Nursing Care for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Immunosenescence
Age-related immune dysfunction increasing inflammation.
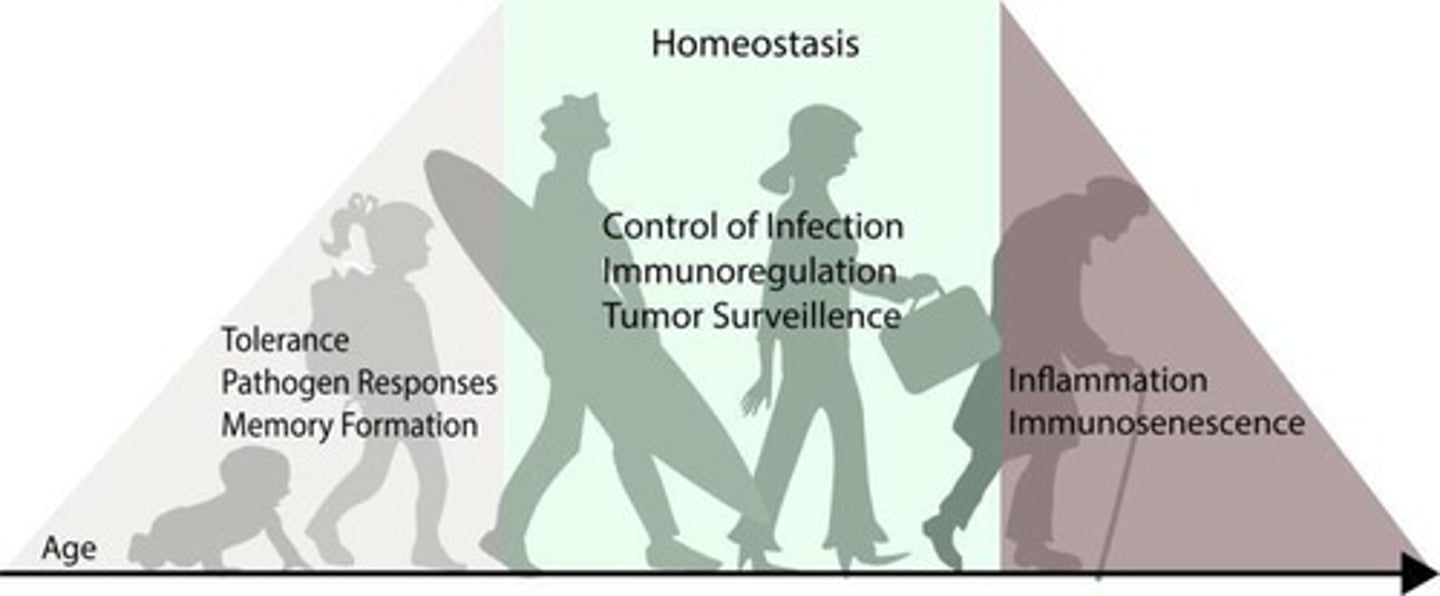
Inflamm-ageing
Hypothesized link between aging and chronic diseases.
B Lymphocytes
Produce antibodies after maturation in bone marrow.
T Lymphocytes
Mature in thymus; kill infected or foreign cells.
Cytotoxic T Cells
Destroy virus-infected and cancerous cells.
Neutrophils
First responders to infections, digest bacteria.
Basophils
Release histamine; involved in allergic responses.
Eosinophils
Combat parasites and respond to allergic reactions.
Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
Found in mucosal areas; protects respiratory/GI tracts.
Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
Most abundant antibody; protects against infections.
Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
First antibody produced in response to new infections.
Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
Involved in allergic reactions; found in mucosa.
Immunoglobulin D (IgD)
Least understood; present in small blood amounts.
Type 1 Hypersensitivity
Common allergic response requiring repeated exposures.
Anaphylaxis
Severe systemic allergic reaction with multiple symptoms.
Type II Hypersensitivity
Cytotoxic response; includes transfusion reactions.
Type III Hypersensitivity
Immune complex-mediated; involves transplant rejection.
Type IV Hypersensitivity
Delayed response mediated by T lymphocytes.
