microscope parts + functions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
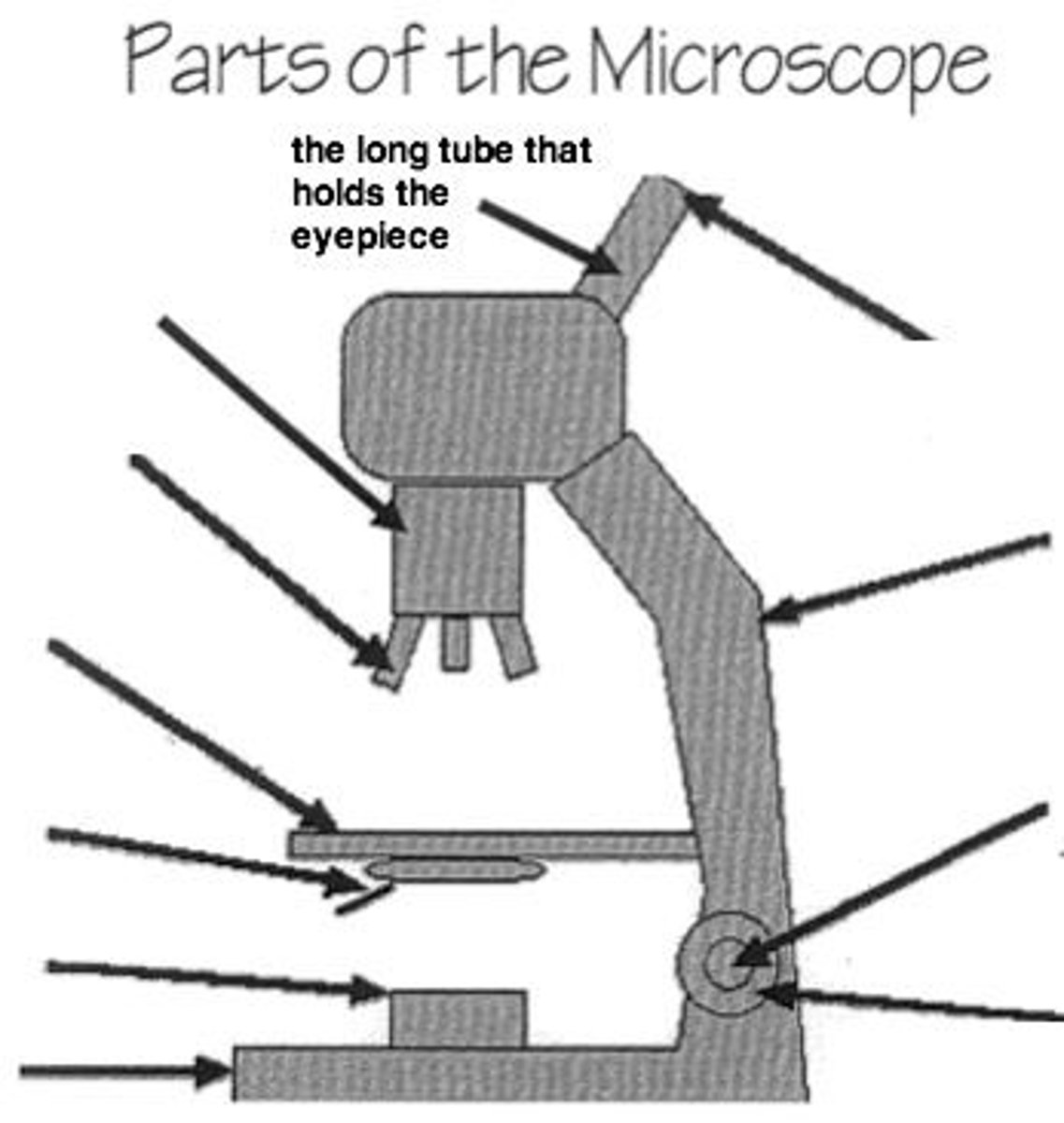
ocular lens
part of the microscope you look through and it magnifies the image produced by the objective lens
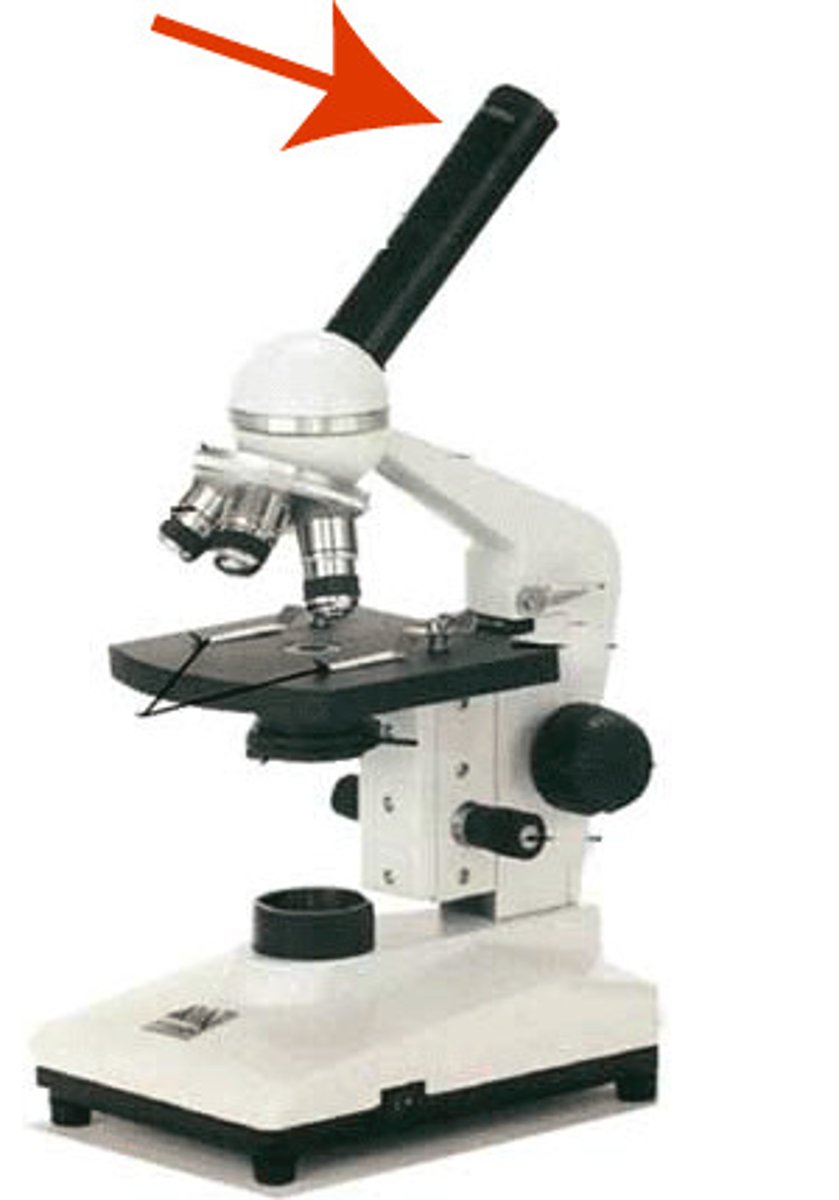
body tube
connects ocular and objective lenses, aligning light to the viewer's eye.
