Benzene and phenol
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Aromatic us alliphatic
Aromatic = ring
aliphatic= chain
Limitations of the kekulé model
Doesn’t decolourise bromine water so no double bonds are present/ compound isn’t unsaturated
Bond lengths - all the carbon to carbon bonds were the same length ( single and double bonds are different lengths)
Enthalpy of hydrogenation - the actual value for hydrogenation of benzene is -208 kj mol-1 whereas it’s theoretical is -360 if there were 3 double bonds present
Explain the new model of benzene
The p-orbitals overlap sideways forming a pi-cloud above and below the plane or carbon atoms. Each carbon atom contributes 1 electron giving rise to a delocalised system of 6 electrons
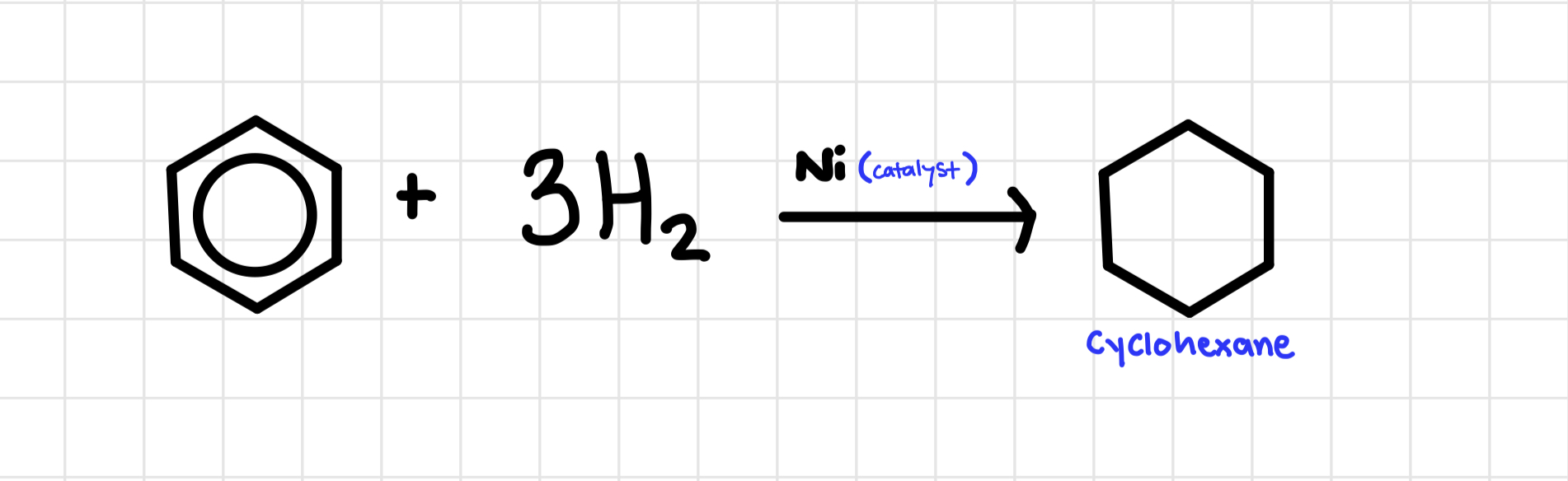
Hydrogenation of benzene
Combustion of benzene
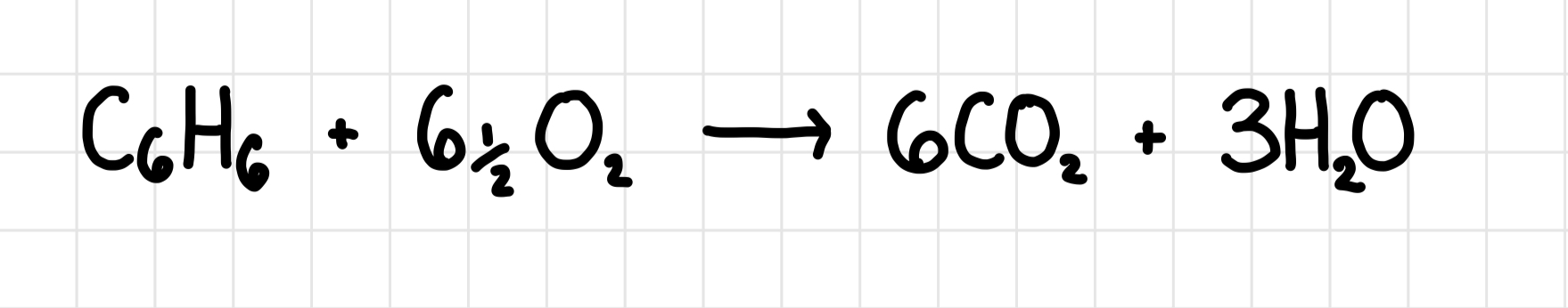
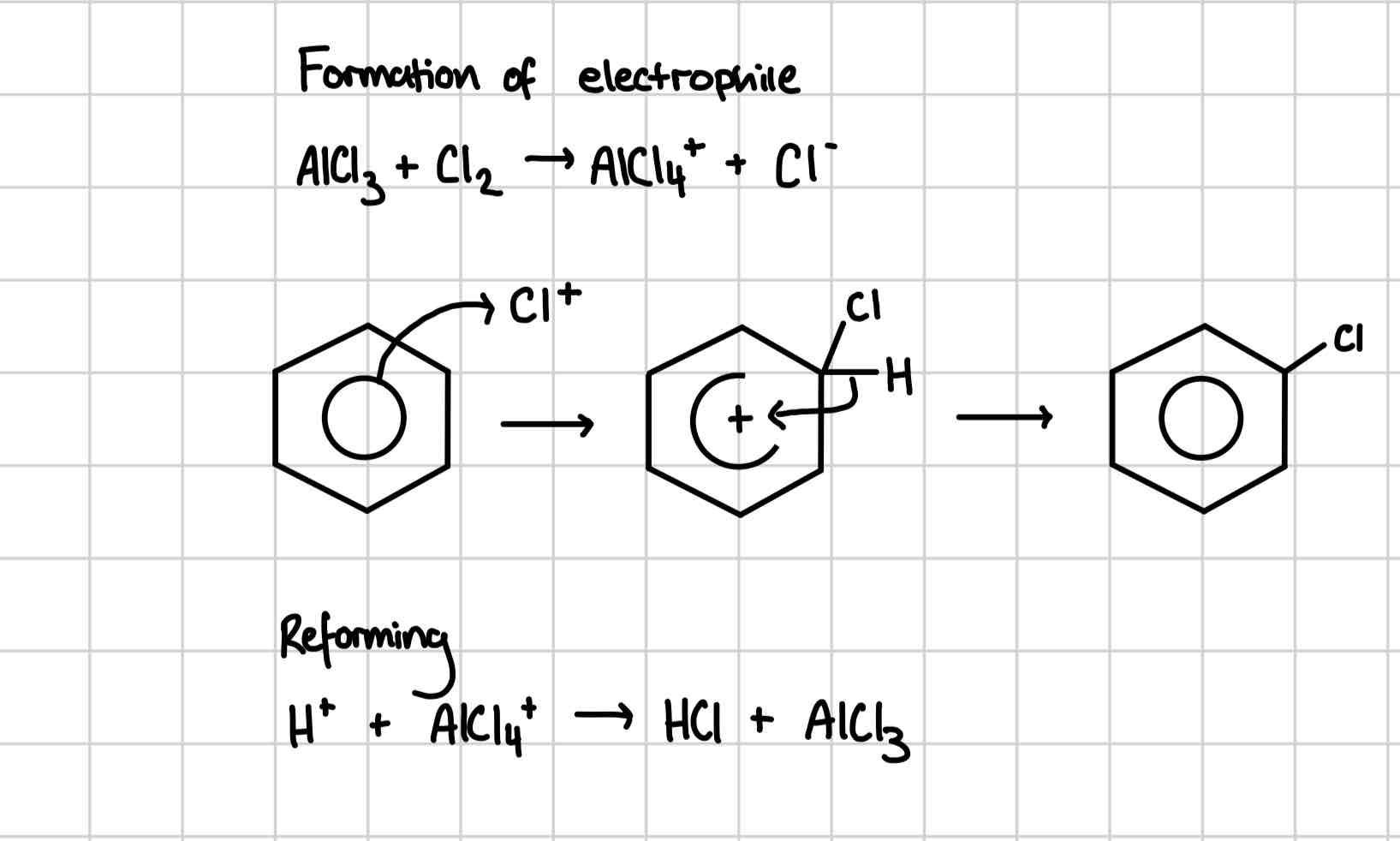
Bromination of benzene
Benzene and bromine are heated under reflux
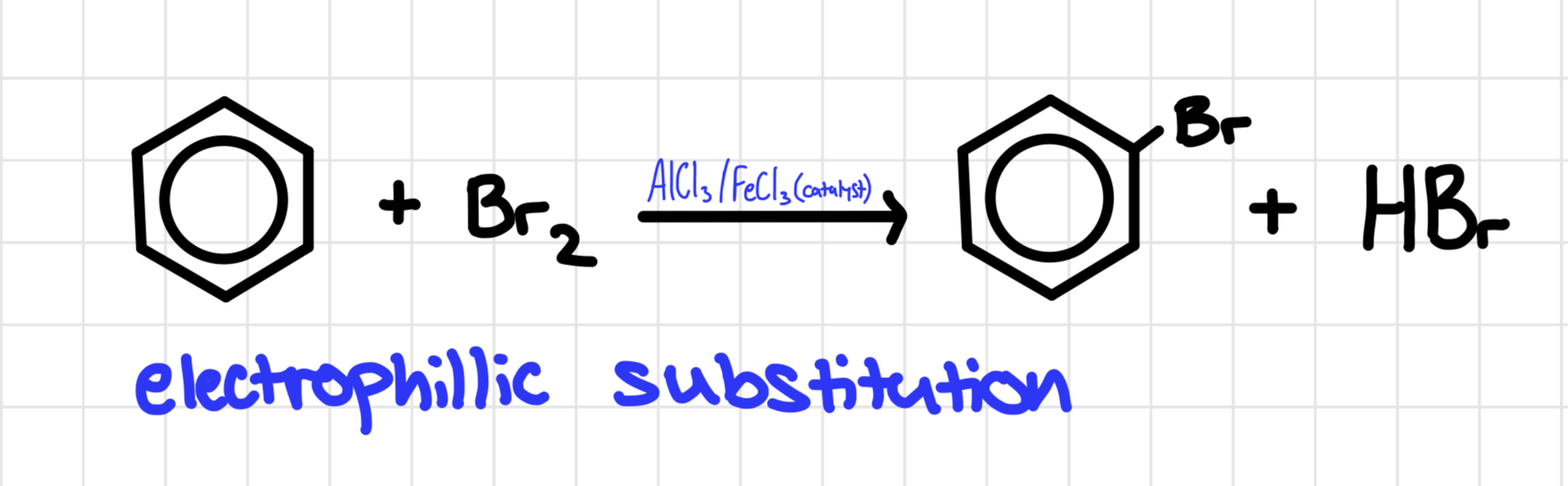
