BCM - lipids
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Definition of lipids
Lipids are as broad group of naturally occurring molecules including fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others
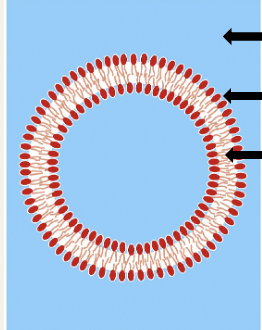
May be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphipathic small molecules; the amphipathic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures e.g. vesicles, liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment
Lipid bilayer in water - types of intermolecular forces
Water-water - hydrogen bonds, electrostatic forces
Water-head group - hydrogen bonds, electrostatic forces
Tail-tail - London dispersion forces (stronger if tails are long, unbranched and saturated)
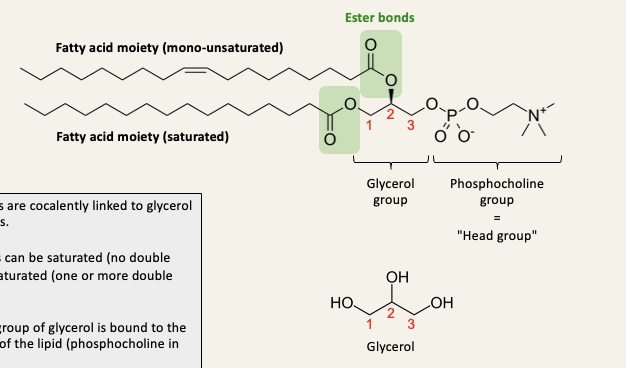
Glycerophospholipids
2 fatty acids are covalently linked to glycerol via ester bonds
The fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated
The third OH group of glycerol is bound to the ‘head group’ of the lipid (phosphocholine in this example)
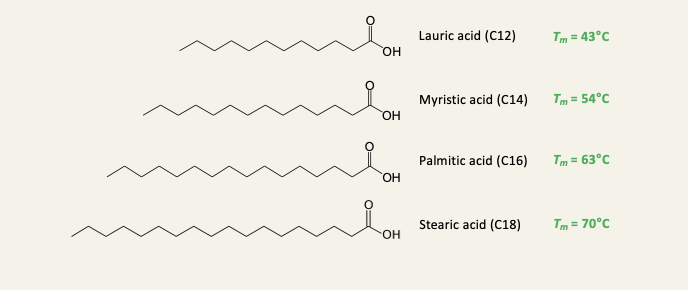
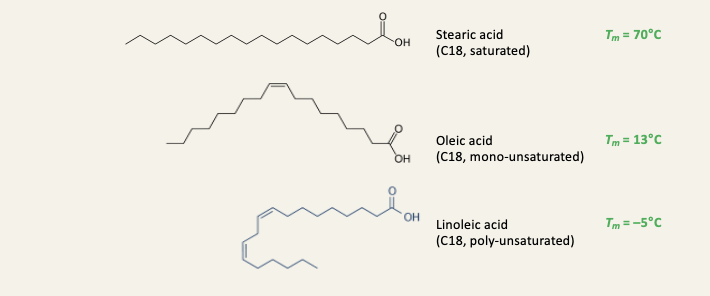
Longer fatty acids have melting points than shorter ones
melting point increases by ~10C per C2 unit
Fatty acids have an even number of C atoms because they are synthesised form C2 units
All saturated fatty acids are solids in their pure form at room temp
Saturated fatty acids have higher melting points than unsaturated ones
The biggest drop in melting point is caused by the first double bond