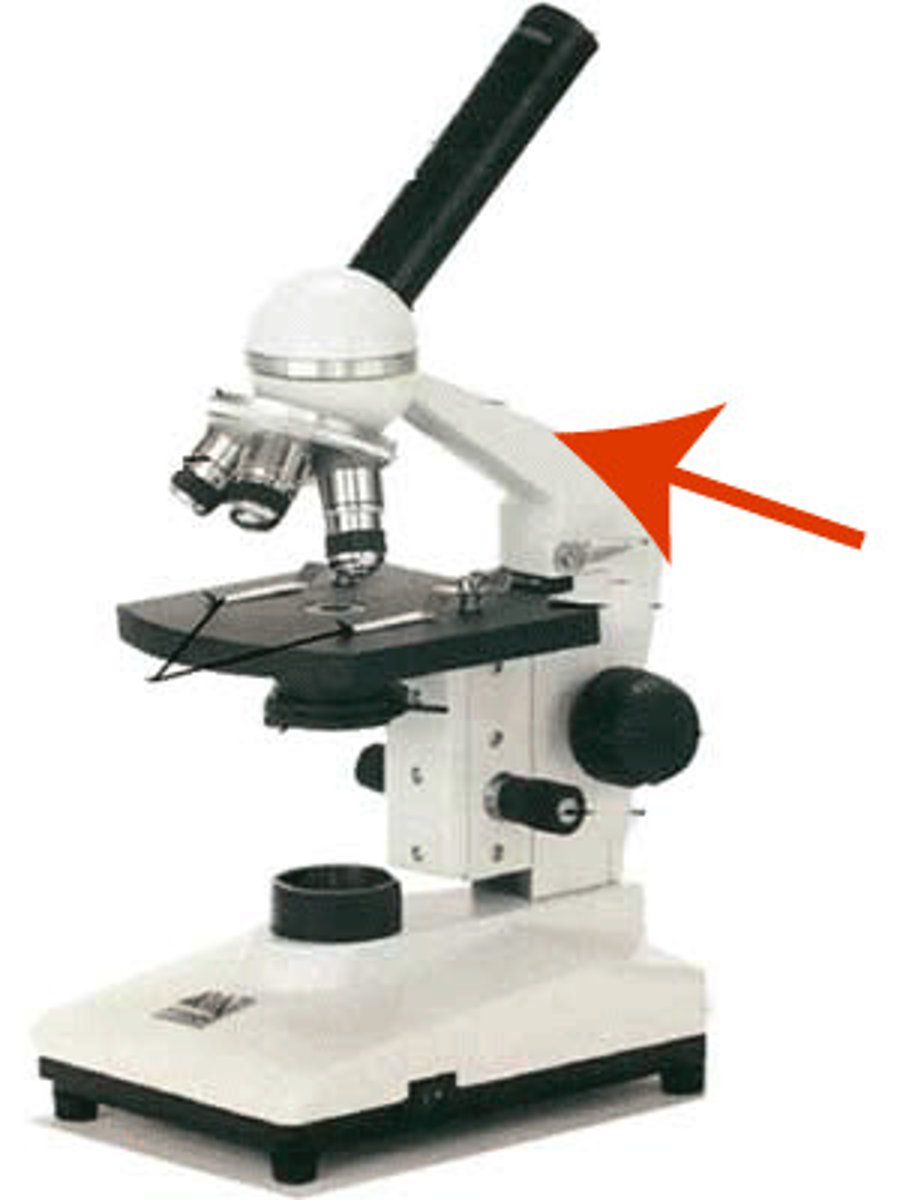
arm
connects the body tube to the base. one hand should be around this when carrying a microscope.
coarse adjustment knob
first knob used for large focus adjustments, used only under low power.
fine adjustment
the second knob you should use under higher power for exact focusing.
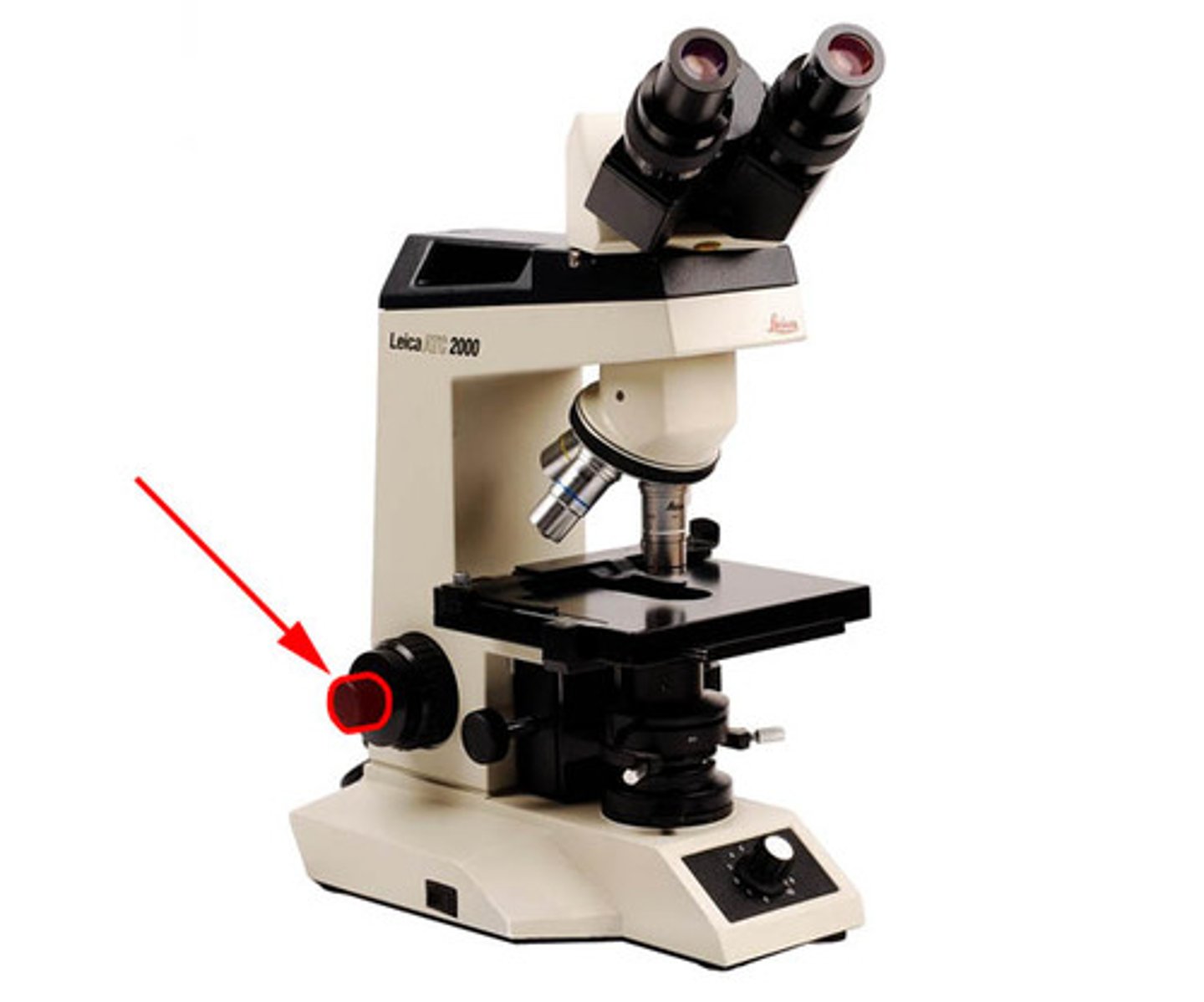
revolving nosepiece
holds the objective lens and can be rotated to change the magnification.
