Lecture 9 -- Ear Anatomy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is the external auditory meatus?
= Ear canal = The space running inside the cartilages to the tympanic membrane.
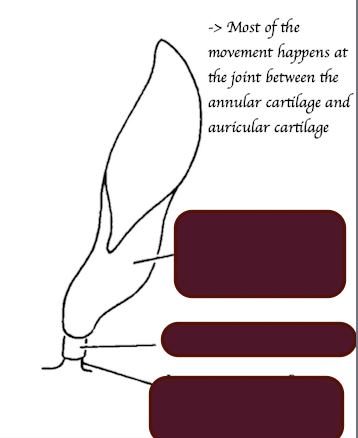
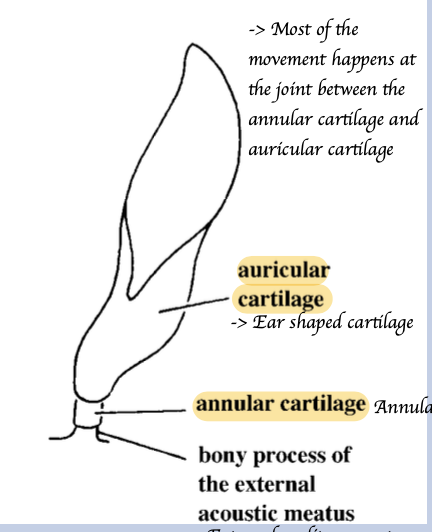
Ring-like.
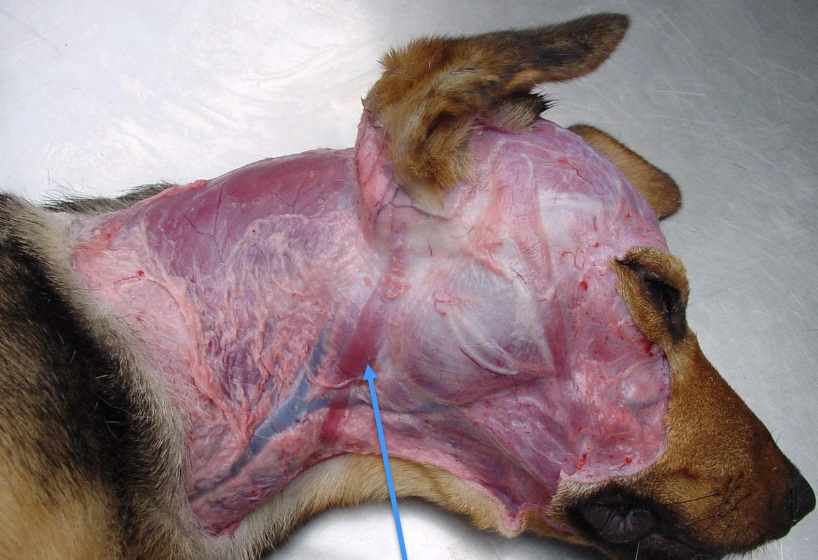
List out three groups of muscles of the external ear and their functions.
Pre-auricular - Move ear forward
Ventral auricular - Move ear ventrally
Post auricular - Move ear caudally and medially
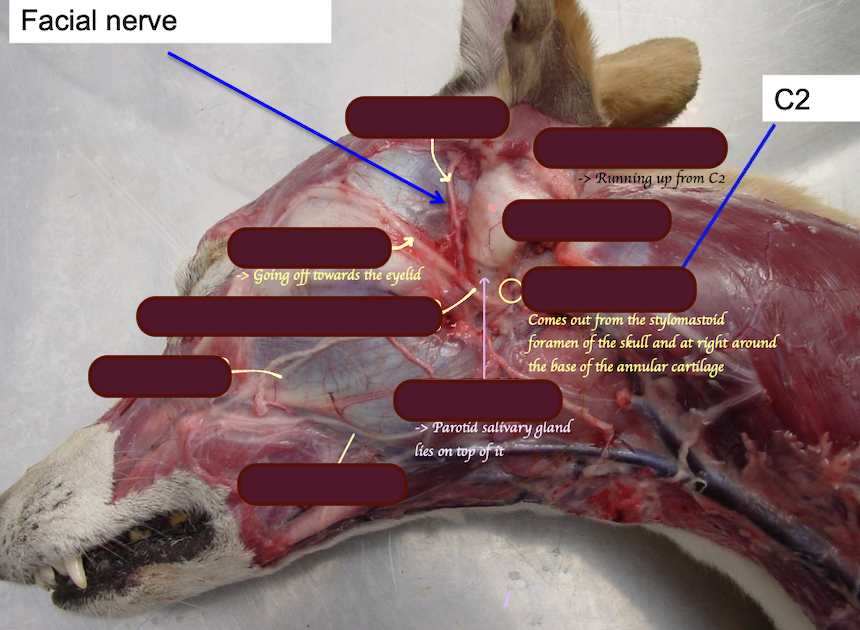
What is the name of the muscle? Where does it originate and insert to? What is its function?