Mechanism for bromination of benzene
Benzene and bromine are heated under reflux
FeBr3 catalyst
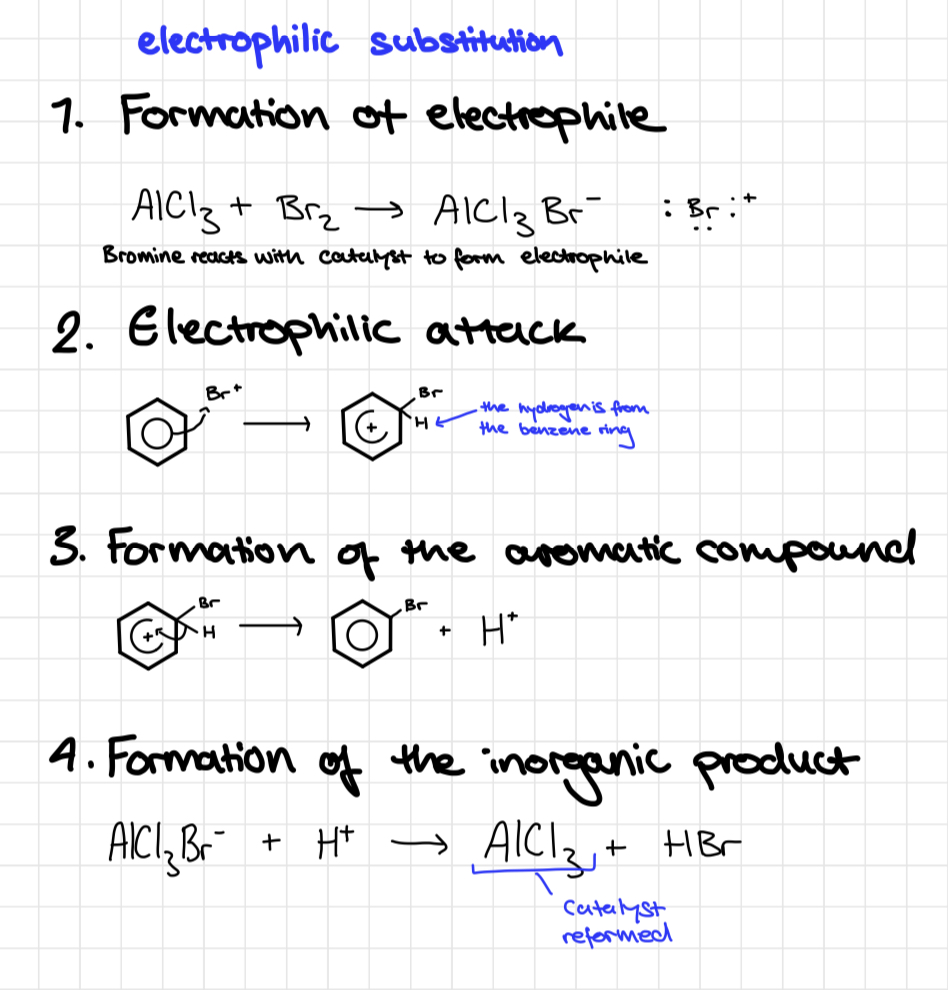
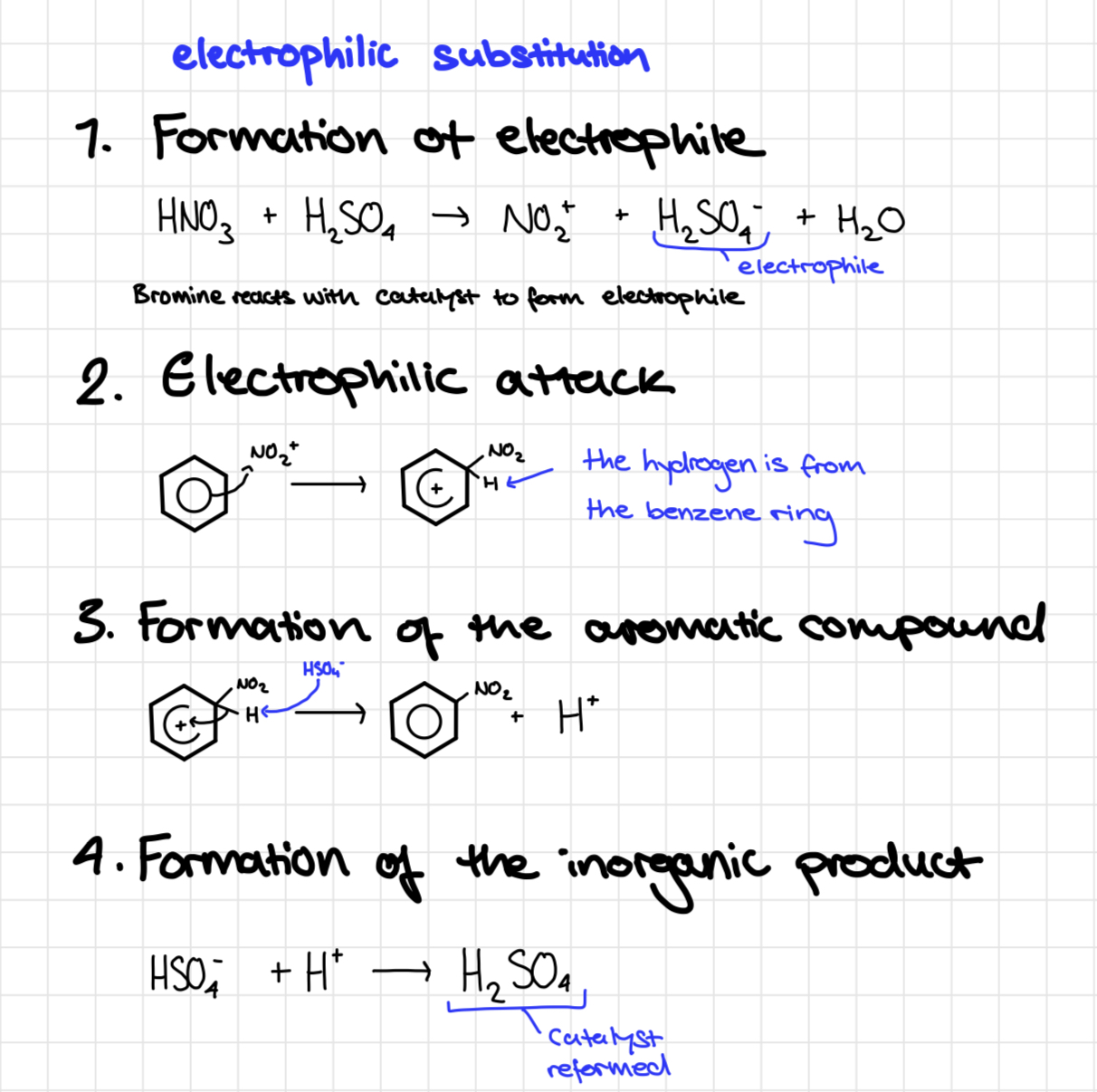
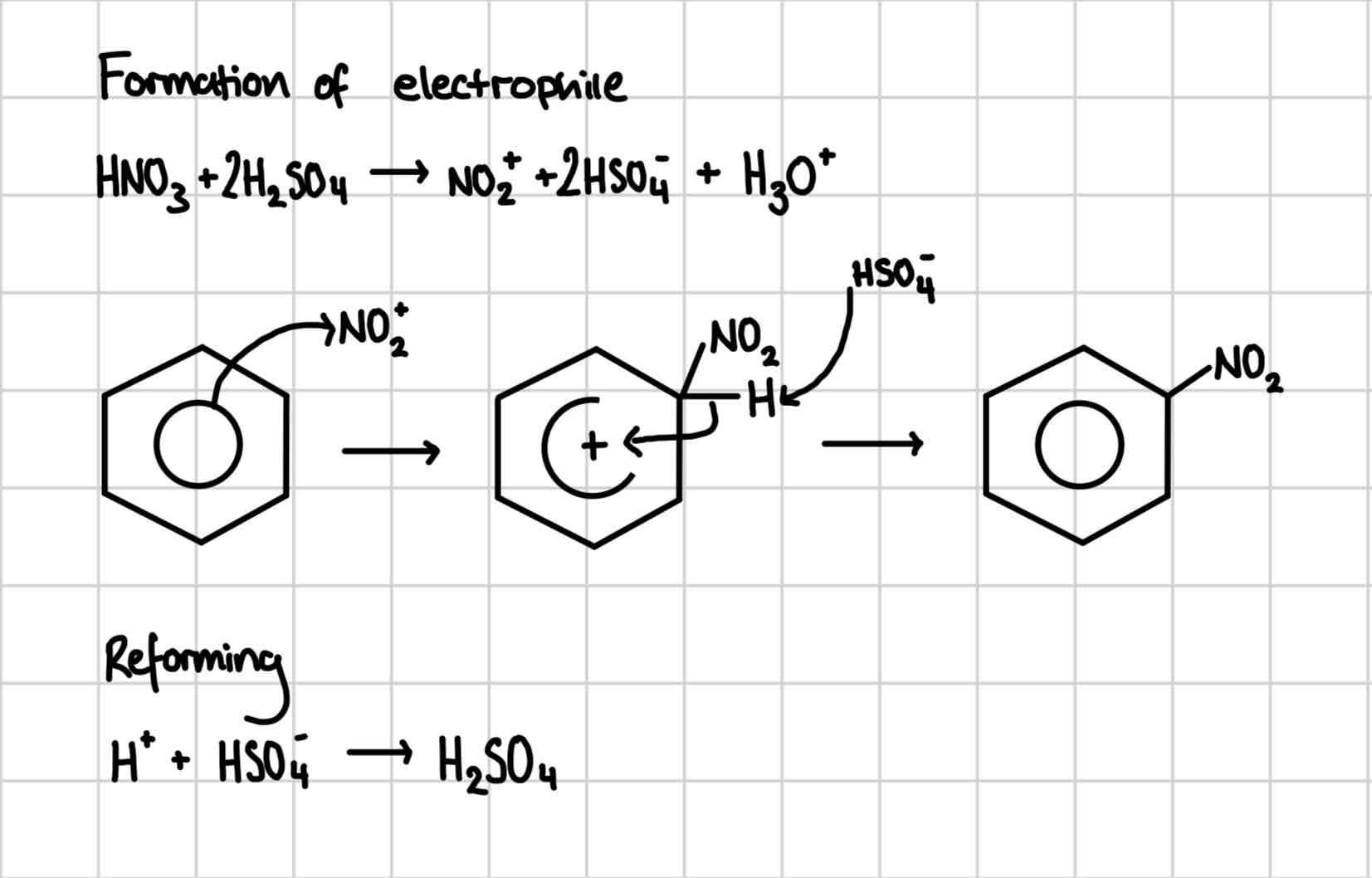
Nitration of benzene condit
concentrated nitric acid in the presence of sulfuric acid catalyst
Mixture is warmed