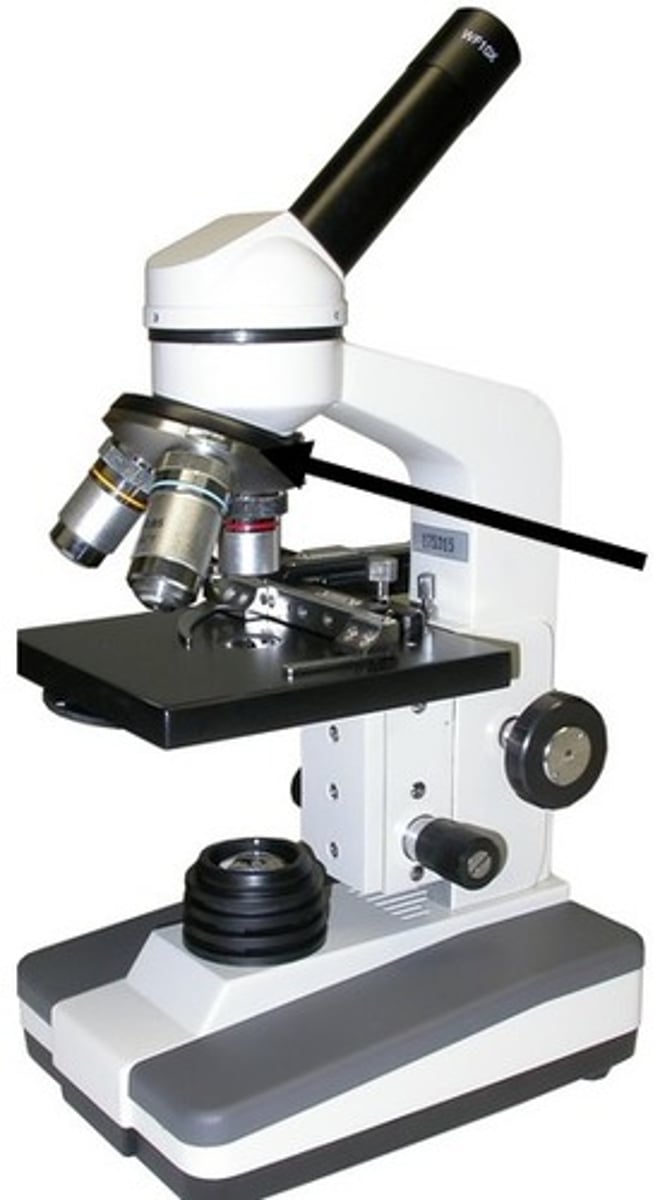

objective lenses
adjustable lens system that permits the use of a low power lens, a medium lens, or a high power lens
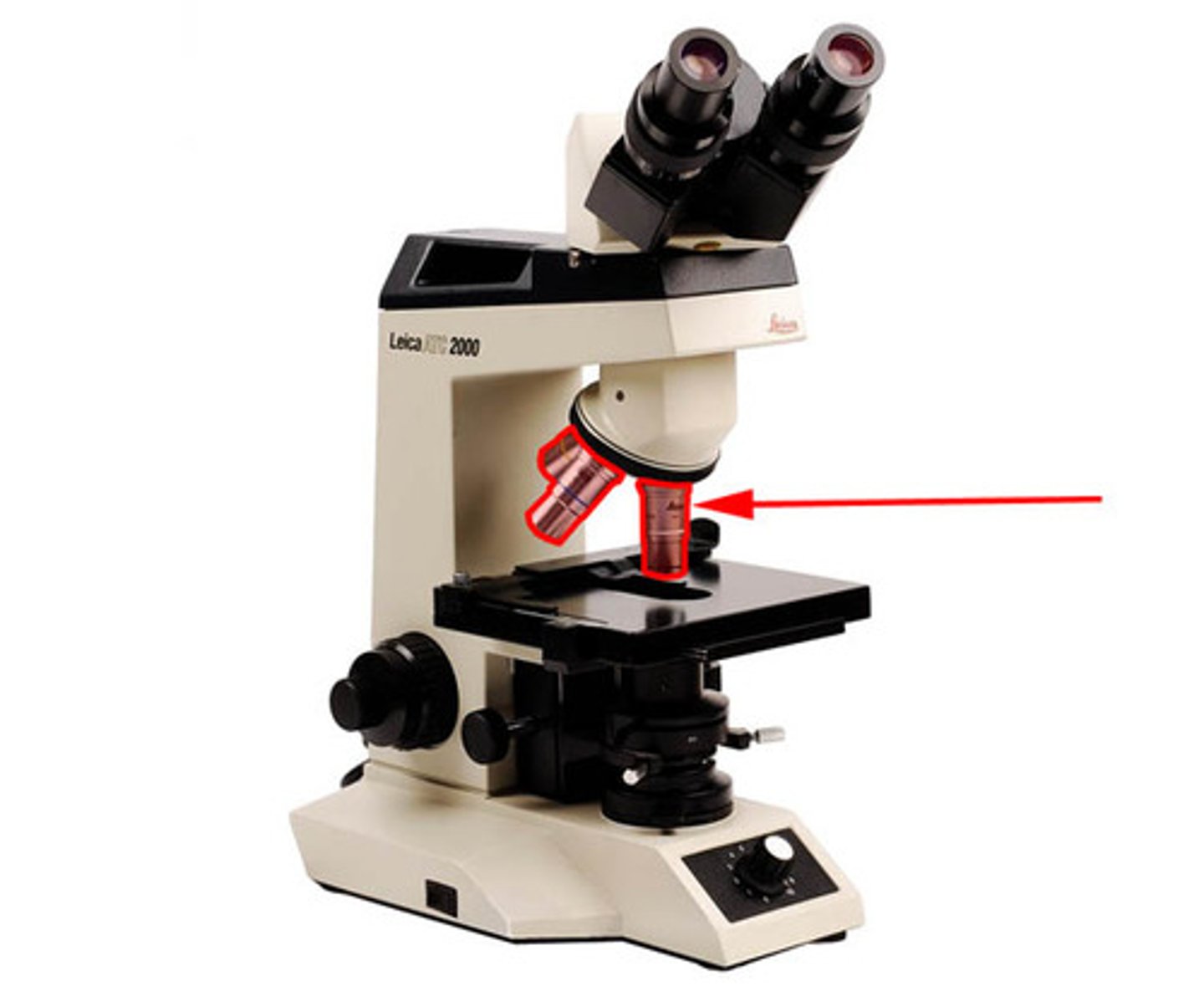
scanning power
