BAE 204
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Methods for Stream Discharge Measurement
Float - Ball Float; Using Acoustics - Doppler Effect; Flow/velocity meter - Spinning Thing; Weirs or flumes - WEIR; Gauging Station USGS
Depth for measuring velocity in streams.
Two measurements 0.8 of the depth and 0.2 of the depth from the water surface for large streams; 0.6 of the depth from the water surface for small streams.
Anthropocene (Implications)
Climate Change, Resource Use, Population Growth. WE ARE FUCKING THE EARTH BUT ALSO WE NEED SOME OF THE DEVELOPMENT
Water Availability
Even in places like NC where rainfall is not depleting, it is min maxing such that we have a stress period in which we must pull from the ground water, this means that the ground water is being depleted.
Solutions for Water Availability
Lower flow appliances; More efficient use of water (including water reuse); Application of use at certain times to prevent evaporation; Advanced irrigation methods.
Excess Water (Implications and Solutions)
Poorly draining soils get water logged; Concentration of rain events; We can help by doing stormwater management and using irrigation techniques.
Pollutants of Concern
Sediment; Nutrients: N and P mostly; Synthetics and Industrial: Oils and PFAS for example; Heavy Metals; Waste Water and Solid Waste
Stream Restoration Structures
J-Hooks: Redirect flows from the bank and provide more aquatic habitat.
Cross Vanes: Redirects the flow to the center of the channel preventing bank erosion.
Meander: Slows flow, provides habitat, and limits bank erosion.
Riffles: Dissipate Energy
Root Wads: Stabilizes bank
Beaver Dams
Decrease nitrate and suspended sediments down stream. Increase pollutants like methyl mercury, dissolved organic carbon, and ammonium downstream. *Unsure if they cause this
Biogeochemical process kinetic rates
Rate Expressions describe reactions in terms of the change in reactant or product concentrations over the change in time. The rate of a reaction can be expressed by any one of the reactants or products in the reaction.
Precipitation
The condensation or freezing of vapor in the air that leads water to fall to the ground.
Evapotranspiration
The total amount of vaporization that happens on plants, in air, from bodies of water and so on. Evaporation + Transpiration
Percolation
The rate of water flow through soil
Infiltration
The rate of water flow into soil
Interception
When vegetation captures and absorbs water before it reaches the ground
Surface Runoff
The flow of water over a surface into streams.
Measurement of Precipitation
Non-Recording Gauge: Has to be watched and emptied after every rain event.
Tipping Bucket Gauge: Intense Storms Fuck With It
Weighing Gauge: I don’t know the limitations TBH
Vapor Pressure
Pressure (amount) of vapor held in the air. Basically when water evaporates it increase atmospheric pressure.
Saturation vapor pressure
Maximum vapor pressure that can be held in the air, based on temperature.
Soil Particle Classification
Clay<0.002 mm
Silt<0.05 mm
Sand<2 mm
Mass Wetness
w = MWater/MSoil
Volumetric Water Content
VWater/VTotal=pb/pw * MWater/MSoil = Asw, Remember pb is dry bulk density
Field Capacity (Percentage Range as Well)
Water that can’t be drained to gravity. 20-40%
Minimum management level
When the plant begins to feel water stress, the point where the plant is receiving less water than it needs.
Permanent Wilting Point vs. Wilting Point
The melting point is when the plant begins to wilt due to lack of water but can recover, for example, a hot day is rough for it but it still can come back. The idea here is that it can wilt depending on other conditions then soil moisture, but is is sensitive because of the soil moisture. A permanent wilting point is when the plant cannot access any water because it cannot create enough pressure. The wilting point is when the plant begins to wilt due to a lack of water but can recover. For example, a hot day can be rough for it, but it can still come back. The idea here is that the plant can wilt depending on other conditions besides soil moisture, but it is sensitive because of the soil moisture. A permanent wilting point is when the plant cannot access any water because it cannot create enough pressure.
Methods of Measuring Temperature
Thermometer (Electronic): Raw Measurement mV and it can be used in the ground.
Black Globe Thermometer, same thing as the other one but with a black body around it.
Method of Measuring Soil Moisture and Wet Leaf Senso
Electronic Soil Moisture Sensors and wet leaf sensor measure the resistance of a soil which decreases with increased water content.
m³water / m³soil for soil, “raw counts” for leaf
All weather sensor
Utilization of doppler sensing, meaning alterations of speed of sound due to wind speed and precipitation.