Nitration of benzene mechanism
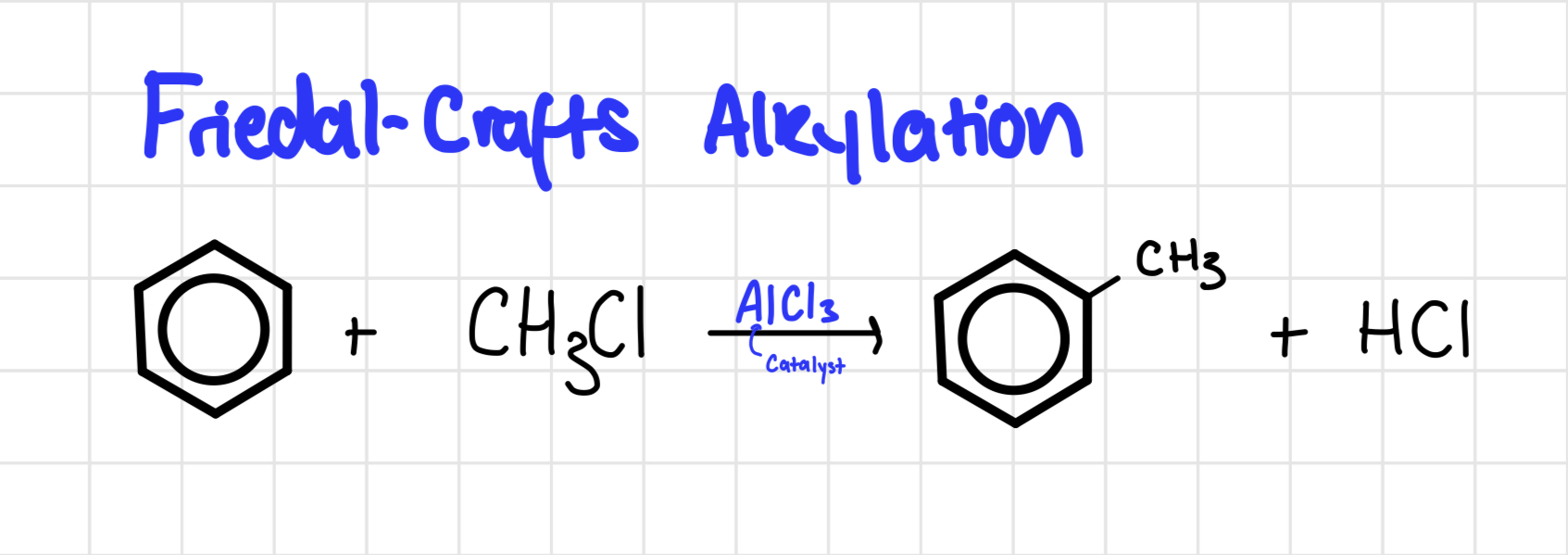
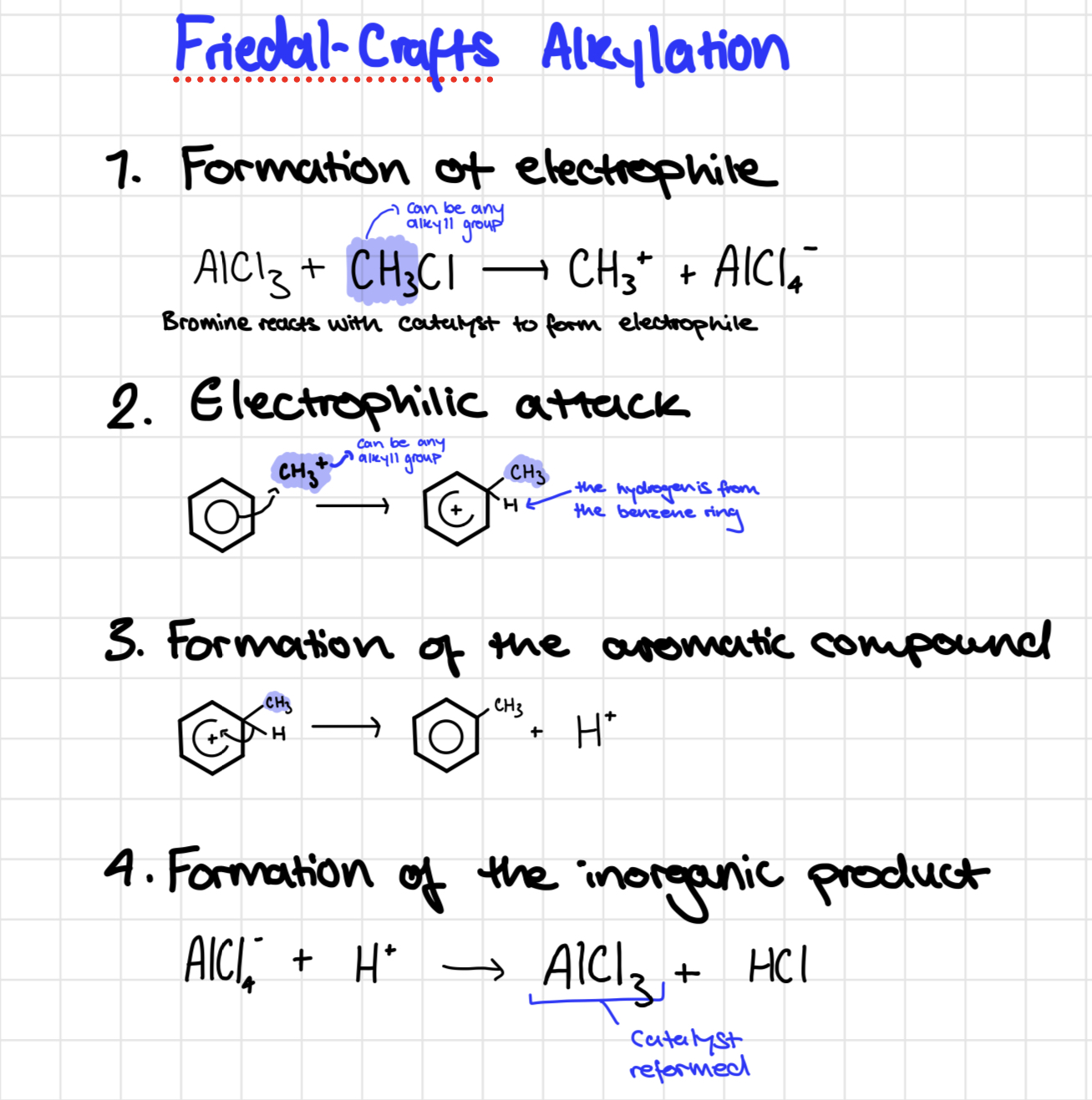
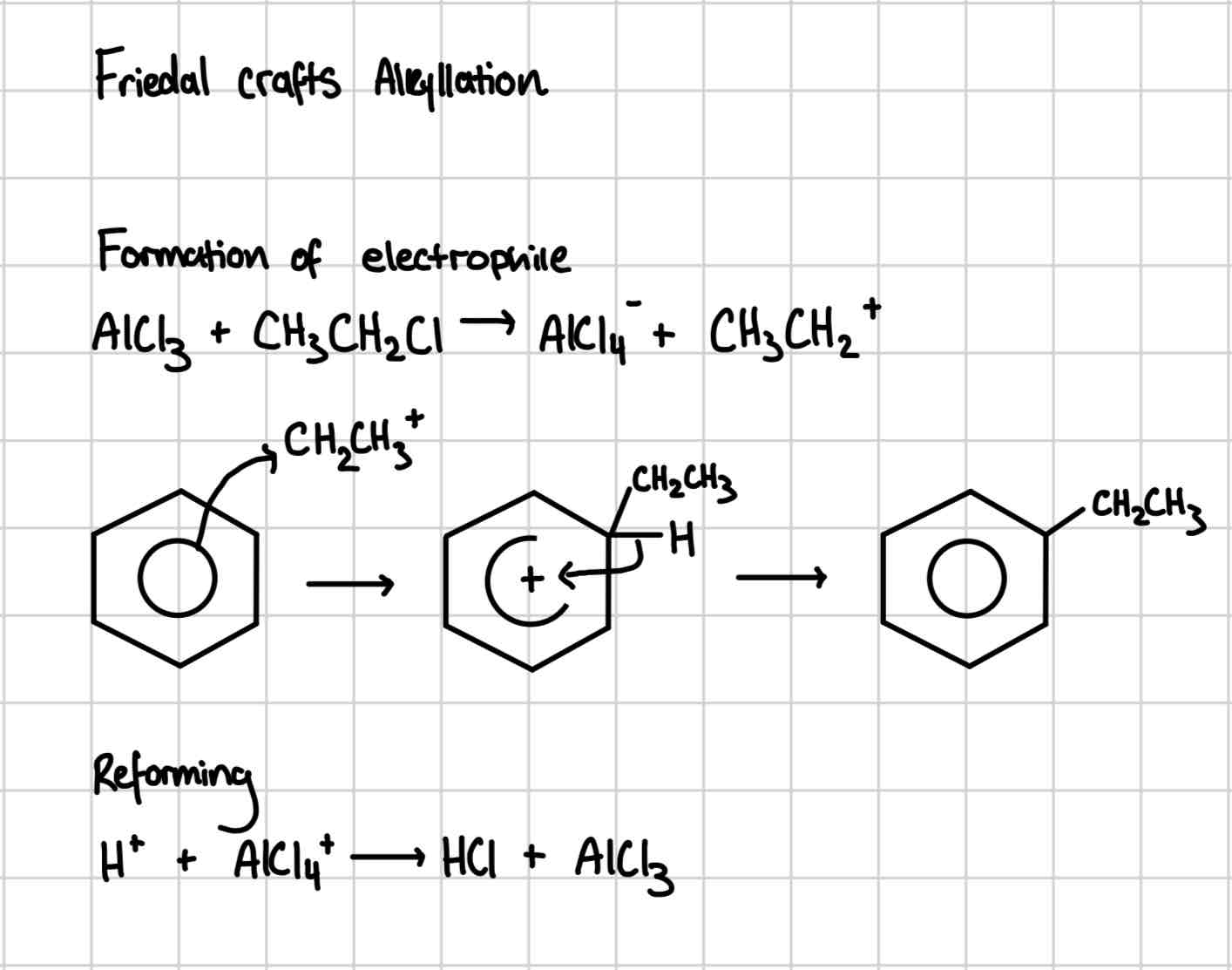
Friedal Crafts Alkylation
Friedal crafts alkylation mechanism
Heat under
AlCl3 catalyst
Reagent: halogenoalkane
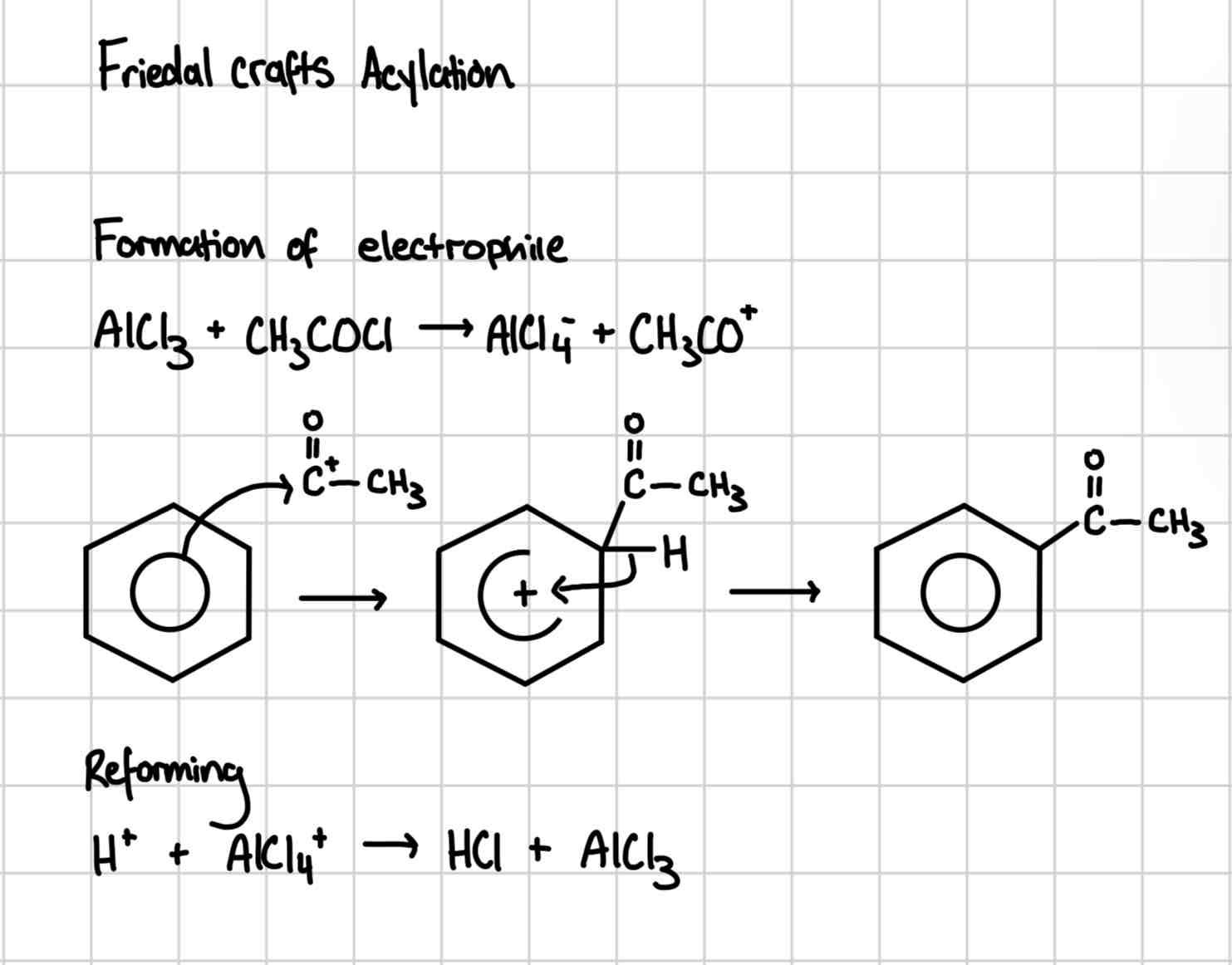
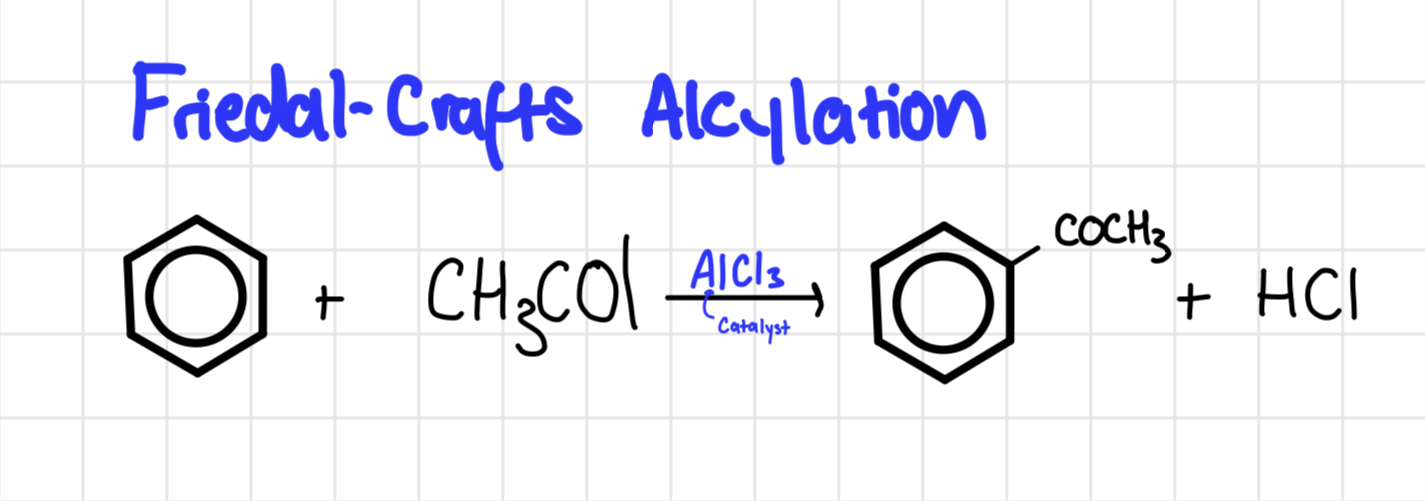