this objective lens provides the lowest magnification, 4x
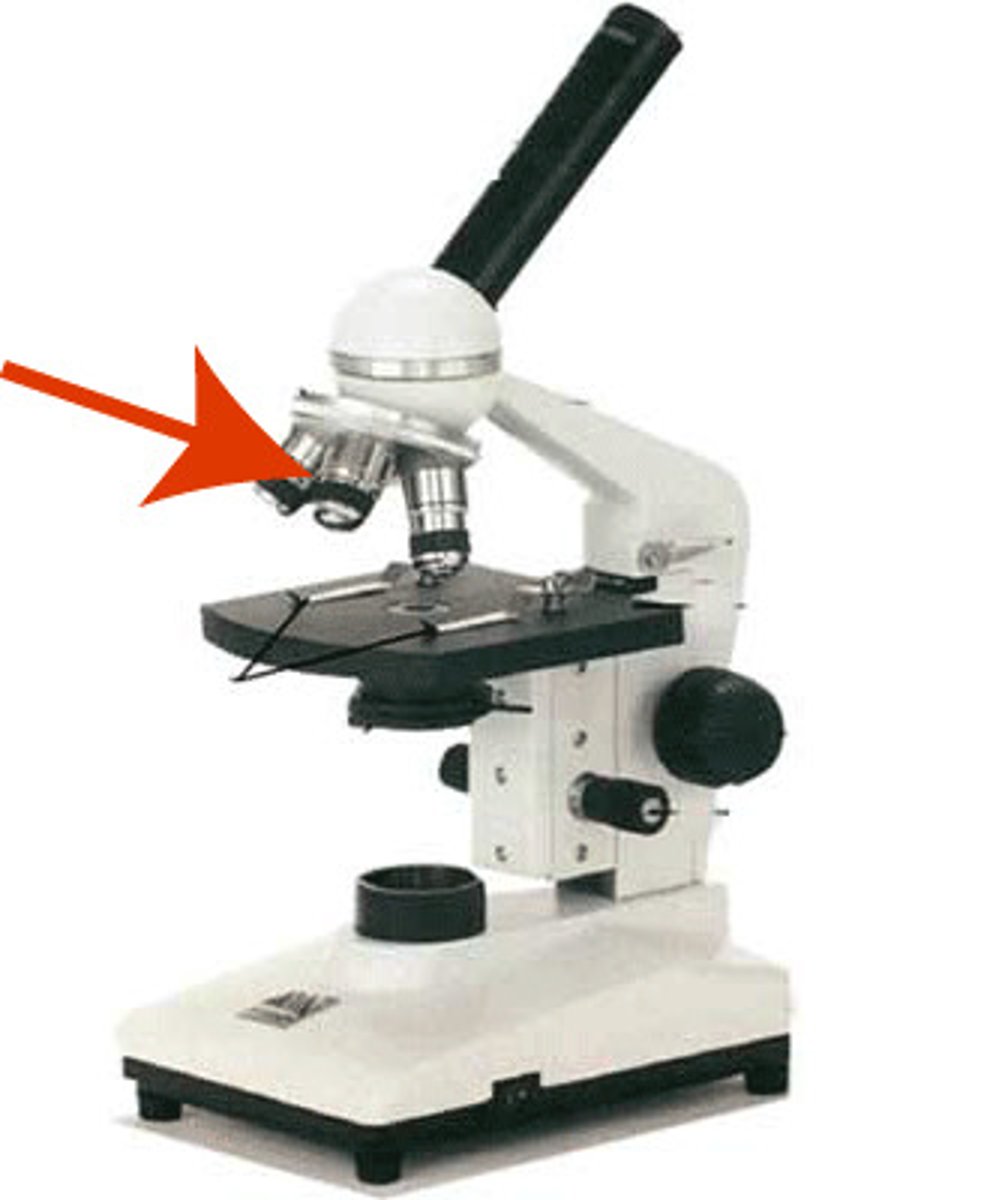

low power
this objective lens provides a low magnification, or power, 10x
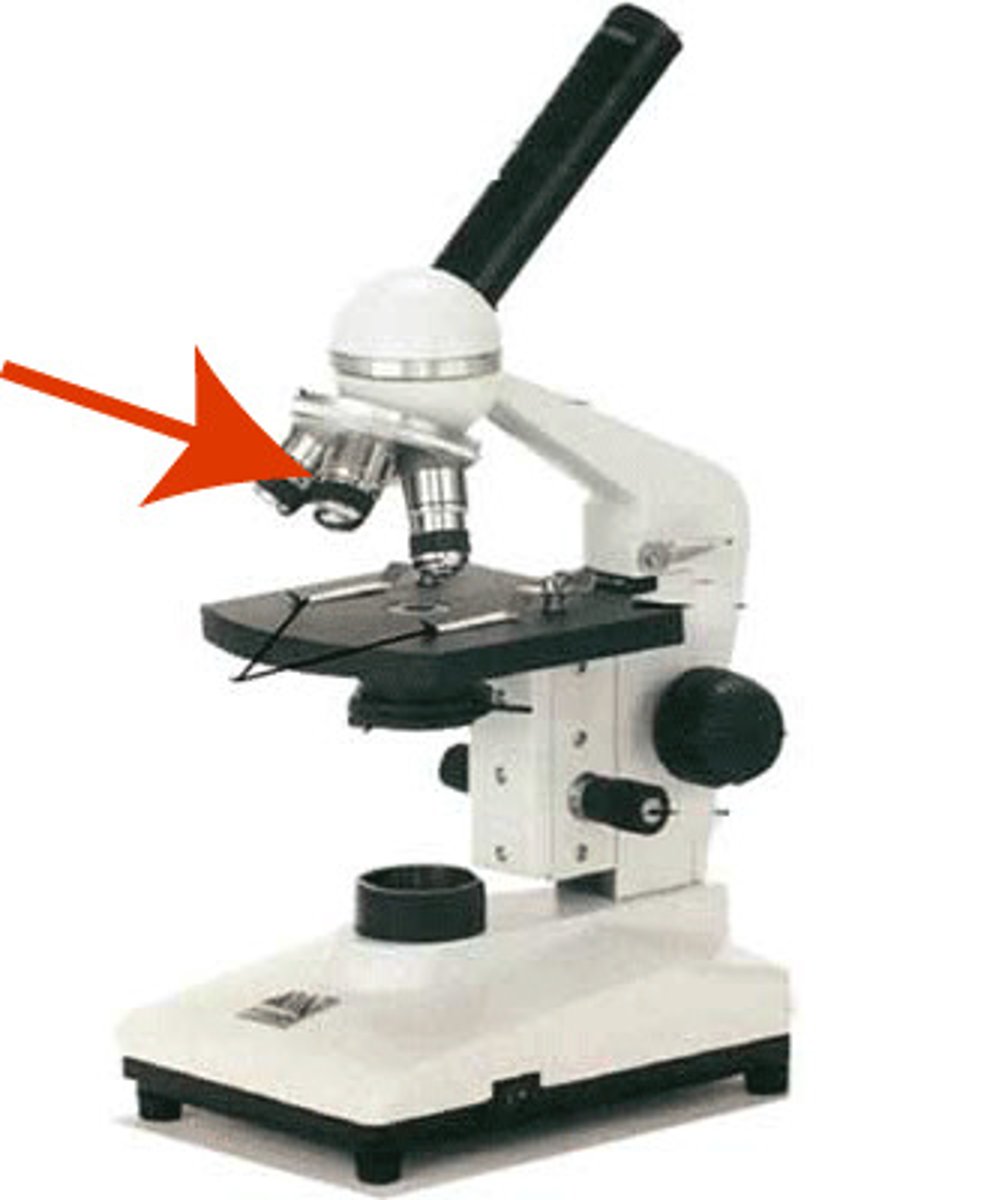

high power
