Geography IGCSE - Coasts
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Coast
The transition zone between the land and the sea or ocean
Swash
movements of waves up the beach
Backswash
movements of waves down the beach
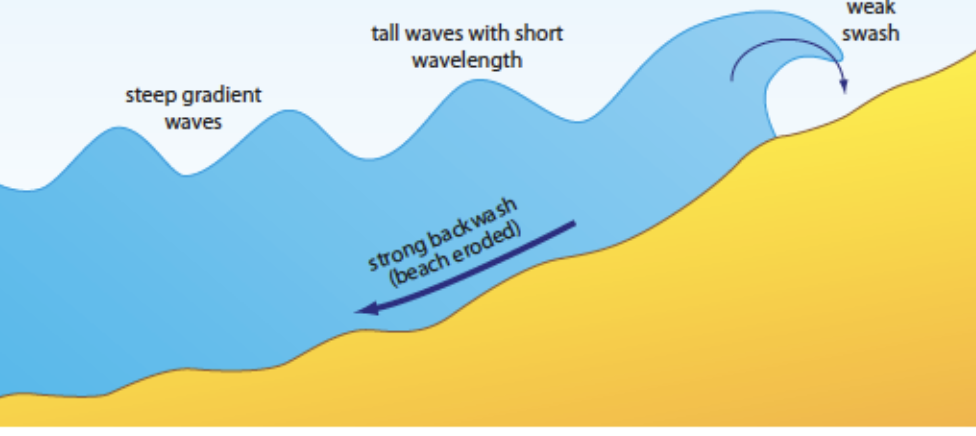
Destructive waves
When waves build up over a long period of time, with strong winds and a long fetch, they have a lot of power and are destructive.
These waves have a stronger backwash and cause erosion
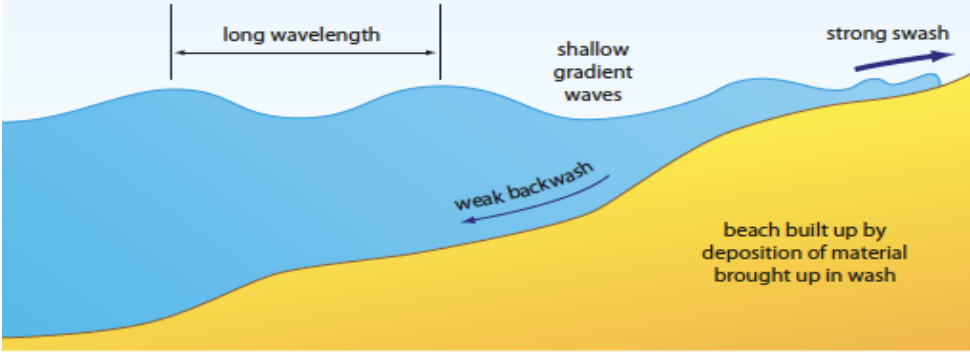
Constructive waves
Waves with less energy → have a stronger swash
They do not cause erosion.
They are more likely to deposit their load and build beaches
3 Factors affecting wave size:
Wind speed
Wind duration - the length of time the wind has blown
Fetch - the distance over open water over which the wind blows
Stronger the wind → the longer its duration is
Greater the fetch → the bigger the wave
The bigger the wave → the greater its energy and therefore erosional power
Erosion
wearing away of the land by the sea
Transportation
movement of eroded material along the coast by the sea
Deposition
when eroded material is dropped/deposited by the sea
Processes of coastal erosion
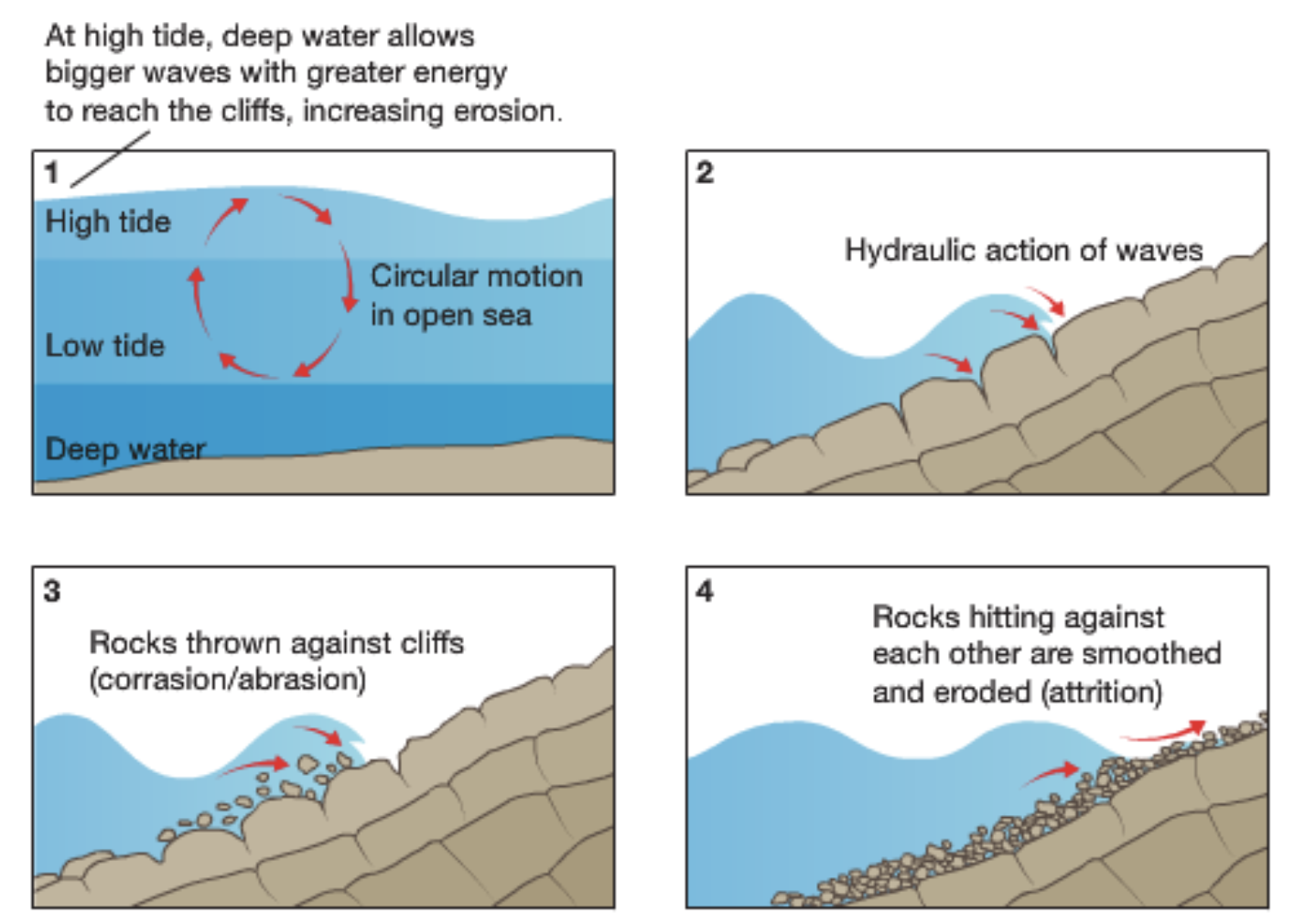
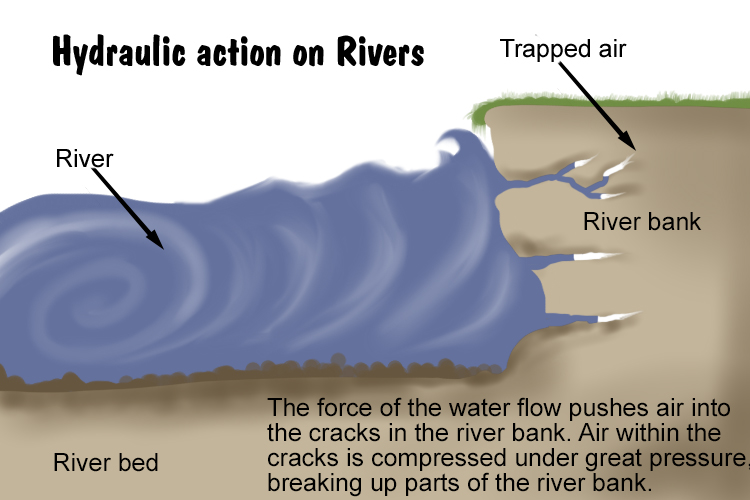
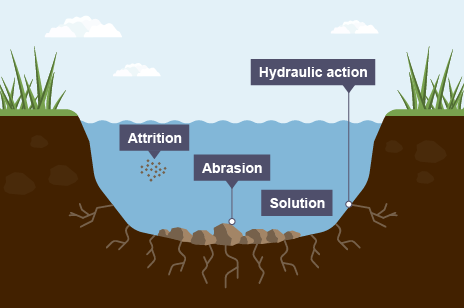
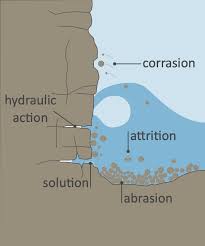
Hydraulic Action
waves hit or break against cliff face → air trapped in joints or cracks is put under pressure → increasing pressure of water and air causes rocks to crack
Abrasion
