Biology - Homeostasis and Response
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Triple Science)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the constant maintence of internal conditions within the body
What does homeostasis control?
Blood glucose concentration/levels
Water levels
Body Temperature
What are receptors?
Cells that detect stimuli (changes in the environment)
What are some examples of coordination centres?
The Brain
Spinal Cord
Pancreas
What do effectors do?
bring about responses which restore optimum levels.
What is the reflex arc?
stimulus → receptor → sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → coordinator → effector → response
What does the sensory neurone do?
It takes impulses from the receptor to the coordination centre
What does the relay neurone do?
It decides what to do and “relays” the impulse from the sensory neurone to the motor neurone…
What does the motor neurone do?
It take the impulse from the relay neurone to the effector.
What is a synapse?
A physical gap between each neurone
How does information cross the junction between neurones?
The neurotransmitters diffuse between the synapses.
What does the cerebrum control?
Conciousness
Language
Thought
Perception
Memory
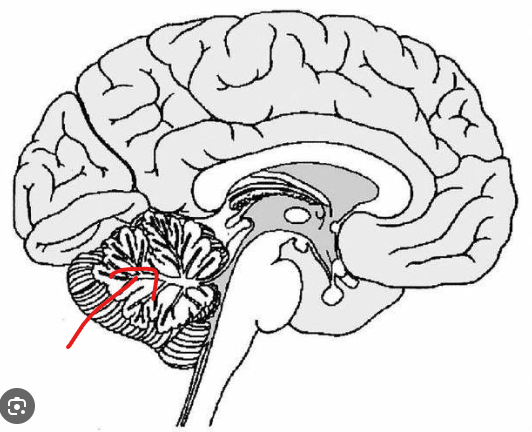
What is the part in the diagram called?
Cerebellum
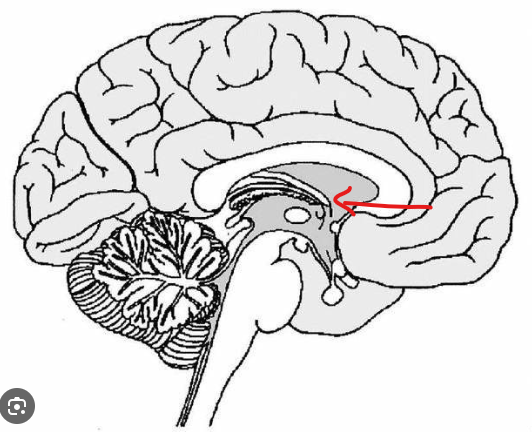
What is the part in the diagram called?
Hypothalamus
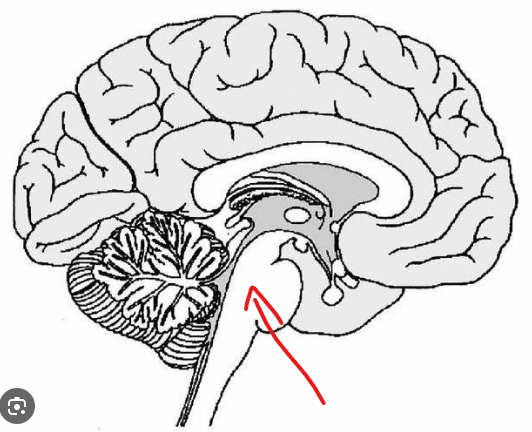
What is the part in the diagram called?
Medulla
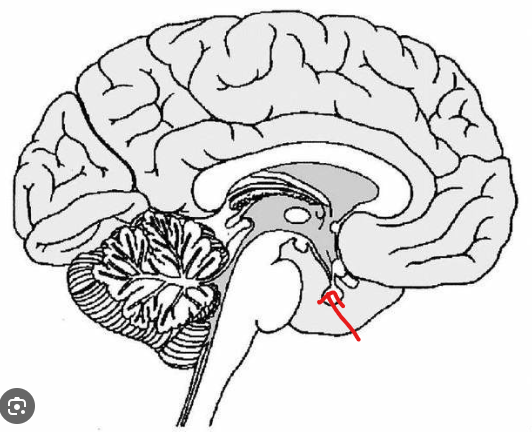
What is the part in the diagram called?
