self control and sexuality
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
SELF-CONCEPT
Is one’s mental image of oneself.
positive self-concept
A ——————— promotes an individual's
mental and physical health. Individuals with a
positive self-concept are bette
positive self-concept
Individuals with a —————- are better able to develop and
maintain interpersonal skills.
poor self-concept
Individuals who have a ——————— may
express feelings of worthlessness, self-dislike, or
even self-hatred.
Self-knowledge
Self-expectation
Social self
Social evaluation
4 DIMENSION OF SELF-CONCEPT:
SELF-KNOWLEDGE
Insight into one's own abilities, nature, and limitations.
SELF-EXPECTATION
Self expectations is what one expects of oneself, which
may or may not be realistic.
SOCIAL SELF
how a person is perceived by others and
the society.
SOCIAL EVALUATION
is the appraisal of oneself into a
relationship to others, events, or situations.
Me Centered
these are people who
value how they perceive their own self
Others Centered
are the opposite, these are people who have a high need for approval from others and they try hard to live up to the expectations of others.
They compare, they compete, they evaluate themselves, and they fear disapproval.
SELF-AWARENESS
relationship between one’s perception of himself or herself and others perception of him or her.
SELF-AWARENESS
knowing the difference, you know the relationship between you, your own self-image, and how others think about you.
SELF-AWARENESS
perception of yourself and the perception of others about you
Projection
you place your own
feelings to another person to justify your own expression.
Introspection
you reflect your own beliefs, your own
attitudes, your strengths, your weaknesses, your limitations.
Introspection
involves the nurse reflecting on personal beliefs,
attitudes, motivations, strengths, and limitations
SELF-CONCEPT
not born with a self-concept; rather, it
develops as a result of social interaction with others
3 steps:
Infant learns that pusical self is separate 4 different from the environment
Child internalizes others attitudes toward self
childs adult internalizes standards of society
Infancy: trust vs. mistrust
Toddlerhood: autonomy vs. shame and doubt
Early childhood: initiative vs. guilt
Early school years: industry vs. inferiority
Adolescence: identity vs. role confusion
Early adulthood: intimacy vs. isolation
Middle-aged adults: generativity vs. stagnation
Older adults: integrity vs. despair
Eric Erickson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
Infancy: trust vs. mistrust
Positive Resolution:
✅Requesting assistance and expecting to receive it
✅Expressing belief of another individual
✅Sharing time, opinions, and experiences
Negative Resolution:
✅Restricting conversation to superficialities
✅Refusing to provide an individual with personal information
✅Being unable to accept assistance
Toddlerhood: autonomy vs. shame and doubt
Positive Resolution:
✅Accepting the rules of a group but also expressing disagreement when it is felt
✅Expressing one’s own opinion
✅Easily accepting deferment of a wish fulfillment
Negative Resolution:
✅Failing to express needs
✅Not expressing one’s own opinion when opposed
✅Overly concerned about being clean
Early childhood: initiative vs. guilt
Positive Resolution:
✅Starting projects eagerly
✅Expressing curiosity about many things
✅Demonstrating original thought
Negative Resolution:
✅Imitating others rather than developing independent ideas
✅Apologizing and being very embarrassed over small mistakes
✅Verbalizing fear about starting a new project
Early school years: industry vs. inferiority
Positive Resolution:
✅Completing a task once it has been started
✅Working well with others
✅Using time effectively
Negative Resolution:
✅Not completing tasks started
✅Not assisting with the work of others
✅Not organizing work
Adolescence: identity vs. role confusion
Positive Resolution:
✅Asserting independence
✅Planning realistically for future roles
✅Establishing close interpersonal relationships
Negative Resolution:
✅Failing to assume responsibility for directing one’s own behavior
✅Accepting the values of others without question
✅Failing to set goals in life
Early adulthood: intimacy vs. isolation
Positive Resolution:
✅Establishing a close, intimate relationship with another individual
✅Making a commitment to that relationship, even in times of stress and sacrifice
✅Accepting sexual behavior as desirable
Negative Resolution:
✅Remaining alone
