Medieval, Byzantine, and Renaissance Art Review (copy)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for Medieval, Byzantine, and Renaissance art terms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Medieval Period
A period influenced by the Fall of Rome and early Christian culture.
Dark Ages
The term "Dark Ages" refers to the early part of the Medieval Period characterized by a decline in cultural and economic activity following the Fall of Rome, as well as the dominance of feudalism and the spread of Christianity.
Middle Ages
a historical period in Europe spanning from the 5th to the late 15th century, encompassing the decline of the Roman Empire and the rise of the Renaissance. (Middle ages and Medieval are more neutral terms for this time period, which also saw significant developments in art, architecture, and education.)
Fall Of Rome
the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in AD 476, which marked the transition to the Medieval Period. (It led to political instability and influenced the rise of Christian culture and medieval society.)
Byzantine Iconoclasm
The destruction of religious images, started by Byzantine Emperor Leo III and ended by Empress Theodora in 843, marking a significant controversy in the Byzantine Empire over the veneration of icons because they were considered idolatrous.
Idolatrous
describing the worship of physical objects or images as deities, often criticized in religious contexts.

Theotokos Mosaics
Mosaics depicting Mary, the Mother of God, found in places like the Hagia Sophia, symbolizing divine protection and intercession
Theotokos
A Greek title meaning “God-bearer" or "Mother of God"
Mosaic Techniques
Techniques used to create mosaics, often with spiritual symbolism. (Art created by assembling small pieces of glass,stone, or other materials to form images.)
Hagia Sophia
A grand church built in Constantinople in the 6th century, originally serving as a cathedral and later converted into a mosque. It is renowned for its massive dome and stunning mosaics.

Ebbo Gospels
An expressive style of manuscript illumination
Scriptorium
A room in a monastery where illuminated manuscripts were created.
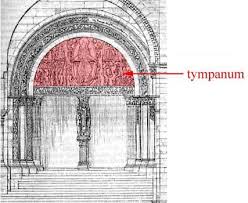
Romanesque Tympanums
Architectural features of Romanesque cathedrals, depicting scenes like the Last Judgment. (The semi-circular area above a church doorway)
Pilgrimages
Religious journeys to holy places.
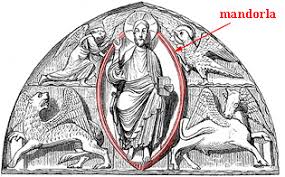
Mandorla
Almond-shaped halo. (Often surrounds figures of Christ or the Virgin Mary in Christian art, symbolizing divine light or glory)
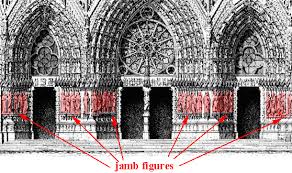
Jamb Sculptures
Sculptures found on the jambs of doorways, particularly in Gothic cathedrals.
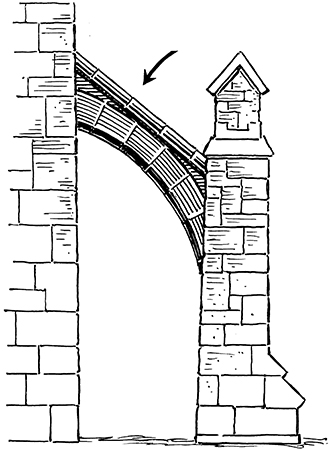
Flying Buttresses
Architectural supports that distribute the weight of Gothic cathedrals.
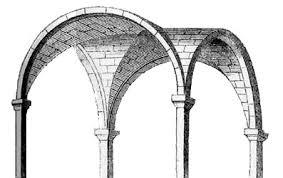
Groin Vaults
A type of vault used in Gothic architecture.
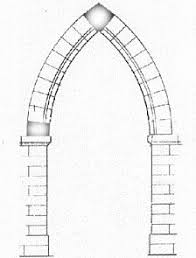
Pointed Arches
A type of arch used in Gothic architecture that allowed for taller structures (pointing to heaven)

Gallery of Kings
Carvings on the Reims Cathedral, including a series of royal figures.