Epinephrine
Treats anaphylaxis by reducing histamine effects.
Antihistamines
Block histamine receptors; alleviate allergy symptoms.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins that mediate immune responses.
Interleukins
Type of cytokine that regulates immune cell communication.
Granulocytes
White blood cells including neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils.
Glucocorticoids
Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents.
Beta2 agonist
Bronchodilator used for asthma treatment.
T-Lymphocyte suppression
Inhibition of T-cell activity in immune response.
Chemotherapeutics
Drugs like cyclosporine and methotrexate for treatment.
Fluid Volume Deficit
Decreased body fluid levels affecting circulation.
Decreased Cardiac Output
Reduced heart output, often in anaphylaxis.
Impaired Gas Exchange
Ineffective oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Infection
Invasion of pathogens causing disease.
Impaired Skin Integrity
Damage to skin barrier affecting healing.
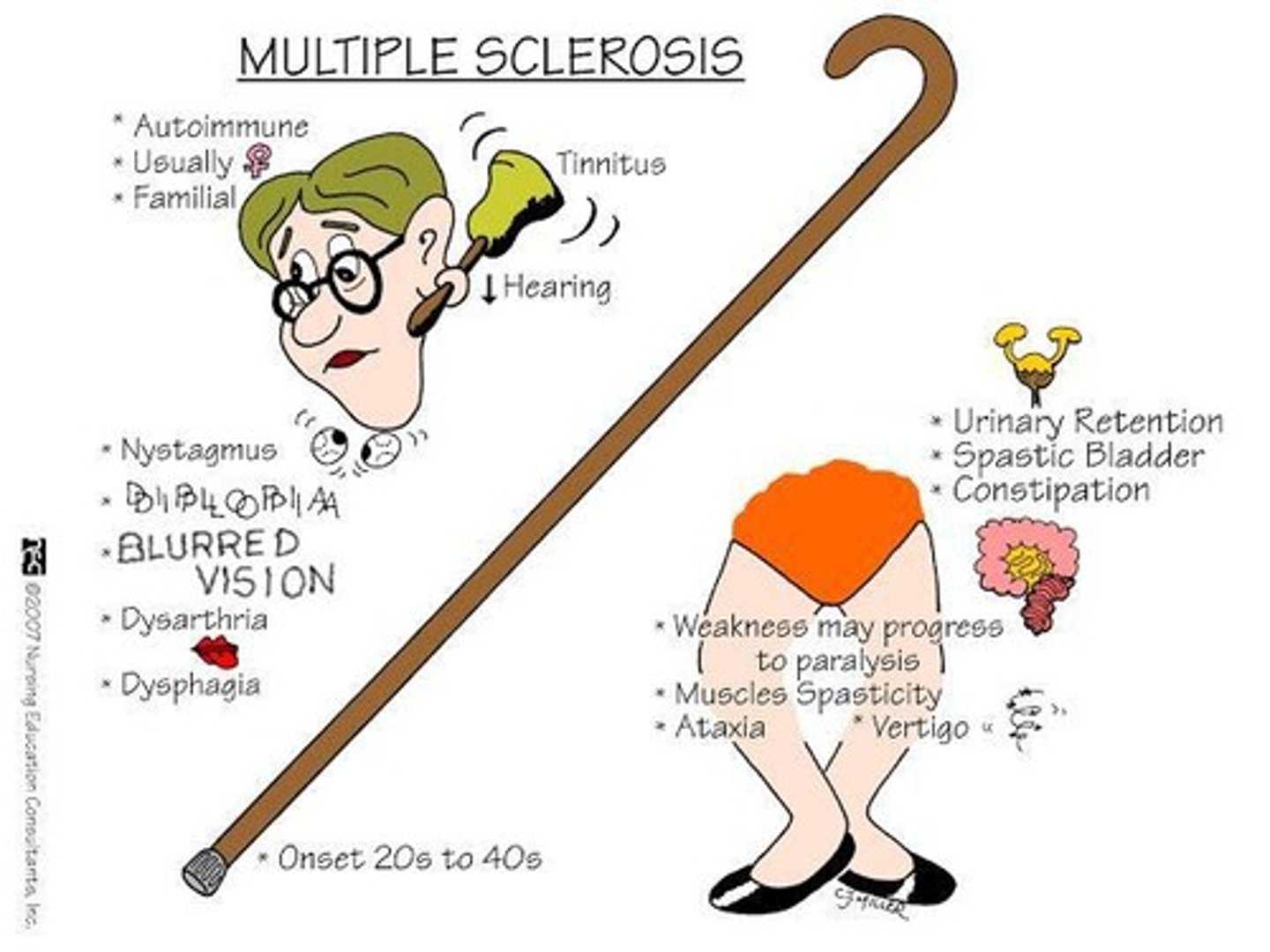
Autoimmune Disorder
Body attacks itself, mistaking self as foreign.