Friedal crafts acylation
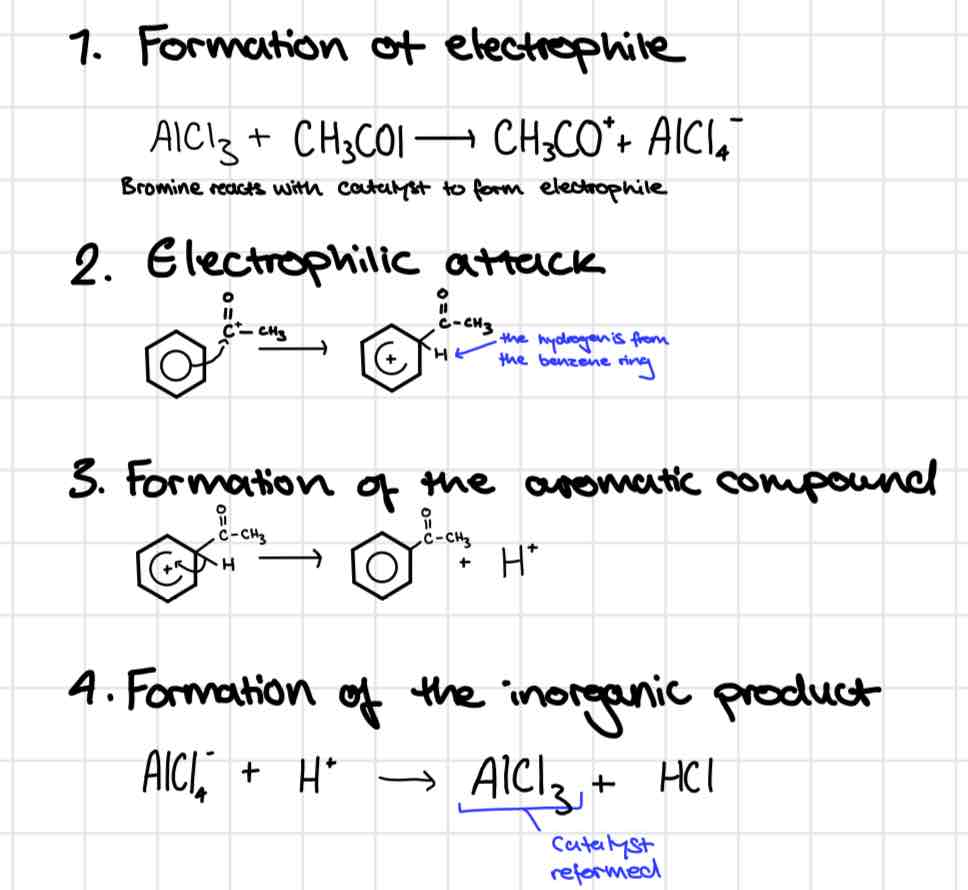
Friedal crafts acylation mechanism
Reagent is acyl chloride
AlCl3 Catalyst
Product = ketone called phenylethanone
Why can benzene easily attract electrophiles
Benzene is lectin rich (delocalised electrons) above and below the plane of the carbon ring structure which will attract electrophiles
Effect of benzene delocalisation on a side group with lone pairs
If a –OH group, a Cl atom or an NH2 group is directly attached to a benzene ring the delocalisation in the benzene ring will extend to include the lone pairs on the N,O and Cl. This changes the properties and reactions of the side group.
