Manifest Destiny & Its Legacy (Chapter 17)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Tariff of 1842
A protective tariff passed by the Whigs and signed by President John Tyler, it raised the general level of duties to about where they had been before the Compromise Tariff of 1833.
Caroline
(1837) Diplomatic row between the United States and Britain. Developed after British troops set fire to an American steamer carrying supplies across the Niagara River to Canadian insurgents, during Canada's short-lived insurrection.
Creole
A U.S. American ship that was captured by rebelling slaves in 1841, the slaves were offered asylum by Britain which increased U.S. and British tensions.
Aroostook War
Series of clashes between American and Canadian lumberjacks in the disputed territory of northern Maine, resolved when a permanent boundary was agreed upon in 1842.
Manifest Destiny
the 19th-century doctrine or belief that the expansion of the US throughout the American continents was both justified, a God-given right, and inevitable.

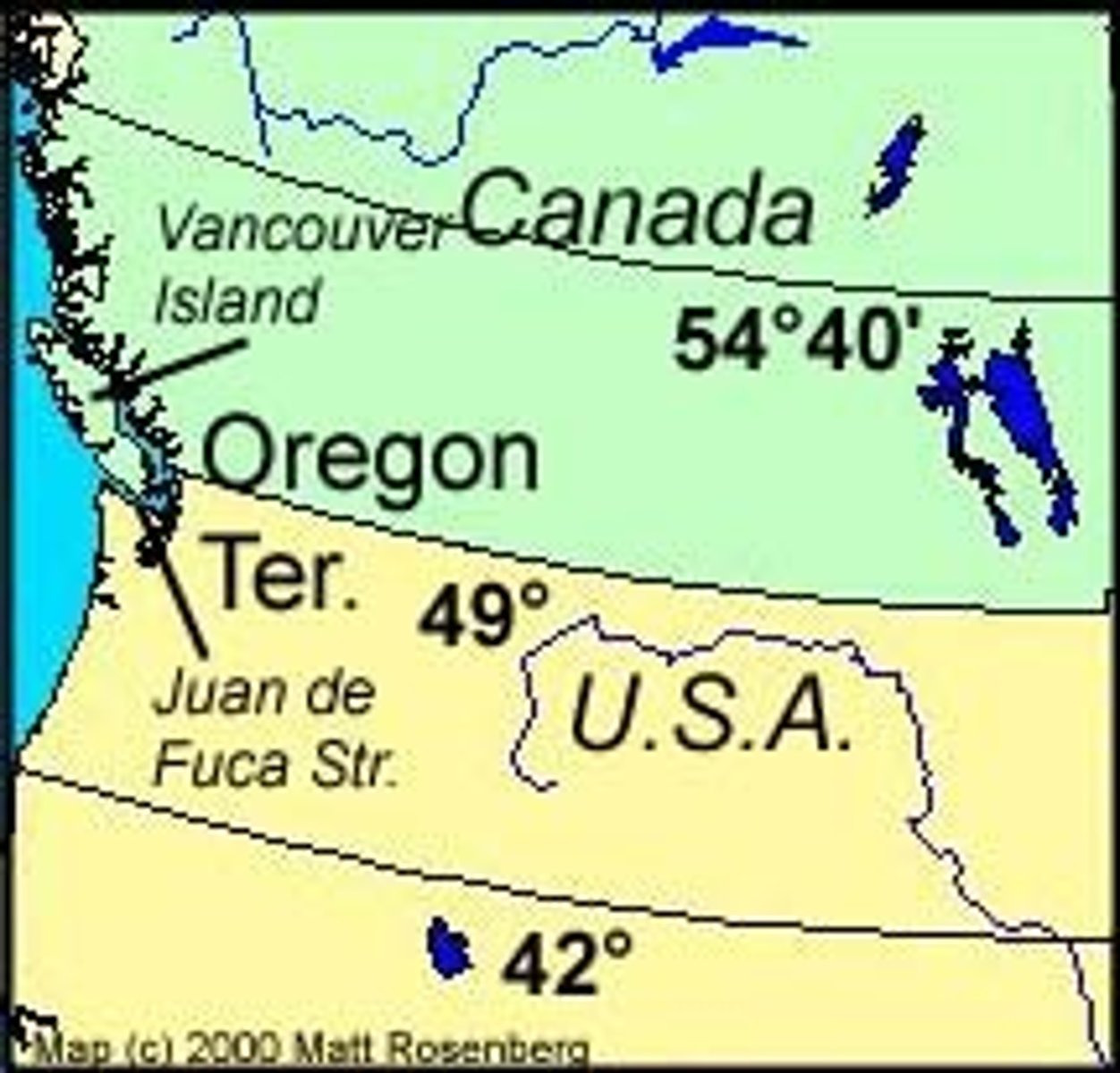
"Fifty-Four Forty or Fight"
Political slogan of the Democrats in the election of 1844, which claimed fifty-four degrees, forty minutes as the boundary of the Oregon territory claimed by the United States
Liberty party
A former political party in the United States; formed in 1839 to oppose the practice of slavery; merged with the Free Soil Party in 1848
Walker Tariff
Revenue-enhancing measure that lowered tariffs from 1842 levels thereby fueling trade and increasing Treasury receipts.
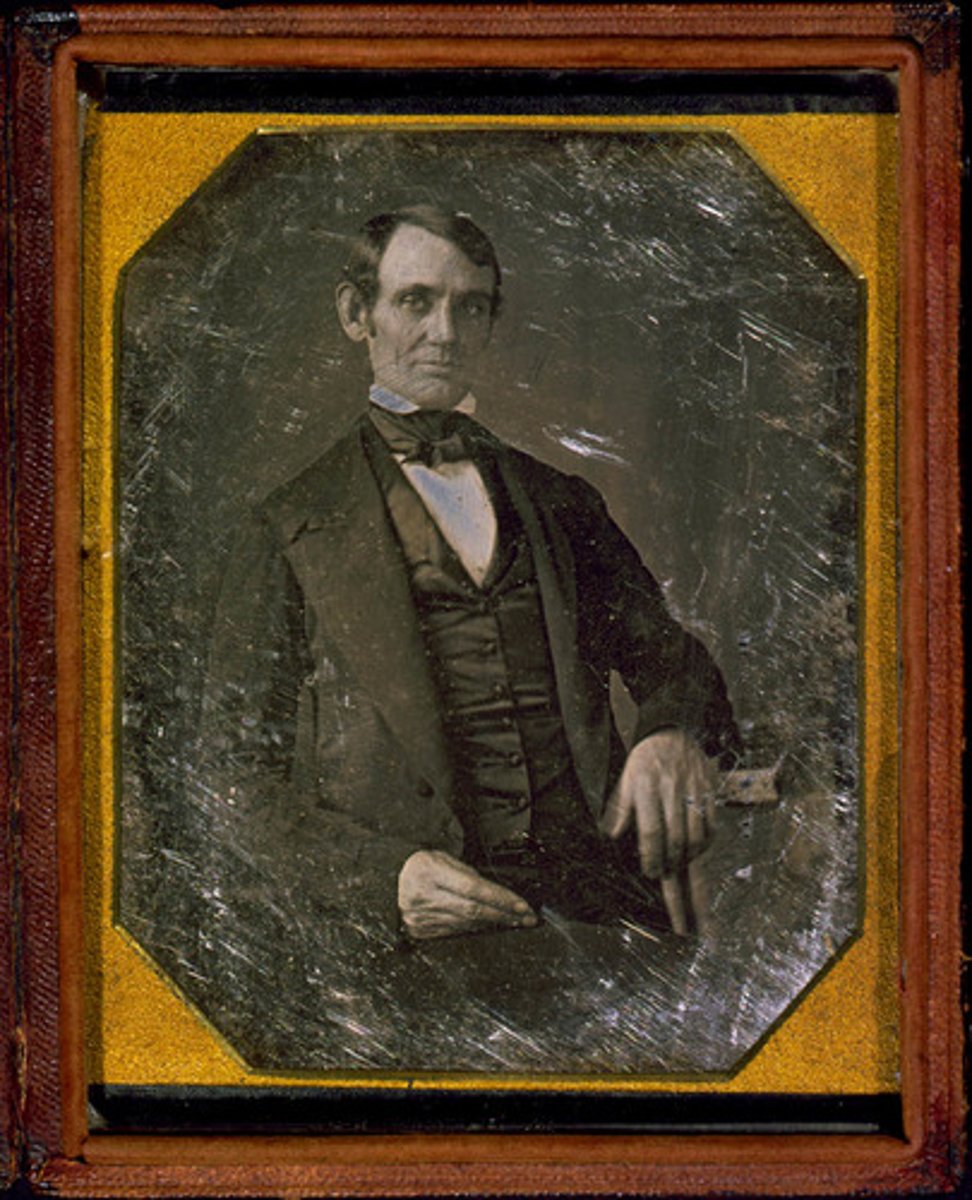
Spot Resolutions
Measures introduced by Illinois congressman Abraham Lincoln, questioning President James K. Polk's justification for war with Mexico. Lincoln requested that Polk clarify precisely where Mexican forces had attacked American troops.

