MIS 200 Exam 3 Herfurth
5.0(5)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:16 AM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
the cloud
elastic leasing of pooled computer resources over the internet
2
New cards
Computer Network
a system that connects computers and other devices via communications media so that data and information can be transmitted among them
3
New cards
LAN
Local area network; computers connected at a single physical site
4
New cards
WAN
Wide Area Network; computers connected between two or more separated sites
5
New cards
Intranet
a network designed for the exclusive use of computer users within an organization that cannot be accessed by users outside the organization
6
New cards
Extranet
a network configuration that allows selected outside organizations to access internal information systems
7
New cards
IP address
A number that uniquely identifies each computer or device connected to the Internet.
8
New cards
URL
An easy-to-remember address for calling a web page (like www.code.org).
9
New cards
HTTPS protocol
uses http in conjunction with the SSL/TLS protocol to provide secure communication
10
New cards
VPN
using the public internet to build a secure, private network connecting distant locations
11
New cards
resource elasticity
automatically adjust resources for unpredictable demand
12
New cards
Pooled computer resources
organizations share same physical hardware through virtualization so the cost decreases
13
New cards
Why many organizations are moving to the cloud V.S. why they are not
ARE: lower costs, ubiquitous access, improved scalability, elasticity, virtualization technology, internet-based standards enable flexible & standardized processing capabilities
ARE NOT: when law or standard industry practive require physical control or possession of the data, financial institutions are legally required to maintain physical control over their data
ARE NOT: when law or standard industry practive require physical control or possession of the data, financial institutions are legally required to maintain physical control over their data
14
New cards
When is VPN used
when you need to remote into the local area network of wherever you need to be
15
New cards
Net Neutrality
the principle that all Internet traffic should be treated equally by Internet Service Providers.
16
New cards
Capital
the investment of resources for future profit
17
New cards
Social media
IT for sharing content amoung networks of users, enables communities of practice
18
New cards
Social capital
social relations with expectation of marketplace returns
19
New cards
Revenue models
Advertising, subscriptions, transaction fees, sales, and affiliate revenue.
20
New cards
Geofencing
location service allowing applications to know when a user has crossed a virtual fence
21
New cards
conversion rate
Frequency someone clicks on ad makes a purchase, "likes" a site, or takes some other action desired by advertiser
22
New cards
vanity metrics
things that dont matter, not tied to organizations strategy or values
23
New cards
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
The quantifiable metrics a company uses to evaluate progress toward critical success factors
24
New cards
success metrics
measurements to track performance toward goals
25
New cards
Social media provider vs. social media user
Providers: facebook, google, linkedin, twitter, etc. attracting demographic groups
Users: individuals and organizations
Users: individuals and organizations
26
New cards
benefits of social media for organizations
customers can have a direct relationship with the products, organizations can get the word out there
27
New cards
pros vs. cons of problem solving via social media
leaving it, respond to it, or delete it; can be pros and cons to all
28
New cards
value of social capital
number of relationships, strength of relationships, and resources controlled; information, influence, social credentials, personal reinforcement
29
New cards
determining the best revenue model for an organization
advertising, freemium, sales; whichever makes more sense for the organization
30
New cards
how social media fits into organizational strategy
social media changes the balance of power amoung users, communities, and organizations
31
New cards
role of social media in value chain activities
value chains determine business processes, processes determine SMIS requirements, dynamic process flows cannot be designed or diagrammed
32
New cards
threat
can come in different ways, hackers, natural disasters, etc.
33
New cards
vulnerability
threats attack vunerabilities, somewhere a threat could attack
34
New cards
target
aim for money or information, most of the time ends in loss
35
New cards
pretexting
someone pretends to be someone else
36
New cards
sniffing
technique for intercepting computer communications
37
New cards
spoofing
another term for someone pretending to be someone else
38
New cards
phishing
a similar technique for obtaining unauthorized data that uses pretexting via email
39
New cards
hacking
breaking into computers, servers, or networks to steal data
40
New cards
denial of service attack
a cyber attack in which an attacker sends a flood of data packets to the target computer, with the aim of overloading its resources
41
New cards
human safeguard
steps taken to protect against security threats by establishing appropriate procedures for users to follow for system use
42
New cards
technical safeguard
identification and authorization, encryption, firewalls, malware protection, application design
43
New cards
cookie
a small text file that a web server stores on your computer
44
New cards
packet-filtering firewall
examines each part of a message and determines whether to let that part pass
45
New cards
Malware
software that is intended to damage or disable computers and computer systems.
46
New cards
Firewall
a part of a computer system or network that is designed to block unauthorized access while permitting outward communication.
47
New cards
Ransomware
Software that encrypts programs and data until a ransom is paid to remove it.
48
New cards
identification vs. authentication
identification - identifies the user
authentication - authenticates the user (password, PIN, smart cards, biometric auth.)
authentication - authenticates the user (password, PIN, smart cards, biometric auth.)