Muqarnas
Decorative, honeycombs like architectural element used in islamic buildings; symbolizes divine complexity.
Abbasid Caliphate
A caliphate that influenced Islamic art and founded Baghdad.
Palatine Chapel (Sicily)
A chapel located in Palermo, known for its exquisite mosaics and mixture of Byzantine, Islamic, and Norman architectural styles.
Renaissance
A period characterized by a renewed interest in classical art and learning.
Donatello
Early Renaissance sculptor known for works like David and Mary Magdalene.

Donatello’s David
A renowned sculpture by Donatello, depicting the biblical hero David in a youthful and contemplative pose, celebrated for its naturalism, symbolizing youthful victory and divine favor. (Made by bronze)

Mary Magdalene
A wooden sculpture showing Mary as a penitent saint. This sculpture represents her in a moment of deep reflection and repentance, often characterized by her elongated form and expressive features.
Giotto
An early Renaissance artist who used naturalism and emotion to move away from the flatness of medieval art, known for his frescoes and contributions to the development of perspective.
Cimabue
An Italian painter and mentor to Giotto, credited with bridging the Byzantine and early Renaissance styles. His works often feature a strong sense of composition and religious themes.

Ognissanti Madonna
A famous altarpiece by Giotto depicting the Virgin Mary holding the Child Jesus, surrounded by saints. This work exemplifies the transition from Byzantine to Renaissance styles, showcasing Giotto's mastery of space and emotion.
Humanism
An artistic and intellectual movement emphasizing human potential and achievement.
Leonardo da Vinci
Renaissance artist known for The Last Supper.

Leonardo’s Last Supper
is a mural painting by Leonardo da Vinci, depicting the final meal shared by Jesus and his disciples before his crucifixion. The artwork captures a moment of emotional intensity and showcases Leonardo's innovative composition and use of perspective.
Michelangelo
Renaissance sculptor and painter known for Pietà, David, and the Sistine Chapel.

Michelangelo’s Pietà
is a marble sculpture representing the Virgin Mary holding the dead body of Jesus Christ, showcasing unparalleled detail and emotional expression.

Michelangelo’s David
is a renaissance marble statue of the Biblical hero David, renowned for its detail and representation of human anatomy, symbolizing strength and beauty.

Sistine Chapel (Michealangelo)
is a famous chapel in Vatican City, renowned for its Renaissance frescoes painted by Michelangelo, including 'The Last Judgment' and the 'Creation of Adam'.

Ignudi
Nude figures painted by Michelangelo on the Sistine Chapel ceiling. (Phrase coined by Michelangelo to describe the 20 seated male nudes he incorporated into the Sistine Chapel ceiling)

Sibyls
Prophetesses painted by Michelangelo on the Sistine Chapel ceiling. (Female prophets who foretold the coming of Christ and are depicted in grandeur and dramatic poses also communicated with the divine)

Chiaroscuro
The use of strong contrasts between light and dark to create dramatic effects.
Renaissance
The ‘rebirth’ of Greek and Roman ideals.
Petrarch
An Italian poet who called the Medieval period the 'Dark Ages'.
Guilds
Associations or groups of craftsmen to promote interests of their members.
Christendom
A kingdom with the political, social, and legal life of a nation that is inspired by the gospel ethic.
Gospels
Christian scripture that documents the life of Jesus Christ.
Jizya
A special tax required of non-Muslims
Iconoclasm
Breaking of images
graeco-arabic translation movement
Greek philosophy and literature translated into arabic.
Qur'an Patterns are used to represent
the eternal nature of God
Norman
Descendents of viking who settled in normandy, became christian, and defended france from viking brethren
Saints
Lived heroically virtuous lives, offered their life for others or were martyred for the christian faith, and who are worthy of imitation
Scriptorium
Writing room within the monastery
Codex
A book made of sheets bound on one edge (an alternative to the scroll)
Historiated capitals
A capital decorated with figure of animals, birds, or human
Pilgrimage
Religious journey to a holy place
Low relief
sculpture that projects slightly from the surface
Ascetic
practicing extreme self-denial
Memento mori
Reminder of death
EL DIVINO
Michelangelo's Nickname, deeply religious
Bonfire of vanities
collecting and burned thousands of objects such as cosmetics, arts and books in the public square of florence.
Fresco
painting on a wall