This is because the double bonds are in the cis configuration, the tails become kinked and do not pack as well as the straight saturated tails - this makes the solid state less stable
Unsaturated fatty acids are liquid in their pure form at room temp
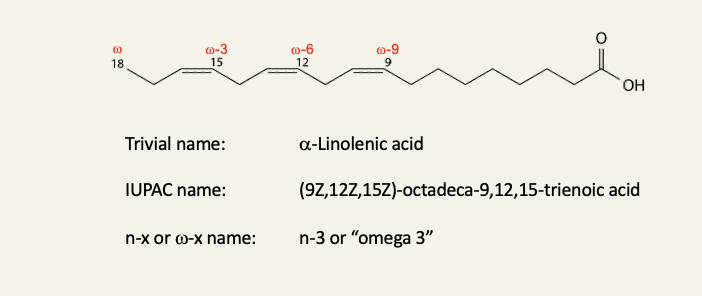
Fatty acid nomenclature
Most dietary fats are triglycerides
butter, coconut oil and palm oil are solids because of their high content of saturated fatty acids - olive oil and rapeseed oil are liquids

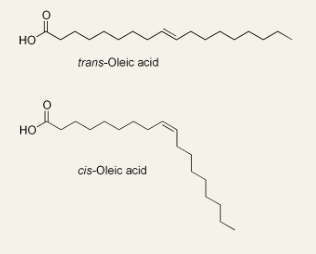
Trans fats
In food production, liquid vegetable oils are hydrogenated to produce saturated fats with a higher melting temperature and longer shelf life
Partial hydrogenation of unsaturated fats converts some of the cis double bonds into trans double bonds
Dietary intake of trans fats is linked to an increased risk of coronary artery disease
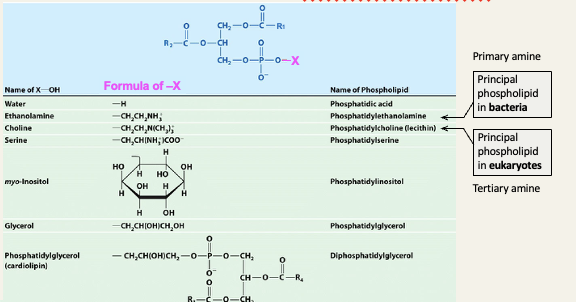
Types of head groups in glycerophospholipids
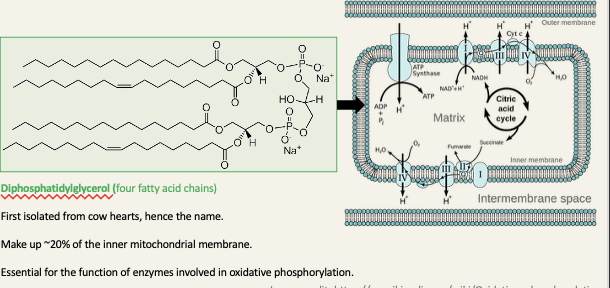
Cardiolipins
contains three glycerol molecules, one in each of the phosphotidylglycerol units and another one linking the units together
First isolated form cow hearts, hence the name
Makes up ~20% of the inner mitochondrial membrane
Essential for the function of enzymes involved in oxidative phosphorylation
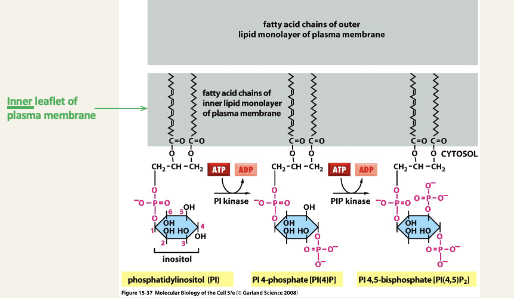
Reversible phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol
PI kinase = phosphatidylinositol kinase, i.e. an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group from ATP onto the inositol group
PIP kinase = phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate kinase, i.e. an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group from ATP onto the inositol 4-phosphate group