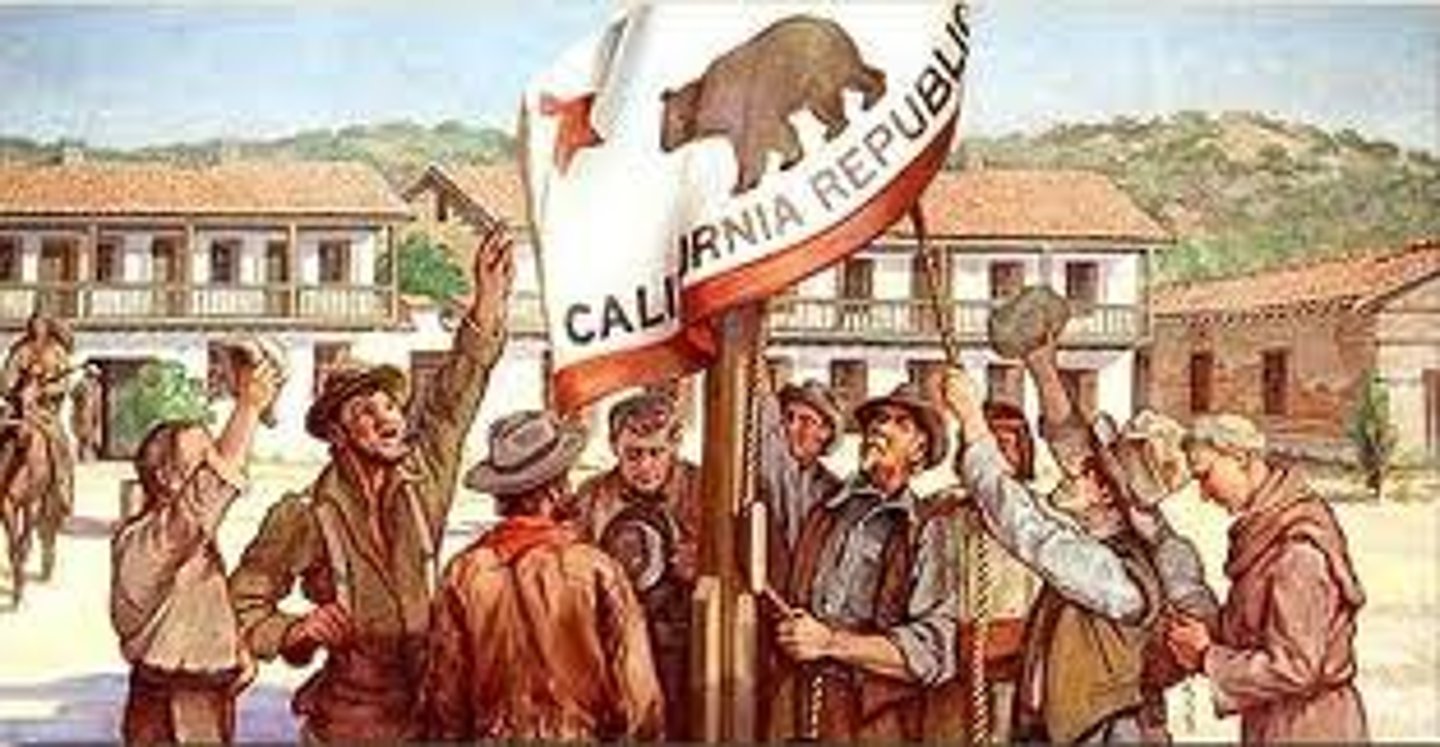
California Bear Flag Republic
(1846) Short-lived California republic, established by local American settlers who revolted against Mexico. Once news of the war with Mexico reached the Americans, they abandoned the Republic in favor of joining the United States.

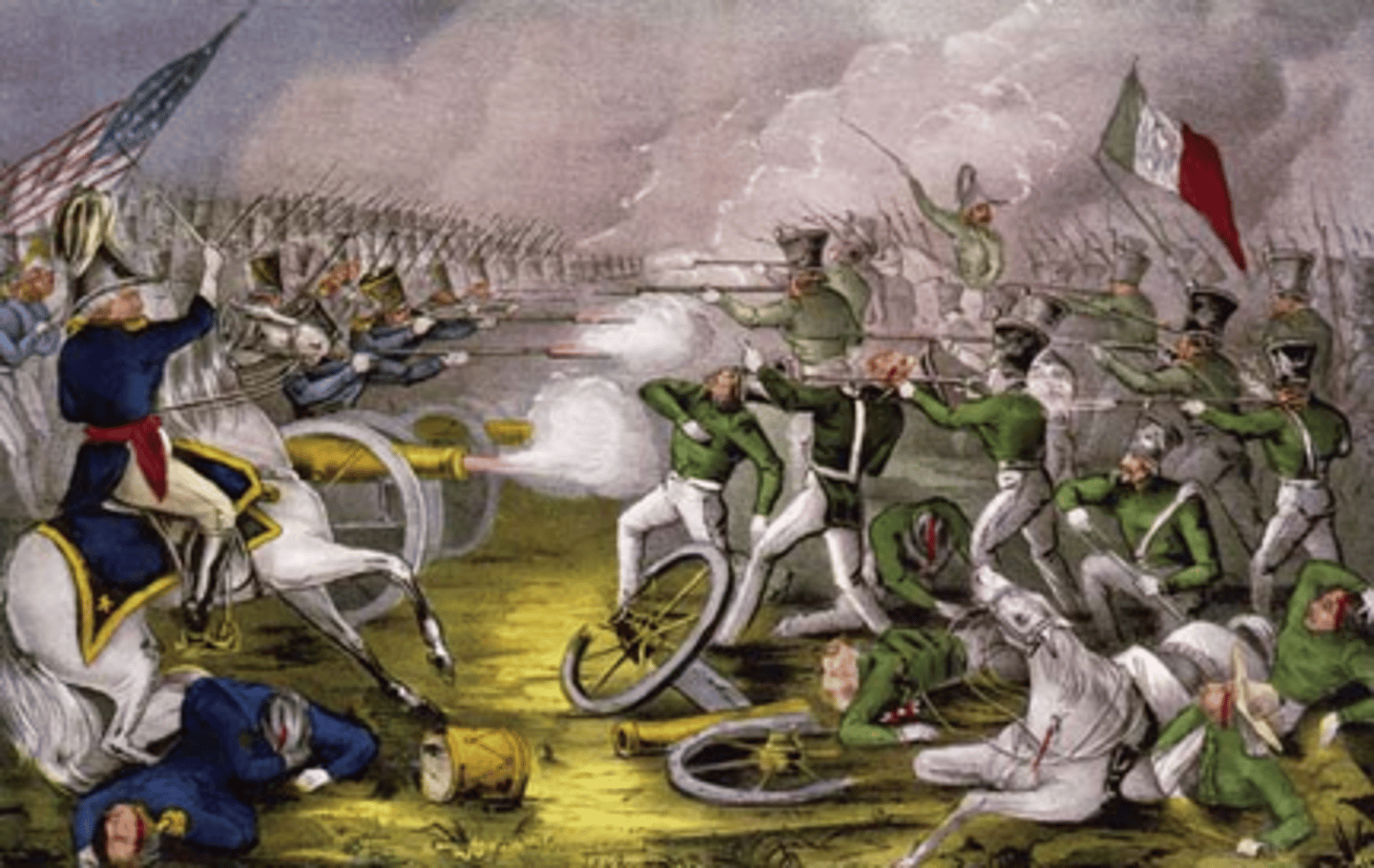
Battle of Buena Vista
(1847) Key American victory against Mexican forces in the Mexican-American War. Elevated General Zachary Taylor to national prominence and helped secure his success in the 1848 presidential election.

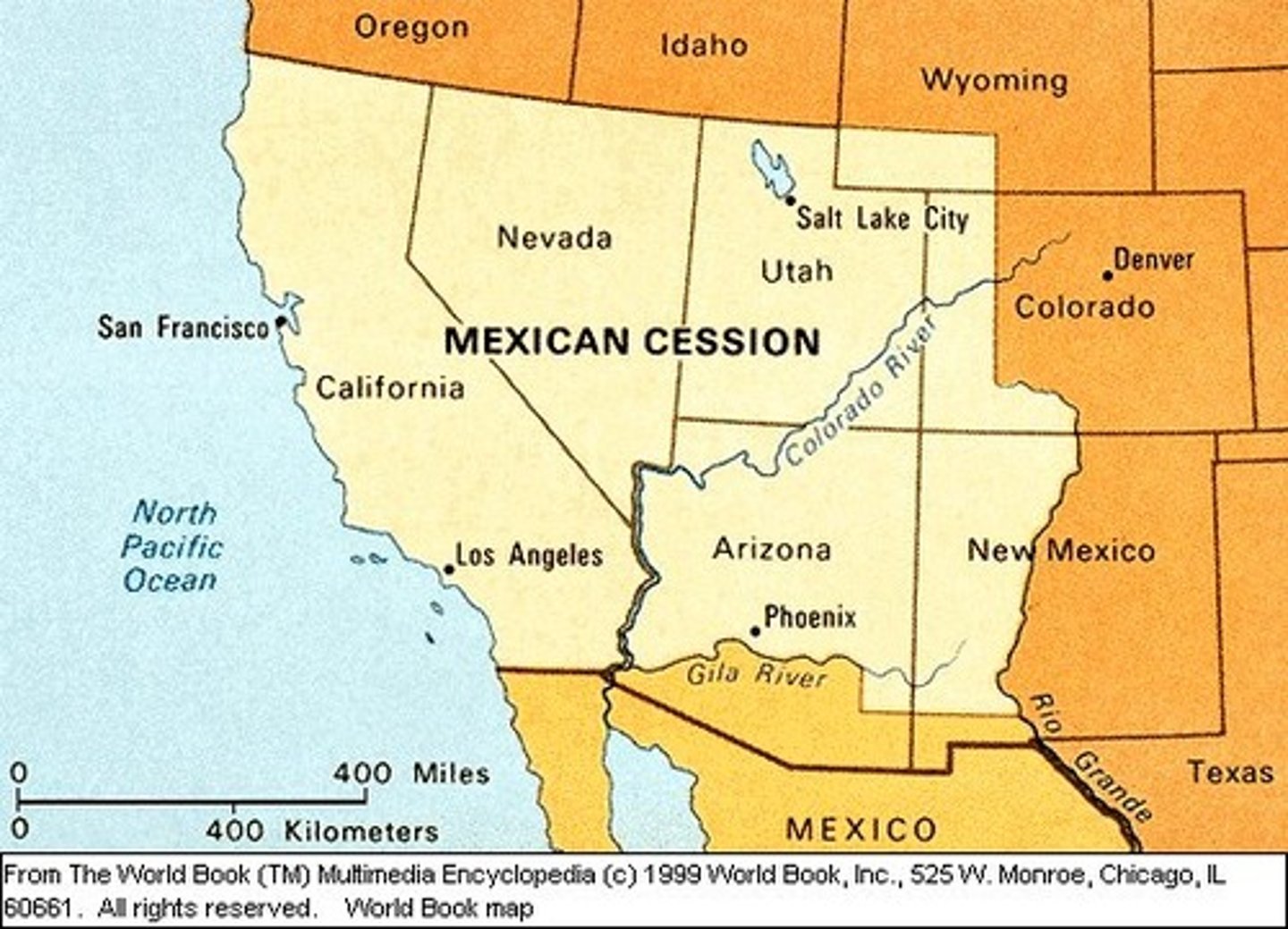
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848)
(1848) treaty signed by the U.S. and Mexico that officially ended the Mexican-American War; Mexico had to give up much of its northern territory to the U.S (Mexican Cession); in exchange the U.S. gave Mexico $15 million and said that Mexicans living in the lands of the Mexican Cession would be protected
Conscience Whigs
Anti-slavery whigs who opposed both the Texas annexation and the Mexican-American War on moral grounds.
Wilmot Proviso
1846 proposal that would outlaw slavery in any territory gained from the War with Mexico. Never passed but was still popular with legislators.
John Tyler
elected Vice President and became the 10th President of the United States when Harrison died 1841-1845, President responsible for annexation of Mexico after receiving mandate from Polk, opposed many parts of the Whig program for economic recovery

