Chemistry (iit jee)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Nonpolar covalent bond
when atoms in the bond pull equally; Electronegativity difference of less than 0.5
Polar covalent bond
when atoms in the bond pull unequally (polar bond); Electronegativity difference from 0.5-1.6
Ionic bond
electronegativity difference of more than 1.6
Assumptions for bonds
identical atoms or CH-->nonpolar
nonmetal+nonmetal-->polar
metal+nonmetal-->ionic
Electron pull
the more electronegative atom attracts electrons more strongly and gains a slightly negative charge. The less electronegative atom has a slightly positive charge.
Polar molecules
one end of the molecule is slightly negative and the other end is slightly positive
Dipole
A molecule that has two poles (dipolar molecule)
Network solids
solids in which all of the atoms are covalently bonded to each other; Melting a network solid would require breaking covalent bonds throughout the solid
Linear
2 atoms OR 1 center and 2 bonded
180º
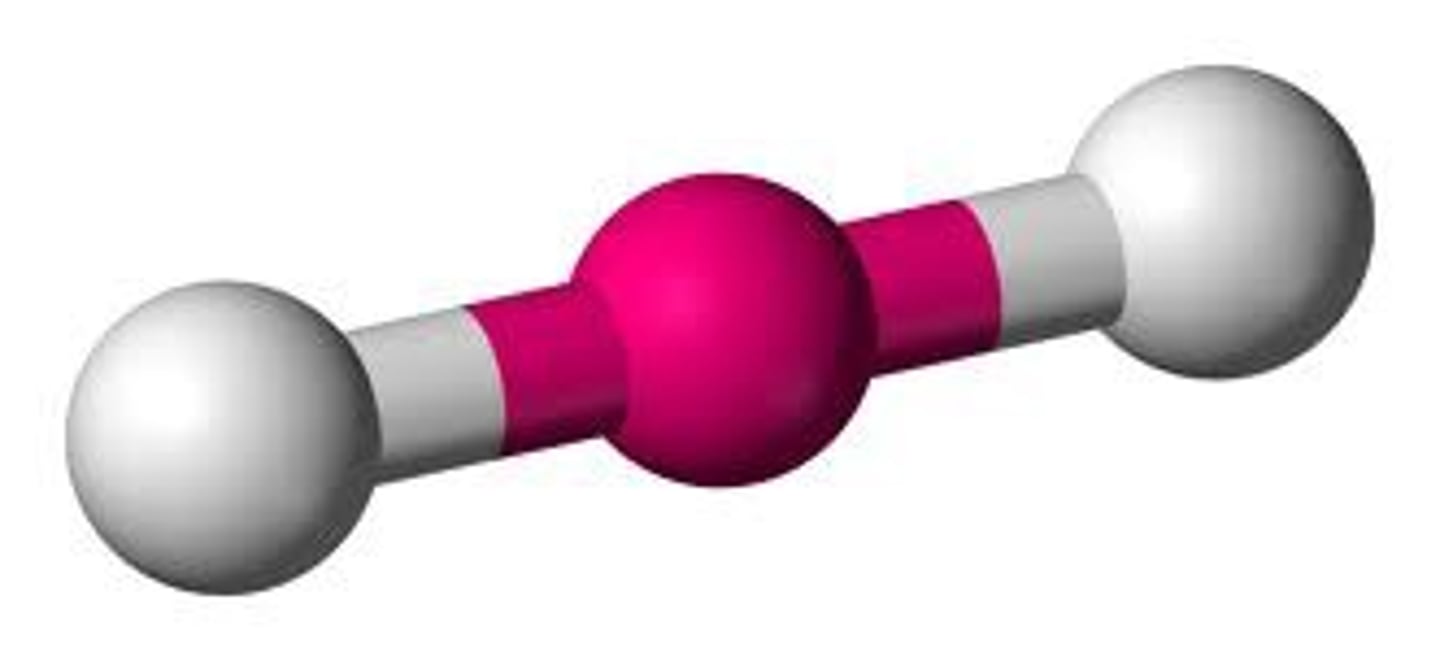
VSEPR theory (aka valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory)
explains three dimensional shape; the repulsion between electron pairs causes molecular shapes to adjust so that the valence-electron pairs stay as far apart as possible.
