Urinalysis & Body Fluids
1/243
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
244 Terms
first morning specimen (description and uses (4))
patient void upon waking, most concentrated and specimen of choice
1. substances requiring concentration or refrigeration
2. confirm postural proteinuria
3. cytology samples
4. routine urinalysis
random urine specimen (description and uses (3))
collected anytime, most convenient, least accurate
1. routine urinalysis
2. cytology studies (requires hydration)
3. fluid depravation tests
timed collection (description and uses (4))
all urine collected during time interval
1. albumin, microalbumin, creatinine
2. clearance tests
3. quantitative chemical analysis
4. evaluation of fistula
random void (technique and purpose (1))
no patient prep, just void into container
1. routine urinalysis
midstream "clean catch" (technique and purposes (2))
void into toilet, void into cup, void rest into toilet
1. routine urinalysis
2. urine culture
catheterized (technique and purposes (3))
sterile catheter inserted through urethra to bladder and urine accumulates into bag, or past bladder into ureters
1. bacterial culture
2. routine screening
3. determine and differentiate between kidney infections
suprapubic aspiration (technique and purposes (2))
directly aspirated from bladder using sterile syringe
1. bacterial cultures
2. infants
pediatric collection (technique and purposes (3))
urine collection bag, high risk for contamination
1. children
2. routine screening
3. quantitative assays
most common way to preserve urine
refrigeration
things increasing in unpreserved urine (2)
1. bacteria
2. nitrite
exclusive site of plasma filtration
cortex
areas of kidney (2)
cortex (outer) and medulla (inner)
flow of urine through kidney
kidneys -> glomerulus -> PCT -> descending limb -> loop of henle -> ascending limb -> DCT -> collecting duct -> papilla -> minor calyx -> major calyx -> renal pelvis -> ureter -> bladder -> urethra