✅Avoiding close interpersonal relationships
Middle-aged adults: generativity vs. stagnation
Positive Resolution:
✅Being willing to share with another individual
✅Guiding others
✅Establishing a priority of needs, recognizing
both self and others
Negative Resolution:
✅Talking about oneself instead of listening to others
✅Showing concern for oneself in spite of the needs of others
✅Being unable to accept interdependence
Older adults: integrity vs. despair
Positive Resolution:
✅Using past experience to assist others
✅Maintaining productivity in some areas
✅Accepting limitations
Negative Resolution:
✅Using past experience to assist others
✅Maintaining productivity in some areas
✅Accepting limitations
Negative Resolution:
✅Crying and being apathetic
✅Not accepting changes
✅Demanding unnecessary assistance and attention from others
GLOBAL SELF
-Refers to the collective beliefs and images one holds
about oneself.
-It is the most complete description that individuals
can give of themselves at any one time.
Global self
It is also a person's frame of reference for experiencing and in viewing the world.
Global Self
-statements that are provided by an individual usually are facts
CORE SELF-CONCEPT
beliefs and images that are most vital to the person's identity.
Vocational performance
Intellectual functioning
Personal appearance and physical attractiveness
Sexual attractiveness and performance
Being liked by others
Ability to cope with and resolve problems
Independence
Particular talents
Individuals are thought to base their self-concept on how they perceive and evaluate themselves in these areas:
IDEAL SELF
How we should be or would prefer to be.
personal identity
body image
role performance
self-esteem
COMPONENTS OF SELF-CONCEPT
Personal Identity
-conscious sense of individuality and uniqueness that is continually evolving through life includes beliefs, your values, personality, your character.
-include both tangible and factual information about a person but it may also include intangible ones, which are now the beliefs and values they have as a person.
Body Image
Refers to your physical self, the image of physical self, how a person perceives their size, their appearance, their functioning body parts
Cognitive Aspects
Affective Aspects
2 Aspects of Body Image
cognitive Aspect
is the knowledge of the material body
affective aspect
includes
the sensations of the body, such as
pain, pleasure, fatigue, and physical
movement.
healthy body image
individual with a ————- will normally show concern for both health and appearance.
unhealthy body image
individual who has an———- is likely to be overly concerned about minor illness and to neglect important activities like sleep and a healthy diet.
Role performance
how a person in a particular role behaves in comparison to the behaviors expected of the role.
Role
is a set of expectations about how the
individual occupying a particular position
behaves.
Role mastery
means that the individual's behaviors meet role expectations.
Role development
involves socialization into a particular role
Role ambiguity
expectations
are unclear, and individuals do not know what
to do or how to do it and are unable to predict the reactions of others to their behavior.
Role conflicts
arise from opposing or
incompatible expectations. In an
interpersonal conflict, individuals have different expectations about a particular role.
Role strain
people undergoing this are
frustrated because they feel or are made to
feel inadequate or unsuited to a role.
Self-esteem
one’s judgment of one’s own words, it’s
the person’s own standards and
performances compared to others, and one’s
ideal self.
global
specific
2 types of self-esteem
Stage of development
family and culture
stressors
resources
history of success and failure
illness.
6 FACTORS THAT AFFECT SELF-CONCEPT (SSHRIF)
Stressors
can strengthen the self-concept as an individual copes successfully with problems
overwhelming stressors
can cause maladaptive responses including substance abuse, withdrawal, and anxiety.
internal resources
include confidence and values
external resources
support network, sufficient finances, and organizations
Self-esteem.
Personal Identity
Body Image
Role Performance
Self-Esteem
What do you Asses in Assessment of self concept?
Assessing the 4 components of self concepts
Diagnosing
Planning
Implementation
Identifying areas of strength
Enhancing self esteem
Evaluating
NURSING MANAGEMENT IN SELF CONCEPT
INFANCY: Birth–18 months
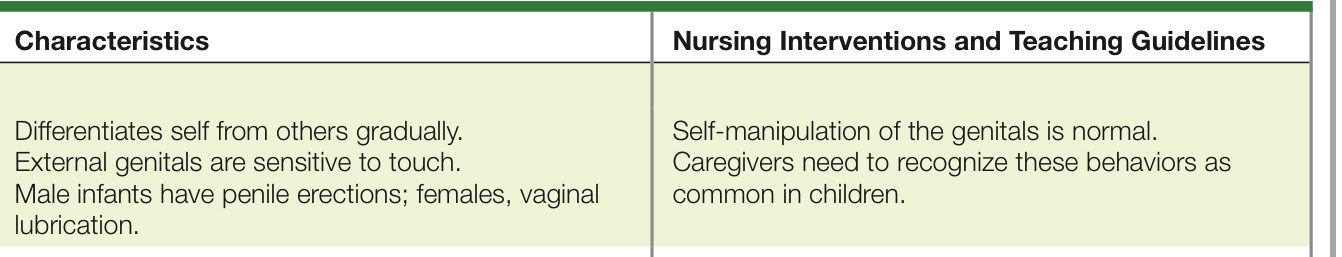
TODDLER: 1–3 years

