BISC 1112: MA2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:31 AM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
polyploidy
an individual getting one or more additional sets of chromosomes; occurs most often in plants
2
New cards
autopolyploid
an individual that has more than two chromosome sets, all derived from a single species
3
New cards
hybrid zones
a geographic region in which members of different species meet and mate, producing at least some offspring of mixed ancestry
4
New cards
adaptive radiation
a period of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptations allow them to fill different ecological roles in their communities
5
New cards
Linnean system of classification
(most inclusive) domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species (most exclusive); mnemonic:
Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Soup
Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Soup
6
New cards
phylogenetic tree
an evolutionary tree that shows the evolutionary relationships between different groups of taxa
7
New cards
cladistics
the study of resemblances among clades
8
New cards
cladogram
a depiction of patterns of shared characteristics among taxa
9
New cards
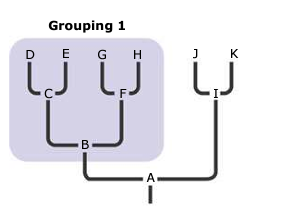
monophyletic clade
a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and all of its descendants
10
New cards
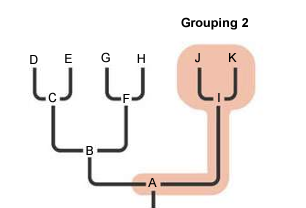
paraphyletic clade
a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
11
New cards
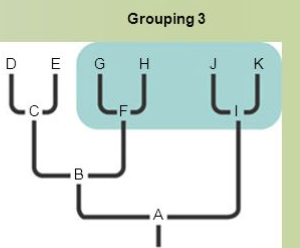
polyphyletic clade
a group of taxa that includes distantly related organisms but does not include their most recent common ancestor
12
New cards
how old is the Earth?
4\.6 billion years old
13
New cards
when did life begin?
4 billion years ago
14
New cards
when did humans emerge?
300,000 years ago
15
New cards
what is the first evidence of life?
stromatolites: layered deposits formed by cyanobacteria
16
New cards
Miller-Urey experiment (1953)
simple inorganic compounds transform into organic ones by mimicking an ancient atmosphere
17
New cards
what was the first genetic material?
RNA; RNA molecules called ribozymes have been found to catalyze many different reactions
18
New cards
know the extinctions
19
New cards
oxygen in the atmosphere
in the beginning, there was little or no oxygen in the atmosphere; autotrophic organisms started around 4 billion years ago and with that, photosynthesis (making organic compounds from inorganic ones)
20
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
theory that mitochondria and plastids originated as prokaryotic cells engulfed by a host cell; the engulfed cell and its host cell then evolved into a single organism; Lynn Margulis
21
New cards
mass extinctions
decreased biodiversity drastically
22
New cards
Cambrian explosion
refers to the sudden appearance of fossils resembling modern phyla in the Cambrian period (535 to 525 million years ago); possible causes: new predator-prey relationships, rise in atmospheric oxygen, evolution of the Hox gene
23
New cards
Hox gene
24
New cards
embryophytes
multicellular, dependent embryo; apical meristems; walled spore (in sporangia) protected by sporopollenin (a polymer); multicellular gametangia and sporangia; alternation of generations
25
New cards
apical meristems
26