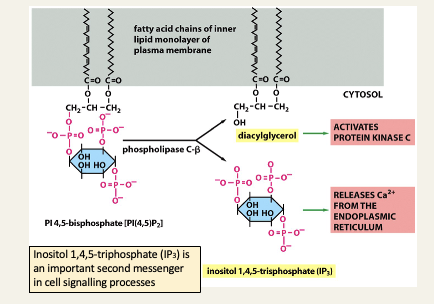
Cleavage of phosphoinositides generates second messengers
Signalling pathways involving cleavage of phosphoinositides -> acetylcholine triggering the release of amylase in the pancreas
Phospholipase C-B is activated by a signal molecule e.g. acetylcholine binding to a receptor protein on the cell surface - the important info is that the head group of PIP2 is cleaved by an enzyme to release the second messenger IP3
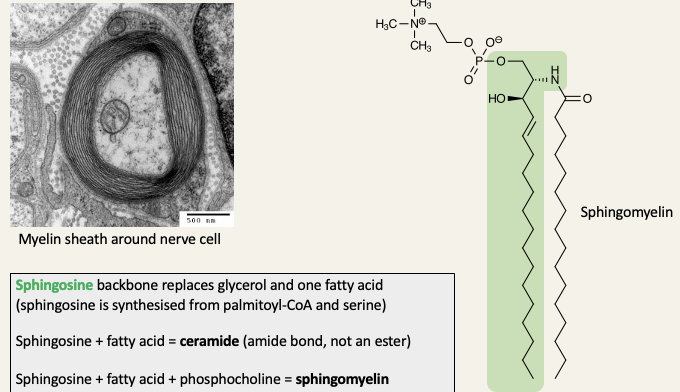
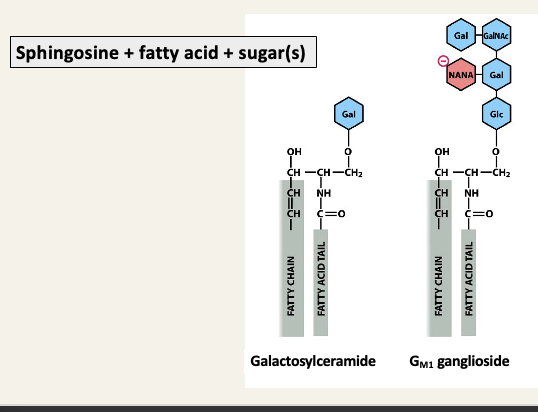
Sphingolipids are a major second class of lipids
Myelin sheaths surround the axons of nerve cells and acts like the insulation around an electrical wire - the myelin sheath is the plasma membrane of Schwann cells, wrapped around the axon in multiple layers
Sphingosine backbone replaces glycerol and one fatty acid
Sphingosine + fatty acid = ceramine
Sphingosine + fatty acid + phosphocholine = sphingomyelin
Glycolipids have important functions in the nervous system
Gangliosids make up 6% of all lipids in the nervous system
The sugar groups project from the plasma membrane and facilitate interactions with proteins and other cells
Gangliosides are a characteristic component of lipid rafts
All gangliosides contain at least one sialic acid group
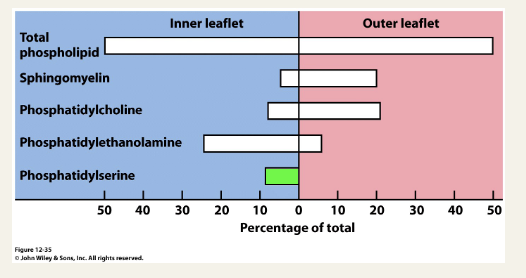
Asymmetric distribution of lipids in the plasma membrane
Phosphatidylserine is excluded from the outer leaflet by an active process - a flippase
Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface is a pro-apoptotic signal