Parotidoauricularis
Runs over the parotid and goes up the auricular cartilage
When this muscle contracts, the ear is pulled out and down
Describe the MOTOR neurone supply to the external ear.
Motor:
Rostral auricular nerve of facial nerve → Supply the rostral ear muscles
Caudal auricular nerve of facial nerve → Supply the caudal ear muscles
Great auricular nerve from C2 → Supply the caudal ear muscles
Describe the SENSORY neurone supply to the external ear.
Small rostral part + deep ear canal: Auricular-temporal branches of mandibular trigeminal
Rest of the outside of ear: Cervical spinal nerve
Inside of the ear canal → Internal auricular branch of the facial nerve
Identify the nerve supply
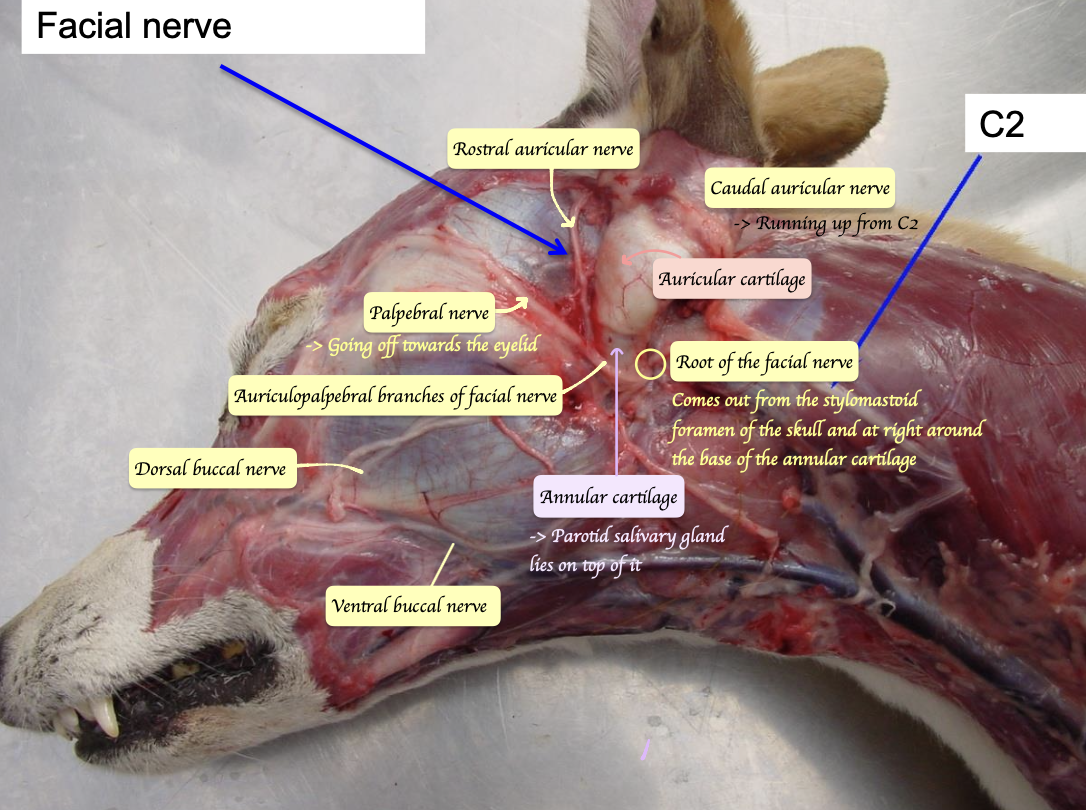
Which nerve, if paralyzed, causes the ears to be stuck in a backwards position?
Facial nerve
→ Rostral auricular nerve of facial nerve innervate the rostral ear muscles, which is responsible for pulling the ear forward
→ If facial nerve is paralysed, the ear will be stuck in backwards position
What is the middle ear?
A cavity that lies within the temporal bone.
What forms the ventral floor of the middle ear?
Tympanic bulla.
What lies laterally to the middle ear?
Tympanic membrane (eardrum).
What lies medially and dorsally to the middle ear?
Petrous temporal bone that house the inner ear
Identify the structure below.