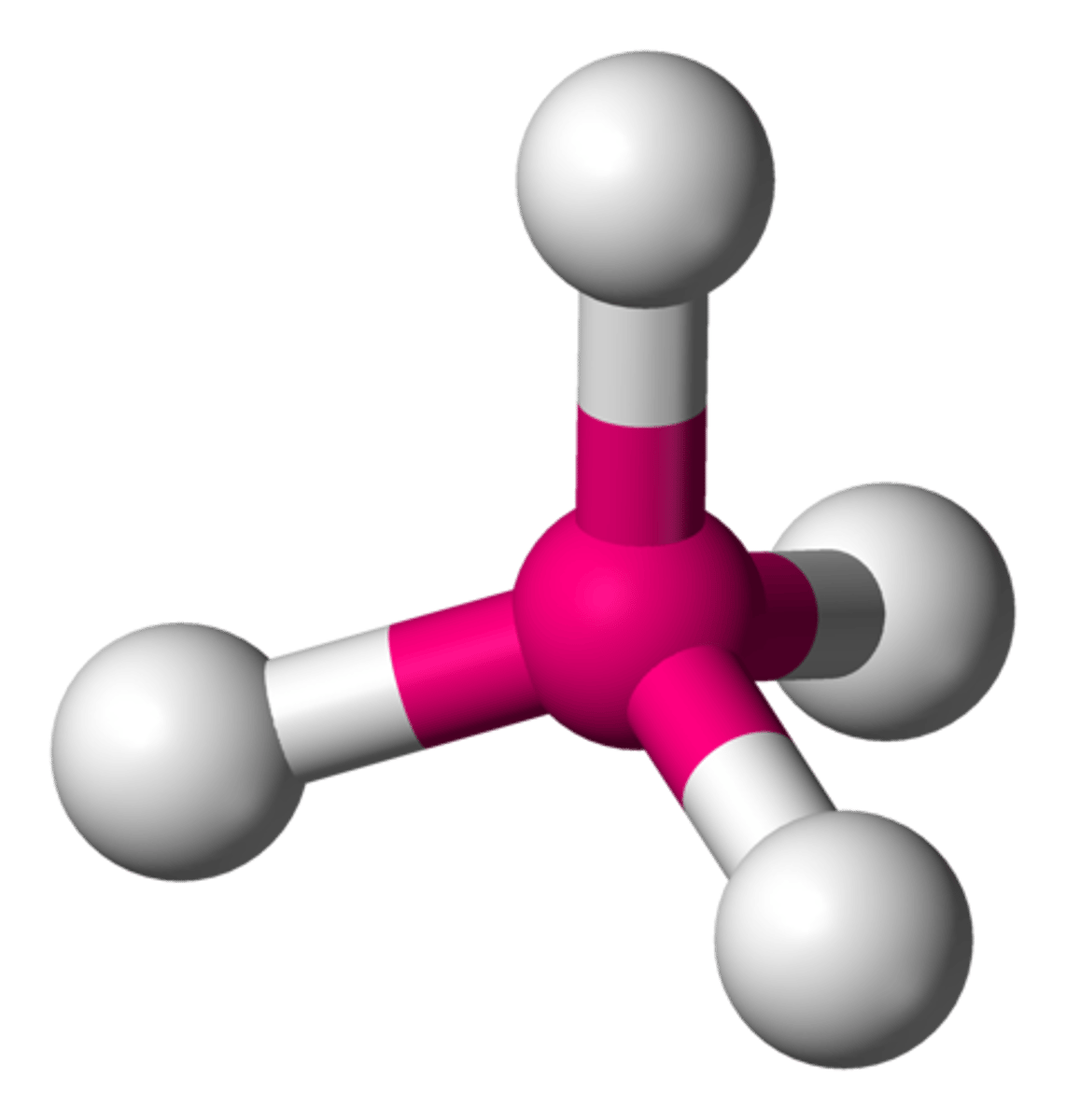
Tetrahedral
1 center and 4 bonded
109.5º
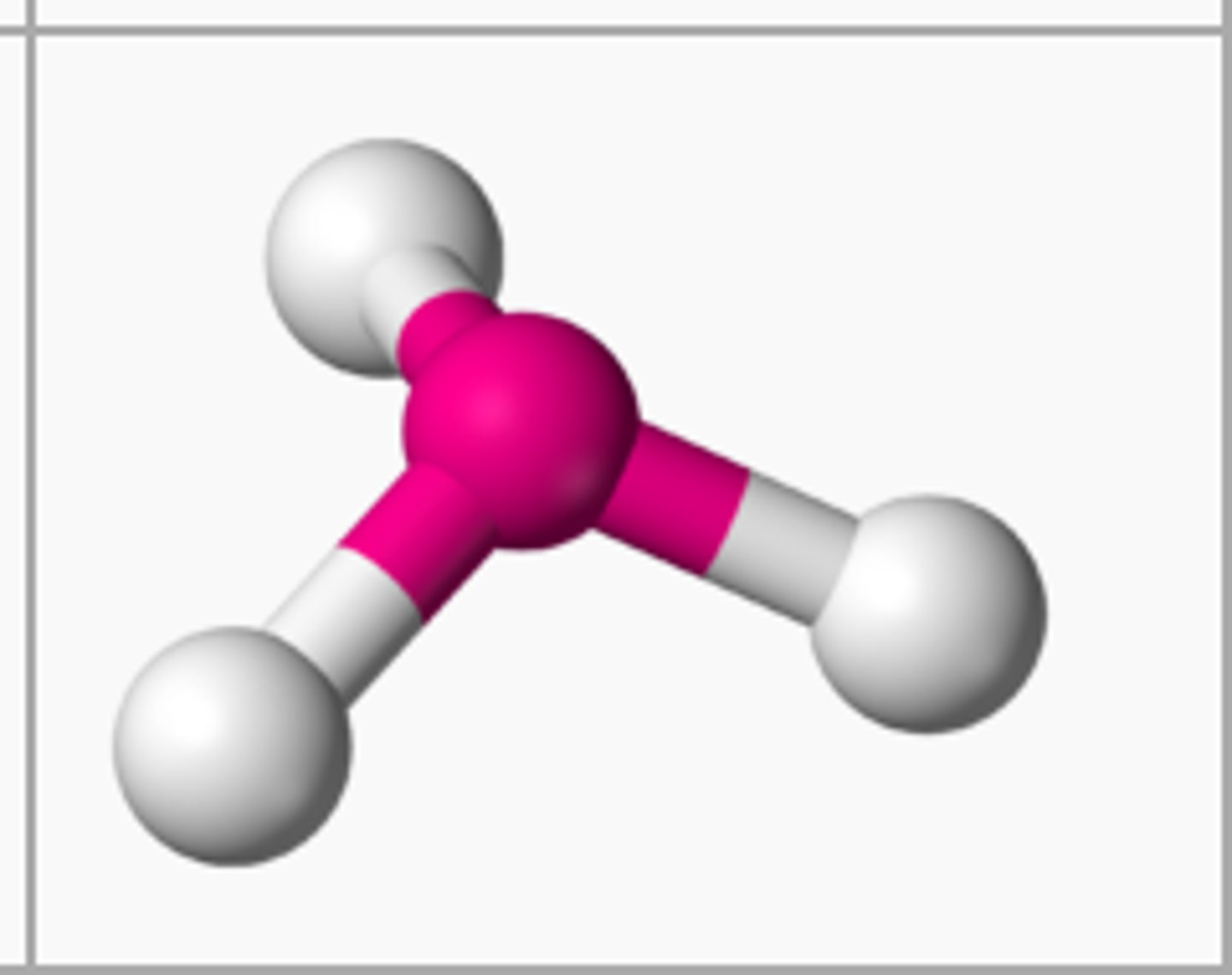
Trigonal Pyramidal
1 central, 3 bonded and 1 lone pair
107º
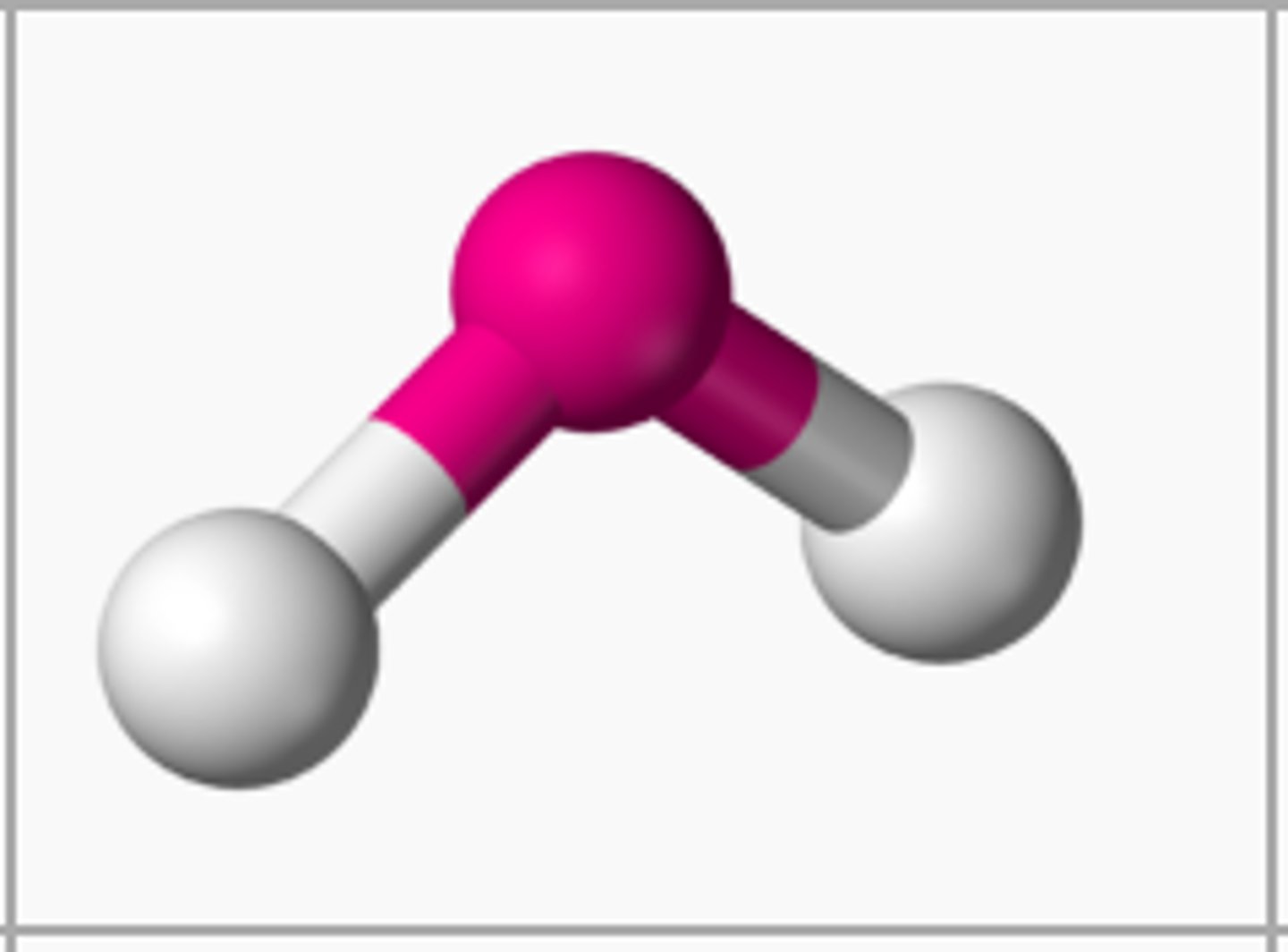
Bent
1 central, 2 bonded, and 2 lone pairs
105º
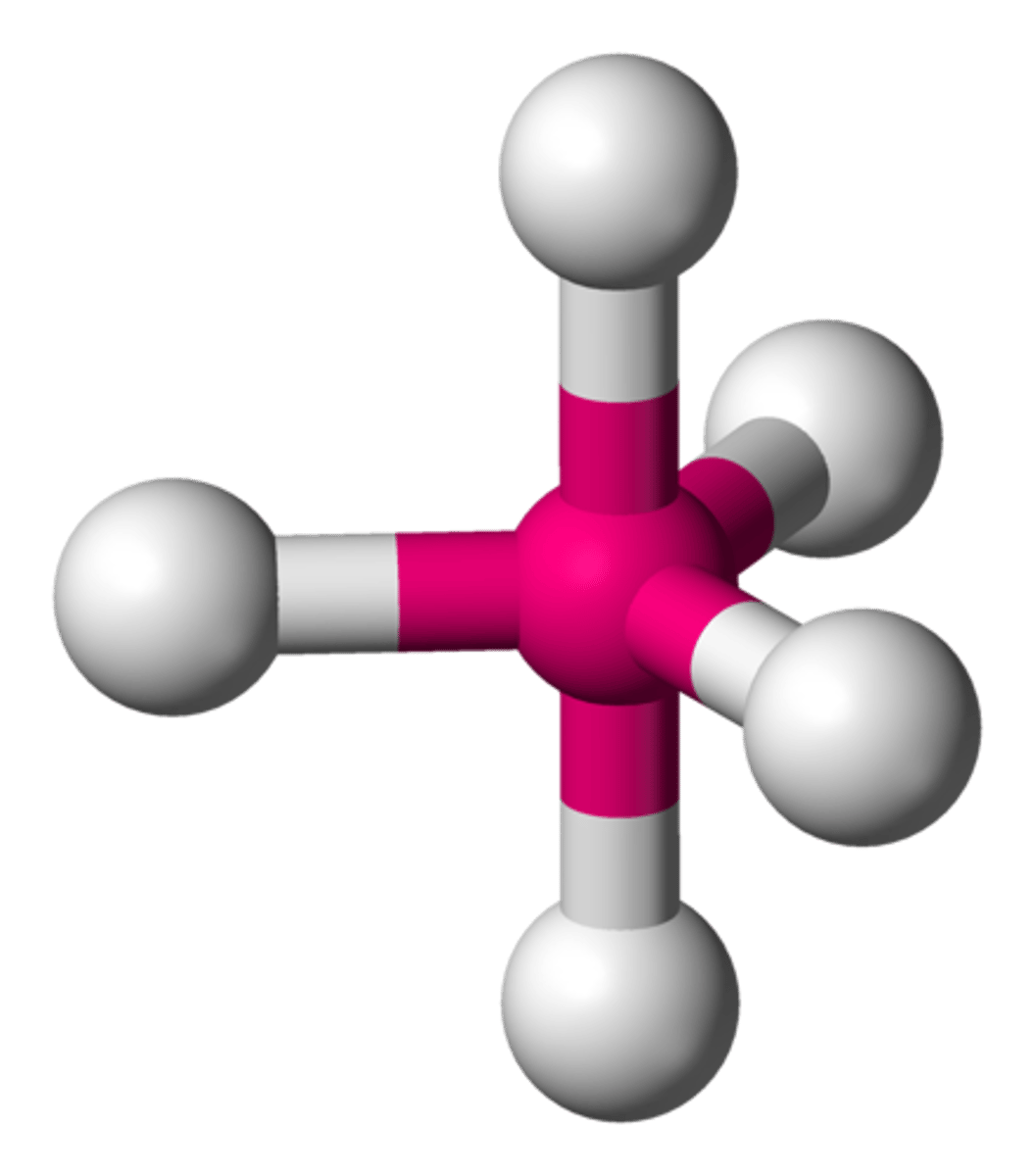
Trigonal Bipyramidal
1 central and 5 bonded
120º and 90º
