6. Cell membranes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Schleiden and Schwann
suggested a “barrier” between cells in 1839
Matthias Schleiden - plants
Theodor Schwan - animals
Ernest Overton
proposed that cell membranes are composed of lipids in 1895
established that molecules enter cells based on their lipid solubility, leading to the "Overton Rule"
Irving Langmuir
developed the Langmuir trough in 1917
a laboratory apparatus used to study and manipulate thin films of molecules, called monolayers, on a liquid surface
Evert Gorter and François Grendel
worked with RBC (red blood cells) in 1925 to determine the structure in the cell membrane
is it a monolayer or bilayer?
a - surface area of RBCs (under calculated)
b - extract the phospholipids (under calculated)
A: ZX = bilayer
wBC's (white blood cells) have more cellular proteins
mudd + mudd (Stuart and Emily Mudd)
described the surface composition of normal and sensitized blood cells
Red Blood cells as oil
White Blood cells as H2O
Hugh Davson - James Danielli Model
aka paucimolecular model
proposed the model of the plasma membrane of a cell in 1935
described the cell membrane as a "sandwich" model, with a central lipid bilayer (like the filling) sandwiched between two layers of protein (like the bread)
protein - phospho-phospho-protein “sandwich”
JD Robertson
proposed a modified version called the "Unit Membrane" model in 1957 based on new electron microscope studies
described as was a single, uniform membrane structure instead (proven wrong)
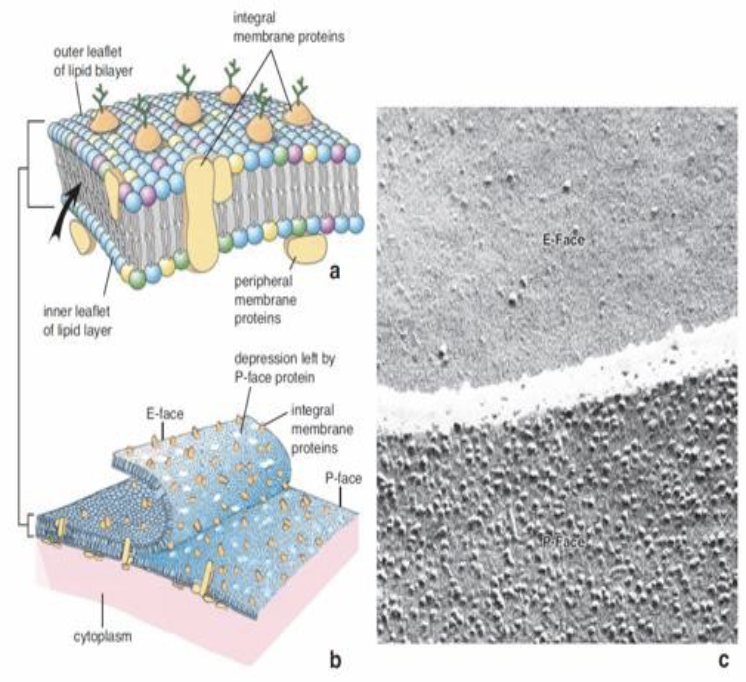
Freeze Fracture (by Dan Branton)
the “mosaic” nature of cell membrane
technique used in electron microscopy to visualize the internal structure of biological samples, especially cell membranes
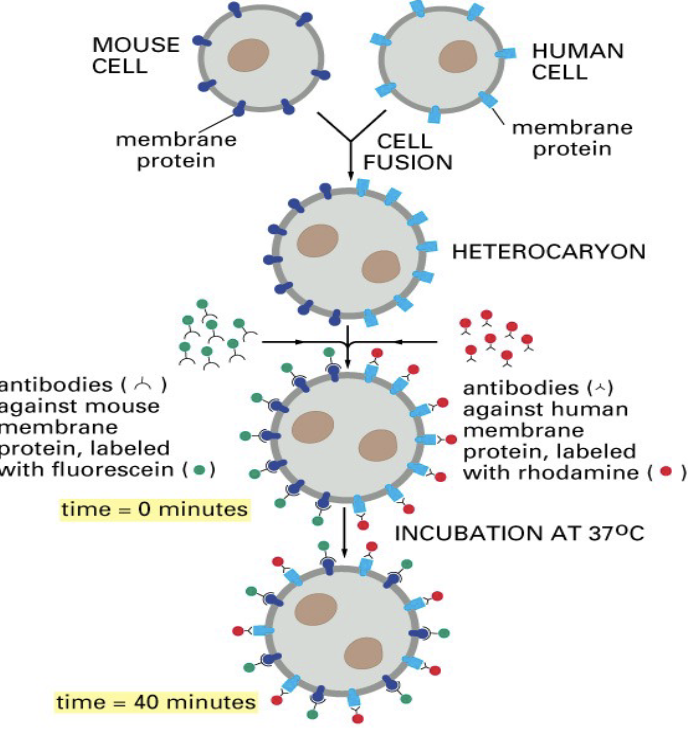
Cell Fusion
heterolaryer - 2 nuclei
proteins are free to move laterally in the plane of the membrane
purpose:
preparation of hybridomas (monoclonal antibodies)
research on development, differentiation, and breeding (transplantation and replacement of nuclei)
research on regenerative medicine and cytotherapy
research on anti-cancer vaccination and cancer immuology
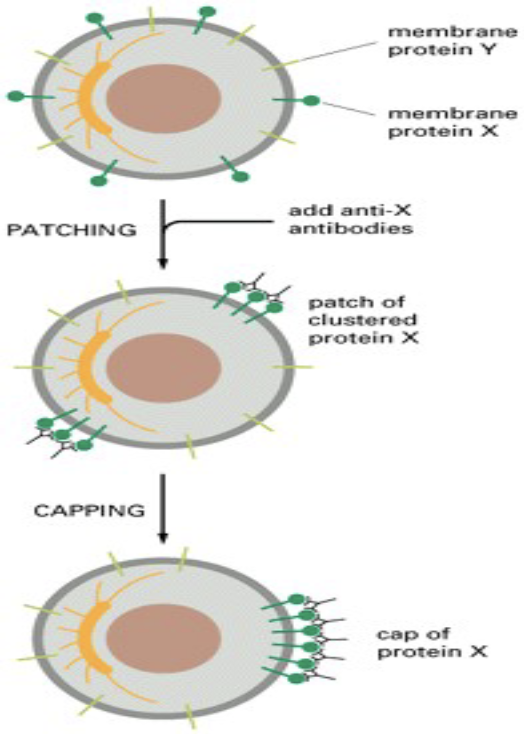
Cell Capping/protecting cell (patching)