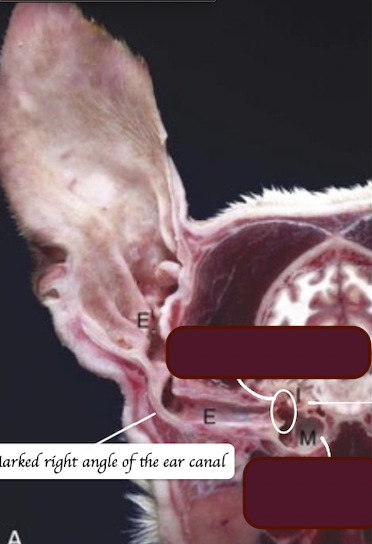
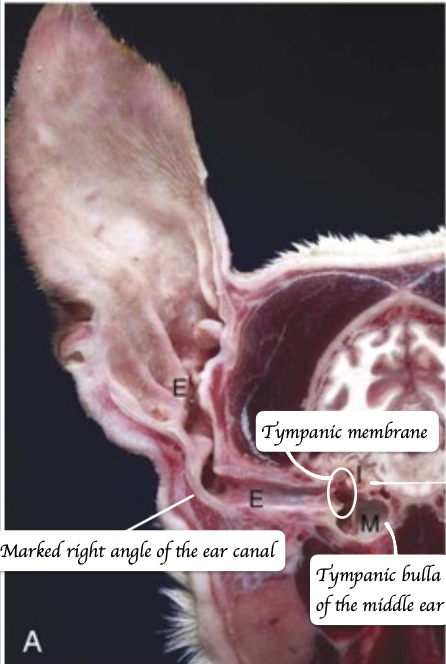
What is tympanic bulla?
Air filled ventral part of the cavity in middle ear
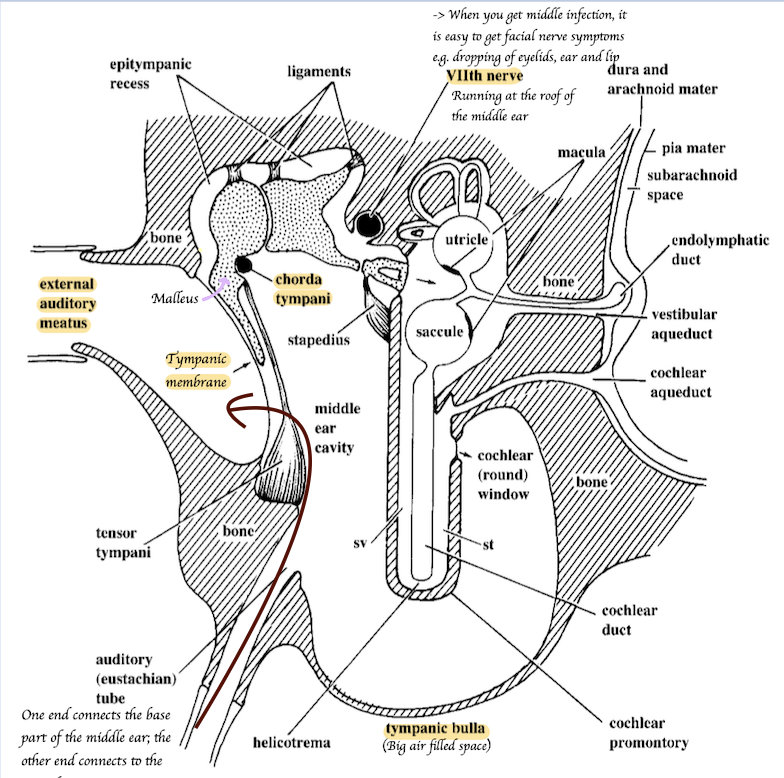
Chorda tympani
Splits off from the main branch in middle ear
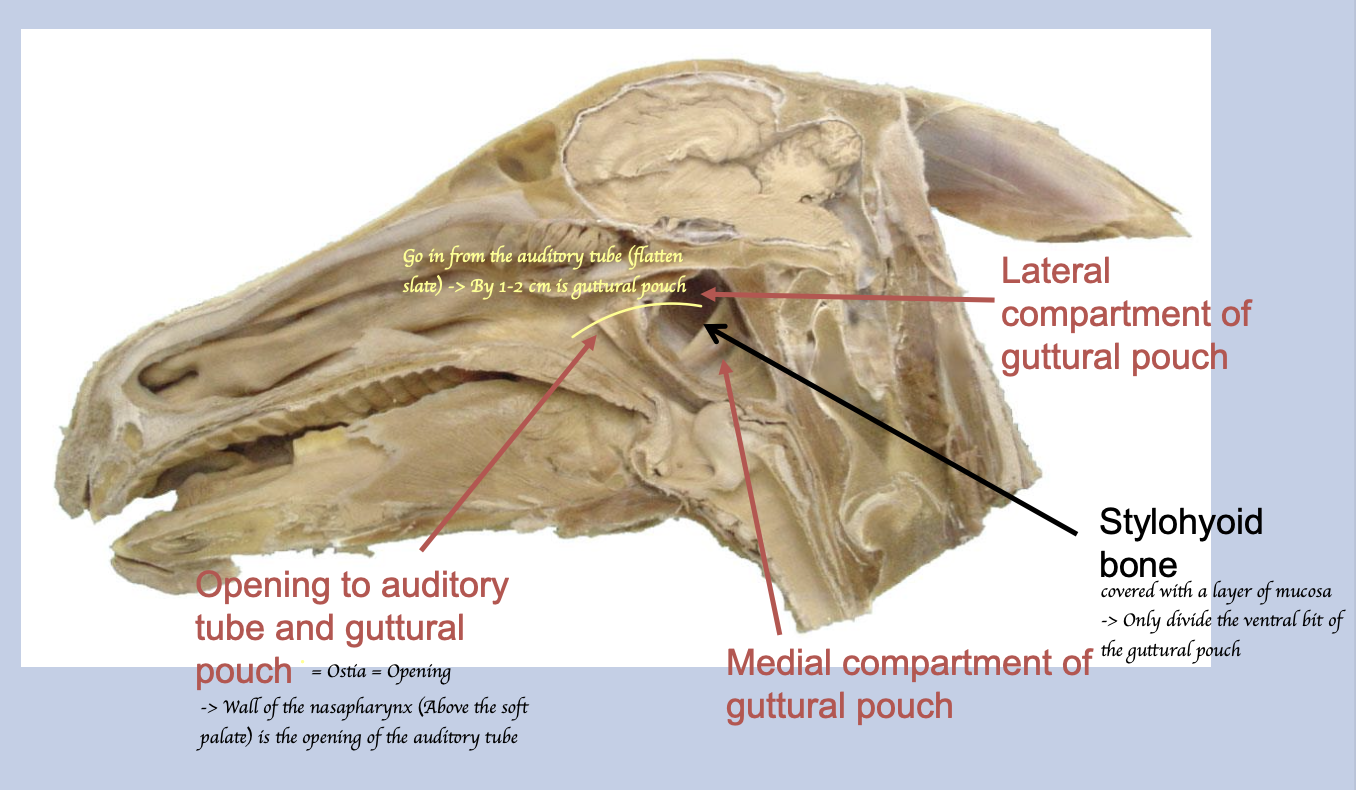
How do the auditory tubes run?
Runs from the wall of nasopharynx to the middle ear cavity
What is the function of the auditory tube?
When swallowing/ yawning, the opening of the auditory tube = osita is forced to open → Air enters + move into the middle ear cavity → Allow to equalize pressure on either side of the eardrum.
In which animals is the guttural pouch found?
Odd-toed ungulates (horses, tapirs, rhinos).
What is the guttural pouch?
An air-filled ventral diverticulum of the auditory tube.
What divides the guttural pouch ventrally into medial and lateral compartments?
Stylohyoid bone
P.S. Medial is large 2/3 vs Lateral 1/3 + The sylohyoid bone only divide the ventral part of the pouch into medial and lateral compartment = Dorsal part communicates freely
What are the suspected functions of the guttural pouch?
NOT KNOWN
?Regulation of internal carotid artery pressure and cooling blood flow to the head?
Where guttural pouch can be found?
Dorsal - Skull and C1 = Locate at the back of the head
Ventral - Pharynx and retropharyngeal lymph node