Pituitary Gland
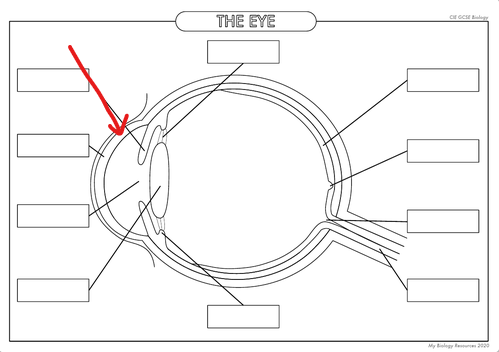
What is the part in the diagram called?
Cornea
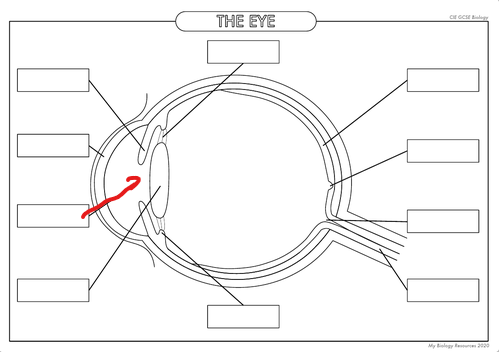
What is the part in the diagram called?
Pupil
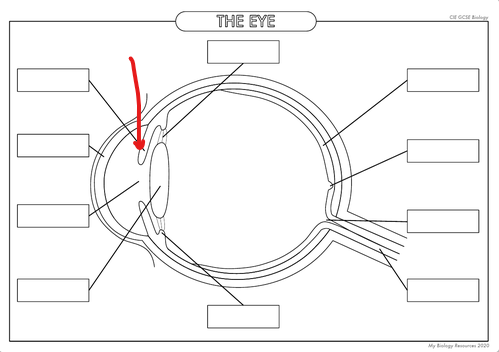
What is the part in the diagram called?
Iris
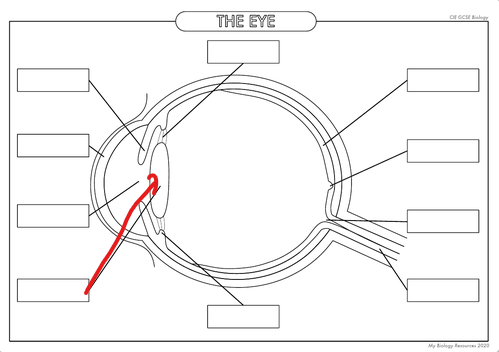
What is the part in the diagram called?
Lens
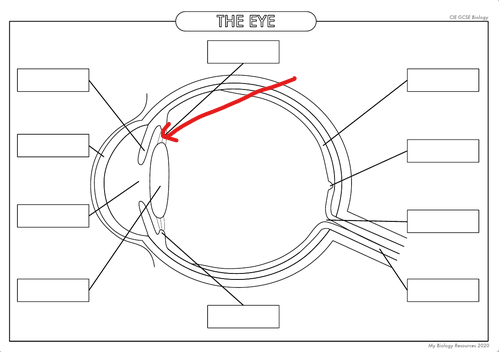
What is the part in the diagram called?
Suspensory Ligaments
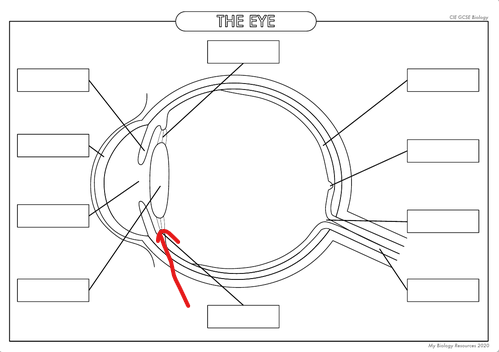
What is the part in the diagram called?
Ciliary Muscles
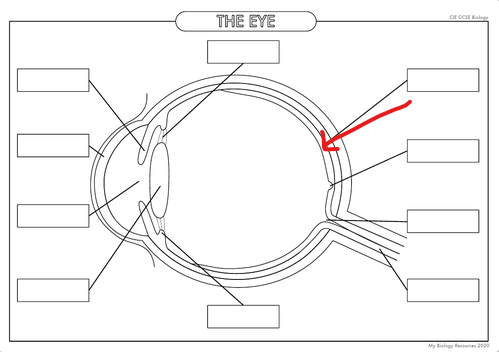
What is the part in the diagram called?