components of glomerular filtration system (3)
1. capillary endothelial cells
2. basement membrane
3. podocytes
how glomerular filtration works
ultrafiltration is passive, nonselective process based on size and charge
primary functions of kidney (5)
1. filtration of blood
2. acid-base
3. fluid/electrolyte balance
4. urine formation
5. hormone regulation
direct active transport
movement of substances across membrane against gradient - exchange of substances
indirect active transport
movement of substances across membrane against gradient - one solute pairs with another
passive transport
requires no energy, movement across membrane along gradient
tubular reabsorption
takes back substances necessary for maintenance of body homeostasis and function
tubular secretion
eliminates waste and other substances not normally present in plasma, adjusts acid-base equilibrium
water is always what kind of transport
passive
PCT function (3)
1. reabsorb 66% of water potassium, chloride, urea - passive
2. reabsorb 100% of glucose, amino acids, proteins - indirect active
3. reabsorb sodium, chloride, and other solutes - active
descending loop of henle function (1)
1. water and urea - passive
ascending loop of henle function (1)
1. sodium, chloride, urea - passive
NO WATER
DCT function (2)
1. sodium, chloride, sulfate, uric acid - active
2. water - passive
collection duct function (3)
1. water and chloride - passive
2. sodium - active
3. water and urea - passive
first mechanism
hydrogen and bicarbonate
second mechanism
phosphate
third mechanism
ammonia
aldosterone/RAAS (reabsorbs, conditions released, parts of nephrons acted on, where secreted from)
1. sodium
2. decreased sodium, decreased blood pressure, decreased blood volume
3. DCT and collecting duct
4. kidney
ADH (reabsorbs, conditions released, parts of nephrons acted on, where secreted from)
1. water
2. decreased arteriole pressure
3. DCT and collecting duct
4. hypothalamus