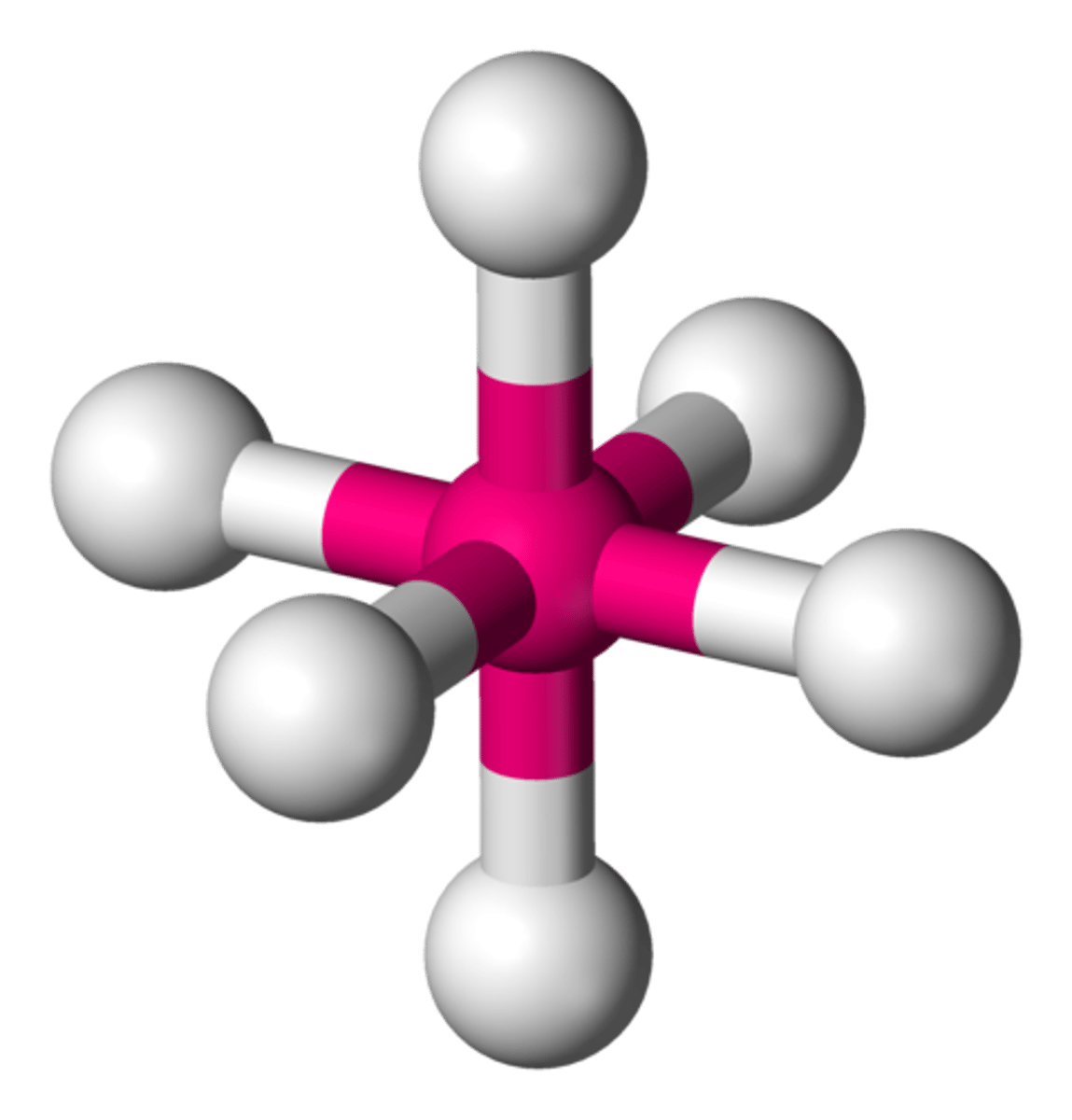
Octahedral
1 central and 6 bonded
90º
Limited Octect
1 central and 3 bonded
120º
ONLY WITH BORON
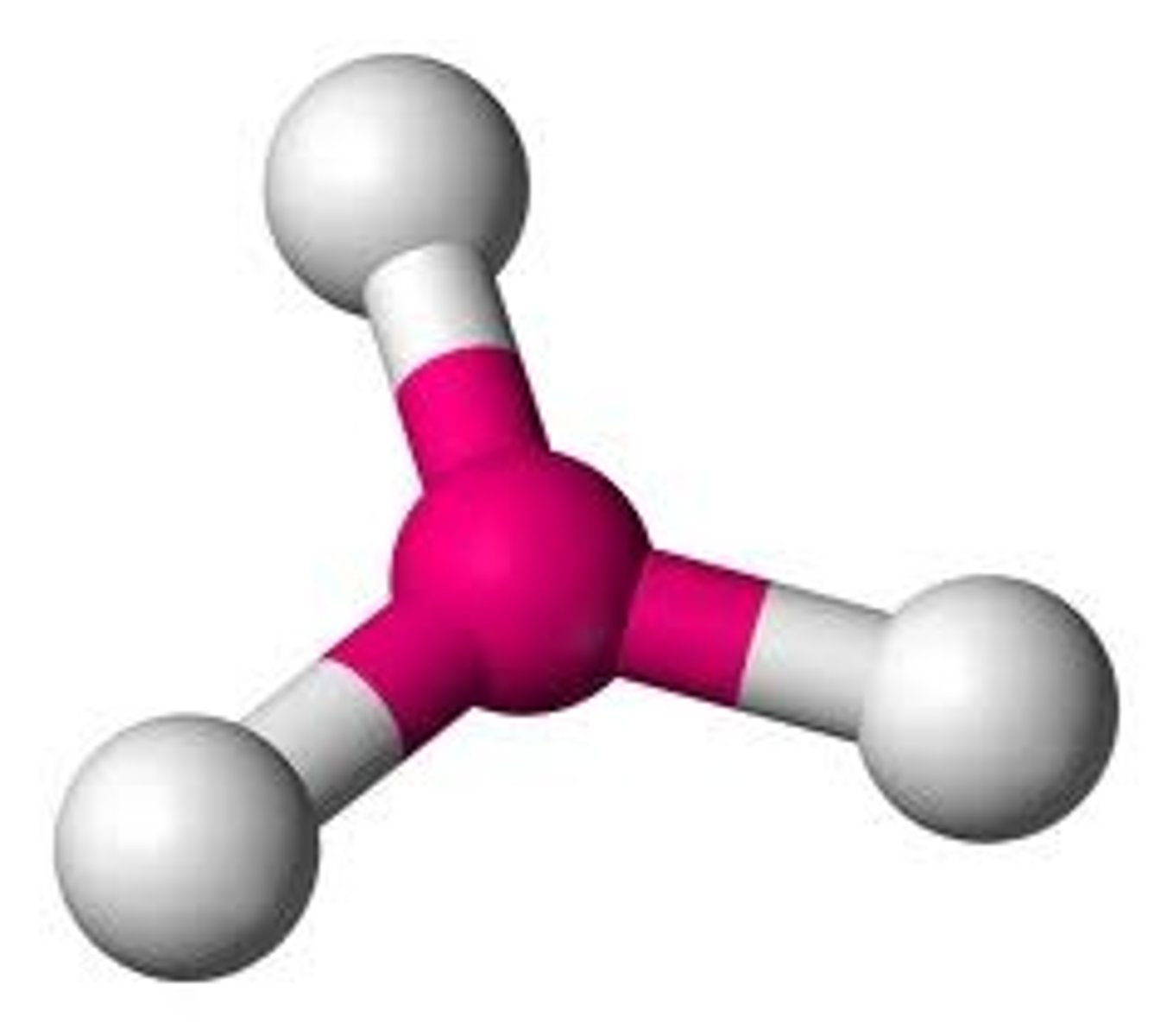
Trigonal Planer
1 center and 3 bonded
120º
Exceptions to the octet rule
the octet rule cannot be satisfied in molecules whose total number of valence electrons is an odd number. There are also molecules in which an atom