James K. Polk
U.S. president from 1845 to 1849. A Democrat who supported the expansion of U.S. territory, particularly through the seizing of Mexican territory.
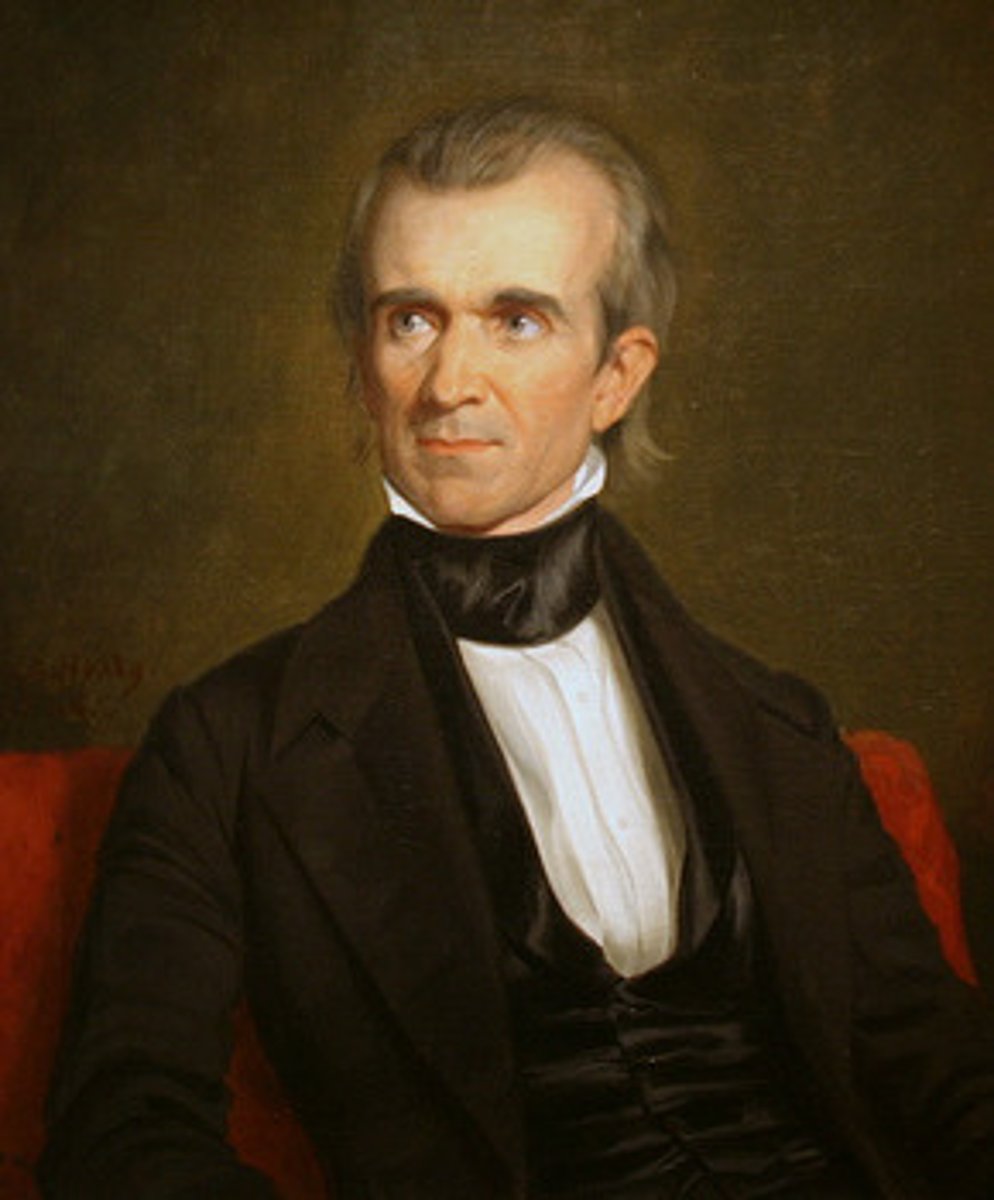

Stephen W. Kearny
(1794-1848) American officer during the Mexican War who led a detachment of troops into New Mexico and captured Santa Fe.
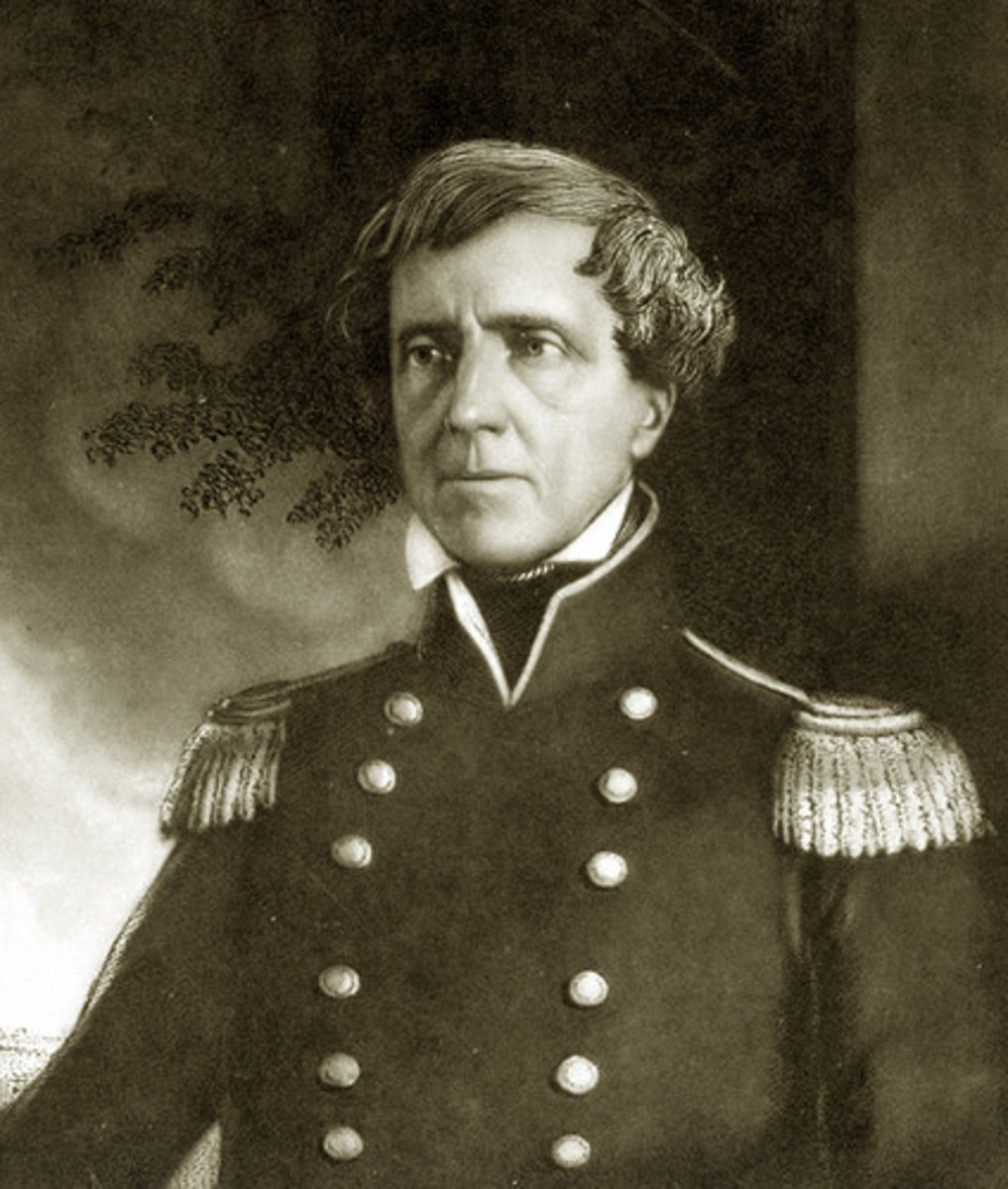