RAAS system
renin released -> angiotensin II -> aldosterone
polyuria
excessive urine (>3L)
oliguria
decreased urine (<400mL)
anuria
no urine
nocturia
excessive urination at night
osmolality
expression of solute concentration in osmoles of solute particles per kg solvent
specific gravity
expression of solute concentration that relates density of urine to water
processes of urine formation (3)
1. glomerular filtration
2. tubular reabsorption
3. tubular secretion
normal urine volume
1200 mL/day
normal urine solutes (8)
1. urea
2. chloride
3. sodium
4. potassium
5. phosphate
6. sulfate
7. creatinine
8. uric acid
substance that best differentiates urine
creatinine
creatinine clearance test
most commonly used clearance test for assessment of glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
creatinine clearance test equation
((U x V)/P)(1.73 m2/SA)
specific gravity - test reaction

specific gravity - test principle
protons released from polyelectrolyte decreases pH
leukocyte esterase - test reaction
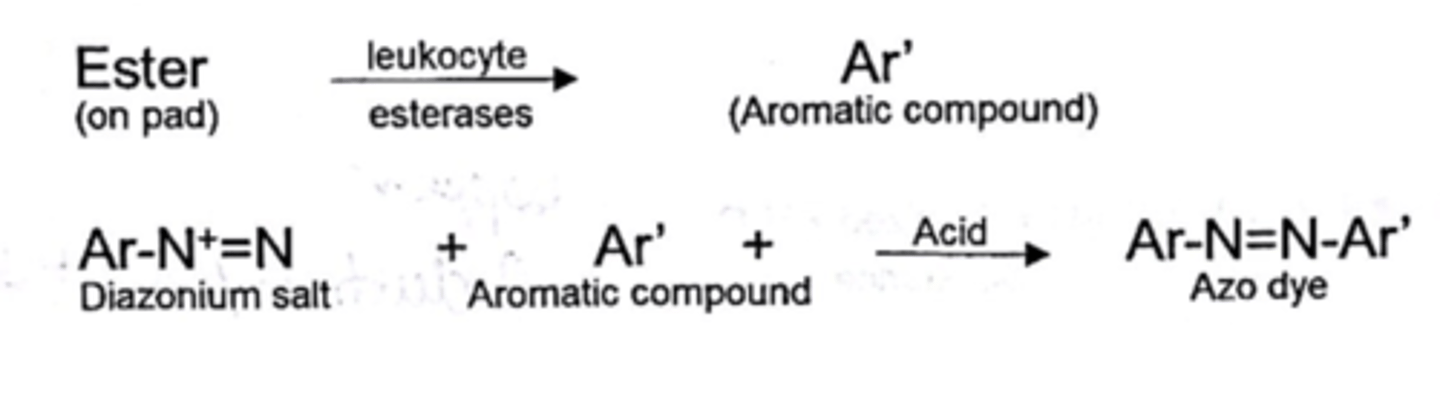
leukocyte esterase - test principle
esterase reaction followed by azo coupling reaction
leukocyte esterase - clinical significance
small amount normal, detects WBC
leukocyte esterase - false positives (2)
1. contamination
2. drugs or food causing sample to be red or pink
leukocyte esterase - false negatives (3)
1. increased protein or glucose
2. high specific gravity
3. antibiotics and strong oxidizers
leukocyte esterase - specificity
doesn't detect lymphocytes
leukocyte esterase - sensitivity
1. chemstrip - 10 WBC/microliter
2. multistix - 11-36 WBC/microliter
CHEMSTRIP MORE SENSITIVE
nitrite - test reaction
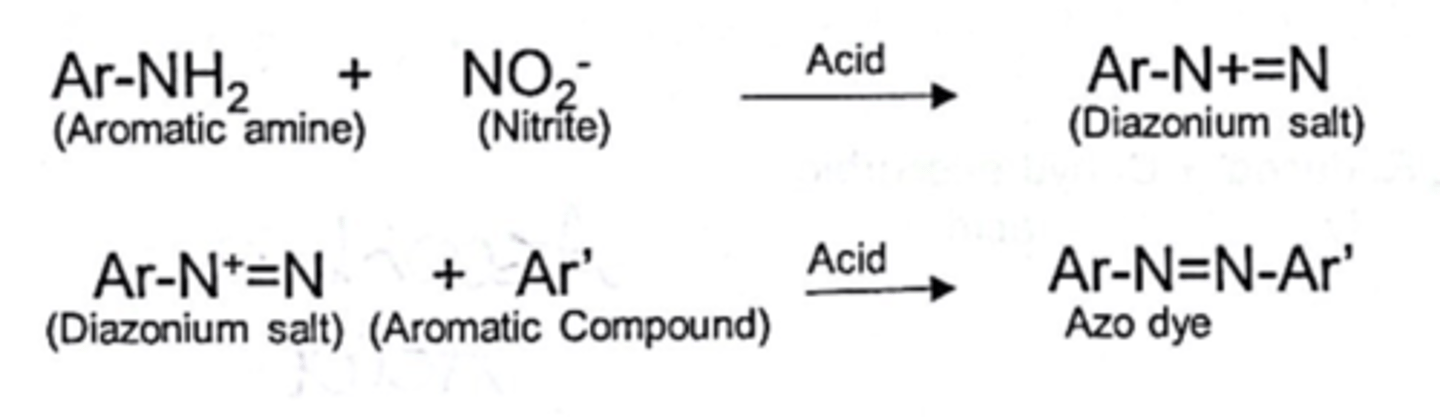
nitrite - test principle
diazo reaction followed by azo coupling reaction
nitrite - clinical significance
UTIs
nitrite - false positives (2)
1. colored substances masking results
2. improper storage
nitrite - false negatives (2)
1. ascorbic acid