Caused by waves picking up materials such as pebbles → throwing them against a cliff face → wearing away surface (like sandpaper)
Chemical weathering
The dissolving of rocks by sea water through a chemical reaction
Attrition
Process by which material carried by waves collide into each other, breaking up and becoming rounder and smaller over time
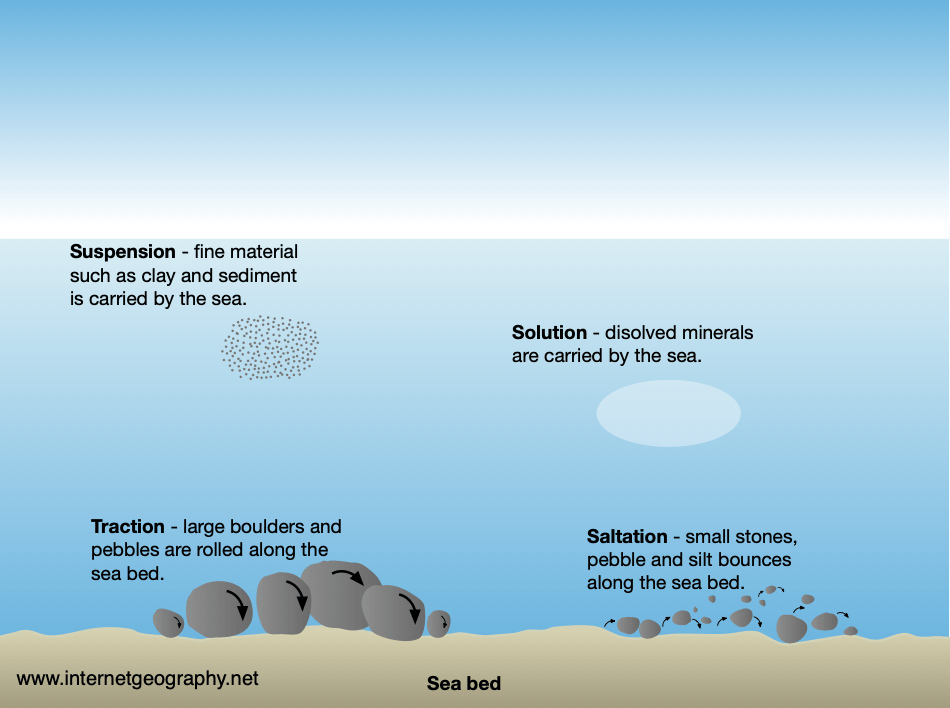
Sea transportation
Traction → Larger, heavier materials, like pebbles rolled along riverbed
Saltation → pebbles are bounced along river bed, commonly near the source
Suspension → fine, light particles lifted by the river's turbulent flow and carried in water column
Solution → when sea water dissolves certain types of rocks
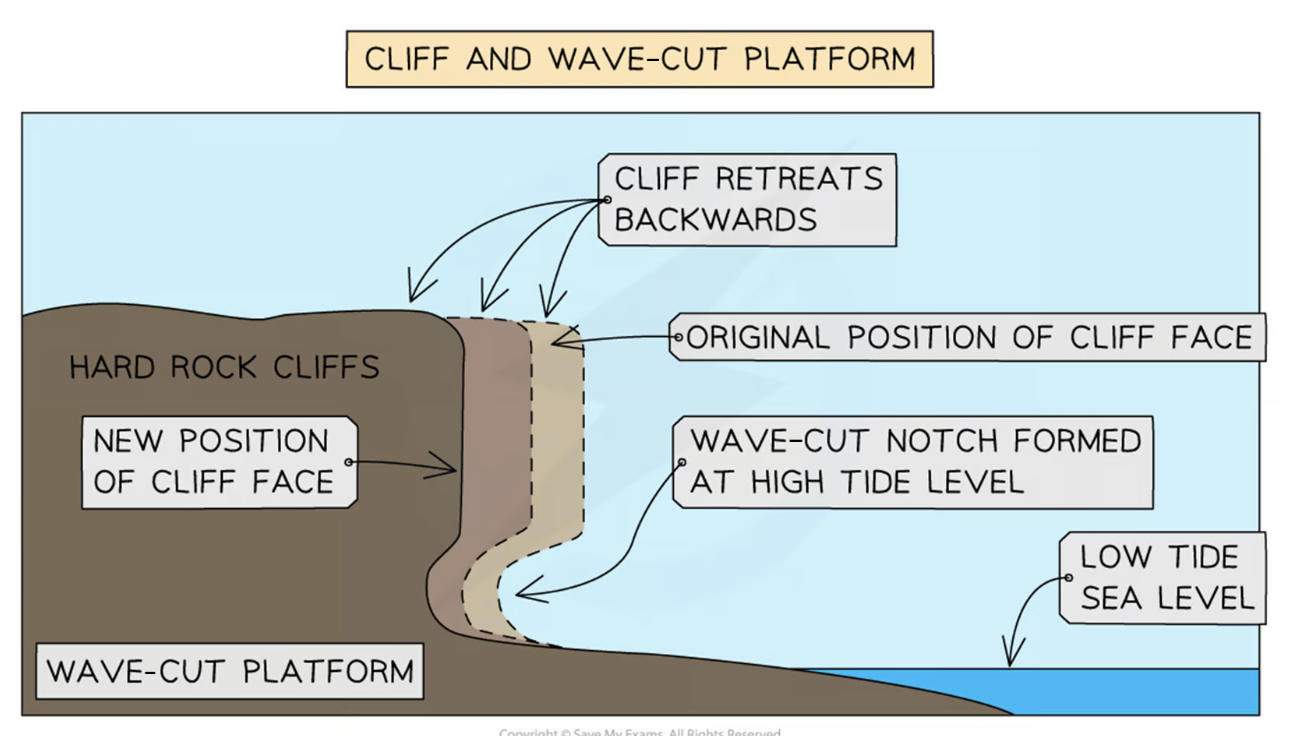
Cliffs + wave cut platforms
piece of land sloping down to the sea - processes of weathering → weaken the rock
section of the cliff base between the high and low watermark → hydraulic action and abrasion → continues and over time rock will break away from the cliff base and collect on the beach → material removed by destructive waves → leaving wave-cut notch
wave-cut notch will become larger → leaving cliff above unsupported
wave-cut notch becomes so large → overhanging cliff collapses due to gravity
Hydraulic action, abrasion and weathering will repeat wave-cut notch formation and cliff collapse, causing the cliff to retreat
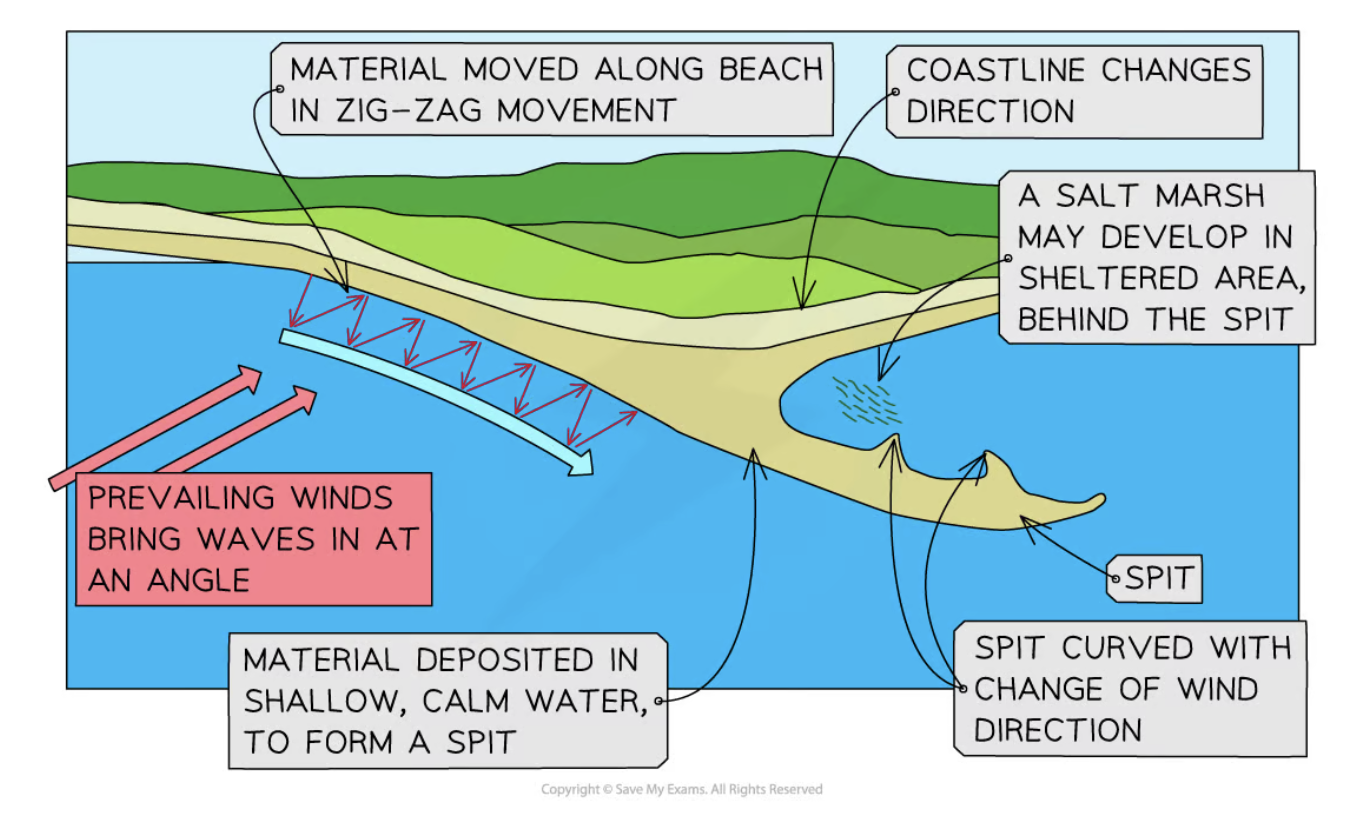
Spit
An extended stretch of sand that extends out to sea from the shore → occurs when change in shape of coastline
Stages of formation:
Longshore drift is process that moves sediment
coastline changes direction → a sheltered area (bay) allows for deposition of sediment
increased friction → more deposition occurs
spit slowly builds up to sea level → extends in length
If the wind changes direction → the wave pattern alters → hooked end
area behind the spit becomes sheltered
Silts are deposited here to form salt marshes or mud flats
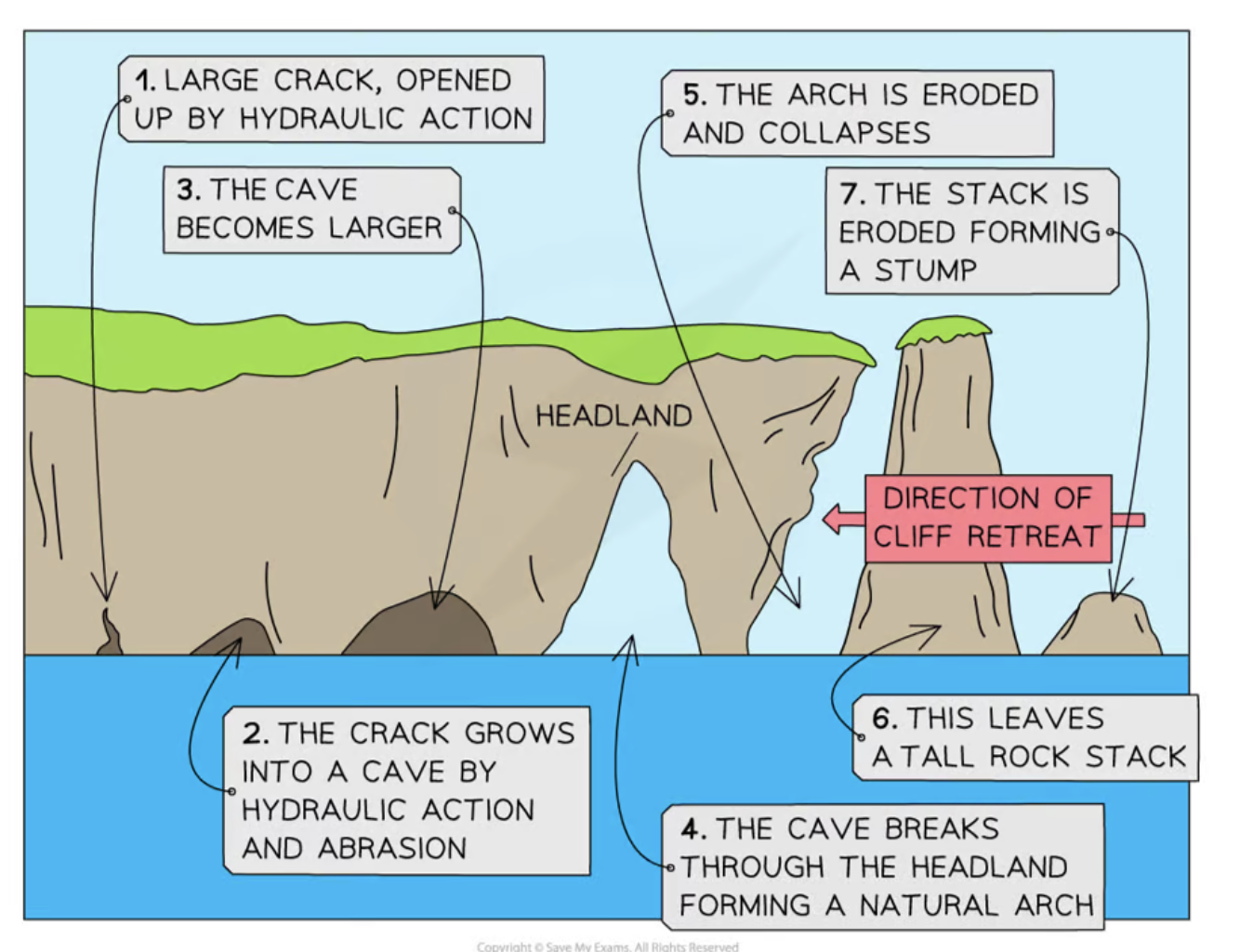
Cave, arch, stumps + stacks
hydraulic action forcing water into a crack → puts pressure on it causing it to grow larger
crack will grow into a notch → then form into cave due to destructive waves that are converging on headland
wave refraction → hitting coastline at an angle, uneven distribution of energy
over time caves will get larger through abrasion
sea may break through the back of them → sea arch
more hydraulic action and abrasion will widen the base of the arch
top of the arch will be weakened → less stable → eventually collapse → stack (detached pillar of rock)
Erosion will cause notches to form at base of stack which makes it unstable → along with weathering processes → stack topple into sea → stump which is only visible at low tide
Beach
Form in sheltered areas (bays)
Deposition occurs through constructive wave movement → swash is stronger than the backwash
Beach formation usually in summer months → weather is calmer
Sometimes sand from offshore bars can blow onto the shore by strong winds
Blown sand can create sand dunes at the backshore of a beach
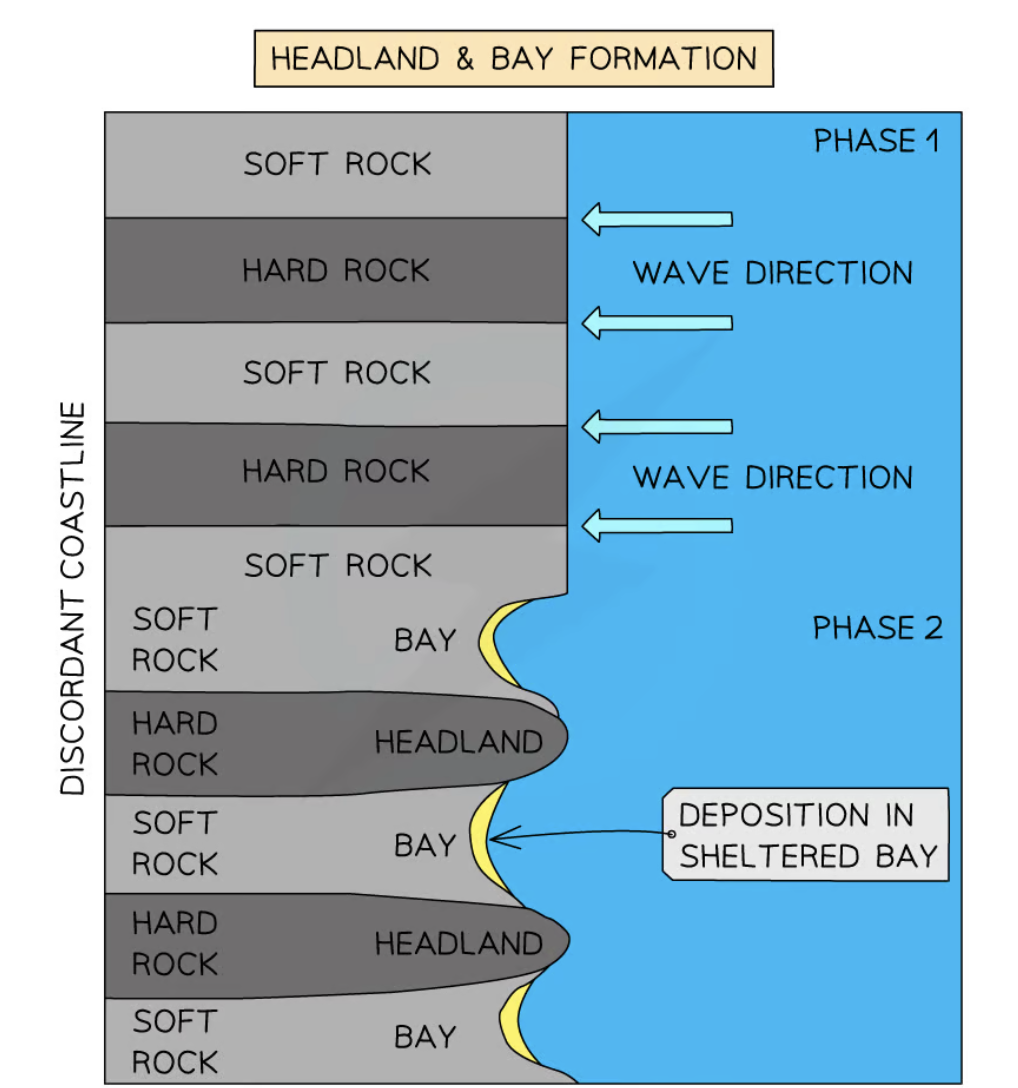