compare and contrast the bromination of benzene and the bromination of phenol
similarities
These are both examples of electrophilic substitution.
Differences
Phenol undergoes bromination much easier than benzene, this is due to the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen of the -OH interacting with the benzene ring making it much more electron rich/dense and more susceptible to attack from an electrophile,meaning that this reaction can occur in room temperature undergoing tri substitution
Benzene requires higher energy to undergo bromination and therefore requires a catalyst FeBr3 for the reaction occur, this is because benzene is less reactive than phenol as its aromatic ring is more stable therefore it only undergoes mono substitution and needs to be heated under reflux in order to undergo mono substitution
Bromination of phenol
Produces a white solid
In phenol the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen (p- orbital) is partially delocalised/incorporated into the ring. The electron density in the ring increases and the Br2 is more polarised thus undergoing a tri substitution
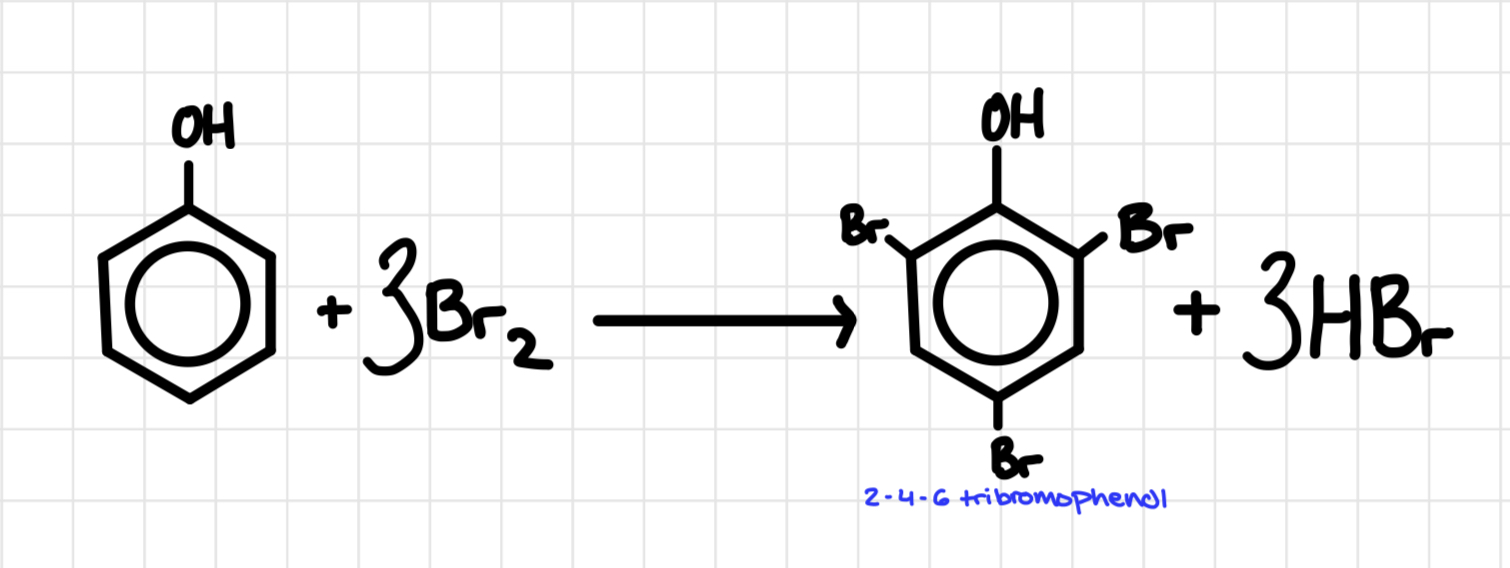
why can phenol react with no catalyst but benzene can’t
Benzene's delocalised π system of electrons makes it not quite electron rich enough for the reaction to take place, the aromatic ring is more stable. The lone pair from the -OH group in phenol adds enough electron density into the ring so that it becomes more susceptible to electrophilic attacks, hence resulting in a reaction.
Halogenation of benzene mechanism
Nitration of benzene mechanism
Friedel crafts alkylation
Friedel crafts acylation