John C. Fremont
an American military officer, explorer, the first candidate of the Republican Party for the office of President of the United States. Collaborated with the California Bear Republic.
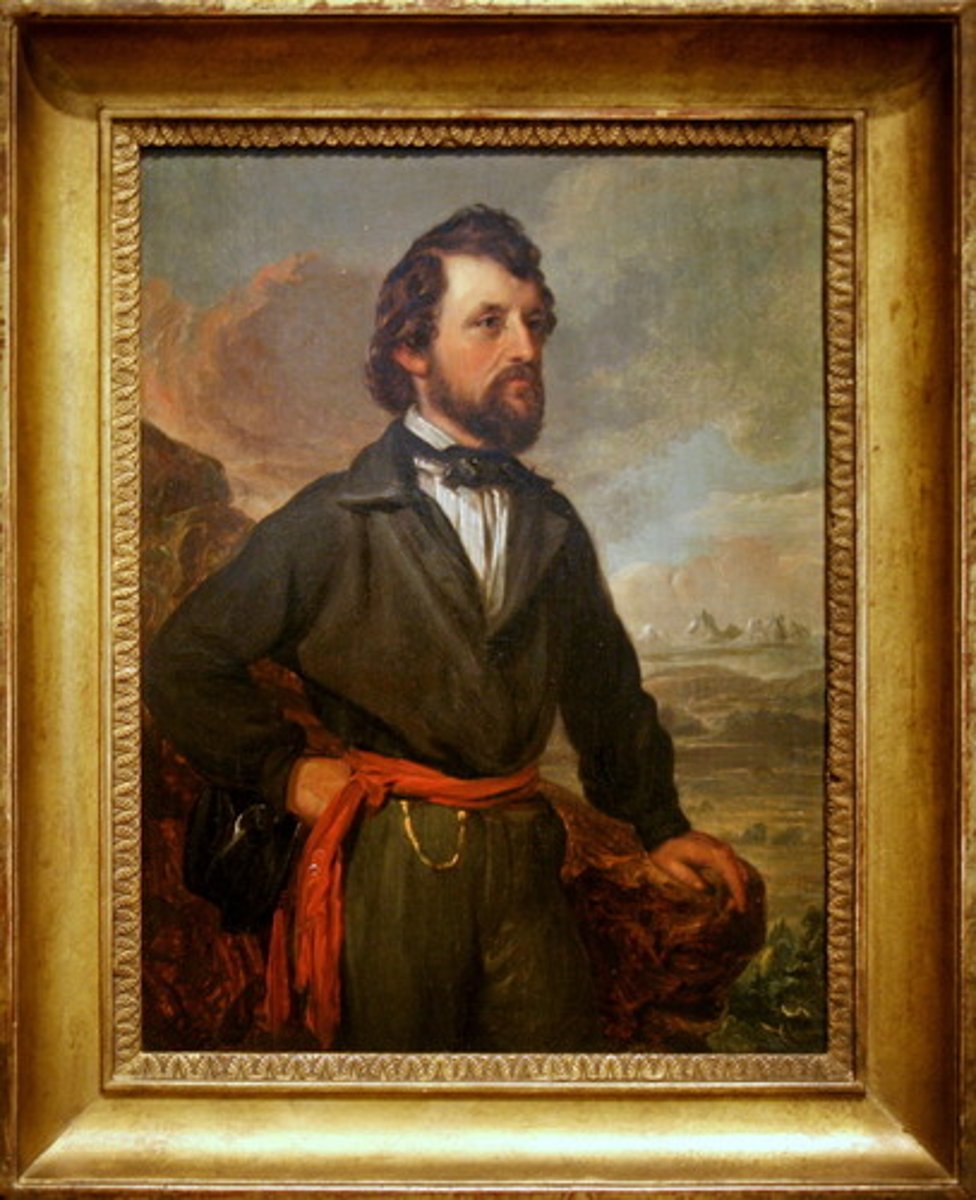

Californios
Hispanic settlers of California, descended from 17th-19th century Spaniards

Winfield Scott
United States general who was a hero of the War of 1812 and who defeated Santa Anna in the Mexican War (1786-1866)
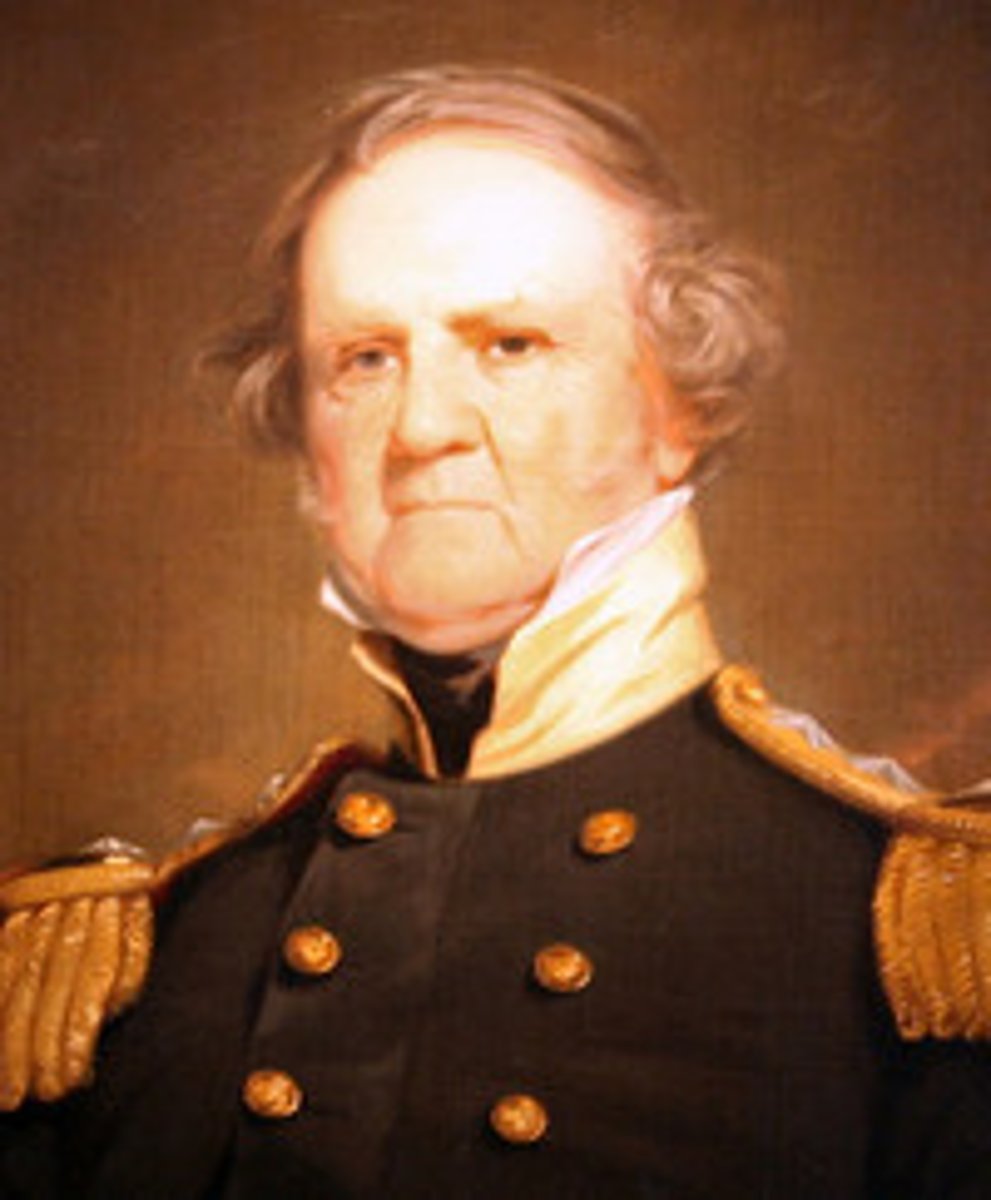

Nicholas P. Trist (1800-1874)
American diplomat who negotiated the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, ending the Mexican-American War and acquiring a vast secession of territory from Mexico.
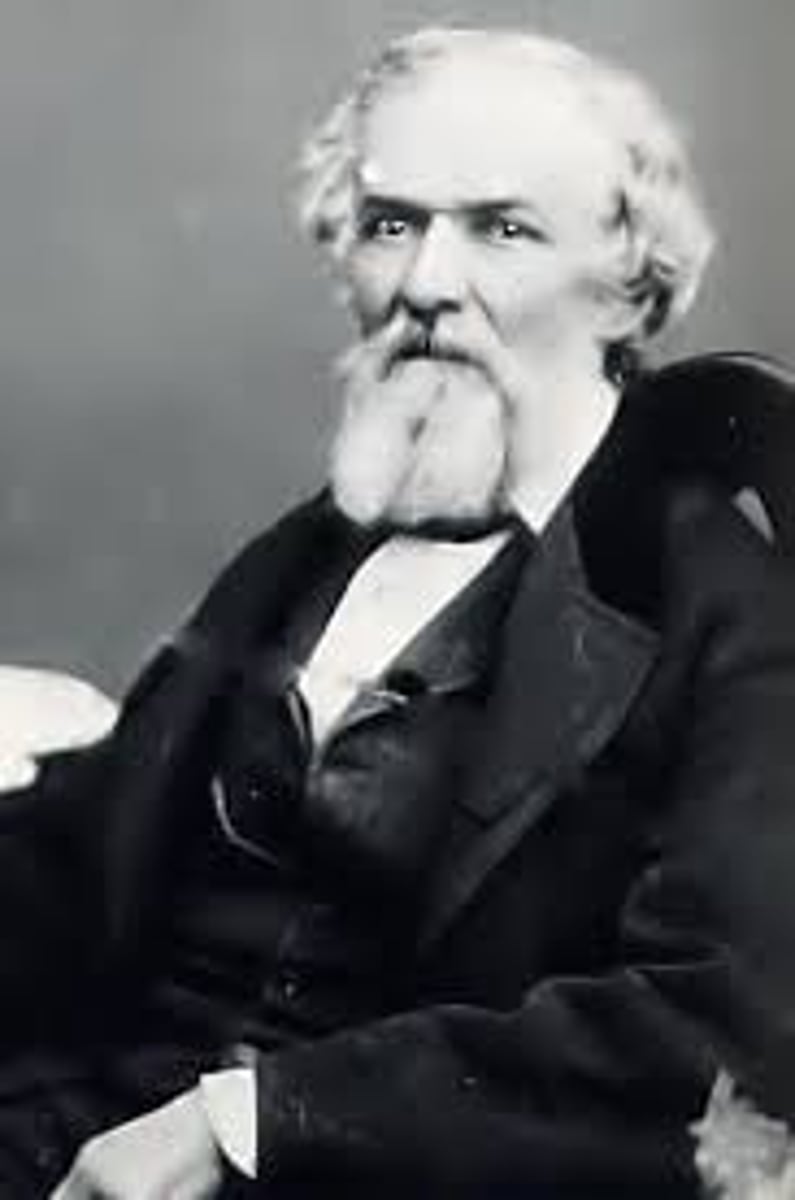