this objective lens provides the highest magnification, 40x
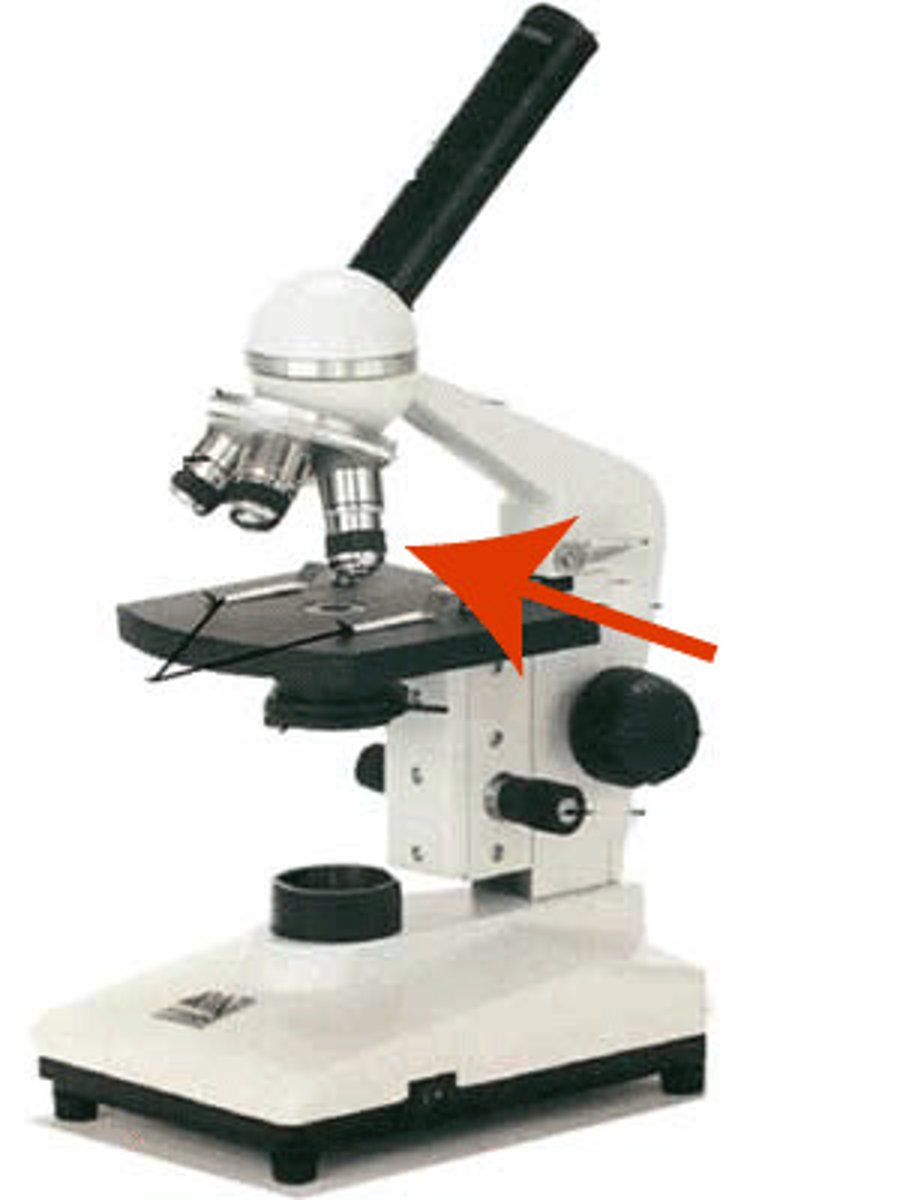
stage
where you place the slide containing the specimen; it contains a hole that allows light to pass through the stage and onto the specimen.