Retina
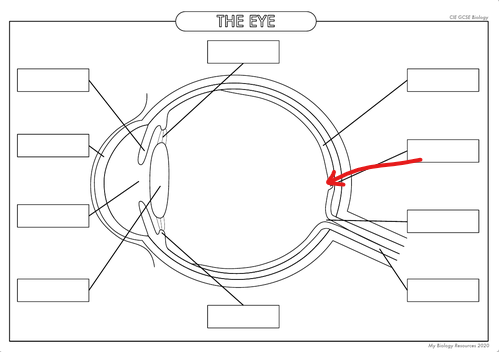
What is the part in the diagram called?
Fovea
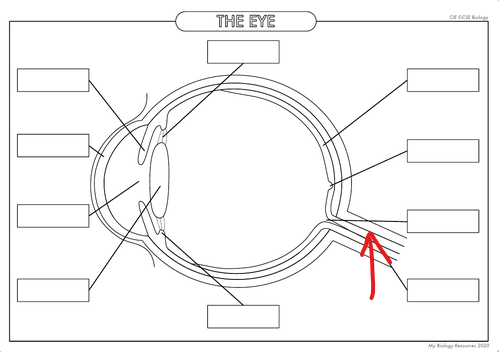
What is the part in the diagram called?
Optic Nerve
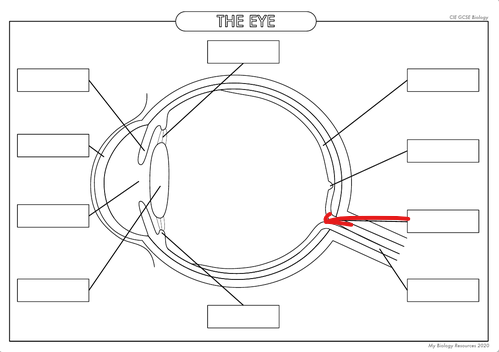
What is the part in the diagram called?
Blind Spot
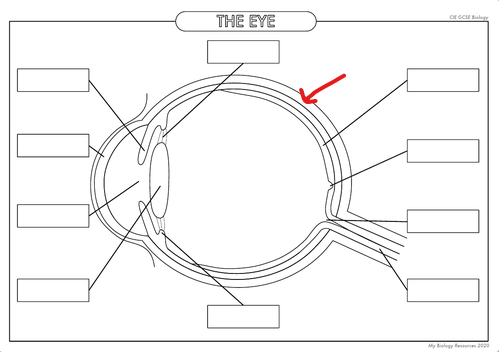
What is the part in the diagram called?
Sclera
What does the cerebellum control?
Coordinates Muscle Movement
Posture
Balance
What does the medulla control?
Controlling heartbeat
Breathing
Vomiting
Blood Pressure
What does the hypothalamus control?
Fight or Flight
Feeding
Mating
What does the pituitary gland control?
The release of hormones
What does the pituitary gland release?
ADH (Anti-Diuretic Hormone) - this controls the water concentration in urine.
GROWTH HORMONE - controls growth in children
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) - stimulates ovaries to release eggs
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) - this controls the release of thyroxine from the thyroid gland.
What does the thyroid gland release?
THYROXINE - this controls the rate of metabolism in the throat
What does the adrenal gland release?
ADRENALINE - this prepares your body for action and affects the glucose, fat and protein metabolism.
What does the pancreas release?
INSULIN -controls glucose levels within the blood.
What do the ovaries release?
OESTROGEN & PROGESTERENE - controls female secondary characteristics / growth / menstrual cycle
What do the testes release?
TESTOSTERONE - sperm production / growth / male secondary characteristics
What hormone is released when glucose levels are too high?
Insulin
What hormone is released when glucose levels are too low?
Glucagon
What does insulin do?
It turns glucose to glycogen in the liver and muscle cells - lowering glucose levels in the blood.
What does glucagon do?
It turns glycogen in the liver and muscle cells to glucose - increasing glucose levels in the blood.
What causes type 1 diabetes?
