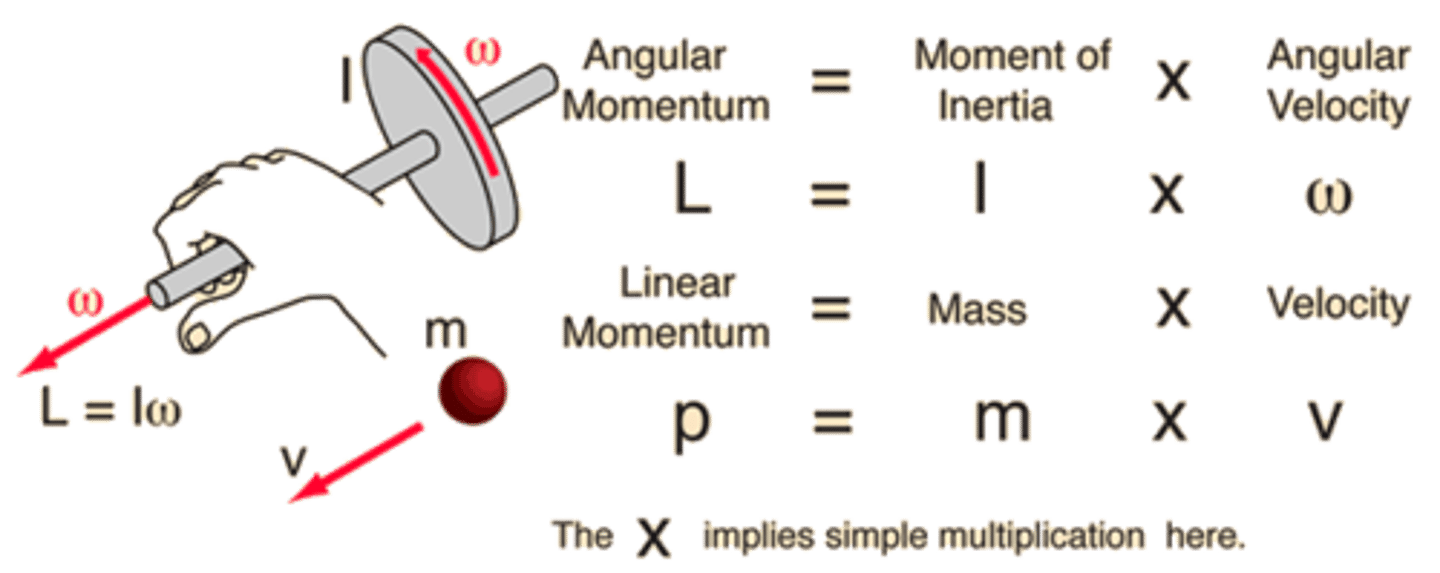
CRB Compare Elastic and Inelastic Collisions, focusing on how total momentum and total kinetic energy are affected.
In Elastic Collisions, both total momentum and total kinetic energy are conserved. In Inelastic Collisions, total momentum is still conserved, but total kinetic energy is not, since it is lost in the collision.
CRB There are also Perfectly Inelastic Collisions. What makes these collisions unique?
These inelastic conditions have the objects stick together after the collision! So their velocity will be the same vector.