David Wilmot
Congressman who proposed the amendment that would have outlawed slavery from U.S. acquired Mexican territories

Corrupt bargain
Refers to the claim from the supporters of Andrew Jackson that John Quincy Adams and Henry Clay had worked out a deal to ensure that Adams was elected president by the House of Representatives in 1824.
spoils system
A system of public employment based on rewarding party loyalists and friends.
Tariff of Abominations
Tariff passed by Congress in 1828 that favored manufacturing in the North and was hated by the South
Nullification Crisis
A sectional crisis during the presidency of Andrew Jackson created by the Ordinance of Nullification, an attempt by the state of South Carolina to nullify a federal law - the tariff of 1828 - passed by the United States Congress.
Compromise tariff of 1833
A new tariff proposed by Henry Clay & John Calhoun that gradually lowered the tariff to the level of the tariff of 1816; avoided civil war & prolonged the union for another 30 years.
Force Bill
1833 - The Force Bill authorized President Jackson to use the army and navy to collect duties on the Tariffs of 1828 and 1832.
Indian Removal Act
(1830) a congressional act that authorized the forced removal of Native Americans who lived east of the Mississippi River.
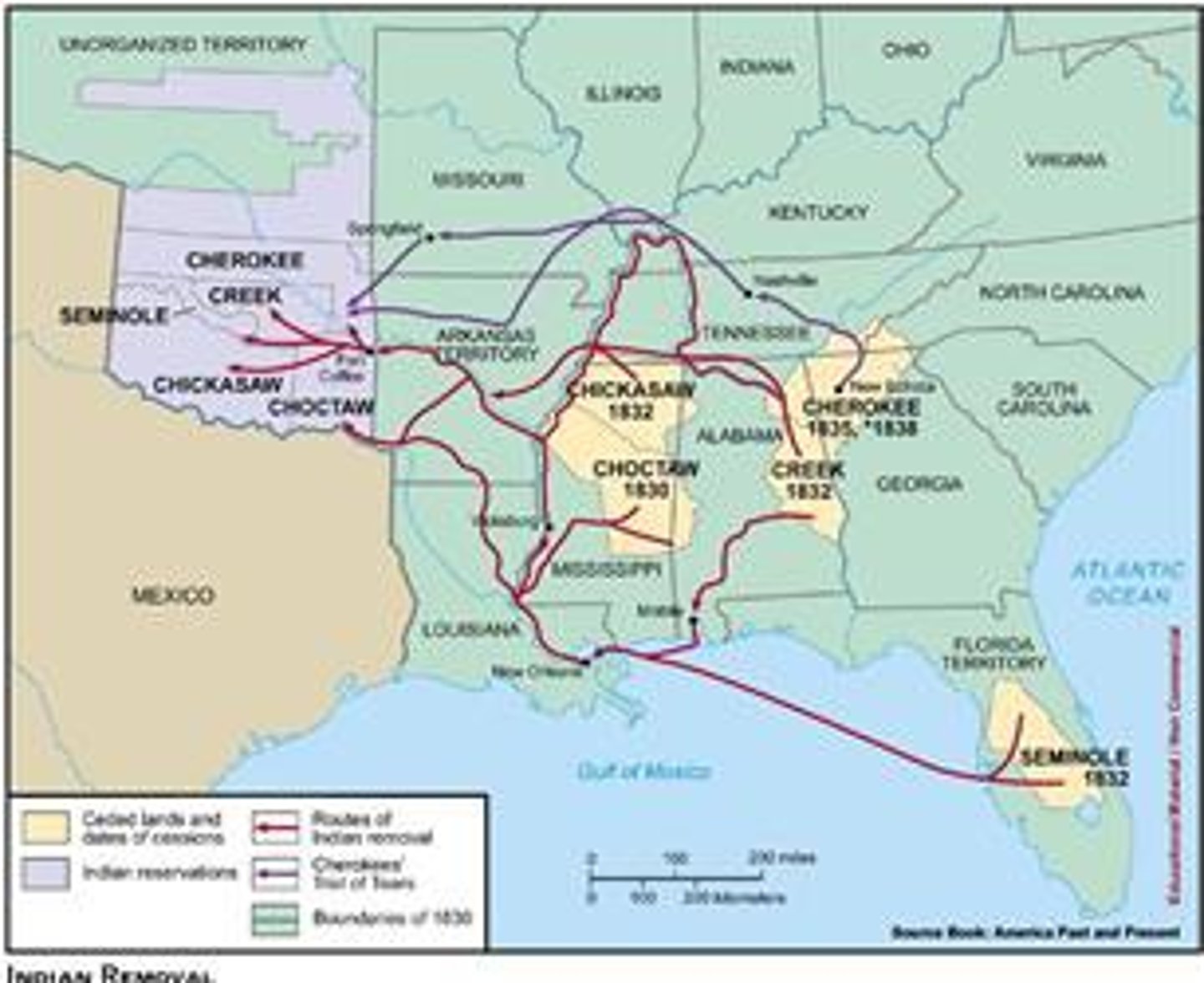
Trail of Tears
The Cherokee Indians were forced to leave their lands. They traveled from North Carolina and Georgia through Tennessee, Kentucky, Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas-more than 800 miles (1,287 km)-to the Indian Territory. More than 4,000 Cherokees died of cold, disease, and lack of food during the 116-day journey.

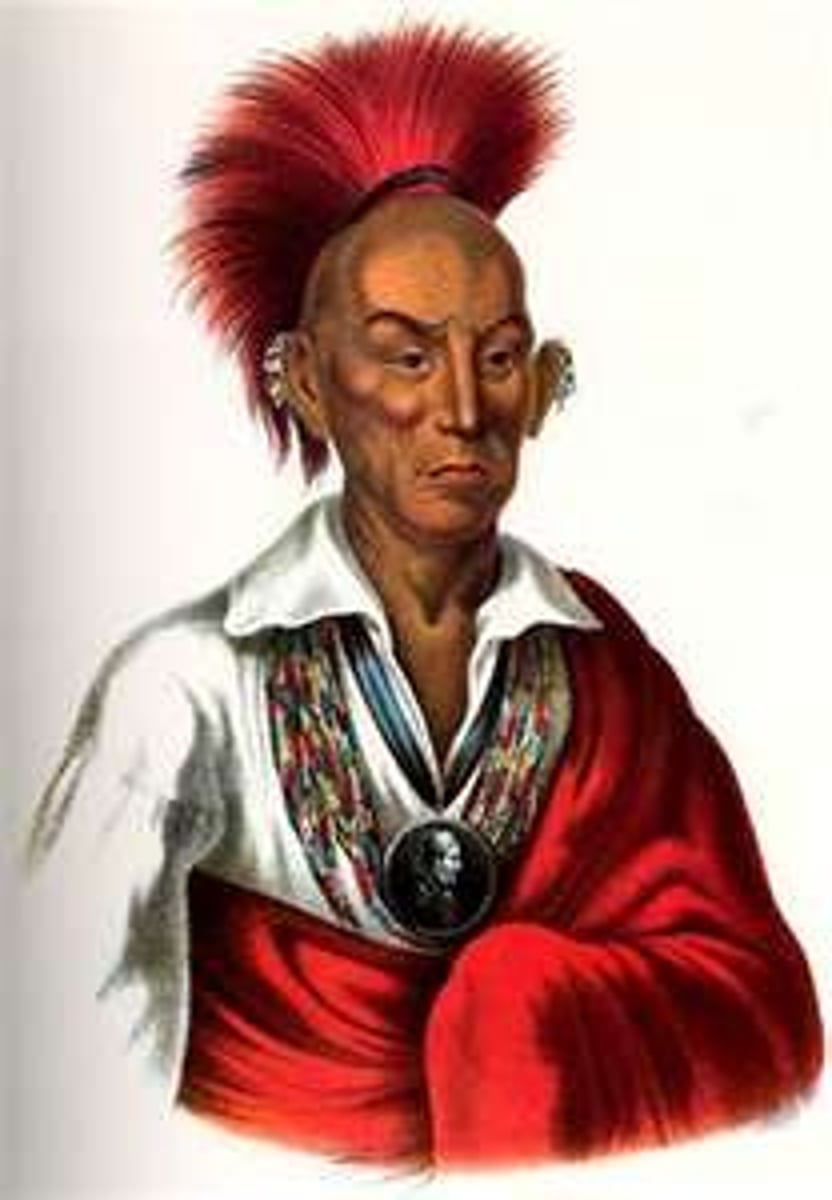
Black Hawk War
Series of clashes in Illinois and Wisconsin between American forces and Indian chief Black Hawk of the Sauk and Fox tribes, who unsuccessfully tried to reclaim territory lost under the 1830 Indian Removal Act.