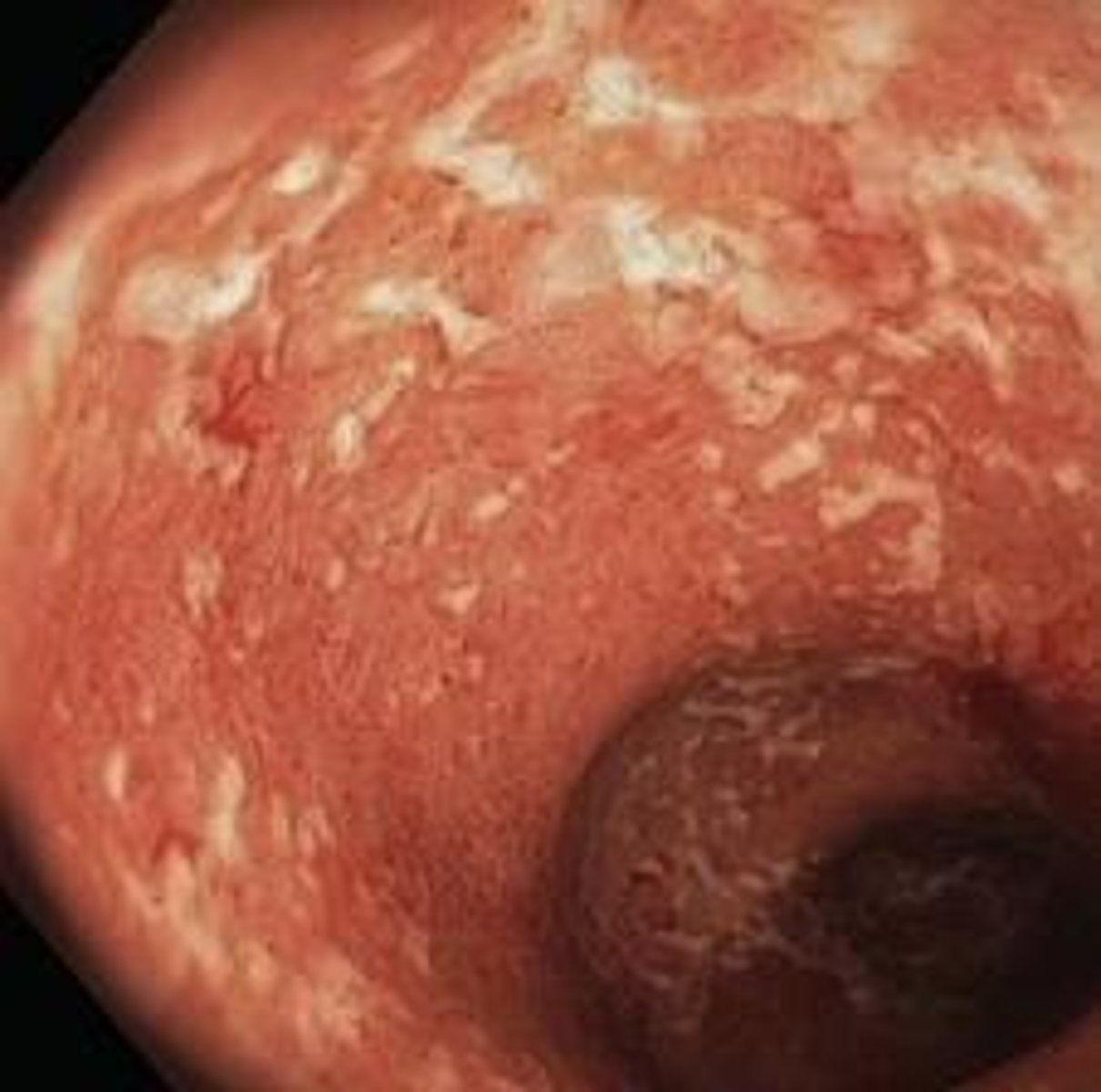
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Chronic inflammation affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
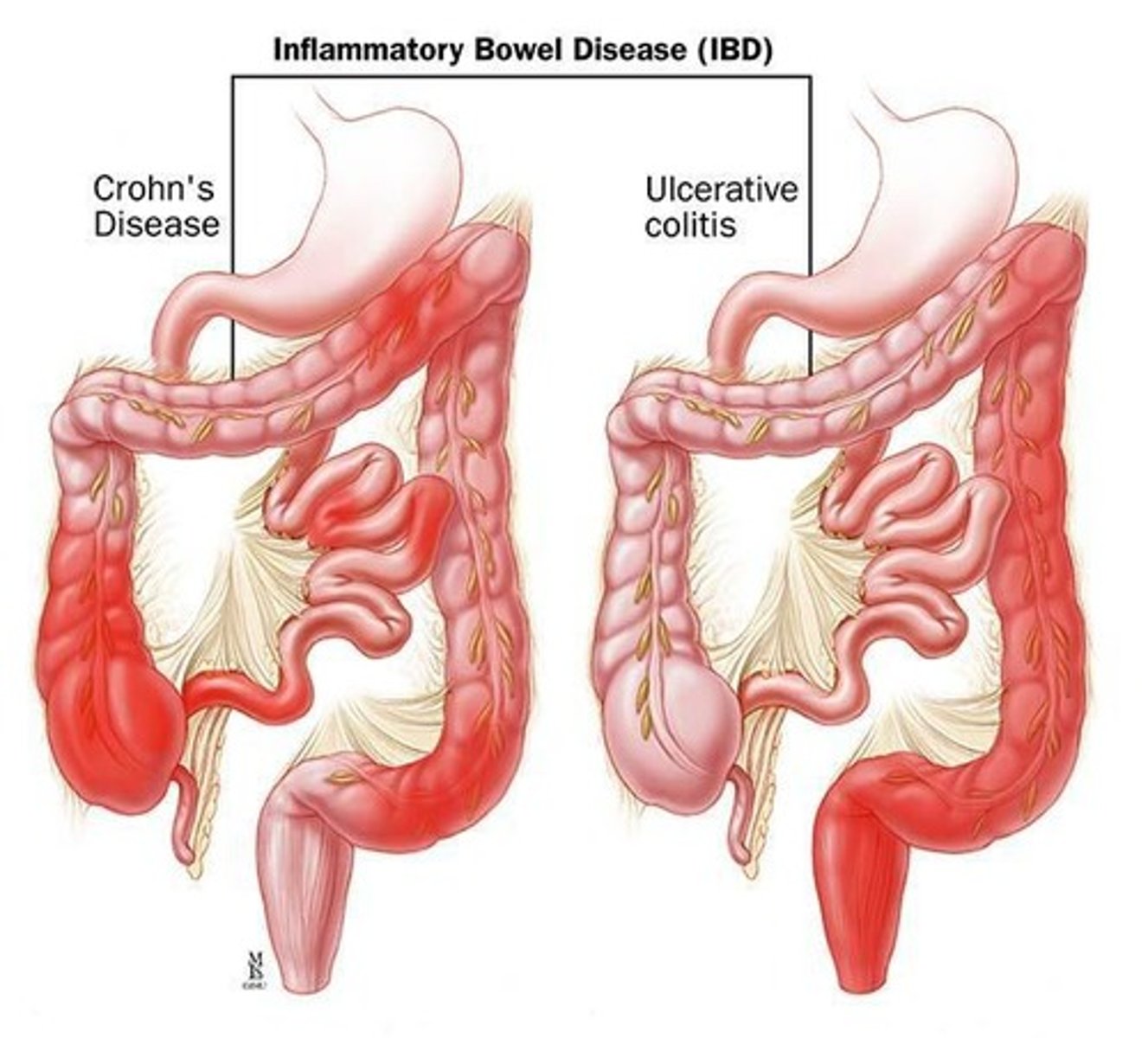
Crohn's Disease
Affects any part of the GI tract.