When the body has little to no insulin.
What causes type 2 diabetes?
When the body becomes resistant to it’s own insulin - allowing glucose levels to rise to dangerous levels.
What can be used to treat type 1 diabetes?
Insulin Injections
What can be used to treat type 2 diabetes?
A carbohydrate controlled diet and regular excersise.
What do the kidneys do?
They act as filters for the blood and allow the correct amount of things back into the bloodstream.
What three things do the kidneys take out of the blood?
Urea
Ions
Water
What is the process in which proteins and amino acids are converted to fats and carbohydrates?
Deamination
Advantages of dialysis treatment?
It can buy valuable time to find a donor.
It saves the life of those with kidney failure.
Disadvantages of dialysis treatment?
It may cause blood clots.
Patients have to attend treatment regularly and it can lead to infections.
It is expensive.
Advantages of a kidney transplant?
The only cure for kidney failure
Cheaper (in the long run)
Can be transplanted from those who are still alive
Disadvantages of a kidney transplant?
Long waiting list for transplants
Kidneys can be rejected by the body
Person who died has to be on the organ donor register or carry a donor card
What is the first part of the menstrual cycle?
Day 1 - Mensuration starts .The uterus lining breaks down for about four days.
What is the second part of the menstrual cycle?
What is te third part of the menstrual cycle?
Day 14 (An egg develops and is released from the ovary) This is known as ovulation.
What is the fourth part of the menstrual cycle?
Days 15 - 28 (The uterus lining continues to thicken) If the egg is not fertilised, the lining breaks down again, leading to menstruation.
What is FSH?
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE -causes egg to mature in follicle and stimulates oestrogen production and is produced in the pituitary gland.
What is LH?
LUTENISING HORMONE - stimulates release of the egg on day 14 and is produced in the pituitary gland)
What is the hormone that maintains the lining of the uterus during the second half of the cycle?
PROGESTERONE (it also inhibits the release of LH and FSH)
What is the hormone that causes the uterus lining to grow?
OESTROGEN (it also stimulates the release of LH and inhibits release of FSH)
How does Oestrogen reduce fertility?
It can be used to prevent the release of an egg,by inhibiting the release of FSH.
How does Progesterone reduce fertility?
It stimulates the production of a thick mucus which stops any sperm getting to the egg.
What are advantages and disadvantages of the pill?
It is over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy, but may cause side effects such as headaches and nausea. It also doesn’t protect against STIs.
Name 3 other hormonal contraceptives.
Progesterone-Only Pill
Contraceptive Patch (only progesterone)
Contraceptive Implant (only progesterone)
What is an IUD and how does it work?
An IUD, or intrauterine device, is a small T-shaped device inserted into the uterus to kill sperm and prevent implantation of the egg .
Name two types of barrier contraception
Condoms
Diaphragm (must be used with spermicide)
What are the two methods of sterilisation?
In women you cut the fallopian tubes which connect the ovaries to the uterus.
In men you cut the sperm duct which connect the testes to the penis
How can FSH be used to increase fertility?
Some women have low levels of FSH so increasing the amount of FSH and LH they have you can stimulate the release of the egg
What is in the “fertility drug”?
FSH and LH
What are the advantages of IVF?
It can allow infertile couples to have children
What are disadvantages of IVF?
Multiple births can happen
The success rate is low - the success rate is about 26% in the UK.
It can be emotionally and physically stressful.
Why are some people against IVF?
It can result in unused embryos that are eventually destroyed. Some people think this is unethical because that is a potential human life.
The genetic testing of embryos before implantation could lead to the selection of preferred characteristics such as gender or eye colour.
What are the three types of tropism?
Gravitropism/Geotropism
Phototropism
Hydrotropism
Where do auxins inhibit growth?
In the roots
Where do auxins promote growth?
In the shoots
What are gibberelins used for in a plant?
Initiating seed germination
What is ethene used for in a plant?
Cell division and ripening of fruits.
What are auxins used for (commercially)?
They are used as weed killers
In rooting powders
For promoting growth in tissue culture
What is ethene used for (commercially)?
It is used to control the ripening of fruit within the food industry during storage and transport.
What are gibberellins used for (commercially)?
They are used to end seed dormancy
To promote flowering in horticulture
To increase fruit size