Headlands + bays
in areas of alternating bands of resistant (hard) and less resistant (soft) rocks
Initially, less resistant rock (e.g. clay) is eroded back→ forming bay
A bay is an inlet of the sea where the land curves inward
more resistant rock (e.g. limestone) is protruding out to sea as a headland
A headland usually features:
Cliffs along sides
Projects out to sea
A bay usually has:
A wide, open entrance from the sea
A roughly semi-circular shape extending into the coastline
Land that is lower than the headlands surrounding it
Sand dune
large piles of sand that form at the back of sandy beaches built by wind
Formation of sand dune (beginning)
Windblown sand is deposited against an obstruction (driftwood)
more sand particles are caught → dunes grow in size → forming rows at right angles to the prevailing wind
process called succession → vegetation will eventually colonise and fix the ridges of the dunes
The first plants (pioneer species) have to cope with:
Salinity
Lack of moisture as sand drains quickly (highly permeable)
Wind
Temporary submergence by wind-blown sand
Rising sea levels
Formation of sand dunes (phase 1)
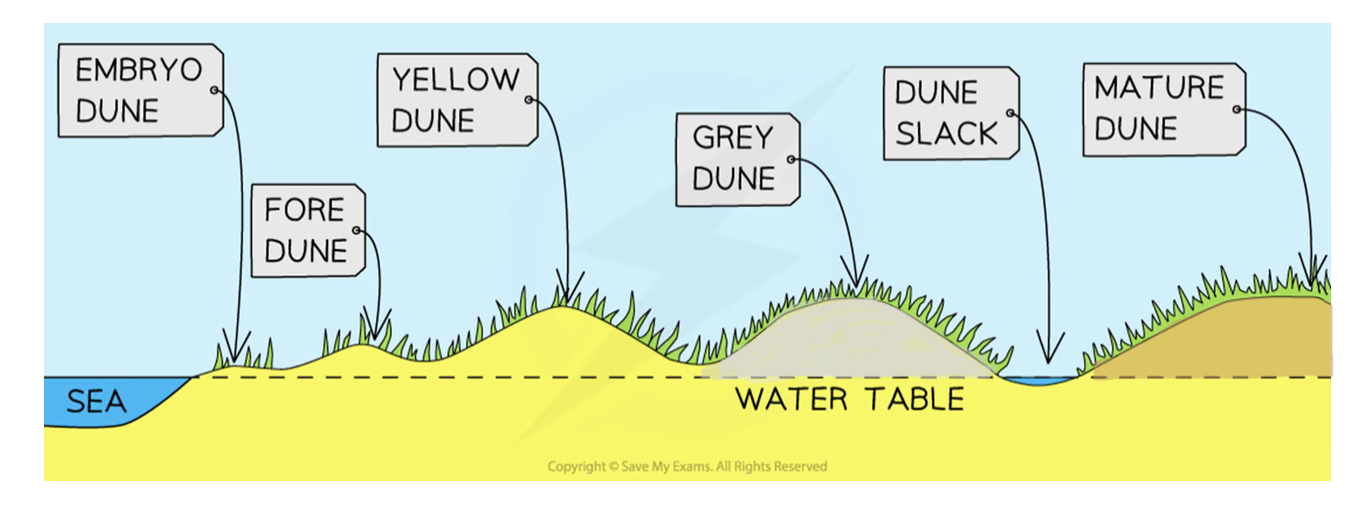
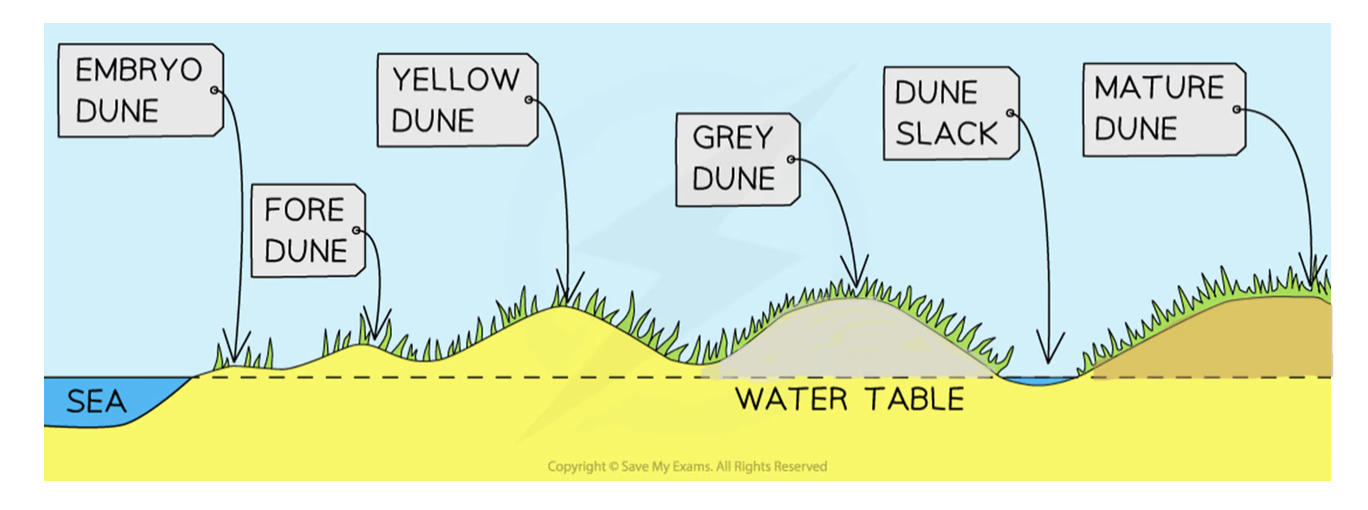
Embryo dunes
Deposition starts when debris traps wind-blown dried sand
Pioneer species (e.g. Lyme Grass and Sea Couch Grass) begin to colonise
little soil content and high pH levels (alkaline)
Embryo dunes reach a maximum height of 1 metre
Formation of sand dunes (phase 2)
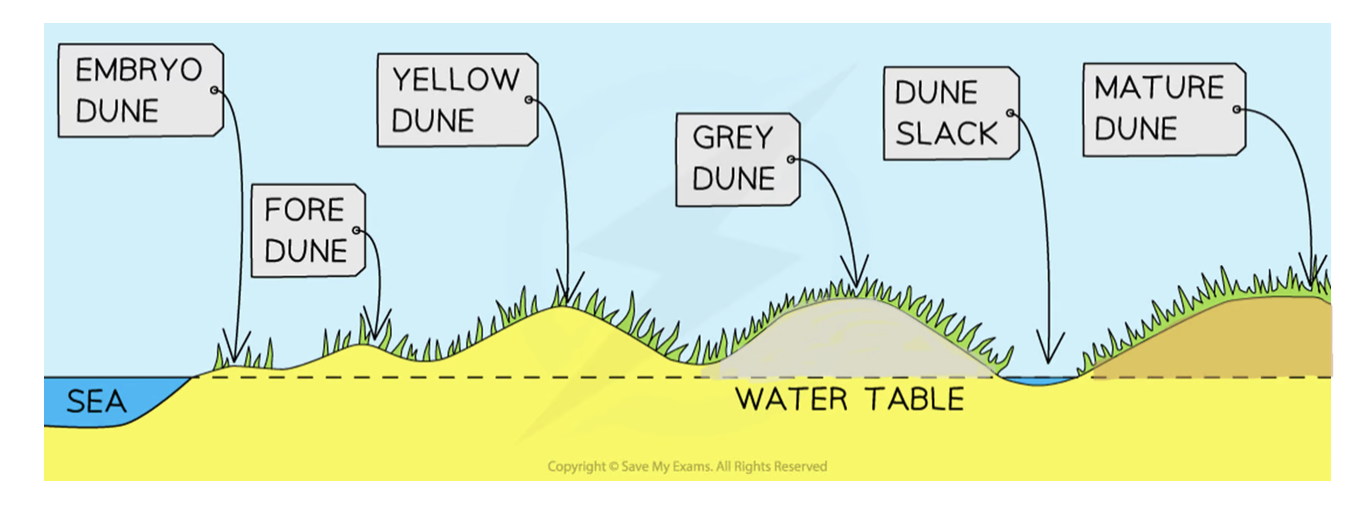