Ulcerative Colitis
Inflammation limited to the large bowel.
Transmural
Involves all layers of intestinal wall.
Fistulas
Abnormal connections between organs or vessels.
Thrombocytopenia
Platelet count less than 150,000 cells/dL.
Immune-mediated Thrombocytopenia
Autoimmune destruction of platelets.
HIT Type 1
Transient platelet decrease during heparin therapy.
HIT Type 2
Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia with thrombi formation.
DIC
Disseminated intravascular coagulation causing bleeding.
Cytokine Release
Cell signaling molecules affecting immune response.
Nutritional Support
Assistance in meeting dietary needs for healing.
DIC
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, a serious condition.
Petechiae
Small red or purple spots from bleeding.
Ecchymosis
Larger bruises caused by bleeding under skin.
Scleral bleeding
Bleeding in the white part of the eye.
Microemboli
Small clots causing ischemia in extremities.
Thrombus formation
Clot formation leading to organ dysfunction.
Altered LOC
Changes in level of consciousness.
Tachycardia
Increased heart rate, often above 100 bpm.
Hypotension
Abnormally low blood pressure.
Dyspnea
Difficulty or labored breathing.
Tachypnea
Increased respiratory rate, over 20 breaths/min.
Cyanosis
Bluish discoloration due to low oxygen.
Hypoxemia
Low oxygen levels in the blood.
ARDS
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, severe lung condition.
Prolonged PT and PTT
Increased prothrombin and partial thromboplastin times.
Increased d-dimer
Elevated levels indicate clot breakdown.
Decreased fibrinogen
Low levels indicate impaired clotting ability.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Chronic, symmetrical inflammation of joints.
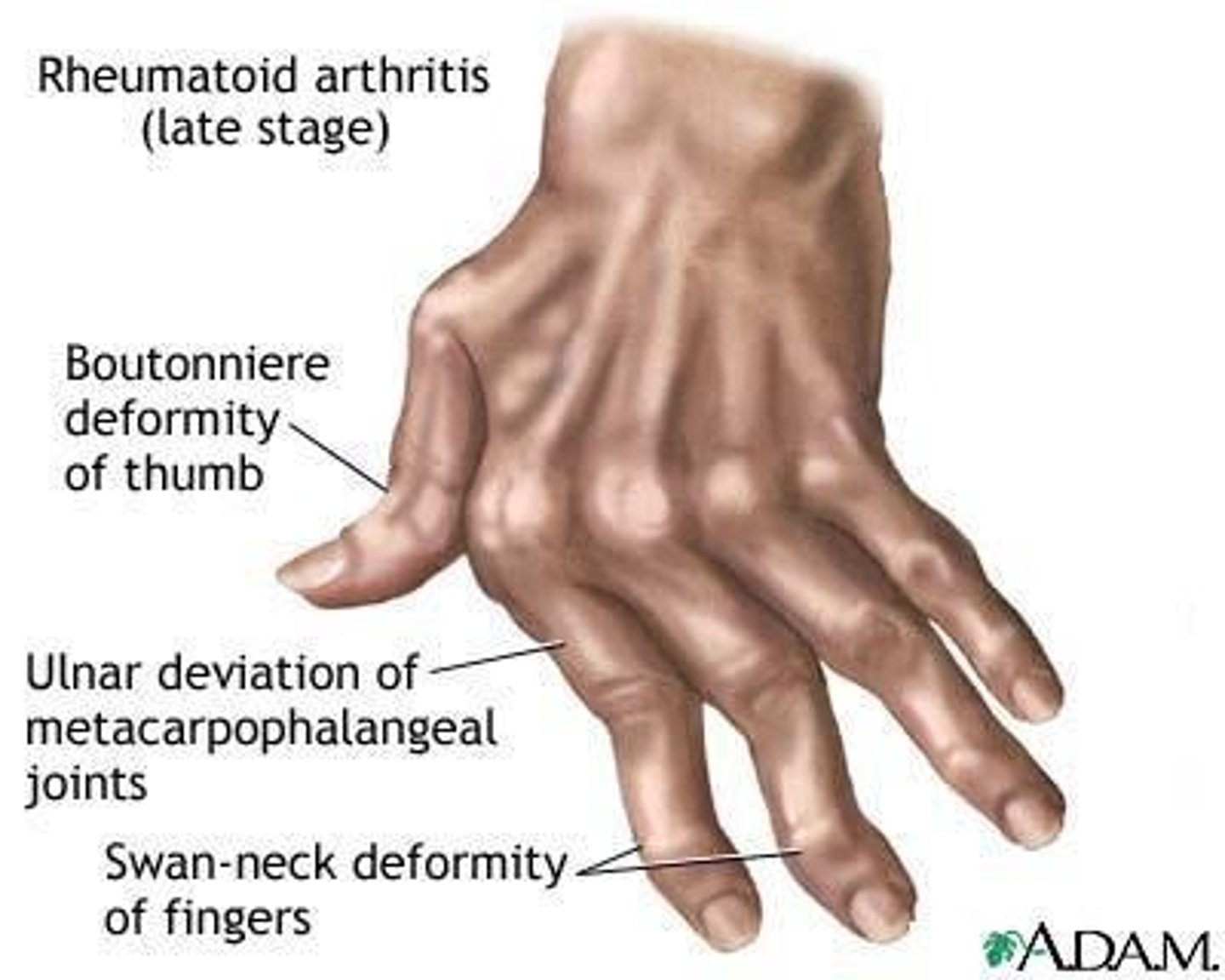
Methotrexate
Disease-modifying drug for rheumatoid arthritis.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Multisystem autoimmune disorder affecting various tissues.
ANA assay
Test for antinuclear antibodies, indicates autoimmune activity.