Bank War
Jackson believed the Bank of US had too much power and was too rich. Vetoed the 2nd Bank charter and withdrew gov't money from the US Banks and put it into "pet banks"
Pet banks
State banks where Andrew Jackson placed deposits removed from the federal National Bank.
Anti-Masonic party
First founded in New York, it gained considerable influence in New England and the mid-Atlantic during the 1832 election, campaigning against the politically influential Masonic order, a secret society. Anti-Masons opposed Andrew Jackson, a Mason, and drew much of their support from evangelical Protestants.
Specie Circular
issued by President Jackson July 11, 1836, was meant to stop land speculation caused by states printing paper money without proper specie (gold or silver) backing it. It required that the purchase of public lands be paid for in specie. It stopped the land speculation and the sale of public lands went down sharply. The panic of 1837 followed.
Panic of 1837
Bank of the U.S. failed, cotton prices fell, businesses went bankrupt, and there was widespread unemployment and distress.
Alamo
A Spanish mission converted into a fort, it was besieged by Mexican troops in 1836. The Texas garrison held out for thirteen days, but in the final battle, all of the Texans were killed by the larger Mexican force.
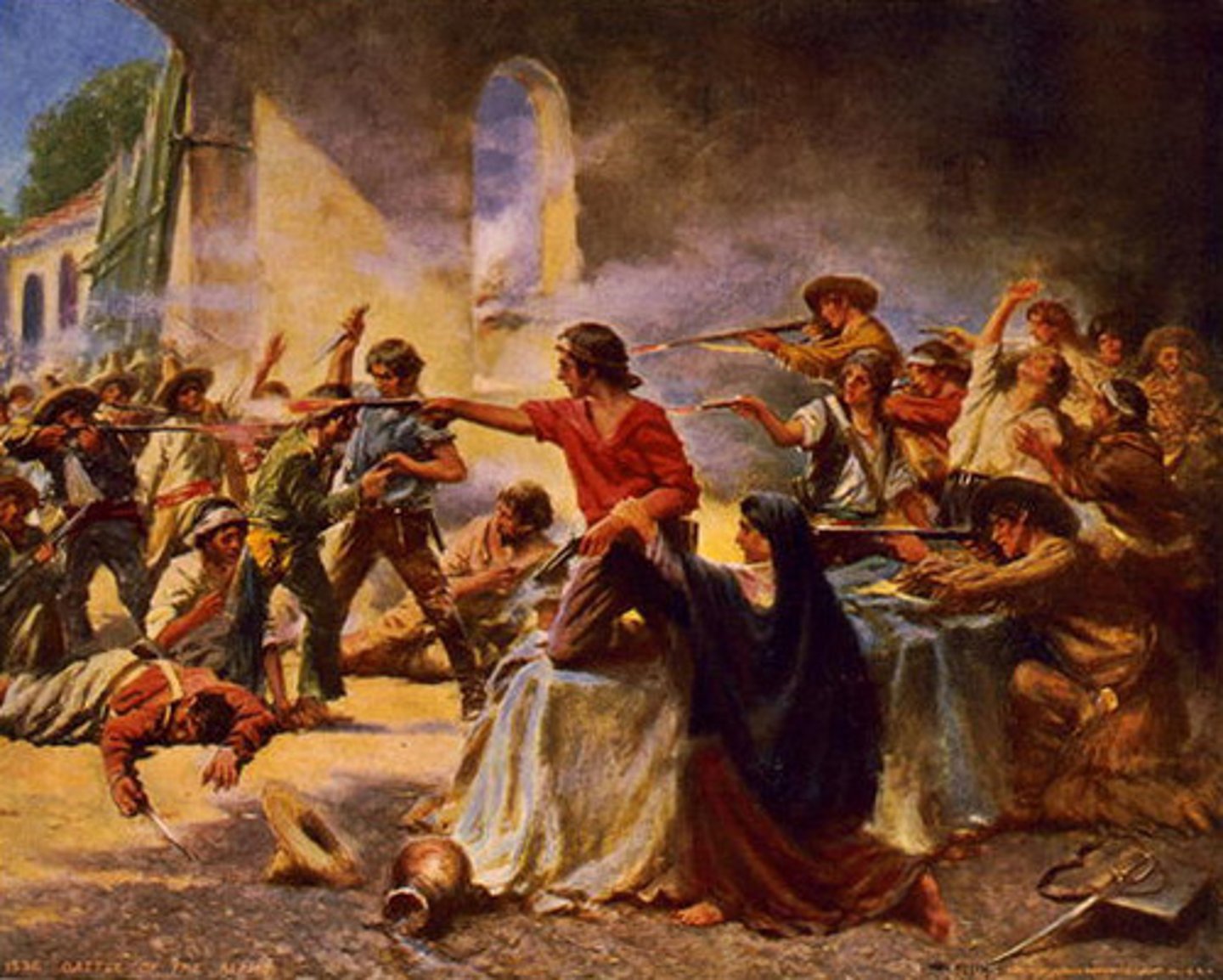

Goliad
Texas outpost where American volunteers, having laid down their arms and surrendered, were massacred by Mexican forces in 1836. The incident, along with the slaughter at the Alamo, fueled American support for Texan independence.
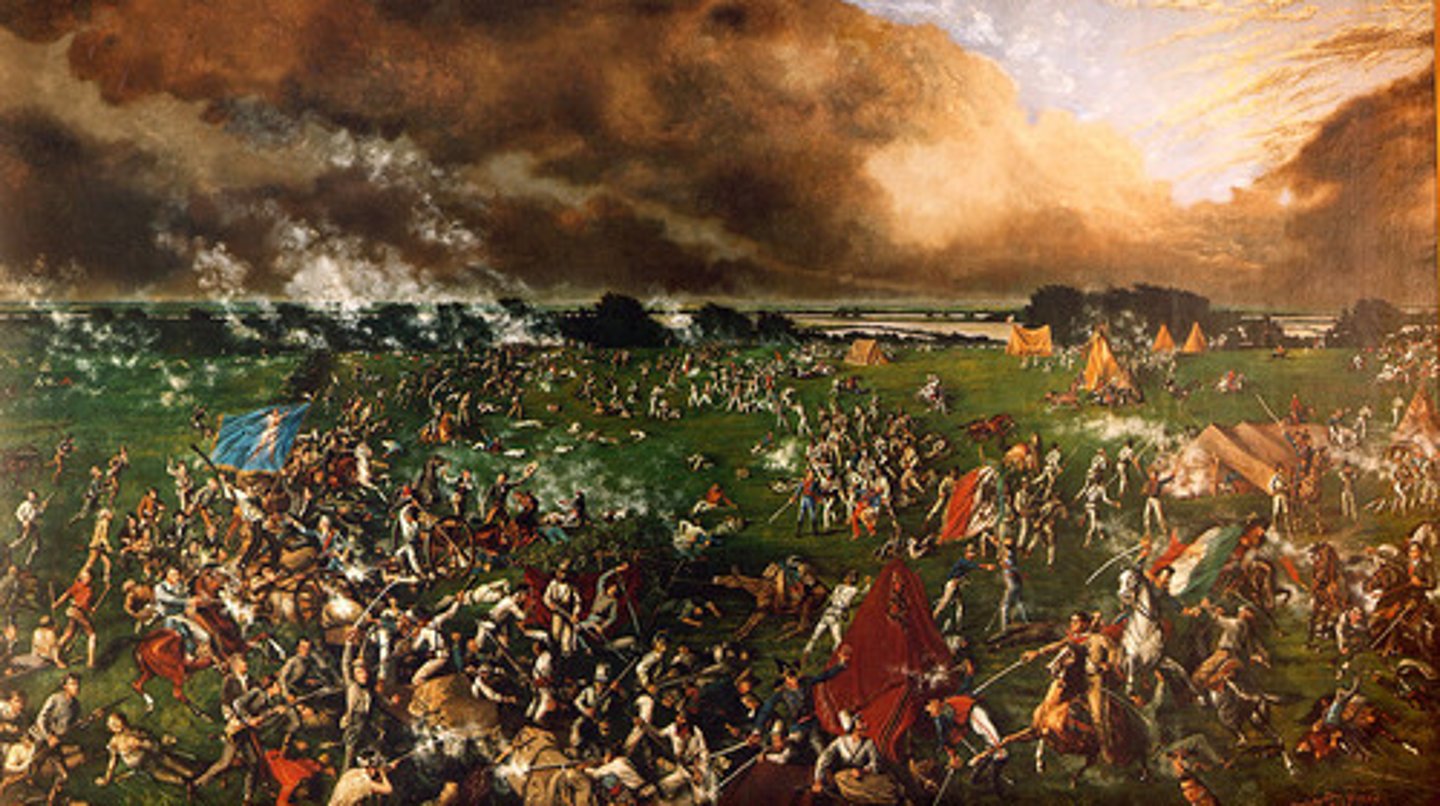
Battle of San Jacinto
(1836) Final battle of the Texas Revolution; resulted in the defeat of the Mexican army and independence for Texas

John Quincy Adams
(1767-1848) Son of President John Adams and the secretary of state to James Monroe, he largely formulated the Monroe Doctrine. He was the sixth president of the United States and later became a representative in Congress.
Andrew Jackson
The seventh President of the United States (1829-1837), who as a general in the War of 1812 defeated the British at New Orleans (1815). As president he opposed the Bank of America, objected to the right of individual states to nullify disagreeable federal laws, supported the forced removal of Native Americans, and increased the presidential powers.