has fewer, or more that a complete octet of valence electrons.
The octet rule
In forming covalent bonds, electron sharing usually occurs so that atoms attain the electron configurations of noble gases.
Single covalent bond
two atoms held together by sharing a pair of electrons;An electron dot structure such as H:H represents the shared pair of electrons of the covalent bond by two dots.
Structural formula
represents the covalent bonds by dashes and shows the arrangement of covalently bonded atoms.
Unshared pair
(aka lone pair, nonbonding pair) a pair of valence electrons that is not shared between atoms
Double covalent bond
a bond that involves two shared pairs of electrons
Triple covalent bond
a bond that involves three shared pairs of electrons
Coordinate covalent bonds
a covalent bond in which one atom contributes both bonding electrons; the shared electron pair comes from one of the bonding atoms
Polyatomic ion
a tightly bound group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge and behaves as a unit
Covalent bond
the atoms held together by sharing electrons
Molecule
a neutral group atoms joined together by covalent bonds
Diatomic molecule
a molecule consisting of two atoms; BrINClHOF
Molecular compound
a compound composed of molecules; tend to have relatively lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds
Molecular formula
the chemical formula of a molecular compound; shows how many atoms of each element a molecule contains
mono
one
di
2
tri
3
tetra
4
penta
5
hexa
6
hepta
7
octa
8
nona
9
deca
10