Lupus nephritis
Kidney inflammation due to systemic lupus.
Neuro
Immune complex deposition causes neuropathies.
End organ damage
Prevent damage to vital organs from disease.
ASA
Acetylsalicylic acid, used for pain relief.
NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, reduce inflammation.
Glucocorticoids
Steroids that suppress immune response.
Hydroxychloroquine
Anti-malaria drug, used in lupus treatment.
Immunosuppressants
Medications that inhibit immune system activity.
Methotrexate
Chemotherapy drug, used for autoimmune diseases.
Azathioprine
Immunosuppressant for organ transplant and lupus.
Mycophenolate
Immunosuppressant, prevents organ rejection.
Cyclophosphamide
Chemotherapy agent for glomerulonephritis.
Dapsone
Anti-leprosy drug, manages skin symptoms.
IV IgG
Intravenous immunoglobulin for thrombocytopenia.
HIV
Virus that infects CD4 T lymphocytes.
Primary Infection
Initial phase with flu-like symptoms.
Clinical latent infection
Phase where virus is inactive but present.
Early symptomatic HIV
Phase with rare infections and lymphadenopathy.
AIDS
Advanced stage of HIV infection.
NNRTI
Non-nucleoside inhibitors prevent RNA to DNA conversion.
NRTI
Nucleoside inhibitors stop viral DNA construction.
Protease Inhibitors
Prevent HIV from entering healthy T cells.
Entry Inhibitors
Block HIV from entering host cells.
PrEP
Pre-exposure prophylaxis, reduces HIV seroconversion risk.
Nursing Management
Monitor infections, kidney failure, and maintain mobility.
Special diet
High protein, high calorie, low-fat meals.
Hydration
2 - 2.5 liters daily intake.
Nutrient dense foods
Foods high in vitamins and minerals.
Safety precautions
Measures to prevent harm or injury.
Social support
Emotional and practical assistance from others.
HIV care priorities
Focus on breathing, infection, and coping.
Breathing pattern assessment
Evaluate respiratory function and oxygenation.
Gas exchange maximization
Improve oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Fluid volume deficit
Insufficient body fluid levels.