John C. Calhoun
South Carolina Senator - advocate for state's rights, slavery, limited government, and nullification
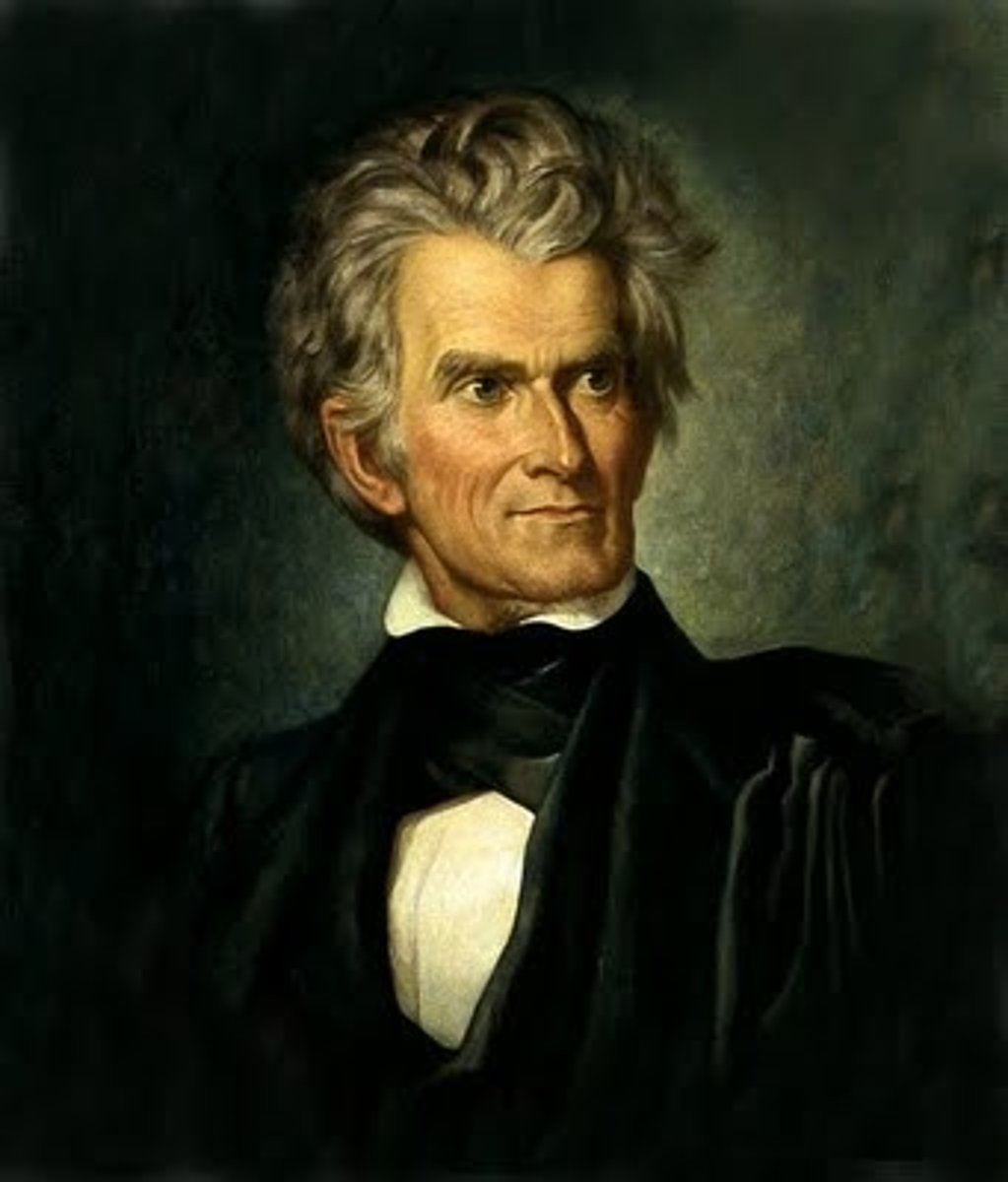

Daniel Webster
Senator of Massachusetts; famous American politician & orator; advocated renewal & opposed the financial policy of Jackson; many of the principles of finance he spoke about were later incorporated in the Federal Reserve System; later pushed for a strong union.
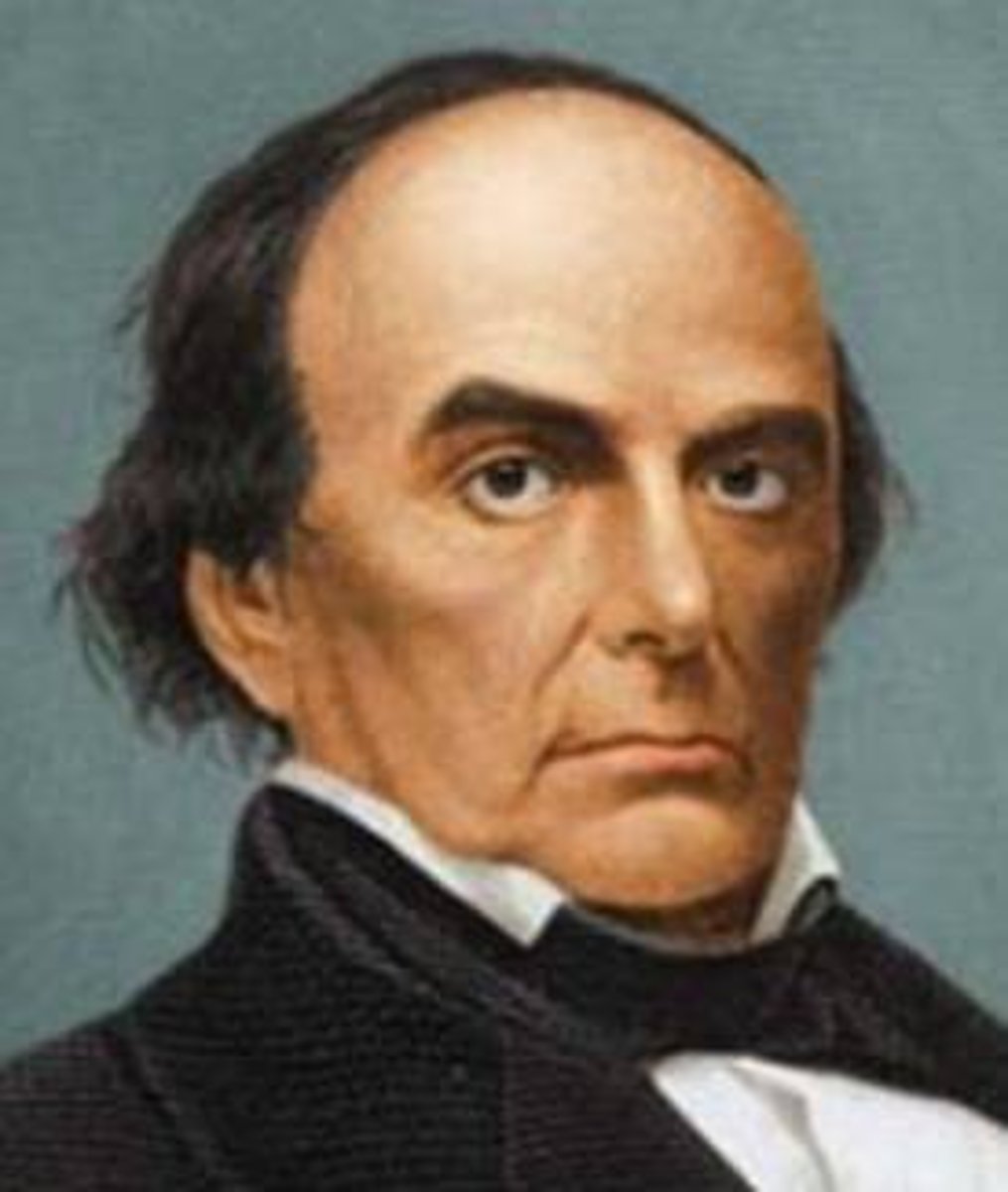