New cards
sporopollenin
covers the outer layer of pollen
27
New cards
gametangia
28
New cards
sporangia
29
New cards
life cycle of a moss
30
New cards
animals
multicellular; heterotrophic eukaryotes; have tissues that develop from embryonic layers
31
New cards
animal characterization
symmetry (radial, bilateral, or no symmetry); germ layers (diploblastic or triploblastic); cleavage/coelom formation/blastopore fate (protostome or deuterstome)
32
New cards
radial symmetry
the body is shaped like a pie or barrel (lacking a left side and a right side) and can be divided into mirror-imaged halves by any plane through its central axis
33
New cards
bilateral symmetry
a central longitudinal plane divides the body into two equal but opposite halves (types: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior)
34
New cards
describe animal embryonic development
zygote → cleavage → blastula (hollow ball of cells) → gastrulation (blastula-stage embryo folds inward) → gastrula (formation of three layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm)
35
New cards
ectoderm
outer germ layer; forms skin and nervous system
36
New cards
mesoderm
middle germ layer; forms muscles, organs, and red blood cells
37
New cards
endoderm
innermost germ layer; forms digestive system
38
New cards
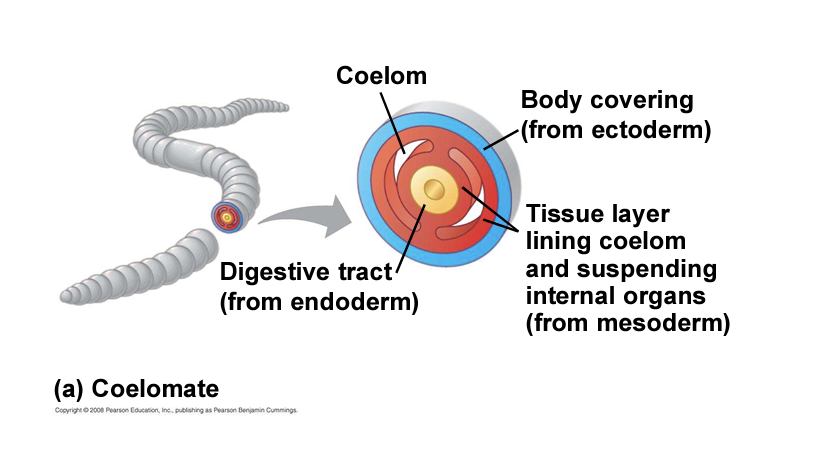
coelomates
posses a true coelom (body cavity)
39
New cards
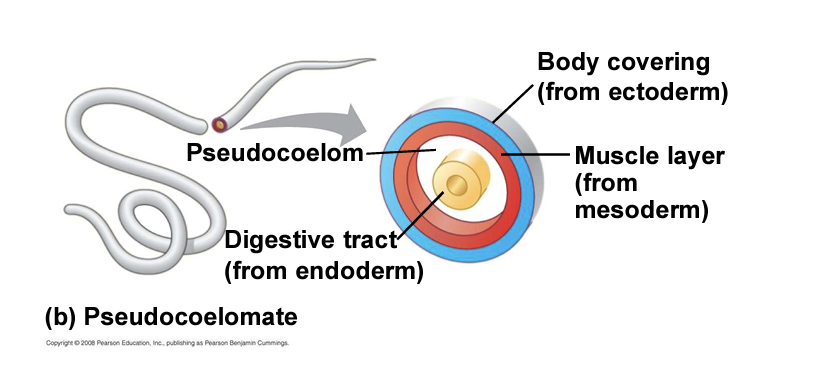
pseudocoelomates
have a body cavity
40
New cards
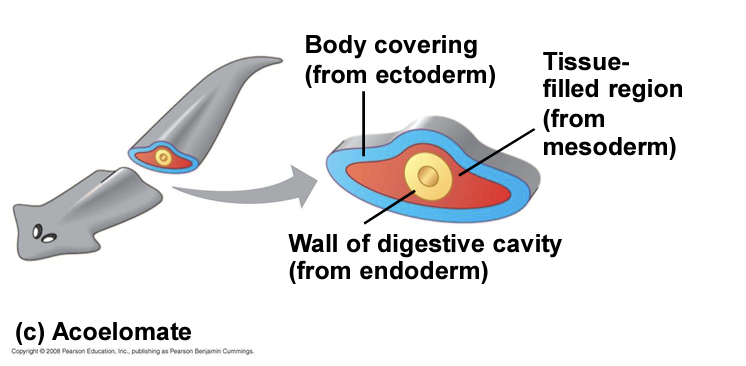
acoelomates
lack a coelom (body cavity)
41
New cards
blastopore
in a gastrula, the opening of the archenteron that typically develops into the anus in deuterostomes and the mouth in protostomes
42
New cards
protostomes
mouth forms first from blastopore
43
New cards
deuterostomes
anus forms first from blastopore
44
New cards
characters that distinguish humans from other apes
upright posture and bipedal locomotion; larger brains; language capabilities and symbolic thought; the manufacture and use of complex tools; shortened jaws; shorter digestive tract
45
New cards
evidence for early bipedalism
fossilized footprints at Laetoli, Tanzania
46
New cards
Hox genes
family of regulatory genes that encode transcription factors and are essential during embryonic development
47
New cards
incomplete metamorphosis
each nymphal stage looks like a small version of the adult but getting slightly bigger with age
48
New cards
complete metamorphosis
the larval body is always markedly different in form from that of the adult
49
New cards
retrieval practice
self-quizzing; retrieving knowledge from memory
50
New cards
spaced out practice
studying information more than once over time
51
New cards
interleaving
mixing up topics and finding connections between them
52
New cards
elaboration
finding additional layers of meaning to new material: relating material to what you already know, explaining it to someone else in your own words
53
New cards
generation
attempting to answer a question or solve a problem before seeing the solution
54
New cards
reflection
reviewing what you learned in class and asking yourself questions
55
New cards
calibration
the act of aligning your judgments of what you know and don’t with objective feedback
56
New cards
mnemonic devices
handy ways to store information