Fore dunes
embryo dunes give some protection against prevailing wind
allows other species of plant to grow (e.g. Marram Grass)
Marram grass begins to stabilise dune with its root system
plants add organic matter to the dunes → making dunes more hospitable for plants to grow
Maximum height is 5 metres
Formation of sand dune (phase 3 and 4)
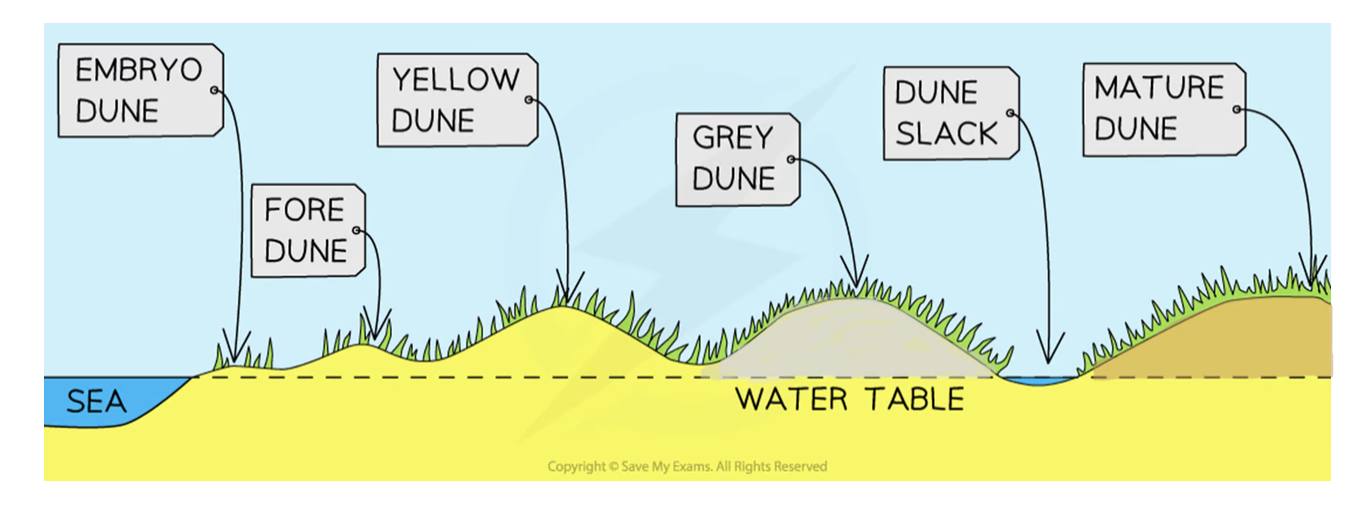
Yellow dunes
darken as organic material adds humus to the soil
Marram grass dominates the vegetation → more delicate flowering plants and insects found in dune slacks
20% of the dune is exposed, down from 80%
Height does not exceed 8 metres
Grey dunes
Grey dunes are more stable → less than 10% of exposed sand → have good range of biodiversity
Soil acidity and water content increase as more humus is added
Shrubs and bushes begin to appear
Height is between 8 - 10 metres
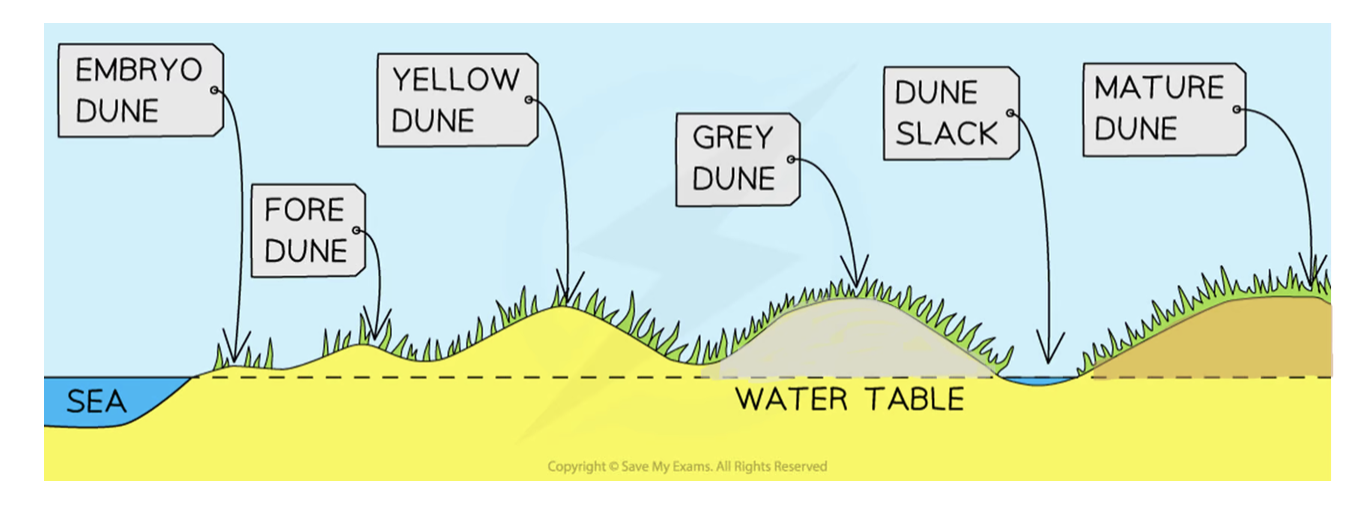
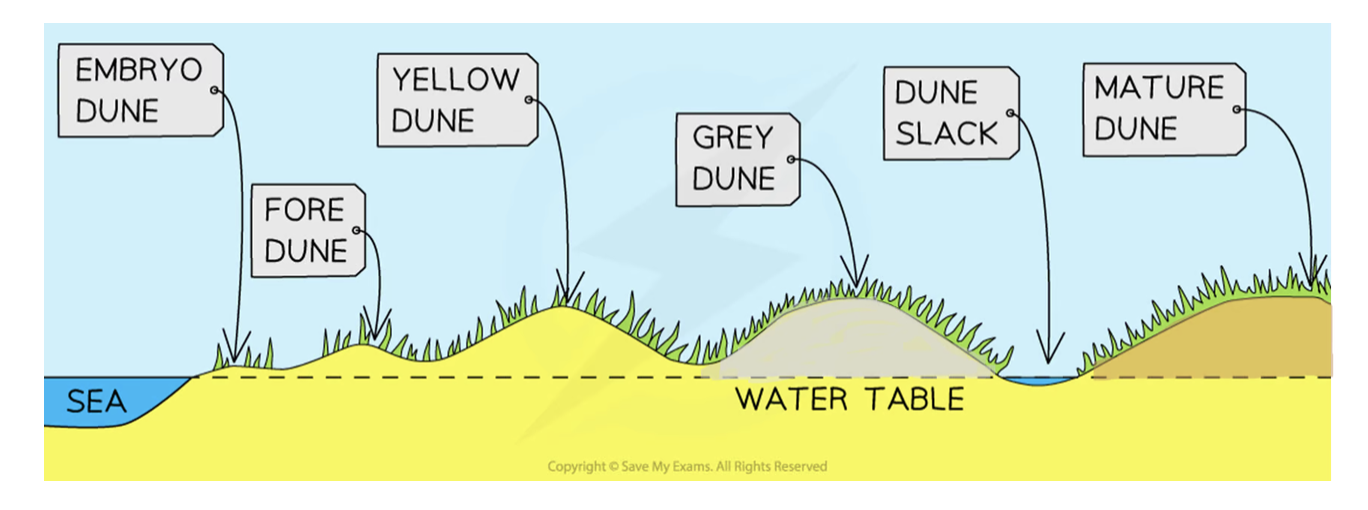
Formation of sand dune (final phase)
Mature dunes
They are found several hundred metres or more from the shoreline
soil can support a variety of flora and fauna such as oak trees and alders (climax vegetation)
Coral reefs
Corals are tiny animals → called polyps
Begin life as a tiny, free swimming larva
Polyps → clear bodies → skeletons are white
Settle on hard area e.g. rock → never move again
Polyp of hard corals makes a hard, protective shell of out calcium carbonate → (soft corals don’t build reef)
Reefs constructed from million of tiny “hard” coral polyps → live together in colonies