Henry Clay
Kentucky senator & representative who drafted the Missouri Compromise, supported the national bank and high tariffs, was an anti-British War Hawk
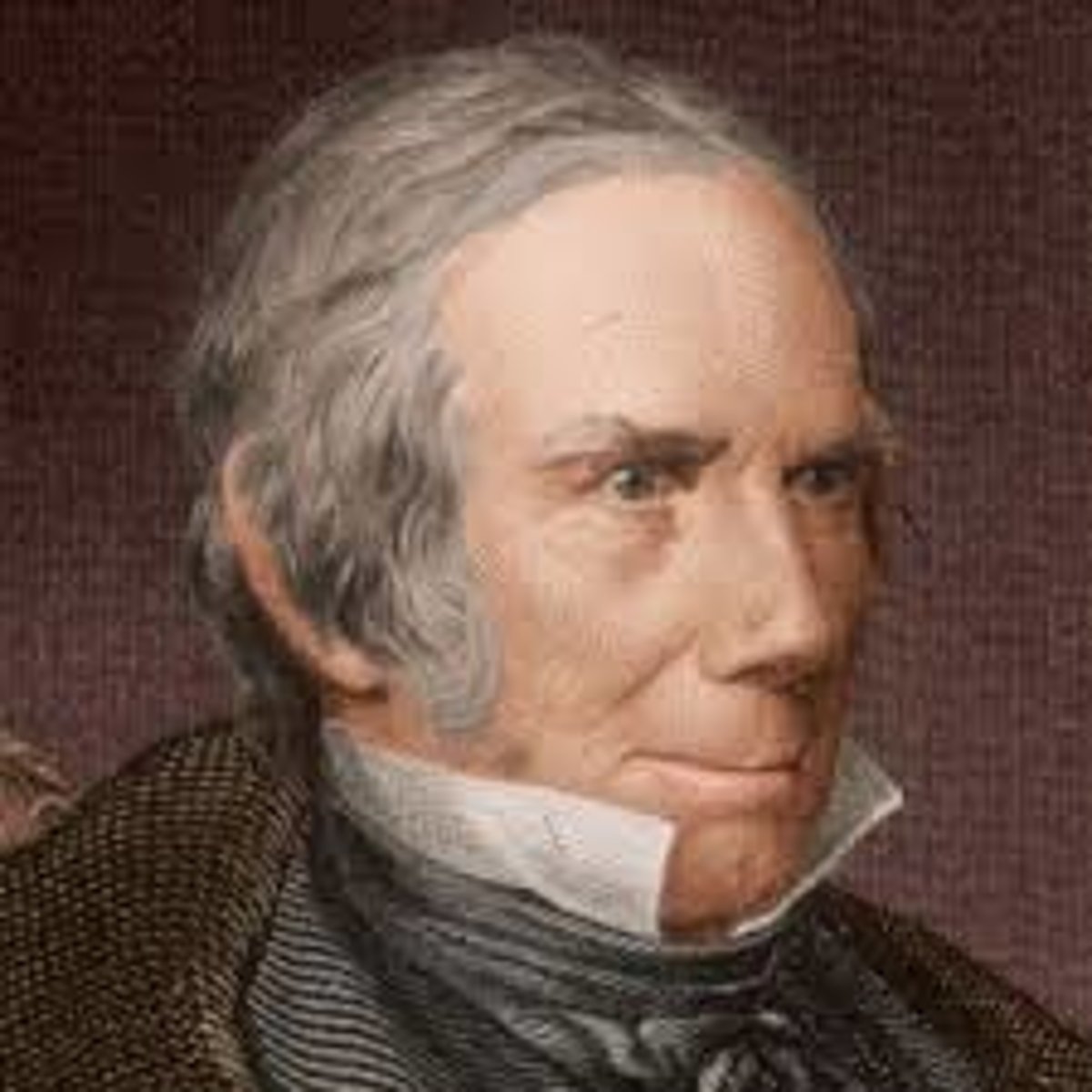

Santa Anna
Mexican general who tried to crush the Texas revolt and who lost battles to Winfield Scott and Zachary Taylor in the Mexican War (1795-1876)
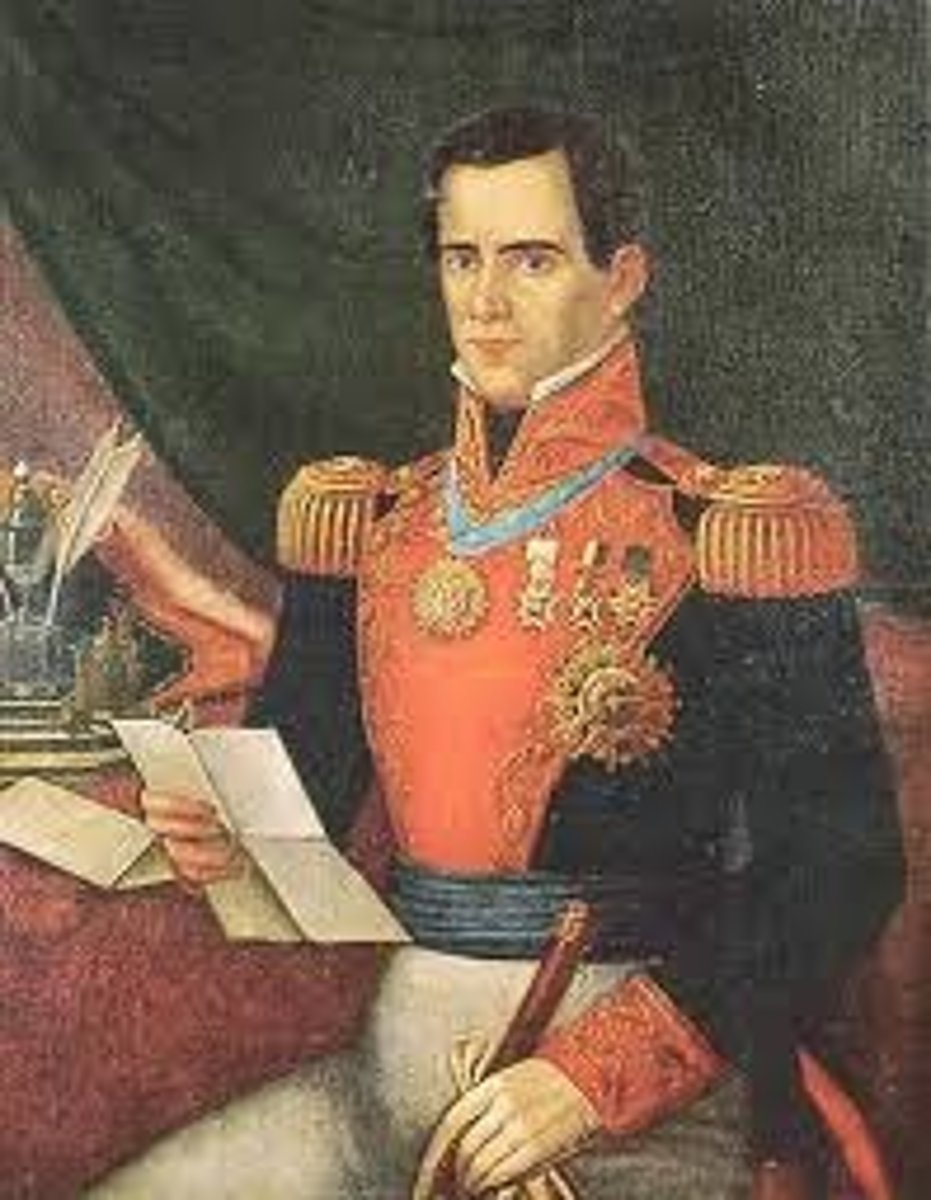

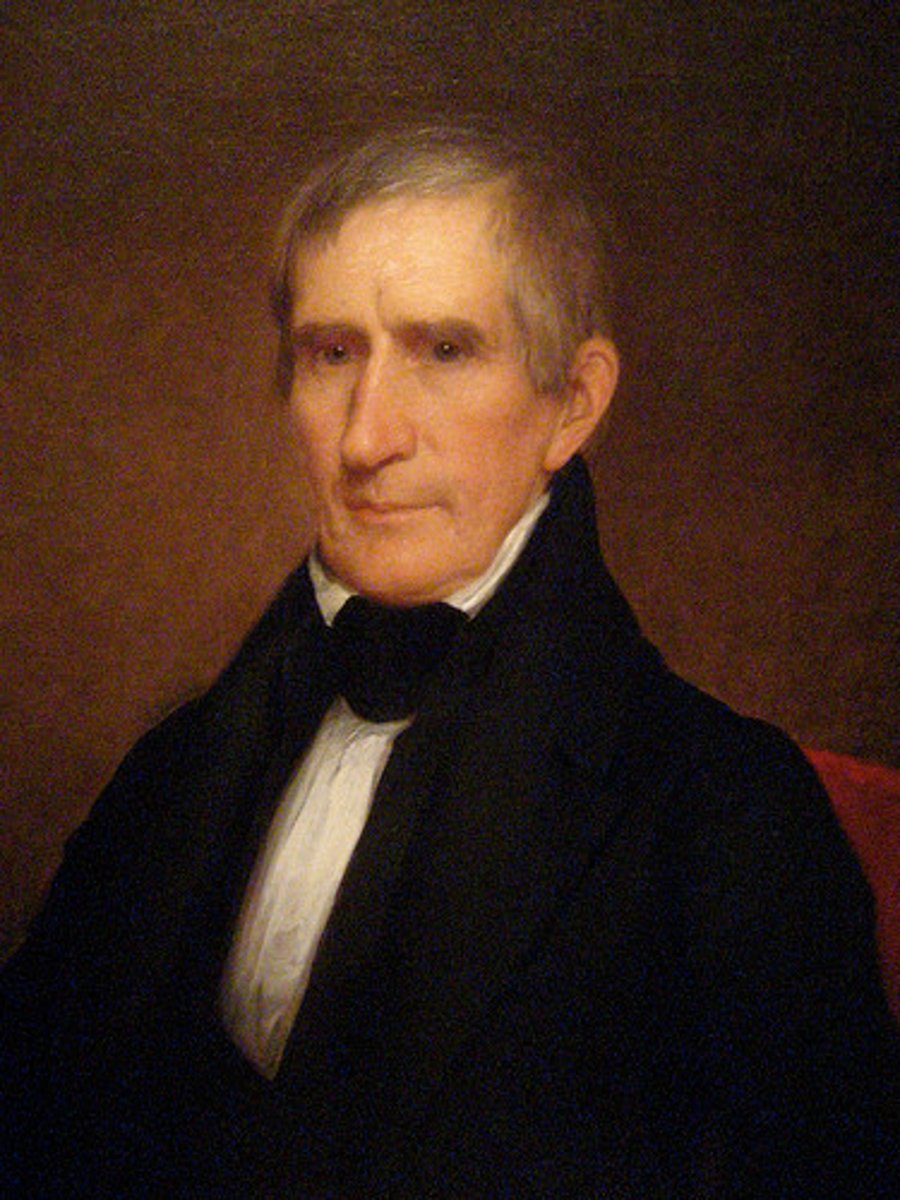
William Henry Harrison
(1841), was an American military leader, politician, the ninth President of the United States, and the first President to die in office. His death created a brief Constitutional crisis, but ultimately resolved many questions about presidential succession left unanswered by the Constitution until passage of the 25th Amendment. Led US forces in the Battle of Tippecanoe.