49
New cards
threat/loss scenario illustration
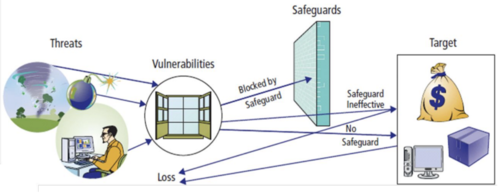
50
New cards
types of security loss and examples of each
1. Unauthorized data disclosure - people gaining access to data they should and being able to sell it
2. Incorrect data modification - changing data in a companies database
3. Faulty service - making services not work
4. Denial of Service - service doesnt work because of an attack or human error
5. Loss of infastructure - physical hardware or software goes down
2. Incorrect data modification - changing data in a companies database
3. Faulty service - making services not work
4. Denial of Service - service doesnt work because of an attack or human error
5. Loss of infastructure - physical hardware or software goes down
51
New cards
common motivations behind hacking
information, money
52
New cards
how DoS works
Human error - inadvertently shut down a web server or corporate gateway router (black friday too many ppl on website)
Malicious hacker intentionally floods a web server with millions of bogus requests to prevent legitamite traffic from getting through
Malicious hacker intentionally floods a web server with millions of bogus requests to prevent legitamite traffic from getting through
53
New cards
Types of security threats
unauthorized data disclosure, incorrect data modification, faulty service, denial of service, loss of infrastructure
54
New cards
Types of IS security safeguards
technical safeguards, data safeguards, and human safeguards
55
New cards
how organizations decide to manage IS risk
having a plan in place, centralized reporting, specific responses (speed, perparation, dont make the problem worse), practice
56
New cards
How does encryption work?
transforming clear text into coded, unintelligible text for secure storage or communication
57
New cards
How do firewalls work?
computing device that prevents unauthorized access
58
New cards
when and how human safeguards are used in IS security
dissemination and enforcement to train employees on computer safety, termination, being aware of security protocalls, account management, password management, help desk policies
59
New cards
when and how technical safeguards are used in IS security
logging into a system using authentication, knowing https is safe, ecryption when you dont want someone to see your message, firewalls so someone cant get passed and get into the network
60
New cards
BI systems
information systems that process operational and other data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends for use by business professionals and other knowledge workers
61
New cards
Data warehouse
obtain data, cleanse data, organize and relate data, catalog data
62
New cards
data mart
contains a subset of data warehouse information
63
New cards
Metadata
data that describes other data
64
New cards
Knowledge management
finding the right information, keeping the information in a readily accessible place, and making the information known to everyone in the firm
65
New cards
content management systems
support management and delivery of documents, other expressions of employee knowledge
66
New cards
artificial intelligence
The ability of a machine to simulate human abilities such as vision, communication, recognition, learning, and decision making in order to achieve a goal
67
New cards
Weak AI vs. Strong AI
weak: focused on completing a single specific taks
strong: can complete all of the same tasks a human can
strong: can complete all of the same tasks a human can
68
New cards
Turing Test
Alan Turing said a machine could be considered intelligent if a human could have a conversation with it and not be able to tell if it was a machine or a human
69
New cards
Tasks of BI Systems
informing, deciding, problem solving, and project management
70
New cards
Three primary activities in the BI process
acquire data, perform analysis, publish results
71
New cards
data acquisition options
72
New cards
Three types of BI analysis
reporting, data mining, BigData
73
New cards
how data mining works and why we do it
use sophisticated statistical techniques to find patterns and relationships
74
New cards
Push vs Pull Publishing
Push happens automatically, pull the knowledge workers have to ask for it
75
New cards
Static vs Dynamic reports
static: prepped once from the underlying data
dynamic: at the time of creation, the reporting system reads the most current data and generates the report using the new data
dynamic: at the time of creation, the reporting system reads the most current data and generates the report using the new data
76
New cards
elements of a BI system
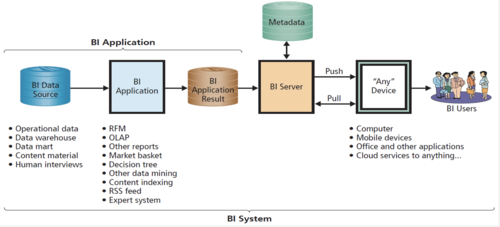
77
New cards
role of humans interacting with BI
78
New cards
potential impact of artificial intelligence on the job market
79
New cards
CONCAT
join two or more text strings into one string
80
New cards
COUNTIF/COUNTIFS
Counts the number of cells within a range that meet the given condition
81
New cards
SUMIF/SUMIFS
Adds the cells specified by a given condition or criteria.
82
New cards
AVERAGEIF/AVERAGEIFS
Finds average(arithmetic mean) for the cells specified by a given condition or criteria.
83
New cards
sparklines
small graphs used to represent a series of data; show trends in a series of values, economic cycles, or highlight max or min values
84
New cards
Importance of KPIs
KPIs are often depicted as dashboards with graphs/charts for an at-a-glance status report