When polyp dies → skeleton remains → another poly will grow on top of it; adding to old coral structure
Beautiful colours come from algae that line inside the tissue
Conditions for coral reefs growth
Temperature → minimum of 18 → grows best 23-25 in tropic seas
Clear water → coral needs light for algae to photosynthesize → corals get energy → clear water with limited suspended material
Shallow water → related to need for light → corals grow in shallow water (depths of 60m)
Salinity → corals are marine creatures → survive in salt water
Mangroves
Coral reefs and mangroves → fundamentally connected ecosystems
Mangroves protect coral reefs from sedimentation → keep water clear of particles and nutrients → important for reef health
Mangroves provide spawning and nursery areas for many animals species that spend adult life on reefs
Coral reefs → provide shelter for mangroves and inhabitants
Calcium carbonate eroded from reefs → provide sediment in which mangroves grow
Conditions for mangrove growth
Intertidal zone - coastal environments and estuarine margins
High salinity (water and soil)
Muddy, sediment with low oxygen content
Tides (regularly submerged in water)
Hazards from coasts
coastal erosion → Areas that are made of less resistant rock will erode faster than those coastlines made up of more resistant rock such as granite
Tropical storms → Hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones are all types of tropical storms
Opportunities for people from coasts
Development including:
Homes
Shops
Hotels
Roads
Schools
Restaurants etc.