2. factors that inhibit nitrite formation
nitrite - specificity
needs enough time to convert, bacteria has to have enzyme to convert, nitrate must be present
nitrite - sensitivity
1. chemstrip - 0.05 mg/dL
2. multistix - 0.06 mg/dL
CHEMSTRIP MORE SENSITIVE
glucose - test reaction
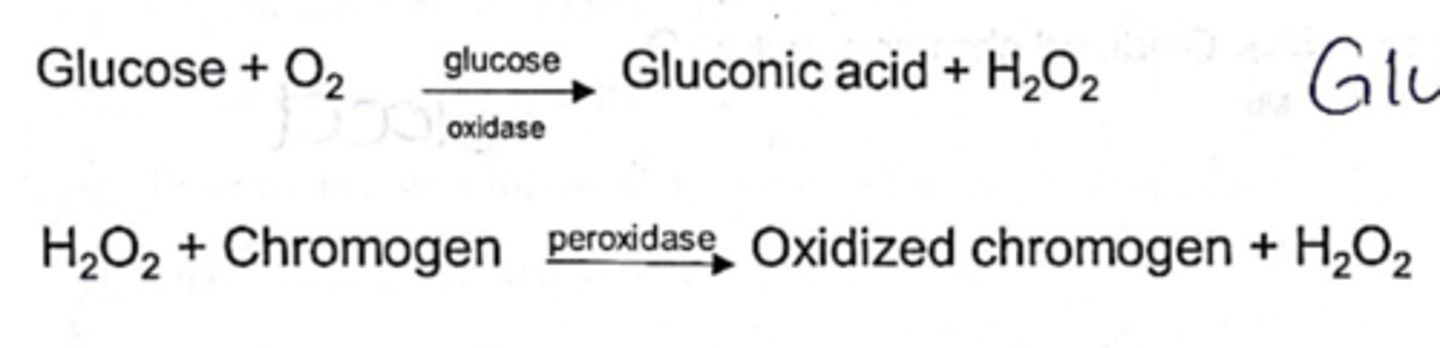
glucose - test principle
double sequential enzyme reaction
glucose - clinical significance
hypergycemia, defective tubular absorption, diabetes mellitus
glucose - false positives (2)
1. strong oxidizing agents
2. peroxidase contaminants
glucose - false negatives (2)
1. ascorbic acid
2. improper storage
glucose - specificity
only detects glucose, not other reducing sugars
glucose - sensitivity
1. chemstrip - 40 mg/dL
2. multistix - 75-125 mg/dL
CHEMSTRIP MORE SENSITIVE
bilirubin - test reaction
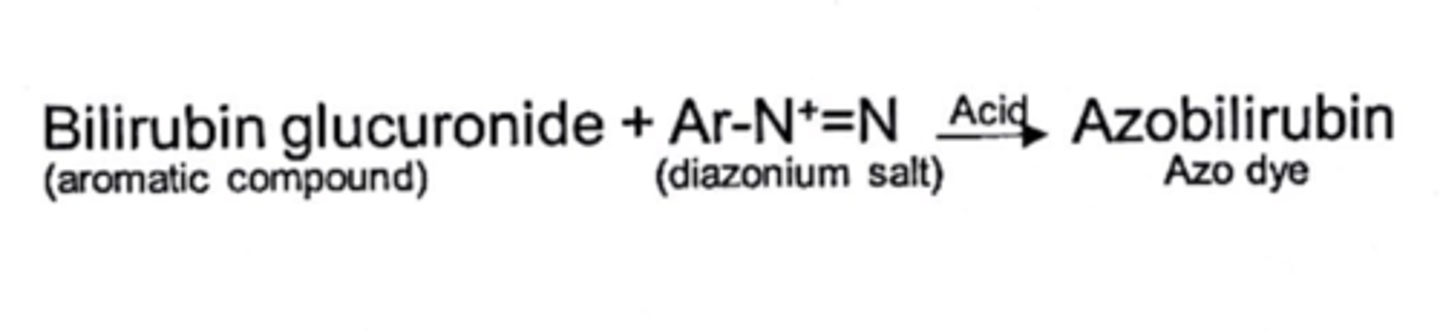
bilirubin - test principle
azo coupling reaction
bilirubin - clinical significance
any detectable amount clinically significant, elevated levels in different disease states, post-hepatic conditions
bilirubin - false positives (1)
1. drug induced color changes
bilirubin - false negatives (3)
1. ascorbic acid
2. high nitrite
3. improper storage
bilirubin - sensitivity
1. chemstrip - 0.5 mg/dL
2. multistix - 0.4-0.8 mg/dL
ABOUT EQUALLY SENSITIVE
urobilinogen - test reaction

urobilinogen - test principle
classic ehrlich's reaction
urobilinogen - clinical significance
small amount normal, prehepatic conditions
urobilinogen - false positives (2)
1. any other ehrlich's substance
2. atypical colors
urobilinogen - false negatives (2)
1. formalin
2. improper storage
urobilinogen - sensitivity
1. chemstrip - 0.4 mg/dL
2. multistix - 0.2 mg/dL
bilirubin metabolism
RBC -> breaks into heme molecule -> unconjugated bilirubin + albumin sent to liver -> liver converts to conjugated bilirubin + glucuronic acid -> small intestine reduces bilirubin into urobilinogen -> urobilinogen reabsorbed or excreted into urine