mAbs - 2 identical Fab regions
same as cell fusion
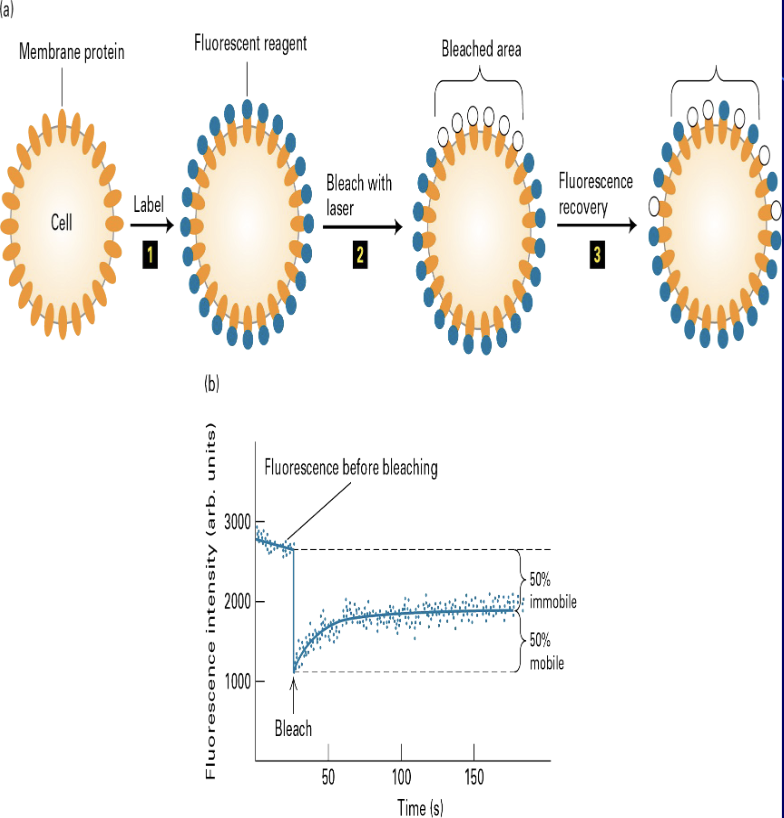
FRA (Fos-related antigen 1)
a protein that is a component of the AP-1 transcription factor
con A FRAP says that some proteins are fluid, some not
binds to As proteins through their carbohydrates groups
half of proteins are mobile and the other half not mobile
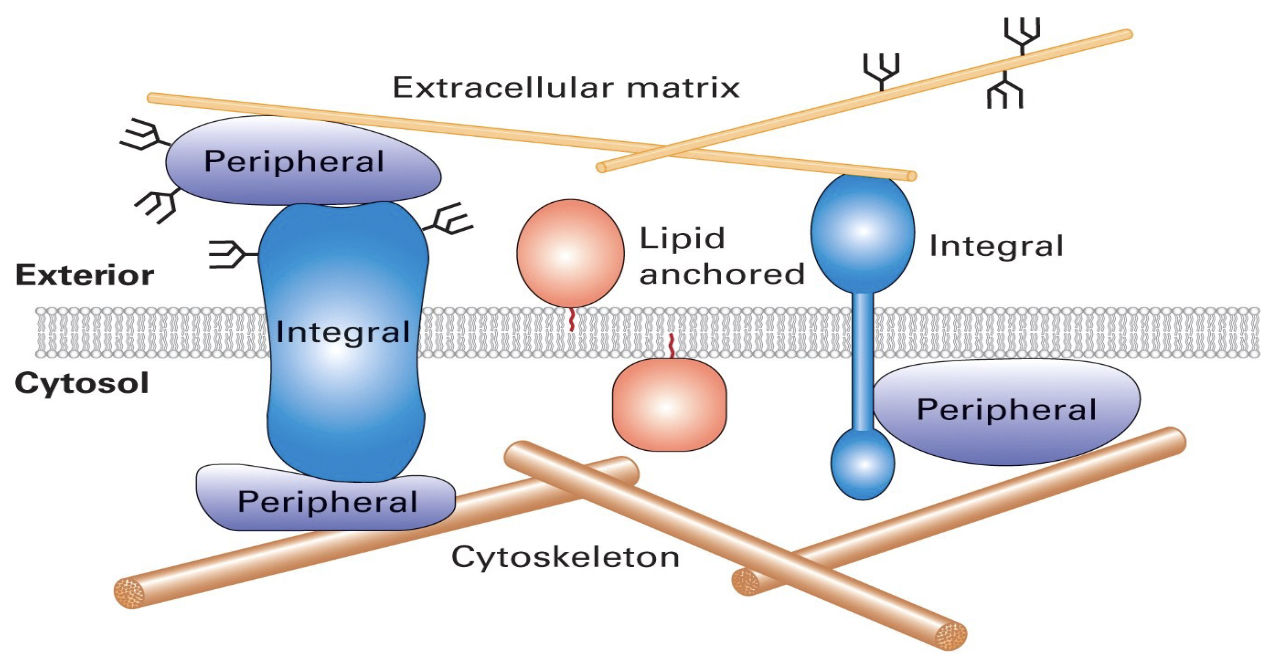
Cytoskeleton and Extracellular Matrix
limit lateral plasma membrane protein mobility
extracellular - gives cell shape and mechanical resistance to deformation
cytoskeleton - deforming the cell and the cell’s environment, and allowing cells to migrate
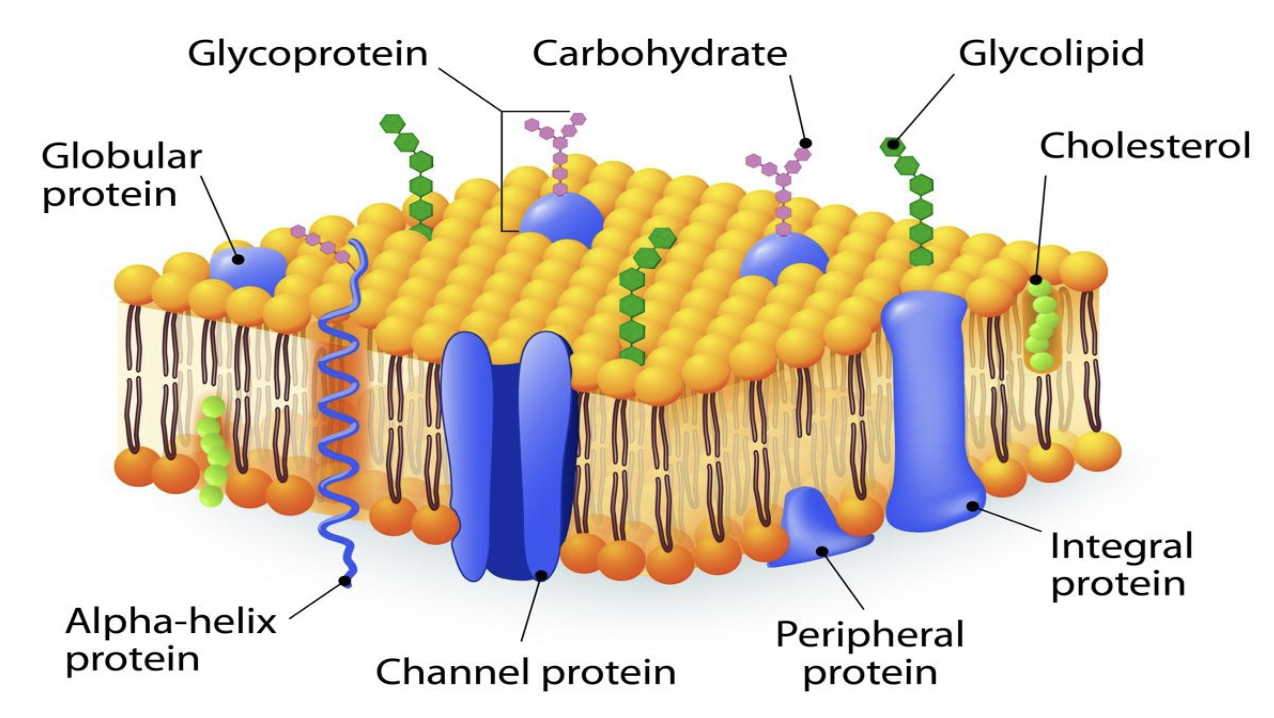
Mosaic Model
propsed by Singer and Nicholson in 1972
to describe the structure of the cell fluid-like, two-dimensional structure composed of a mosaic of phospholipids with embedded or attached proteins and carbohydrates, which can move laterally within the membrane
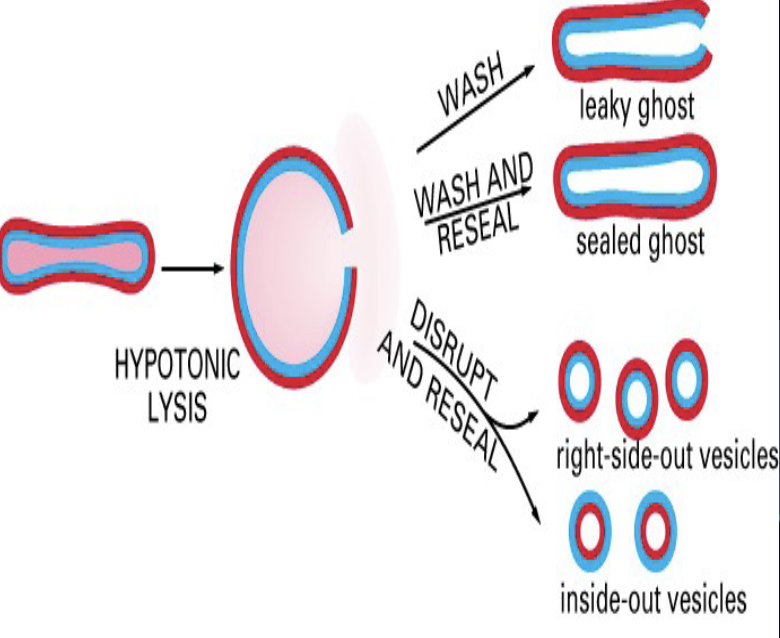
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
benefits:
plentiful and easy to get
pure cell population
few contaminating membranes