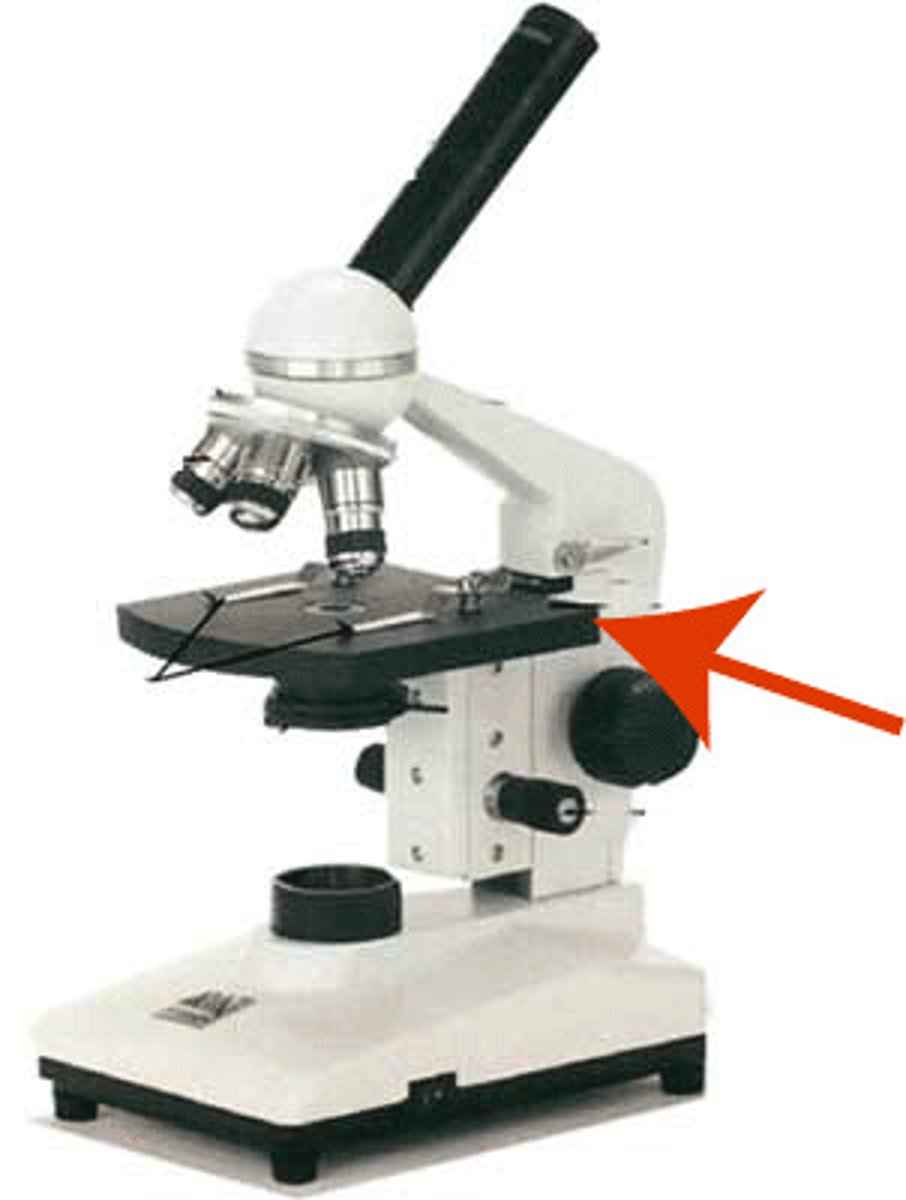
stage clips
holds the slides in place on the stage for viewing.
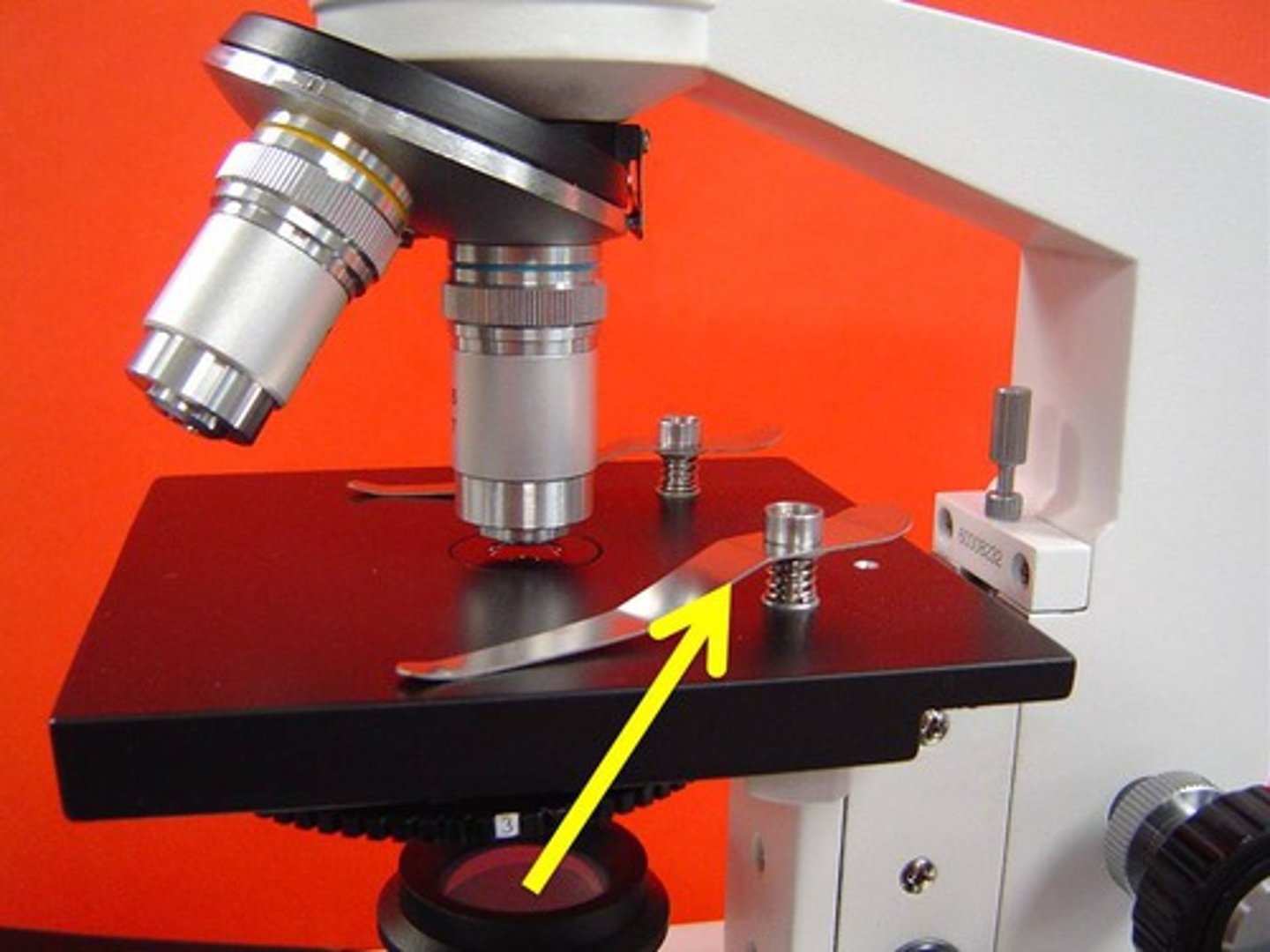

diaphragm
adjusts amount of light reaching the specimen.