PRESCHOOLER
4–5 years

SCHOOL AGE: 6–12 years

ADOLESCENCE
12–18 years

YOUNG ADULTHOOD
18–40 years

MIDDLE ADULTHOOD
40–65 years

LATE ADULTHOOD
65 years and older

Sexual Misconceptions

Sexual Facts

GONORRHEA
Male: Painful urination; urethritis with watery white discharge, which may become purulent.
Female: May be asymptomatic; or vaginal discharge, pain, and urinary frequency may be present.
SYPHILIS
Male: Chancre, usually on glans penis, that is painless and heals 4-6 weeks.
Female: Chancre on cervix or other genital areas that heals in 4-6 weeks.
GENITAL WARTS
Male: Single lesions or cluster of lesions
Female: Lesions appear at the bottom part of the vaginalopening and on the perineum, labia, inner walls of the vagina, and cervix.
GENITAL WARTS
Male: Urinary frequency; watery, mucoid urethral discharge.
Female: Vaginal discharge, dysuria, urinary frequency
CHLAMYDIAL URETHRITIS
Male: Urinary frequency; watery, mucoid urethral discharge.
Female: Vaginal discharge, dysuria, urinary frequency
TRICHOMONIASIS
Male: Slight itching; moisture on top of penis; slight early morning urethral discharge.
Female: Itching and redness of the vulva and skin inside the thighs; copious watery, frothy vaginal discharge.
CANDIDIASIS
Male: Itching, irritation, discharge, plaque of cheesy materialunder foreskin.
Female: Red and excoriated vulva; intense itching of vaginaand vulvar tissues; thick, white, cheesy or curd-like discharge.
SEXUAL HEALTH
-Is a state of well-being in relation to sexuality acrossthe lifespan that involves physical, emotional, mental,social, and spiritual dimensions.
-individual and constantlychanging phenomenon falling within the wide rangeof human sexual thoughts, feelings, needs, and
desires.
Sexual self-concept
Body image
Gender identity
Gender-role behavior
ANDROGYNY
COMPONENTS OF SEXUAL HEALTH
Sexual self-concept
how one values oneself as a sexual being
Body image
The central part of the sense of self that is constantly changing. This is how they feel about their body in relation to one's
sexuality.
Gender identity
- is one’s self-image as a female or male.
Gender-role behavior
- this is the expression of maleness and femaleness, as well as expression of
what is gender appropriate.
ANDROGYNY
-Describes the degree of flexibility a person has regarding gender stereotyping behaviors.
-flexibility in gender roles, is the belief that most characteristics and behaviors are human qualities that should not be limited to one specific gender or the other
Sexual Orientation
Gender Identity
Erotic Preferences
VARIETIES OF SEXUALITIES
Sexual Orientation
- One’s attraction to individuals of the same sex, other sex, or both sexes,
Homosexuality
same-sex attraction
lesbians
women attracted only to women
gay
men attracted to men
Gay
also a general term for homosexual
bisexual
individuals attracted to individuals of both genders
■Lesbian
■ Gay
■ Bisexual
■ Transgender
■ Queer
■ Questioning
LGBTQQ stands for
Transgender
someone who identifies with a different
gender than their anatomic designation is
Queer
someone who rejects gender stereotypes may be considered
Questioning
those who have not decided on their orientation
Intersex
Transgenderism
Cross - Dressers
Gender Identity Includes
Intersex
An increasing number of babies are born with an intersex condition in which there are contradictions among chromosomal sex, gonadal sex, internal organs, and external genital appearance.
Transgenderism
For the transgender individual, sexual anatomy contradicts gender identity.
male-to-female (MtF) transgender persons.
physically male but are emotionally and psychologically female
female-to-male (FtM) transgenderpersons.
born female but are emotionally and psychologically male
Transgender
is a broader
term that includes all individuals who do not
identify with the gender that corresponds to the sex they were assigned at birth.
Transsexual
is a narrower term that includes
individuals who desire to physically transition to the gender with which they identify.