Nature reserves
Swimming and sports
Industry
Fishing and aquaculture
Tourism
Agriculture
Ports and harbours
Reasons for coastal protection
Prevent Erosion → prevent erosion of beaches and cliffs → safeguarding land + properties from being washed away
Manage Flooding → reduce risk of flooding from storm surges + high tides → protects coastal communities + habitats
Maintain Beaches → help preserve beaches, → vital for tourism, recreation + local economies
Protect Habitats → conserve important natural habitats → e.g. mangroves + coral reefs → crucial for biodiversity + environmental health
Safeguard Infrastructure → safety of critical infrastructure → e.g ports, roads + residential areas that are vulnerable to coastal hazards
Manage impacts of coastal erosion (soft engineered defences)
natural coastal protection → mangroves + coral reefs
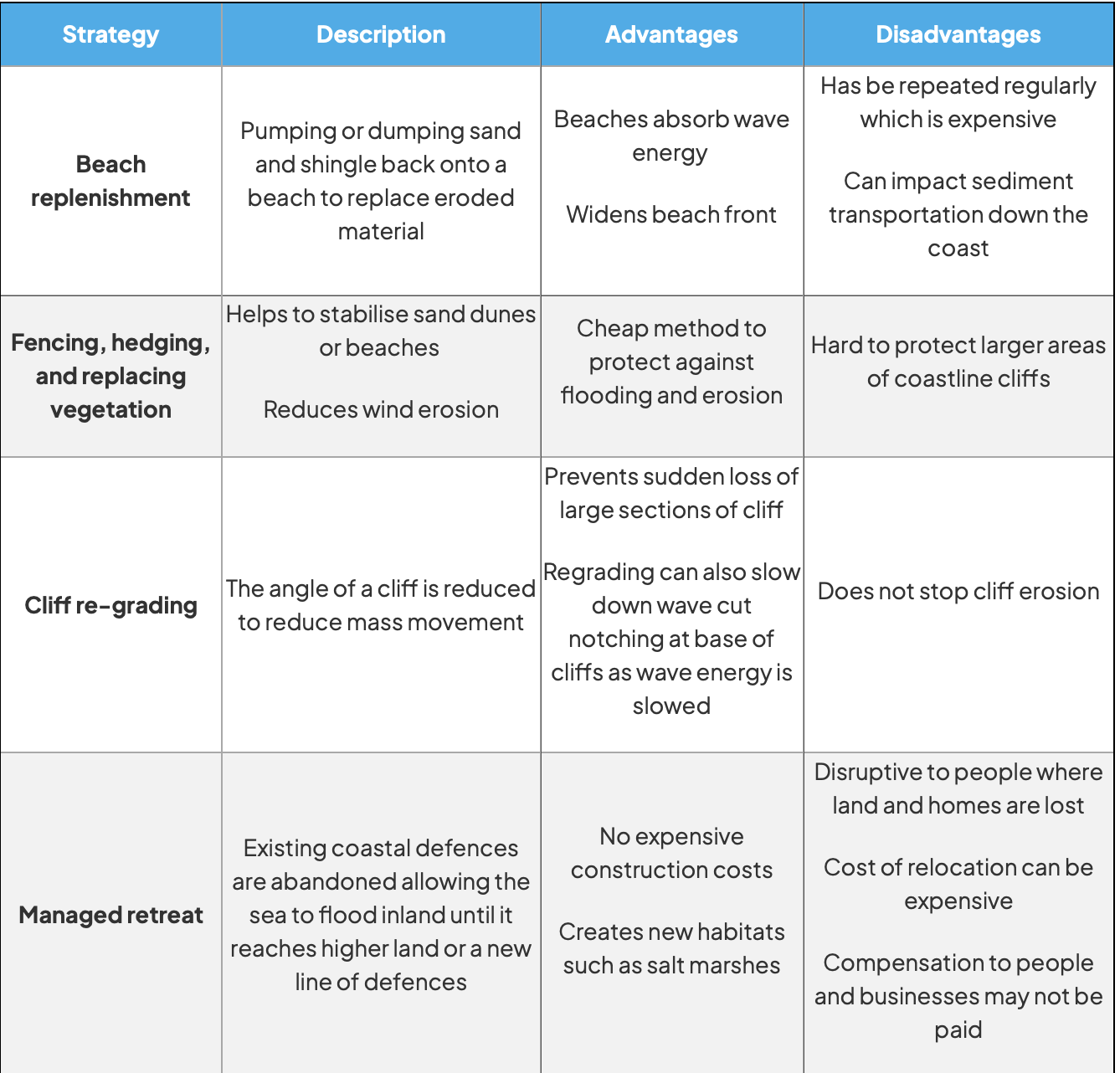
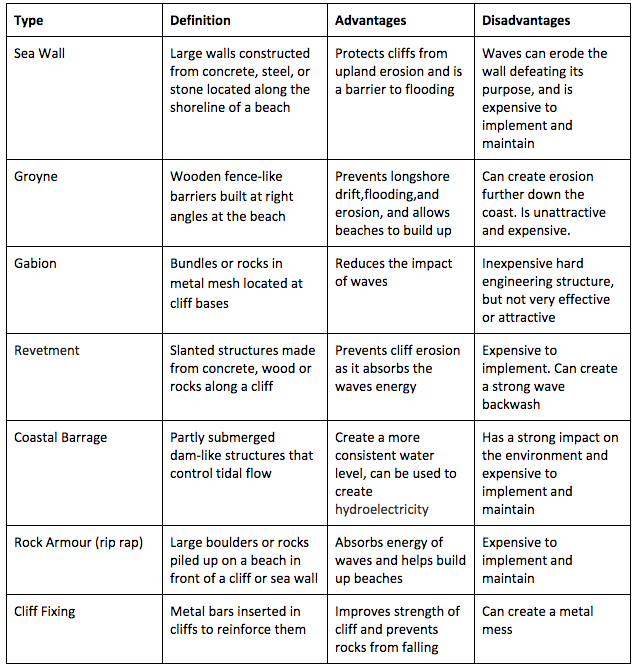
Manage impacts of coastal erosion (hard engineered defences)
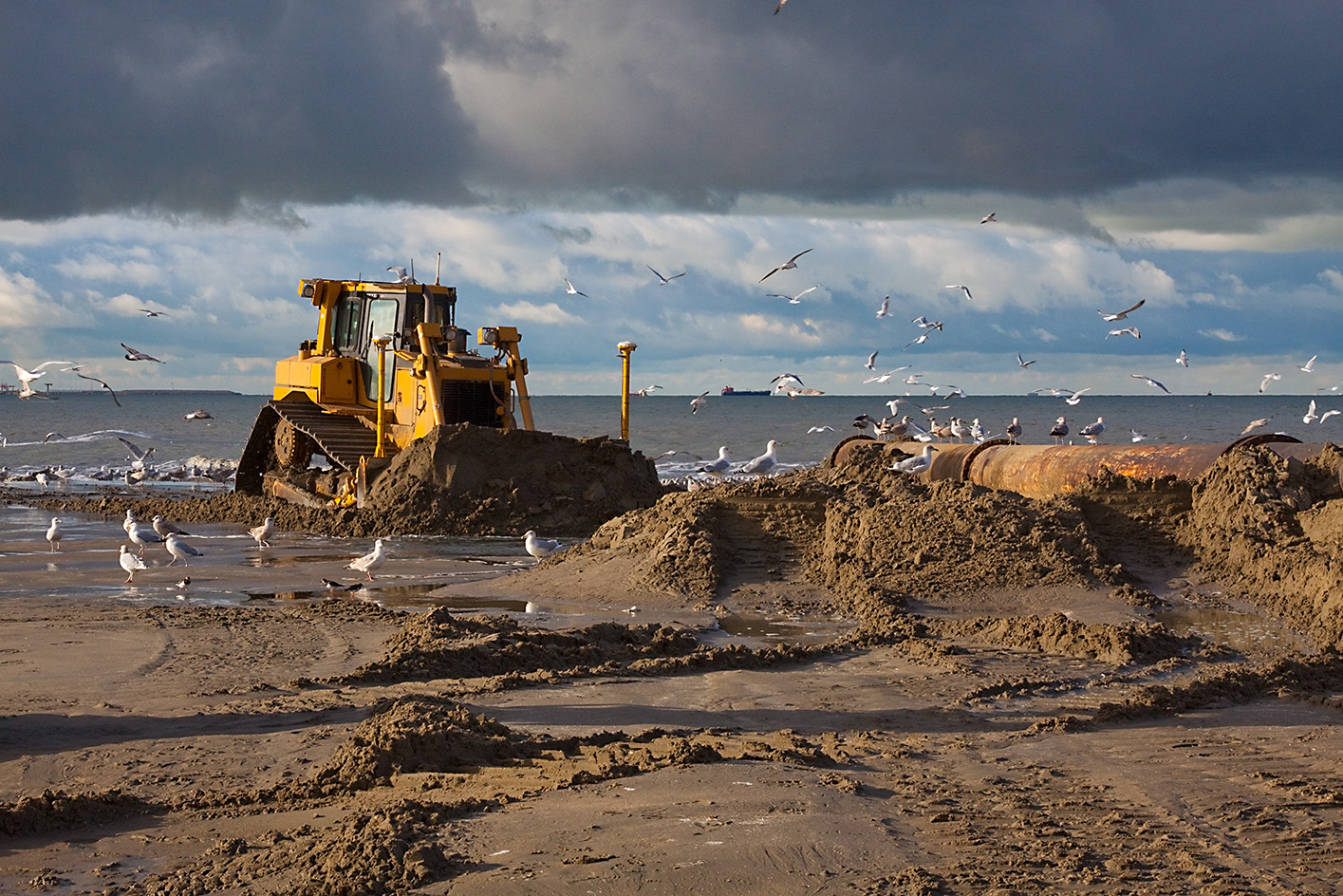
Beach Replenishment (soft engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
Sand + shingle are dumped onto a beach → replace material that eroded away | helps absorb + dissipate wave energy → protects coastline by widening the beach front → acts as a buffer zone against wave action |

Fencing, Hedging, and Replacing Vegetation (soft engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
fences and hedges, and planting or replanting vegetation to stabilize sand dunes → reduce wind erosion on beaches | Vegetation helps stabilize soil + sand with root systems → reduces displacement by wind + water, → fences trap sand + help build up dunes |
