AP Biology - Unit 0
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 2 and 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass
Element
A substance that can’t be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions
Compound
A substance that consists of 2 or more different elements in a fixed ratio
What four elements make up of 96% of all living matter?
Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen, Nitrogen (HCON)
Essential Element
Elements needed for organisms to live a healthy life (ex. HCON)
Trace Element
Elements that are needed in small quantities (ex. Iron/Fe)
Model of Helium (including the electrons, protons, neutrons, and atomic nucleus)
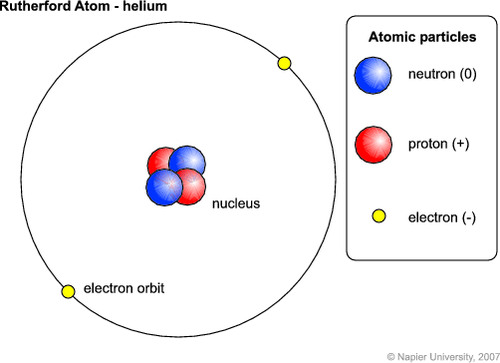
Atomic Number and Atomic Mass of Helium
2, 4
Neutron
Subatomic particle with no electric charge (in the nucleus)
Proton
Subatomic particle with a positive charge (in the nucleus)
Electron
Subatomic particle with a negative charge (orbits the nucleus)
Atomic Number
Number of protons
Atom
Smallest unit of matter that still has the properties of an element
Atomic Mass
Total mass of an single atom
Isotope
Different form of an element (same number or protons, different number of neutrons)
Electron Shells
Region surrounding the nucleus of an atom where electrons are found
Energy
The capacity to cause change (ex. doing work)
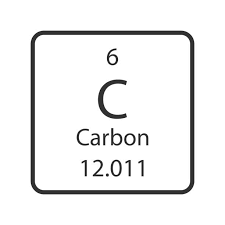
What is the atomic mass?
What is the atomic number
How many electrons?
How many neutrons?
12
6
6
12
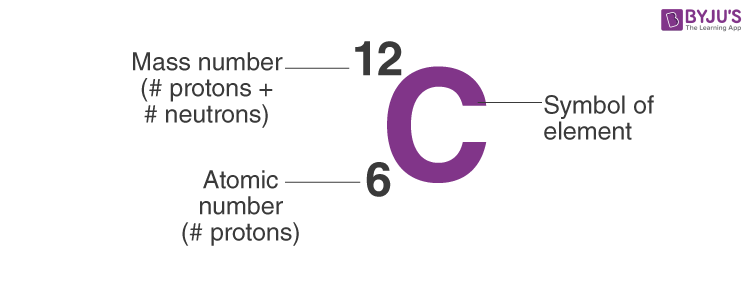
How to calculate mass number?
Atomic number?
Neutrons?
Protons + Neutrons
Protons or Number of Electrons in Neutral Atom
Mass Number - Atomic Number
Which is the only subatomic particle that is directly involved in the chemical reactions between atoms?
Elections
What is potential energy?
Energy that matter processes because of its location or structure
Explain which has more potential energy in each pair:
Boy at the top of a slide/boy at the bottom
Electron in the first energy shell/electron in the third energy shell
Water/glucose
Boy at top
Third shell
Glucose (larger and more complex structure)
What determines the chemical behavior of an atom?
Distribution of electrons in the atom’s electron shells (mostly on the outmost shell)
Molecule
2 or more atoms held together by covalent bonds (2 nonmetals)
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons
What type of bond is seen in O2? Explain what this means.
Double bond, sharing of 2 pairs of valence electrons (1 pair = 2 valence electrons)
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract other electrons in a chemical (covalent) bond
Explain the difference between a non polar covalent bond and a polar covalent bond
Nonpolar = electrons are equally shared (atoms have equal electronegativity)
Polar = electrons are unequally shared (one atoms is more electronegative)
Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative.
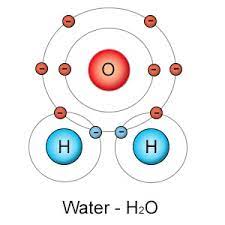
Oxygen is more electronegative (larger atomic nucleus with 8 protons).
More positive = Hydrogens
More negative = Oxygen
Why is water considered a polar molecule?
Water is polar because of the unequal sharing of electrons, Oxygen has a higher electronegativity than Hydrogen so electrons favor Oxygen. This gives Oxygen a slight negative charge and Hydrogen a slight positive charge.