Medial - Meidan septum
Lateral - Pterygoid muscle, parotid and mandibular salivary glands
What is the opening of the guttural pouch?
Ostia
What can be appreciated within the medial and lateral compartment of the guttural pouch?
Medial compartment:
Internal carotid artery
Cranial cervical ganglion
Glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve
Accessory nerve
Hypoglossal nerve
Longus capitus muscle
Lateral compartment:
External carotid artery
Maxillary artery
Facial nerve
Mandibular trigminal nerve
Where is the Ostia located?
Dorsal to most pouch when head horizontal
→ Only drain when head is down and horse swallows
What are common diseases of the guttural pouch?
Tympany (air distension), empyema (bacterial infection), mycosis (fungal infection).
What is the name of the lateral surgical approach to the guttural pouch?
Viborg's Triangle
Cranial border - Caudal mandible
Caudal border - Tendon of insertion of sternocephalicus
Ventral border - Linguofacial vein
What are the symptoms relate to the structures affected?
Nosebleed
→ Internal/ external carotid artery
Nasal discharge
→ Infection of the guttural pouch
Nerve dysfunction
→ Laryngeal paralysis = Vagus nerve
→ Homers syndrome (Drooping eyelid; constricted pupil)
→ Facial asymmetry
Swelling
How guttural pouch disease can be diagnosed?
Endoscopy and radiography