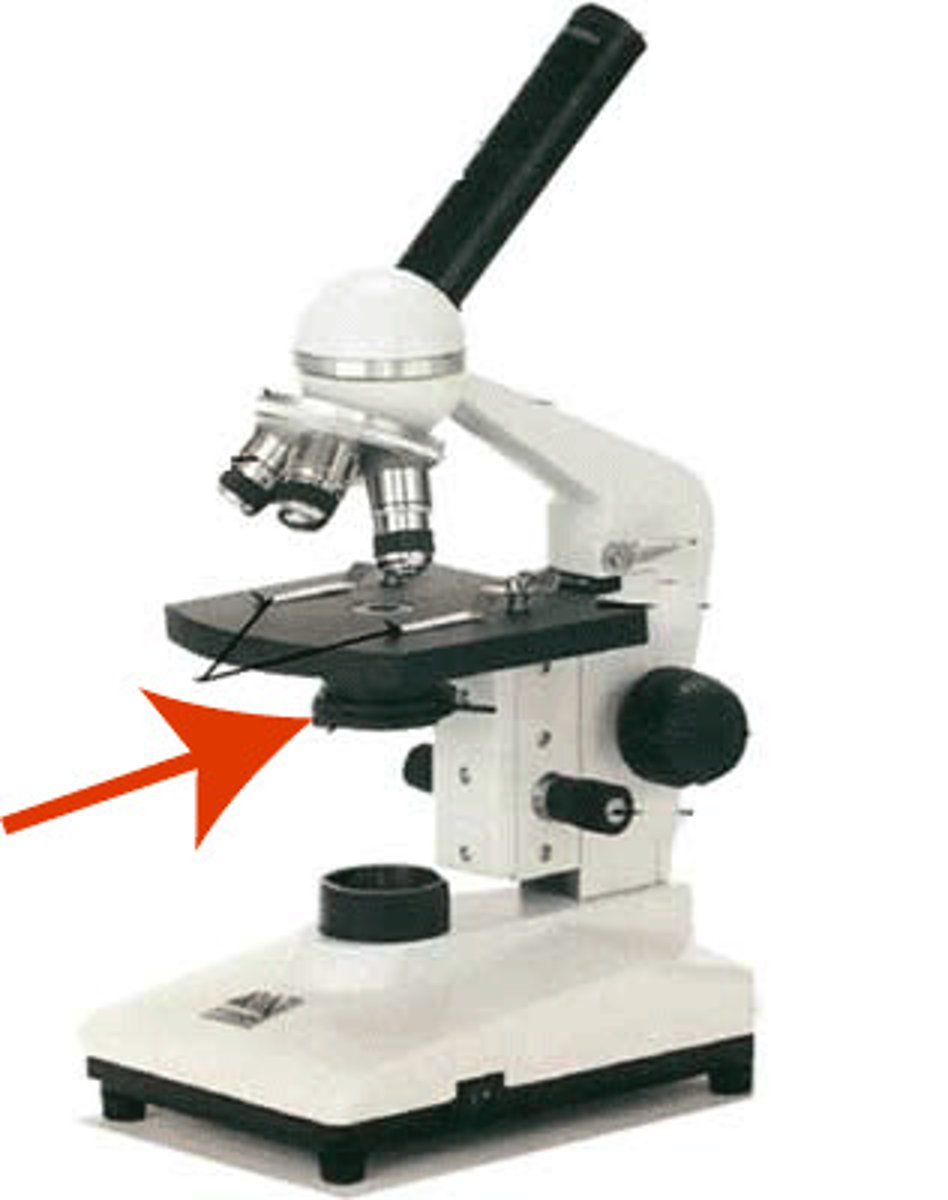
base
supports the weight of the microscope. contains the electronics and the light source.
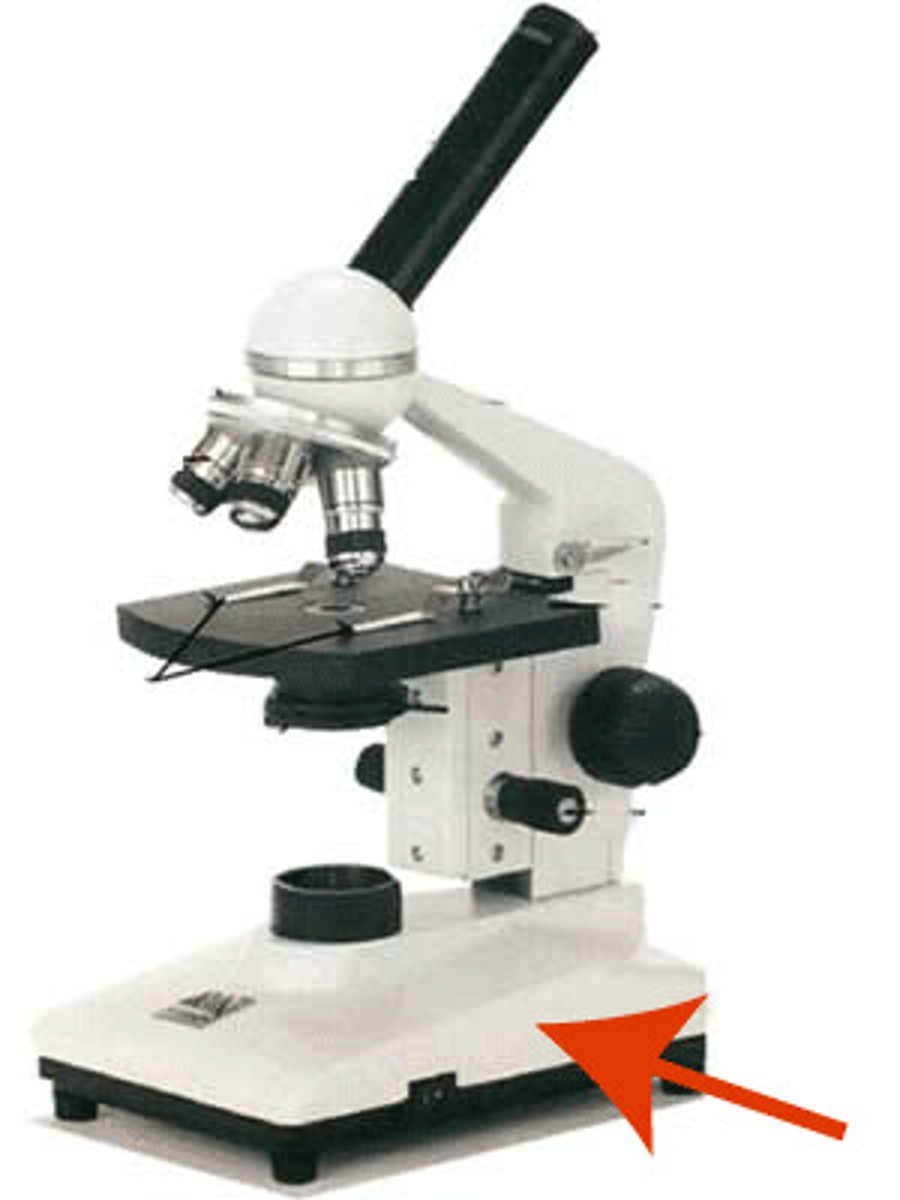

illuminator
an electric source of illumination or a mirror used to direct light upward.