Watershed properties that affect runoff depths
soil type, land use, slope, initial soil water content
Runoff Fraction
Depth of Runoff/Depth of Rainfall
5 Requirements for Life
(L)iquid Water
(E)nergy: Solar or chemical
(E)lectron Acceptors: O2
(N)utrients: CHONSP
(T)emp that is suitable: 2-50 C
Carbohydrates: Function and Nutrients
Provides energy and structure (for plants)
C H O
Lipids: Function and Nutrients
Energy and Compartmentalization (Cell Walls)
C H O N(Small Amounts) P
Proteins: Function and Nutrients
Enzymes, Regulates Transport and Exchanges
C H O N S
Nucleic Acids: Function and Nutrients
Holds genetic code
C H O N P
Phenolics: Function and Nutrients
Structure: Tannins and Lignins (Aromatic Rings)
C H O
How does an autotroph find nutrients
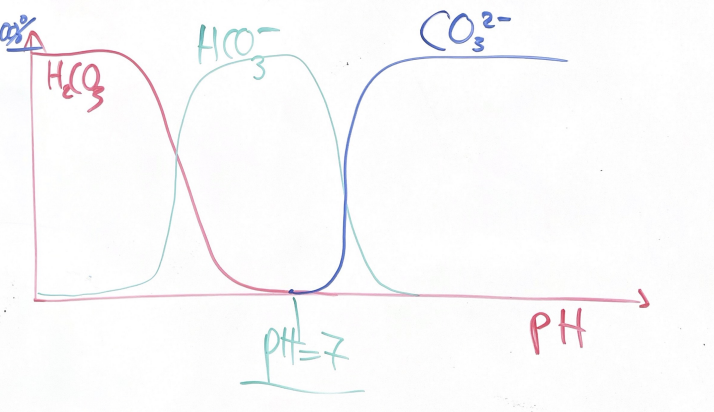
C: CO2 and Carbonates (H2CO3,HCO3-,CO32-)
H and O: H2O
N: Nitrate (NO3-)
S: Sulfate (SO42-)
P: Phosphate (PO43-)
Vector and Storage of Energy (Life)
Electrons
Where are electrons stored? (Life)
The most electronegative atom of a molecule.
How does energy release? (Life)
Electrons go from a donor to an acceptor. More electronegative atoms steal the electrons
Ultimate electron acceptor? (Life)
Oxygen O2
Electronegativity Order of Nutrients
O>N>S>C>H>P
Carbonate as pH changes
What makes up runoff
Rain, snowmelt, and interflow (water that leaves the soil before it reaches the groundwater)
Importance of Quantifying Runoff Amounts (Two Important Reasons)
It allows us to design structures based on certain rain events.
It allows us to estimate pollutant loads.
Stream Order (Explain it to yourself and then use the image to confirm)
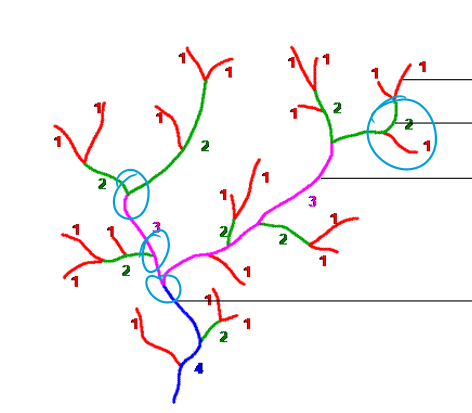
What contributes to the hydrograph.
Baseflow and precipitation. There is a delay in stream flow depending on the watershed size.
Water Budget for a Watershed
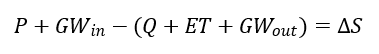
The driving force in open channel flow
Gravity
What is Hydraulic Radius
The area of the stream cross-section divided by the wetted perimeter.
It is useful because it accounts for the differences in behavior of streams with different surface areas even though the cross-sectional areas may be similar or the same.
Uniform
Uniform flow means that the depth, cross-sectional area, and velocity of the stream do not change along the stream section of focus.
Foude number

Critical flow
Fr less than one then sub critical, critical at 1, and supercritical above 1
Hydrological Seasons (What happens during summer and winter)
They begin early September because that is when the cycle of varying precipitation and ET begins.
During summer flow levels off because ET is so high. During winter there is a great increase in cumulative flow because ET is low.
Bioretention Pond Features and Function
Vegetation
Drainage Pipes
Media: Mostly sand with 5-10% silt-clay, 5% OM
Overflow system
Water Storage
The area and percentage of the U.S.’s cropland that requires improved drainage.
40 million ha, and about 25% of the nations cropland
The area and percentage of the worlds cropland that needs drainage.
500 million ha and 33% of total cropland
Why drainage?
To wet or too dry
Drainage controls soil salinity because evaporation brings up salt through soil horizontal layers.