prehepatic conditions
increased urobilinogen in urine and no bilirubin, hemolytic conditions
hepatic conditions
both urobilinogen and bilirubin in urine, liver diseases
posthepatic conditions
increased bilirubin in urine, obstructions
neutrophil functions (2)
1. protect body from infection using phagocytosis
2. common in bacterial infections
lymphocyte functions (3)
1. antibody production
2. mediate immune response
3. killing tumor cells or virus infected cells
monocyte functions (3)
1. phagocytosis
2. antigen presentation
3. removal of debris and dead cells
eosinophil functions (3)
1. allergic reaction
2. chronic inflammation
3. parasites
basophil functions (3)
1. mediate immune response
2. initiate allergic inflammation
3. hypersensitivity reactions
fluids mesothelial cells can be found in
pleural, peritoneal, pericardial
factors controlling serous fluid formation (4)
1. permeability of capillaries in parietal membrane
2. hydrostatic pressure in these capillaries
3. oncotic pressure produced by presence of plasma proteins
4. absorption of fluid by lymphatic system
synovial fluid functions (2)
1. joint lubrication
2. nutrients for articular cartilage
synovial fluid formation
ultrafiltrate of plasma across synovial membrane + synoviocyte secretions
arthrocentesis
surgical puncture of a joint to remove fluid
synovial fluid tubes
1. plain red top tube for chemical and immunologic evaluation
2. anticoagulant tube (lavender/EDTA) for microscopic examination and cell counts
3. sterile tube (with or without anticoagulant/yellow top) for microbiological studies
lumbar puncture indications (6)
1. infections
2. hemorrhage
3. neurologic disease
4. malignancy
5. tumor
6. treatments
lumbar puncture procedure (adults, children)
1. third or fourth lumbar space
2. fourth or fifth lumbar space
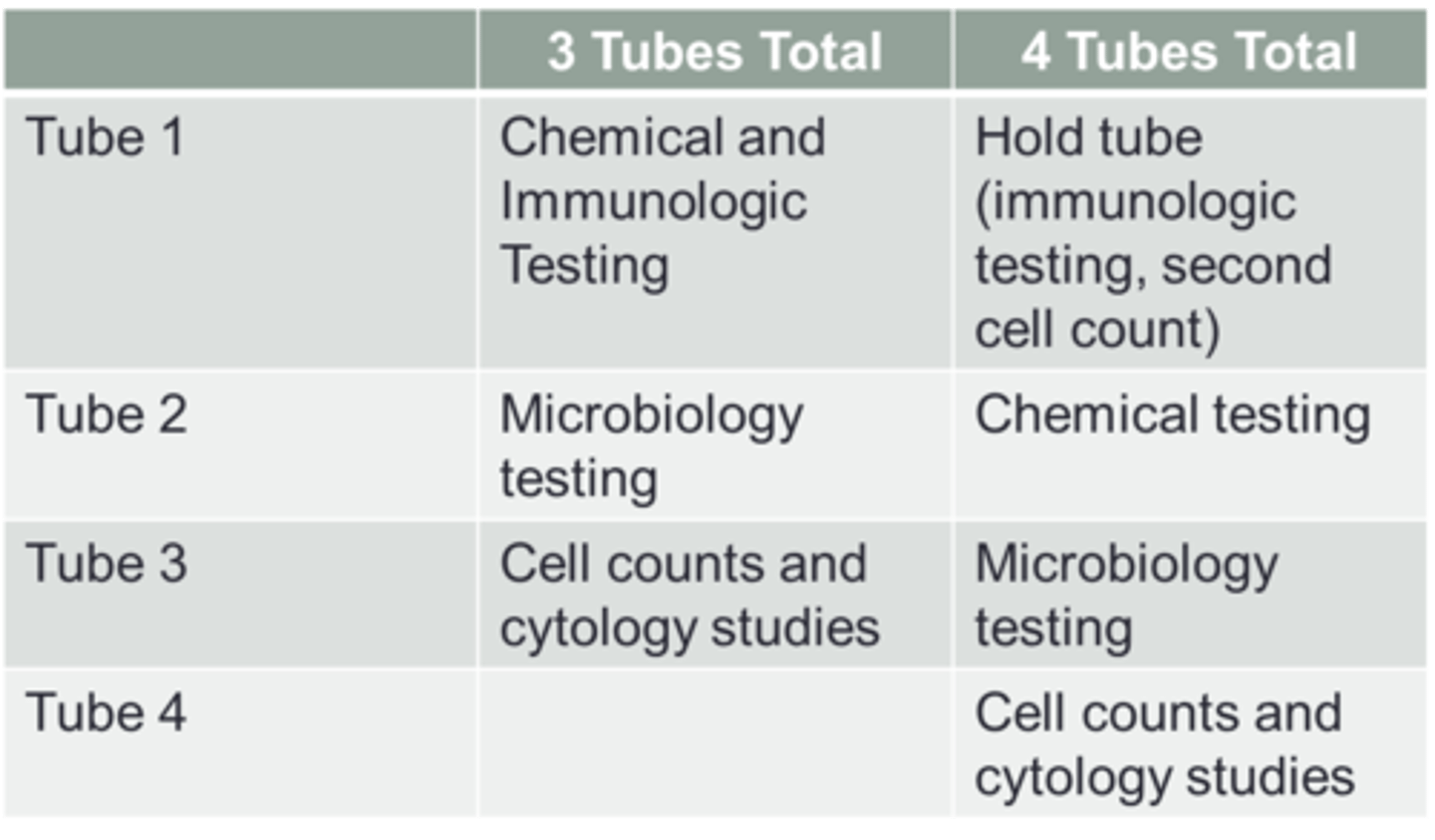
csf tubes
normal csf
clear and colorless
pleocytosis
increased number of cells in csf