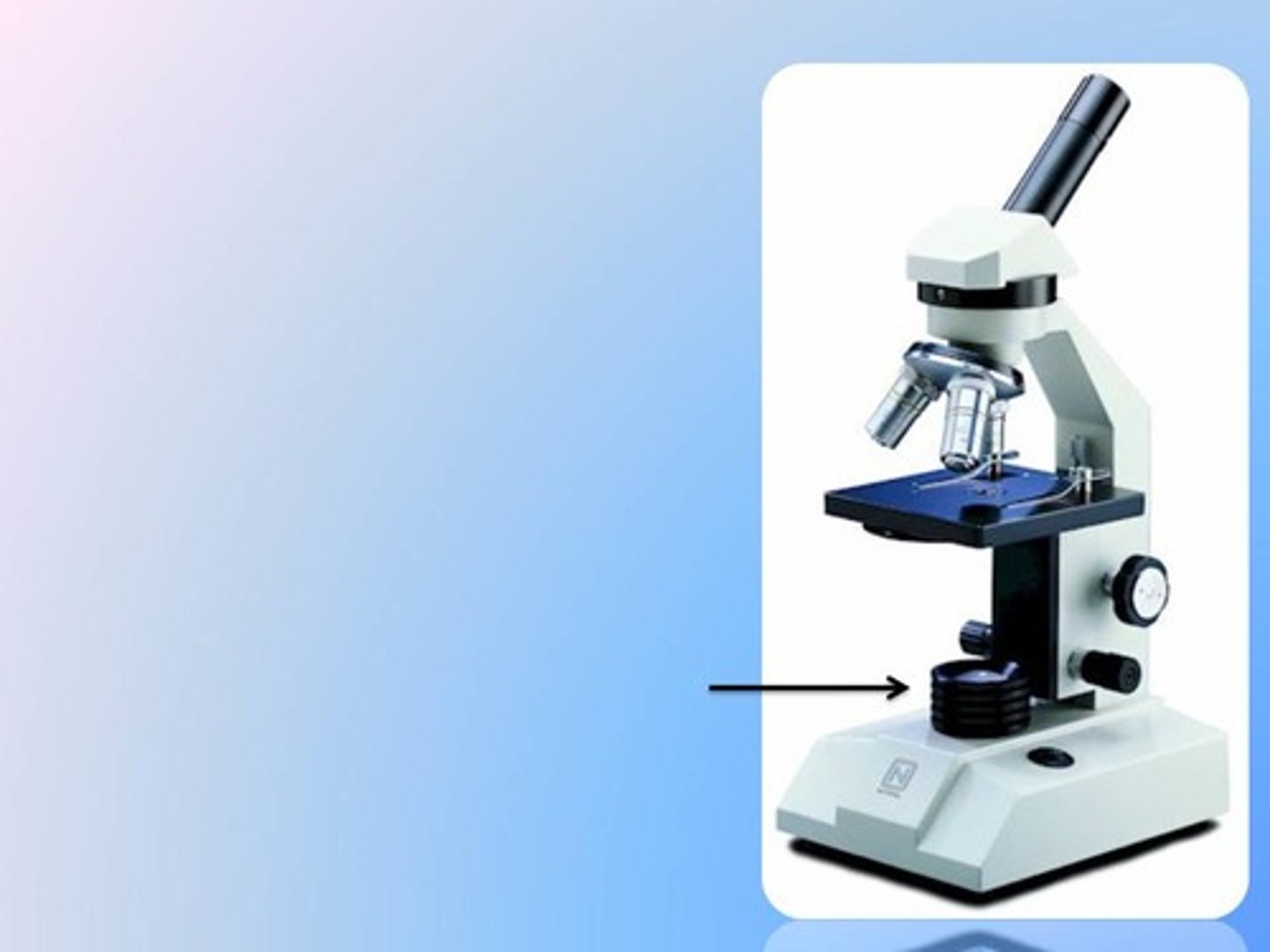
condenser lens
the lens under the stage that focuses light from the illuminator through to the hole in the stage

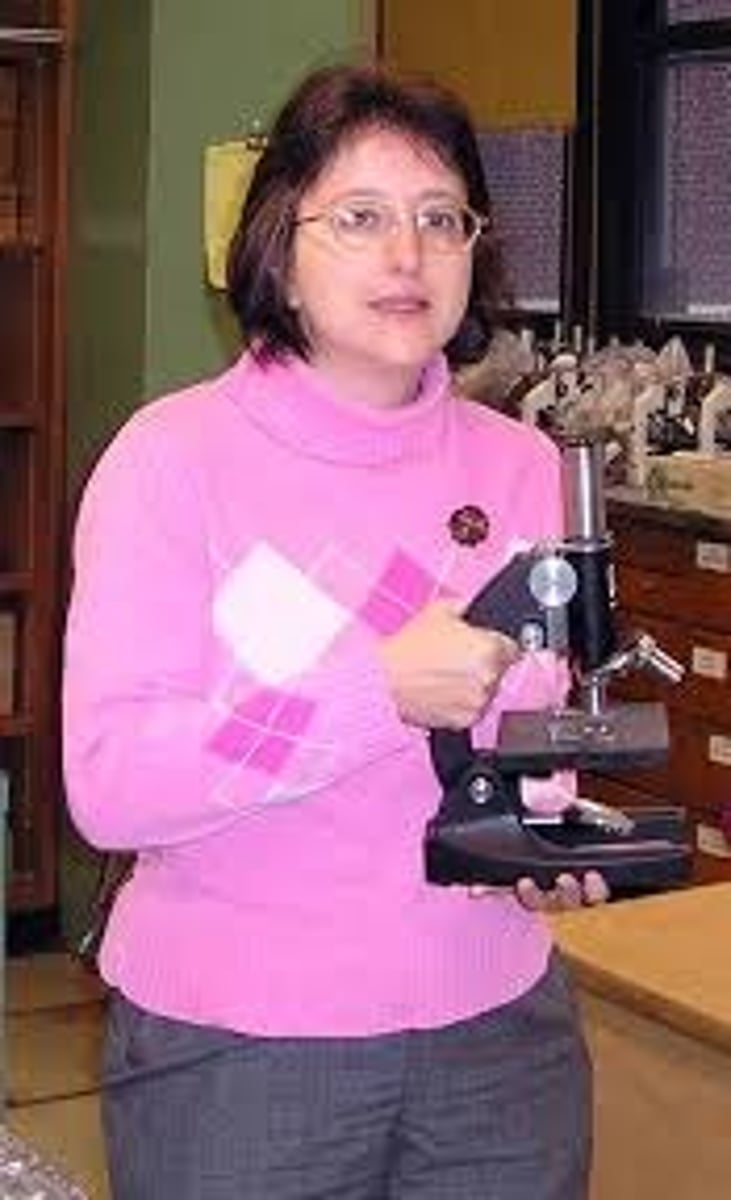
how to carry a microscope
always carry the microscope by:
the arm with the other hand supporting the base

total magnification =
ocular lens magnification x objective lens magnification
example: 4 × 10 = 40x → total magnification is 40x
oil immersion objective
an objective lens that has the greatest magnification and has a total magnification of 1000x (10x eyepiece lens x the 100x objective equals 1000).