Cliff Re-grading (soft engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
slope of cliff is altered → made less steep → reduce risk of mass movements + rockfalls | reducing the angle of the cliff → decreases gravitational pull on loosened materials → slowing down processes that lead to cliff erosion + collapse. |
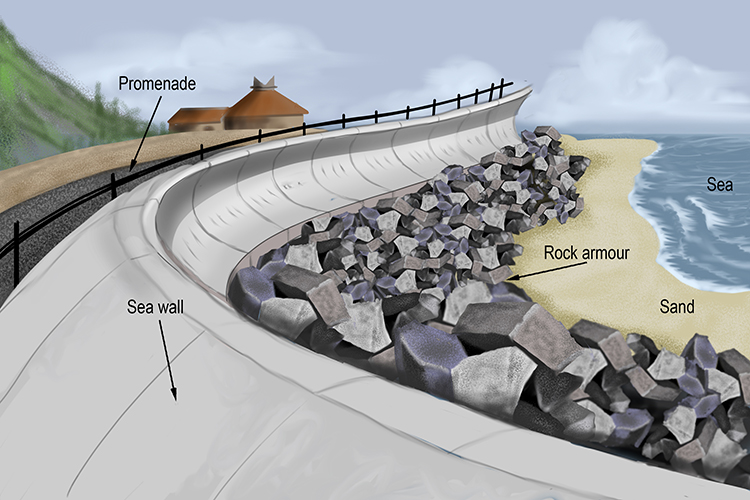
Sea wall (hard engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
Solid barriers built parallel to the coastline → protect land behind from wave action | reflect wave energy back into the sea → reduces erosion + preventing coastal flooding |

Revetments (hard engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
Sloping structures on cliffs in coastal zones → made from wood, concrete, rocks | absorb + dissipate energy of waves before they hit the shore → reduces erosion |

Rock armour (riprap) (hard engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
Large boulders piled up along coast → absorb energy of incoming waves | breaks up + dissipates wave energy → protects coastline by reducing erosive force of waves on shore |
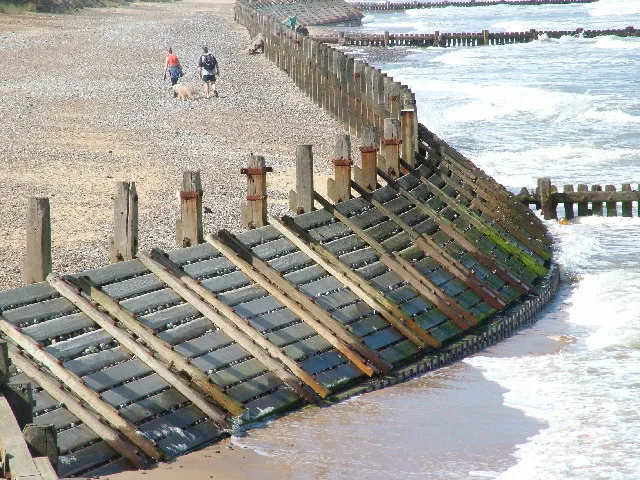
Groynes (hard engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
Barriers built perpendicular to shore at regular intervals along beach → trap sand moving down beach due to longshore drift | help build up beach → trapping sediment → acts as buffer against wave energy → protects coastline from erosion |

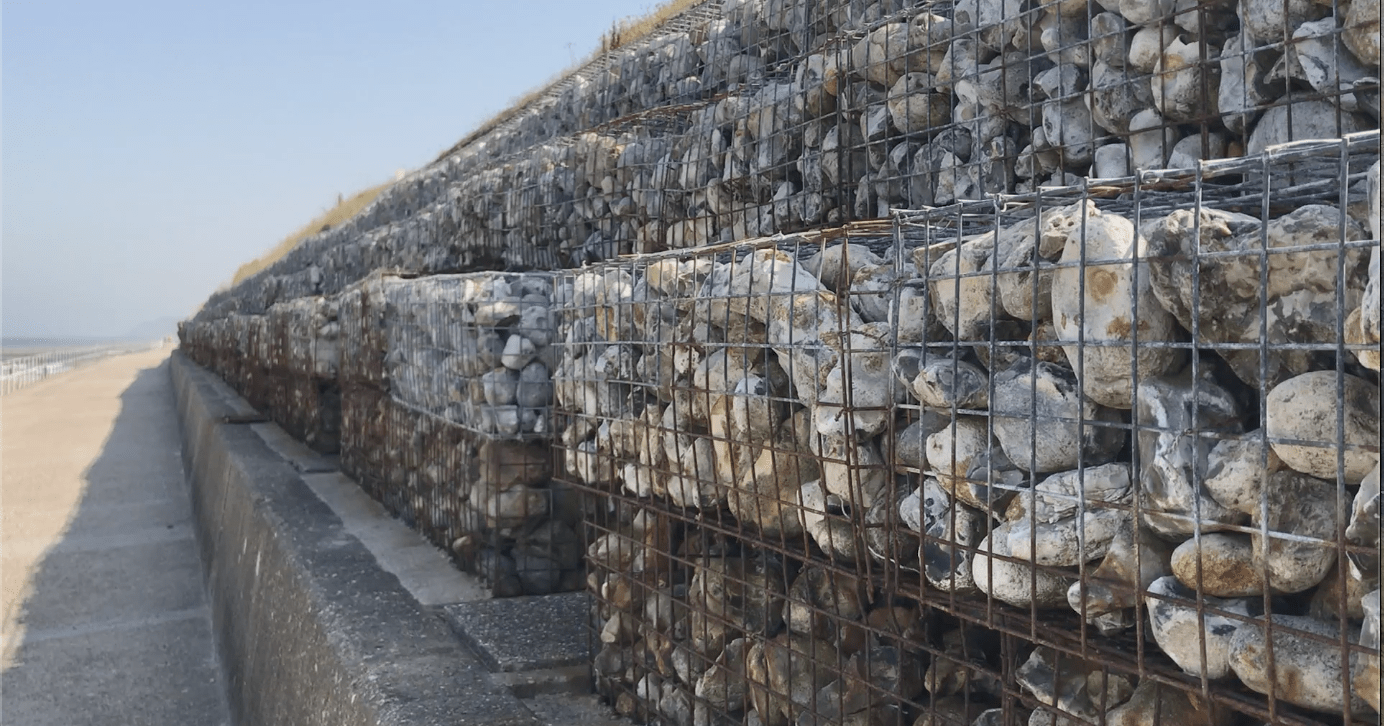
Gabion boxes (hard engineered defences)
Features | Prevent Erosion |
boxes filled with rocks placed in areas → absorb wave energy | reduce impact of waves → prevent removal of soil + beach material → stabilize slopes + shoreline areas |