Issues due to drainage
More leeching of fertilizers which increase nitrate and phosphorus and ground water.
Current Irrigation Efficiencies
25-45% in developing countries
50-60% in Taiwan, Israel, Japan
Sprinkler Irrigation Types
Hand Movement
Travelling Gun
Center pivot and Linear Move
Micro Irrigation Types
Surface Drip
Subsurface Drip
Microspray
Water Application Efficiency
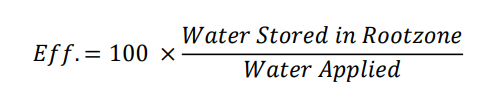
Uniformity Coefficient
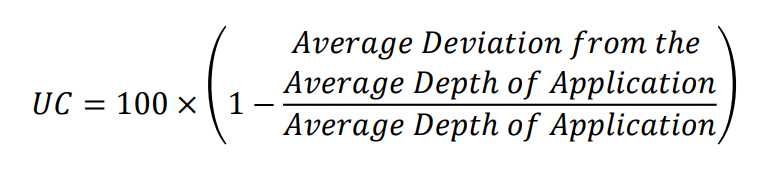
Carbon Inorganic Molecules
Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Carbonate (CO32-), Carbonic Acid (H2CO3), Bicarbonate/Hydrogen Carbonate (HCO3-), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Methane (CH4)
Nitrogen Inorganic Molecules
Nitrate (NO3-), Nitrate (NO2-), Nitrogen Gas (N2), Ammonium (NH4+), Ammonia (NH3), Nitrogen Monoxide (NO), Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
Sulfur Inorganic Molecules
Sulphate (SO42-), Sulfite (SO32-), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), Hydrogen Sulfide (HS-), Sulfide (S2-)
Phosphate Inorganic Molecules
Phosphates (PO43-), Hydrogen Phosphate (HO42-), Dihydrogen Phosphate (H2PO4-), Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
What is the name of this functional group.
AMINE
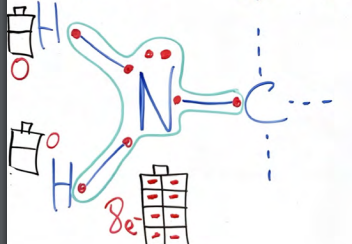
What is the name of this functional group.
THIOL
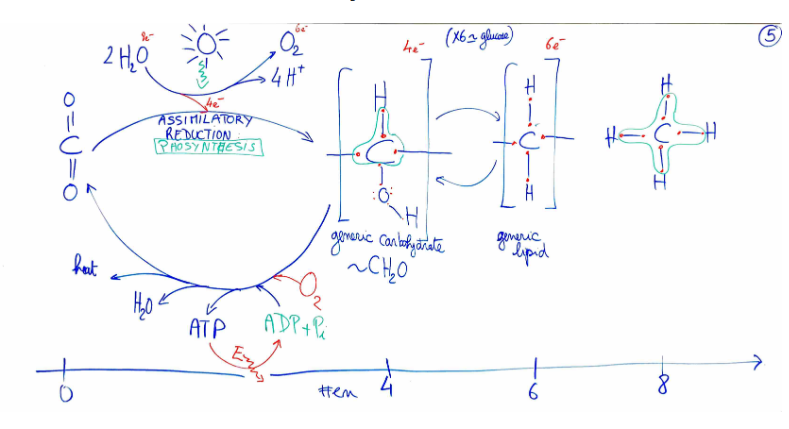
FROM DUST TO DUST CYCLE
Criteria for Organic Molecule
#em(C)>=1
At least one carbon to carbon bond.
Flow-Weighted Average
Cumulative load of a substance divided by cumulative flow in a stream. It gives you a better understanding of the actual average concentration
Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) concentration trends during rain effects
Concentrations tend to be diluted, but it is not always diluted. In many cases the land-use and variables effect the amount of carbon that reaches a waterbody during a rain event.
What does the flow-weighted average tell us?
The flow-weighted average gives a better idea of if the concentration of a substance increases or decreases during flow events. We can determine if it is diluted or concentrated by comparing the FWA to the time weighted average.
Fabaceae family (ability and how they do nitrogen fixation)
These are legumes that use diazotrophs to fix nitrogen. They typically exist in root nodules.
What are the two main cellular components of cyanobacteria
Akinete: Robust and resistant cells that can produce new vegetative growth
Heterocysts:Specialized cells with cyanobacteria that can fix nitrogen.
Trees that can N-Fix and their families
Red Buds - Fabaceae
Alders and Birches - Betulaceae
Freshwater Concentration Thresholds for Eutrophication
0.3 mg N/L
0.03 mg P/L