few proteins
right-side out and inside-out RBC vesicles
RBC Ghosts
the membrane remnants of red blood cells that have lost their internal contents like hemoglobin
formed in the body as a result of cell rupture (hemolysis) or in labs to be carriers
RBC membrane proteins
vital for maintaining the cell's structure, function, and transport properties
key proteins:
Band 3 and glycophorin - span the membrane,
cytoskeletal proteins like spectrin and ankyrin
band 4.1 - attached to the inner side of the membrane to provide structural support and flexibility
RBC membrane protein network
a complex system of integral and skeletal proteins that provides structural integrity, flexibility, and function to the cell
Elliptocytosis and Spherocytosis
inherited red blood cell disorders that involve abnormalities in the cell membrane, but they differ in the shape of the red blood cells
spherocytosis is characterized by spherical-shaped cells that are less flexible and have a decreased surface area, often leading to more severe hemolytic anemia
Elliptocytosis involves oval or elliptical-shaped cells that are typically more mild, with many patients being asymptomatic
Vernon Ingram
the “father of molecular medicine”
research on sickled cell anemia
found a single aminoacid substitution that caused sickle-cell anaemia
Phospholipid Bilayers
consists of two layers of molecules with hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing the watery environments inside and outside the cell
while their hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails are oriented inward, creating a selective barrier
protecting the cell and regulating the passage of substances to maintain a stable internal environment
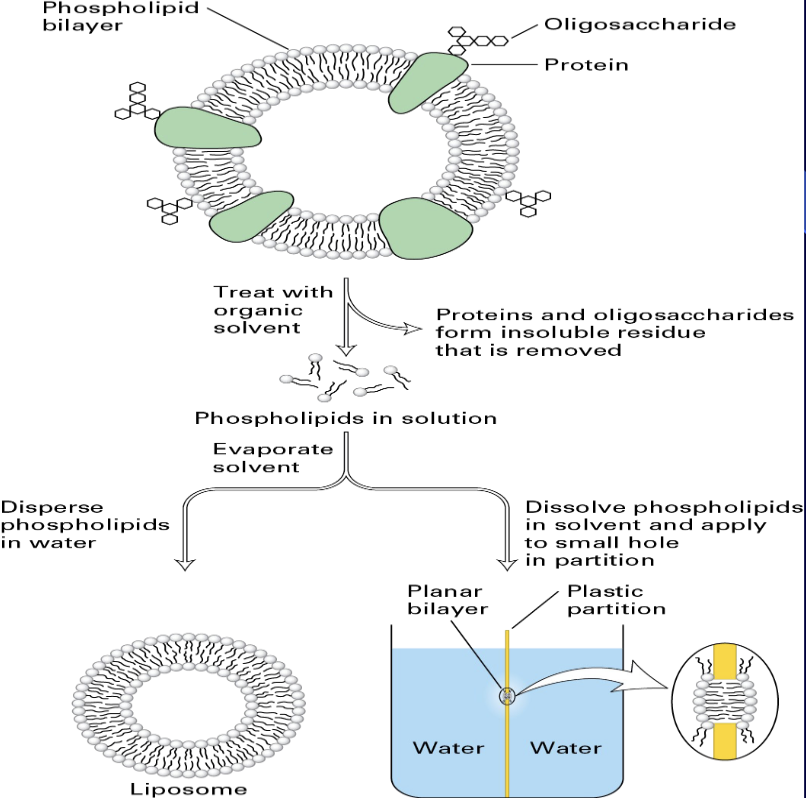
Phospholipids
hydrophilic (water-loving) phosphate "head" and two hydrophobic (water-fearing) fatty acid "tails
dual nature, called amphipathic, allows them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane in water, with the tails facing inward and the heads facing outward
Synthesized on the
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) with
Flippase playing a critical role
LDL (low-density lipoprotein)
Excess cholesterol causes
AtherosclerosisStatins decrease LDL by
inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase
Cell Membranes
three possibilities of on how phospholipids and cholesterol move from ER to other organelle membranes:
Vesicular Transport (Vesicles)
Transfer at Membrane Contact Sites (Hypothetical Proteins)
Cytosolic Carrier Proteins (Binding Protein)
MinION
sequencing device that uses a highly stable, engineered membrane protein (alpha -hemolysin) inserted into a synthetic membrane to act as a nanoscale sensor that identifies the sequence of DNA bases by measuring the subtle, characteristic electrical current changes each base produces as it passes through the pore
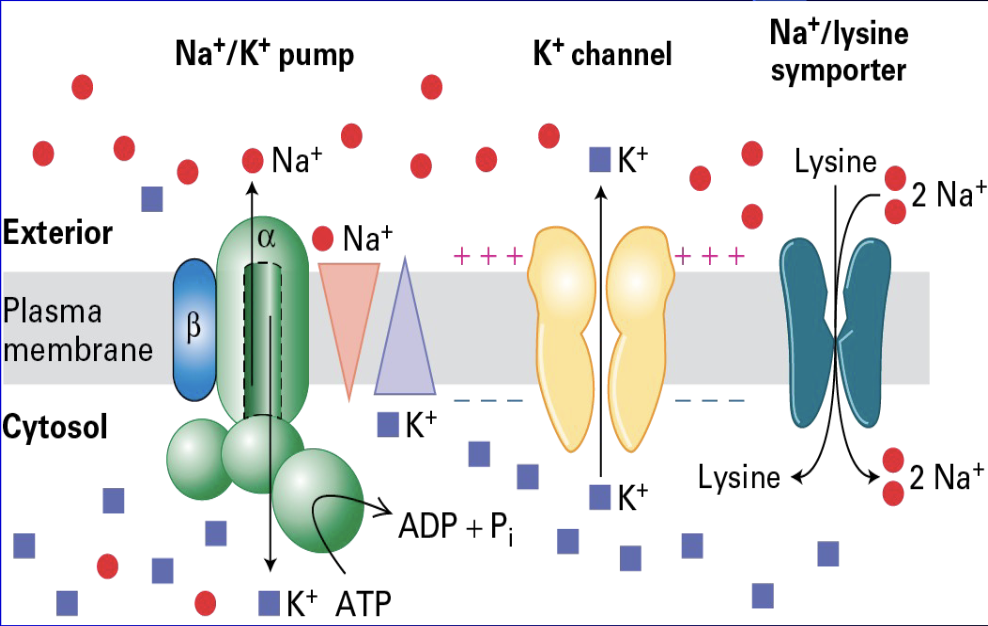
Sodium potassium pump
Uniport, Symport and Na+/K+ Pump (ATPase) working together
critical for quick
rehydration in cases with Cholera Toxin
Cell Membrane Proteins
discovery of Flippase that is required for fluorescent probes
channels - fastest:
non gated
ligand - gated
vintage-gated
transporters - no ATP required
cholera toxin:
drink Na+ and Glucose
quick to rehydrate
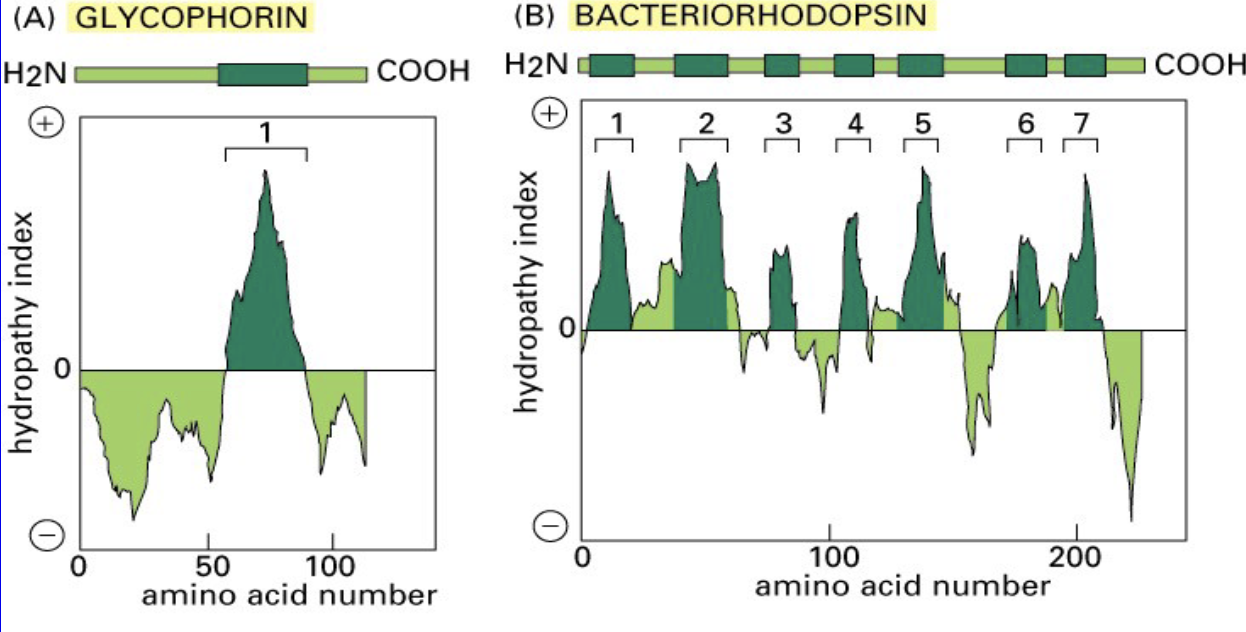
Hydropathy Plots
explain multipass nature of integral
membrane proteinsscores each amino acids based on its hydrophobicity
Membrane Specializations
differentiated structures of the plasma membrane that allow a cell to perform specific functions
includes:
Microporous membranes and kidney cells
Adherens
Adhere Junctions
F-acting is critical (E-cadherin - Ca+2)
encircles the cells in the apical region
in NaCa+2 no E-cadherin function
does:
cell adhesion
cis-configuration
trans-configuration
Desmosomes
cell adhesion “spot welds”
skin (epidermis) like Hemidesmosomes
cadherins
ex: Pemphigus -an autoimmune disorder that attack __ in humans and canines
Tight Junction
kidney intestinal
epithelial cells of the bladder
separate liquid
sodium Fluorescein leakage assay 9an in vitro test that measures how a substance affects the permeability of an epithelial cell layer by using sodium fluorescein dye)
lanthanum hydroxide
Gap Junctions
aka electrical junction
allows communication between cells
allows small molecules or ions can pass through
Neurochemical/(mixed) Synapses
using chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) to send signals across a gap called the synaptic cleft