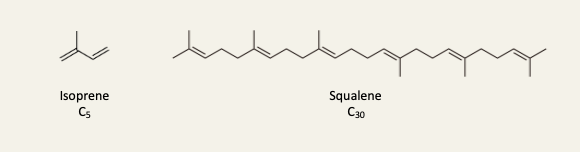
A 3rd major class of lipids contain isoprenyl units
Terpenes are hydrocarbons formally derived from the condensation of isoprene units
Terpenoids are modified terpenes containing oxygen atoms, but the distinction is often not made, and all 3 terms are used interchangeably
e.g. of isoprenoids are cholesterol, steroid hormones, and retinal
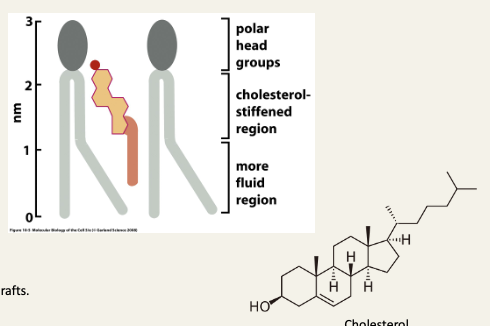
Cholesterol has complex effects on membrane fluidity
Rigid steroid rings stiffen the membrane, it becomes less fluid above the transition temperature
They also interfere with the crystallisation of fatty acid chains, preventing a sharp freezing below the transition temperature
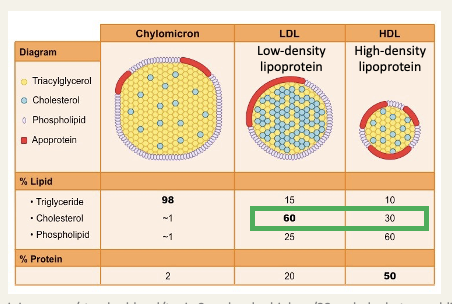
Lipoproteins
because of their limited solubility in water, lipids are transported by the circulation as micelle-like particles
Core - triglycerides and cholesteryl esters
Coating - protein, phospholipid and cholesterol
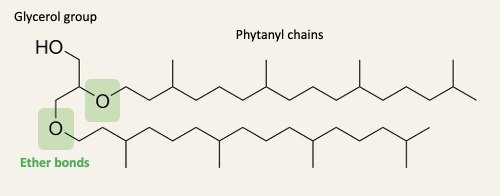
Archaea have unique lipid membranes
Other lipids apart from archaeol have head groups and/or double bonds in the tails
The ether linkages make archaeal lipids resistant to hydrolysis in extreme conditions
Methanopyrus kandleri grows at temperatures up to 122 C in hydrothermal vents
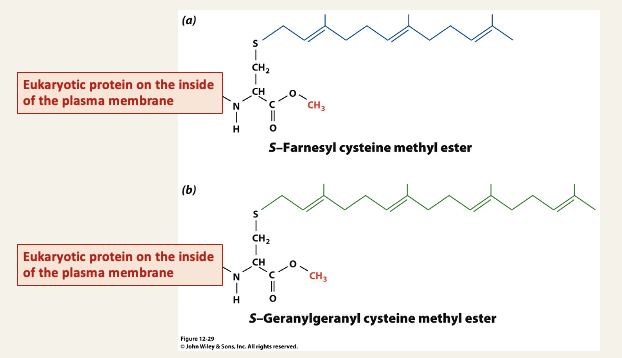
Isoprenylation of cysteins anchors intracellular proteins to membranes
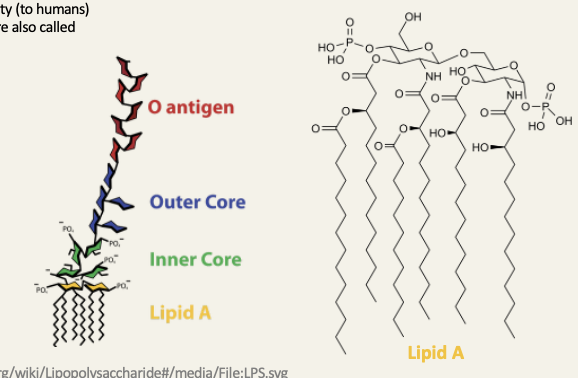
Lipopolysaccharides in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria
because of their toxicity lipopolysaccharides are also called endotoxins