Ionic Bond
Transfer of electrons (between a metal and nonmetal)
Ion
Atom or molecule with a net electrical charge (gained or lost electrons)
What is a hydrogen bond? Indicate where the hydrogen bond occurs in this figure.
Noncovalent attraction between Hydrogen and a electronegative atom
Explain van der Waals interactions.
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules. When electrons are unevenly distributed they may accumulate by chance resulting in changing regions of positive and negative charge, allowing atoms and molecules to stick together.
Place them from Strongest to Weakest: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions, covalent bonds, iconic bonds
Ionic Bond
Covalent Bond
Hydrogen Bond
van der Waals Interactions
Use morphine and endorphins as examples to explain why molecular shape is crucial in biology.
Molecular shape is important because it determines how molecules recognize and respond to each other with specificity. Morphine and endorphins bind to the same brain receptors because of their similar shapes, causing pain relief.
Write the chemical shorthand equation for photosynthesis. Label the reactants and the products.
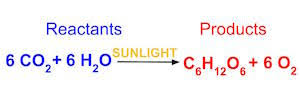
Using the equation for photosynthesis:
How many molecules of carbon dioxide are there?
How many molecules of glucose?
How many elements in glucose?
6
1
3
What is meant by dynamic equilibrium? Does this imply equal concentrations of each reactant and product?
The rate where reactions are going in both directions (forward and reverse) resulting in no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products.
No, dynamic equilibrium doesn’t imply equal concentrations of each reactant and product. It means the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time.
Surface Tension
Measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
Distinguish between cohesion and adhesion.
Cohesion = Hydrogen bonds holding a substance together
Adhesion = Hydrogen bonds cling one substance to another
Define cation and anion.
Cation = positive ion (cats = good)
Anion = negative ion (onions = bad)
What is demonstrated when you see beads of water on a waxed hood?
Cohesion
Which property explains the ability of a water strider to walk on water?
Surface tension
Define calorie (unit of heat)
The amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1°C
What does high specific heat mean? How does water’s specific heat compare to alcohol’s?
The amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1°C.
Water has a greater high specific heat than alcohol, more energy is needed to raise the temperature of water than alcohol.
Explain how hydrogen bonding contributes to water’s high specific heat.
A significant amount of energy is needed to break the hydrogen bonds between water and oxygen before water molecules can increase its temperature.
Summarize how water’s high specific heat contributes to the moderation of temperature. How is this property important to life?
When it’s hot outside water can absorb the heat with little change to its temperature. It prevents an extreme fluctuation of temperature in both the environment and living organisms.
Define evaporation. What is the heat of vaporization? Explain at least three effects of this property on living organisms.
Evaporation is when a liquid substance changes into a gaseous state.
Heat of vaporization is the amount of energy it takes to change a substance from liquid to gas.
It helps regulate body temperature, transfer of water in living organisms, and maintains climate stability.
Consider what would happen if ponds and other bodies of water accumulated ice at the bottom. Describe why this property of water is important. Explain why ice floats.
If ice didn’t float and froze from the bottom up aquatic life would suffer. Ice floating allows for aquatic life to survive as there’s water under the layer of ice.
As water cools down and turns to ice it forms a 3-dimensional matrix with decreased density which allows ice to float.
Define these terms:
Solvent
Solution
Solute
The dissolving medium
A homogeneous mixture of a solute dissolved into a solvent
The substance that’s being dissolved
Consider coffee to which you have added sugar. Which is the solvent? The solute?
Solvent = coffee
Solute = sugar
Explain why water is such a fine solvent.
Since water is polar, its partial positive and negative charge allows it to attract and break apart other polar or charged molecules and ions.
Define hydrophobic and hydrophilic
Hydrophobic = repels water
Hydrophilic = attracts water
Some materials, such as olive oil, will not dissolve in water. Explain this property in terms of hydrogen bonding.
Nonpolar molecules like oils and fats don’t have regions of partial positive or negative charge so they aren’t attracted to water molecules.
Define molarity
The number of moles of solute per one liter of solution (the concentration of a solution)
Because the pH scale is logarithmic, each numerical change represents a 10X change in ion Concentration.
How many times more acidic is a pH of 3 compared to a pH of 5?
How many times more basic is a pH of 12 compared to a pH of 8?
Explain the difference between a pH of 8 and a pH of 12 in terms of H+ concentration.
100x
10,000x
A pH of 12 has 10,000 times less H+ ions than a solution of pH of 8
Define acid and base
Acid = A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution (donates H+)
Base = A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution (accepts H+)